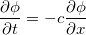A Python driven, Fortran powered Finite Difference solver for arbitrary hyperbolic PDE systems. This is the mini-app for the Miranda code.
The PDE solver defaults to a 10th order compact finite difference method for spatial derivatives, and a 5-stage, 4th order Runge-Kutta scheme for temporal integration. Other numerical methods will be added in the future.
Pyranda parses (through a simple interpreter) the full definition of a system of PDEs, namely:
- a domain and discretization (in 1D, 2D or 3D)
- governing equations written on RHS of time derivatives.
- initial values for all variables
- boundary conditions
At a minimum, your system will need the following installed to run pyranda. (see install notes for detailed instructions)
- A fortran compiler with MPI support
- python 2.7, including these packages
- numpy
- mpi4py
A few tutorials are included on the project wiki page that cover the example below, as well as few others. A great place to start if you want to discover what types of problems you can solve.
The one-dimensional advection equation is written as:
where phi is a scalar and where c is the advection velocity, assumed to be unity. We solve this equation in 1D, in the x-direction from (0,1) using 100 points and evolve the solution .1 units in time.
from pyranda import pyrandaSim
pysim = pyrandaSim('advection',"xdom = (0.0 , 1.0 , 100 )")
pysim.EOM(" ddt(:phi:) = - ddx(:phi:) ")
pysim.setIC(":phi: = 1.0 + 0.1 * exp( -(abs(meshx-.5)/.1 )**2 )")
dt = .001
time = 0.0
while time < .1:
time = pysim.rk4(time,dt)
pysim.plot.plot('phi')
Please us the folowing bibtex, when you refer to this project.
@misc{pyrandaCode,
title = {Pyranda: A Python driven, Fortran powered Finite Difference solver for arbitrary hyperbolic PDE systems and mini-app for the LLNL Miranda code},
author = {Olson, Britton},
url = https://github.com/LLNL/pyranda},
year = {2023}
}