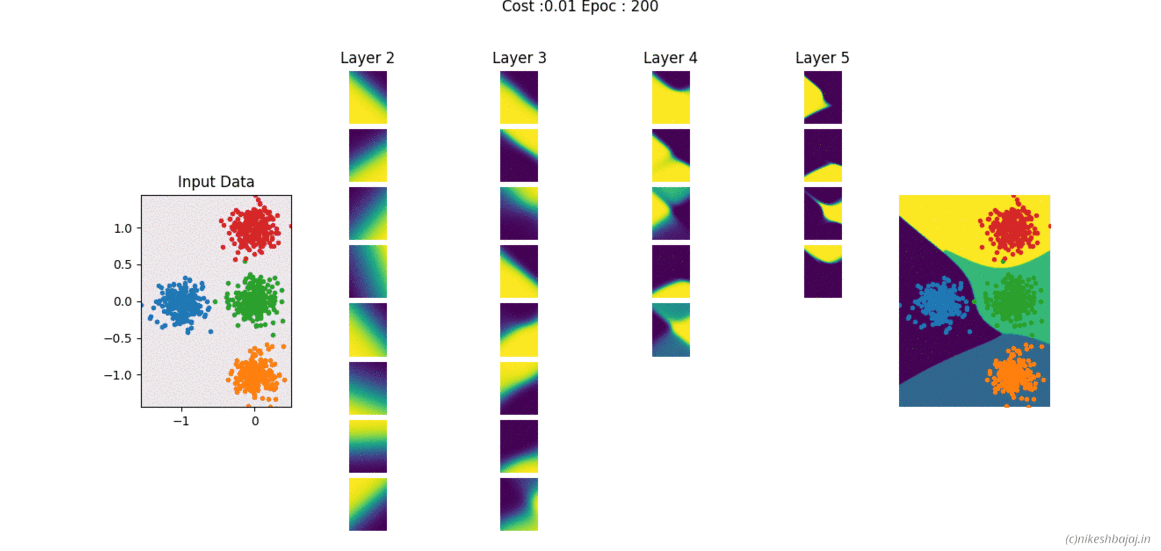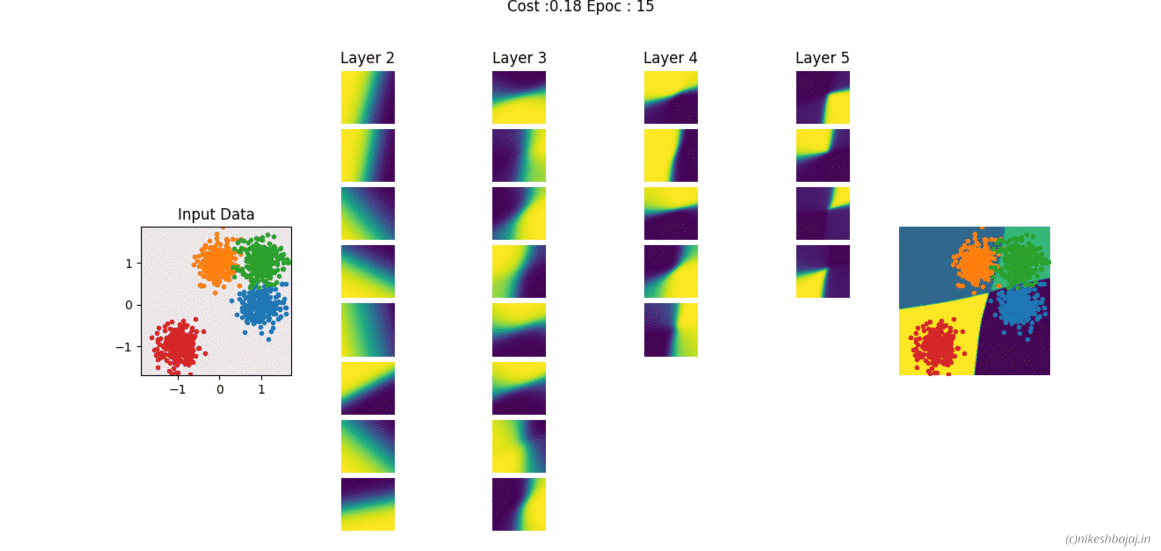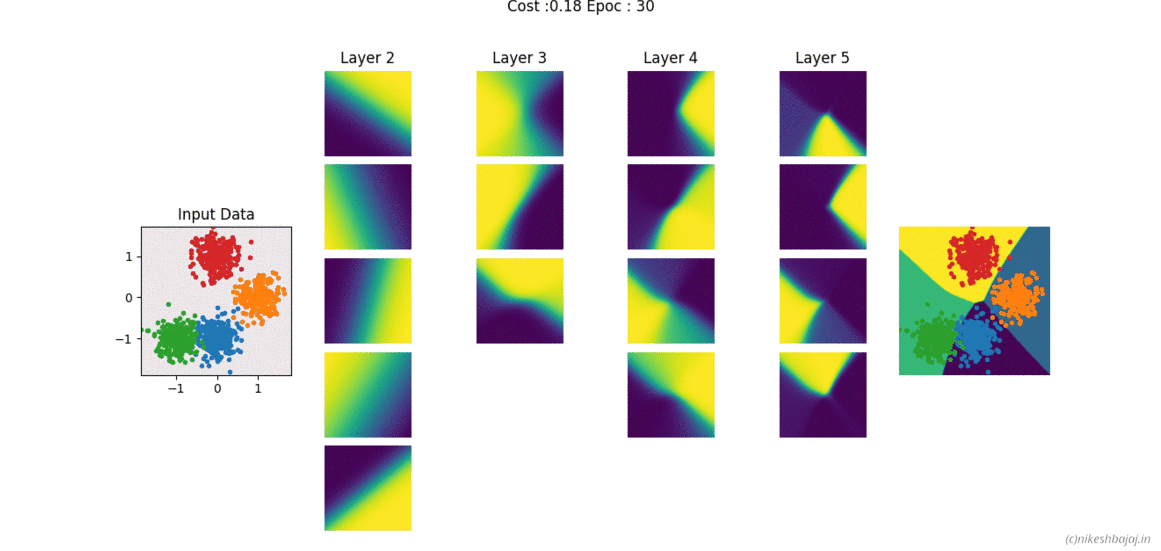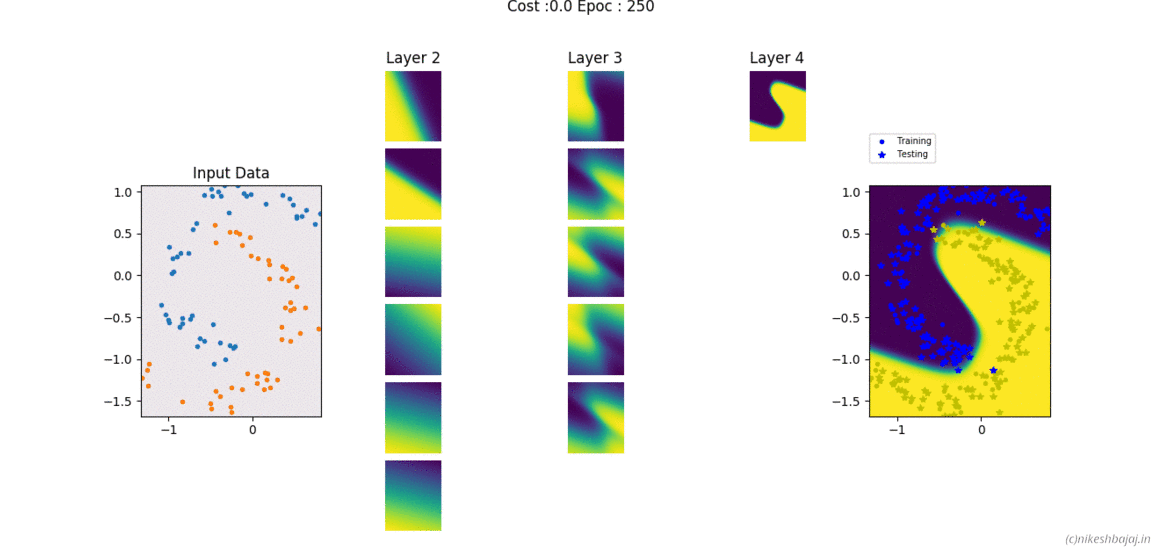
Now available in spkit library
Install spkit pip install spkit
from spkit.ml import LR, NaiveBayes, ClassificationTree, RegressionTree
(Few visualisations are limited to 2D data only, others can be used for any dimenntions)
- Logistic Regression
- Naive Bayes
- Decision Tree
- Neural Network (matlab/octave)
- Deep Neural Network-DeepLearning
- Convolutional Network
- Recurrance Neural Network
- Kernel Learning & Regularization
- Support Vector Machine (yet to implement)
- Extra Tree; Classification & Regression
- Random Forest
- Linear discriminant analysis (LDA)
Code ans examples are here
#from LogisticRegression import LR # given code
##NOW USE spkit library (pip intall spkit)
from spkit.ml import LR
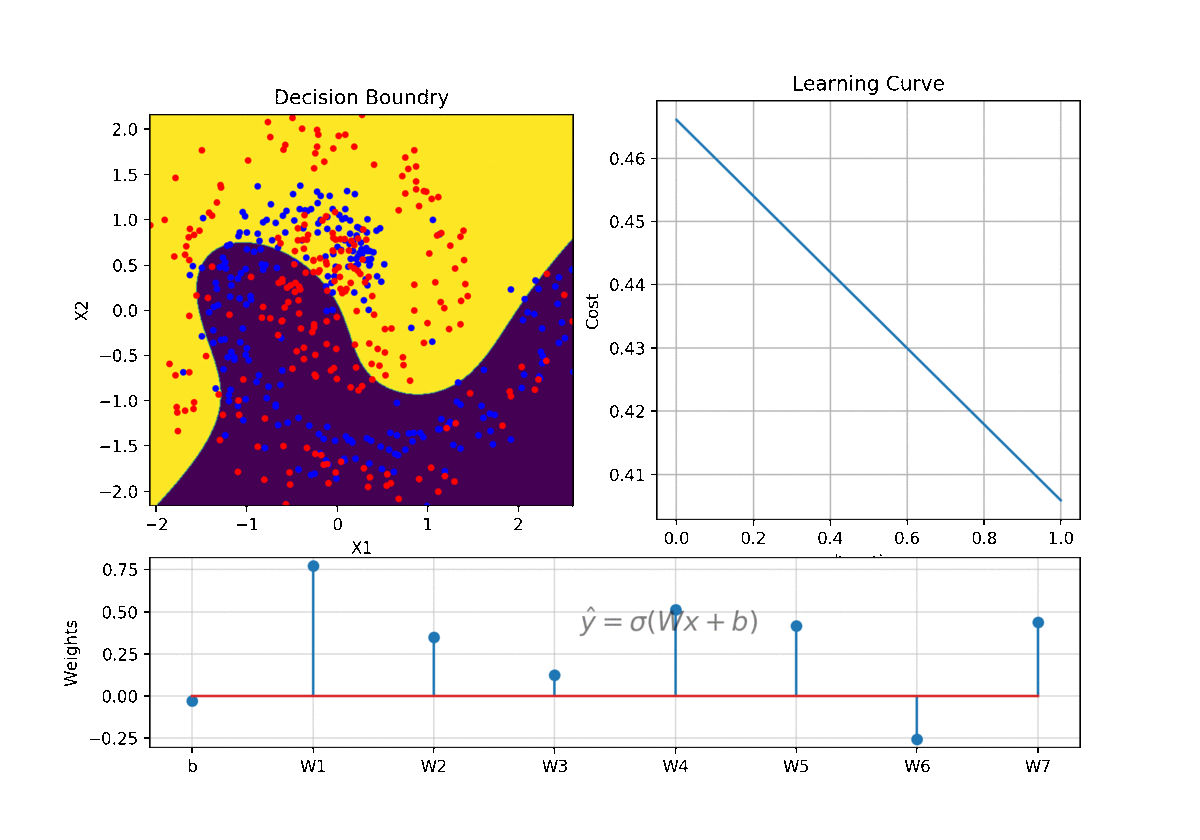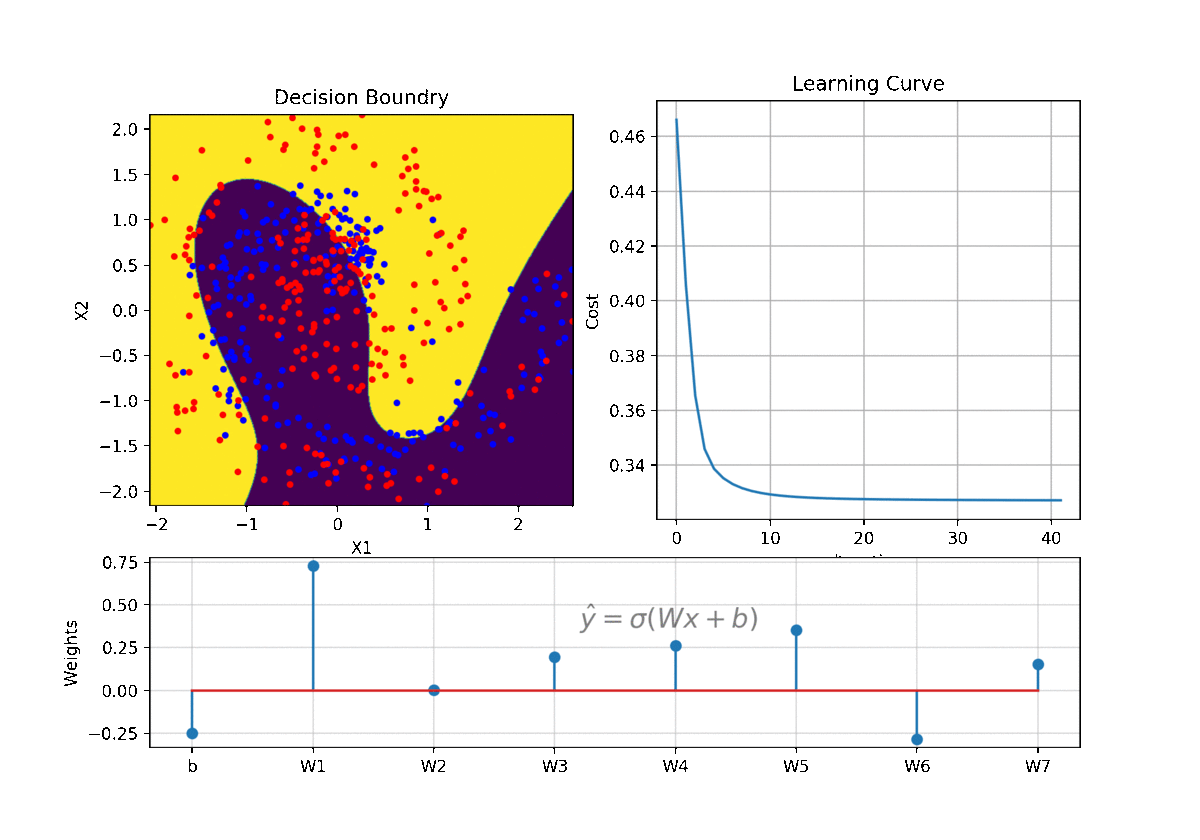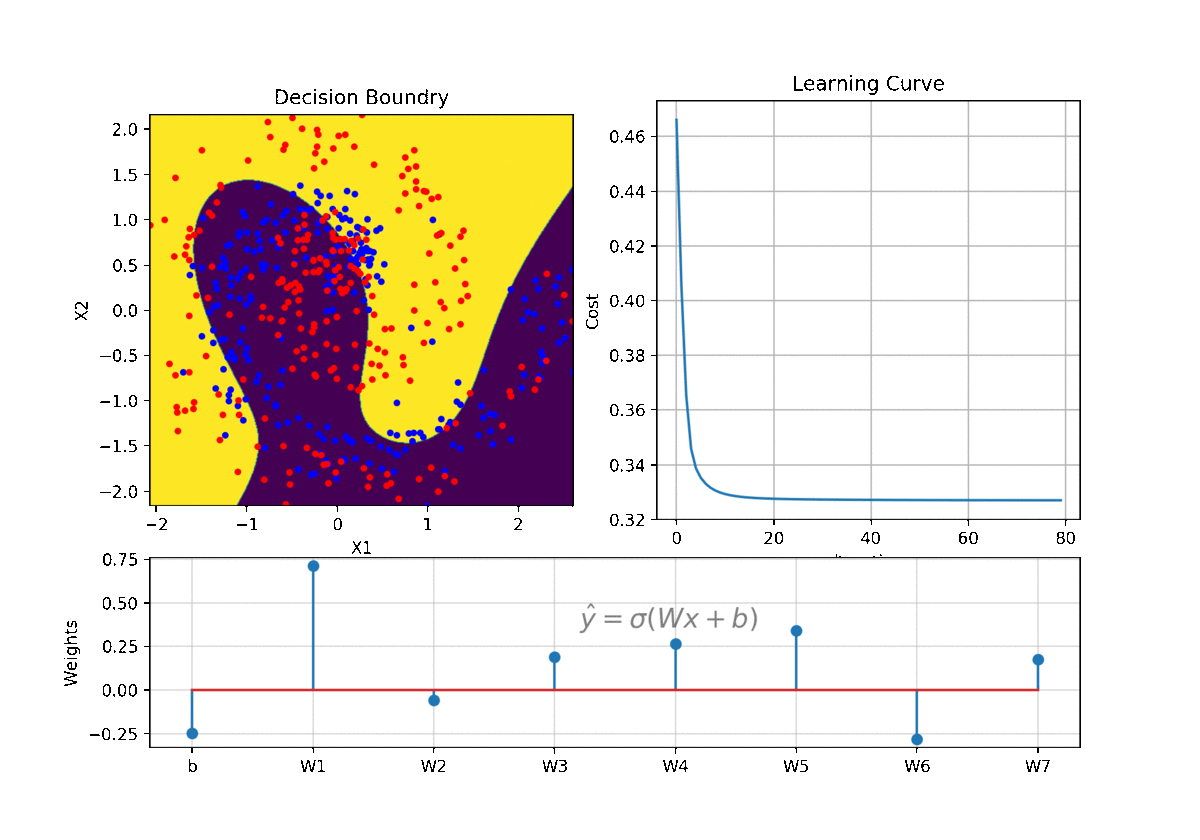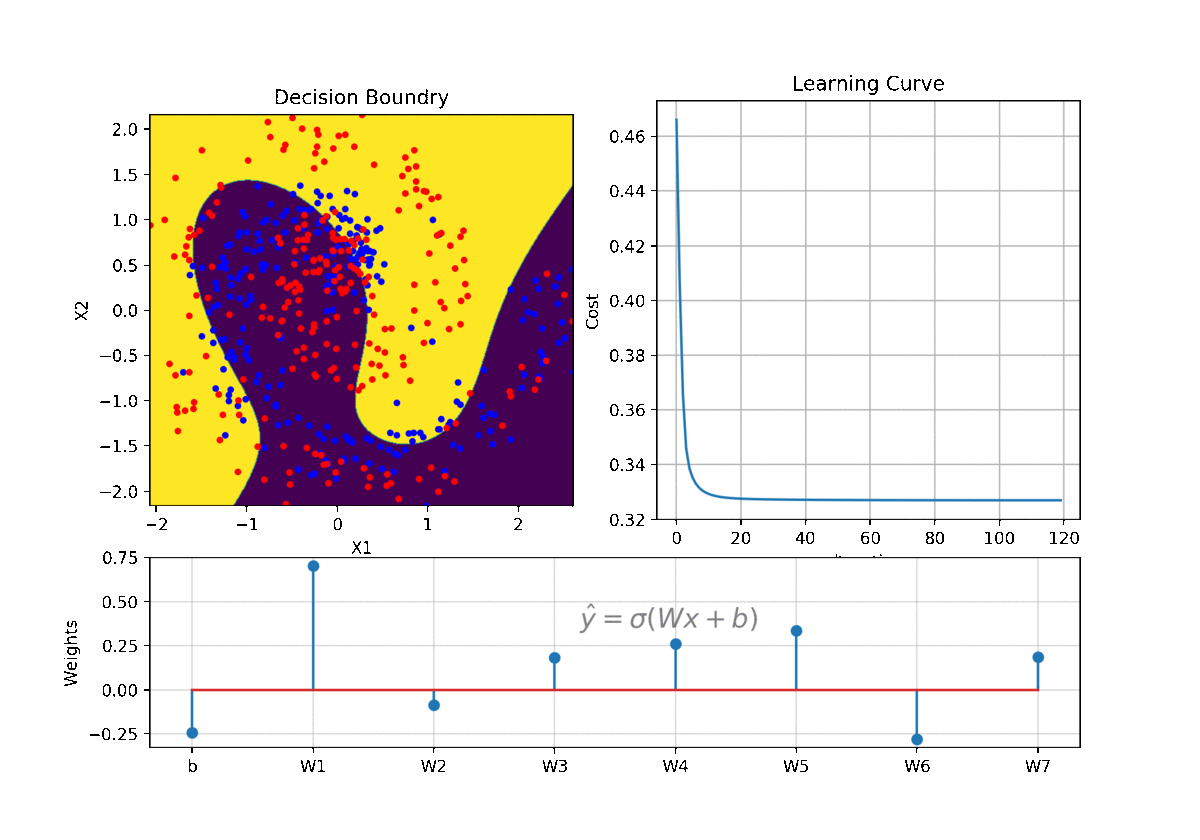
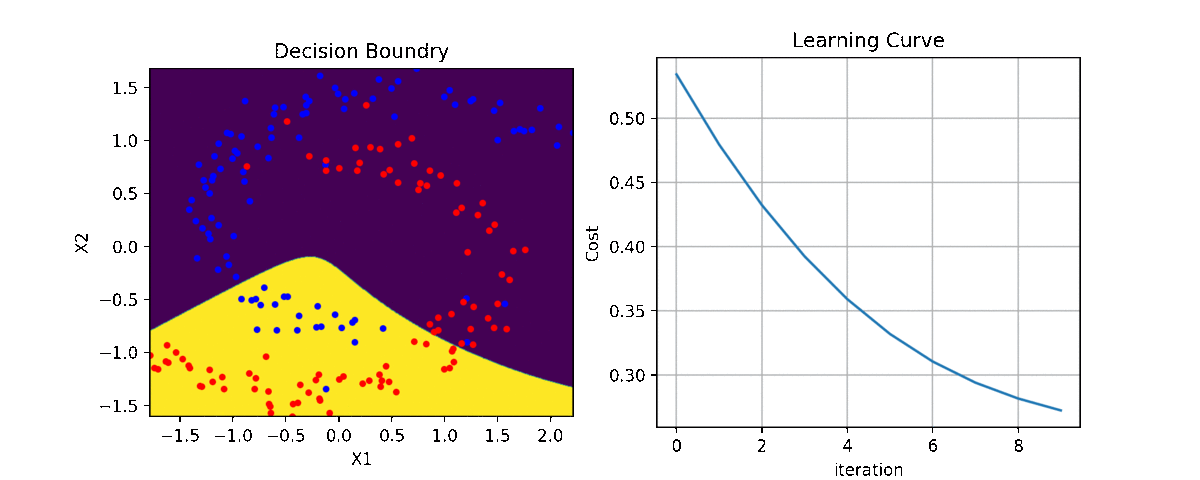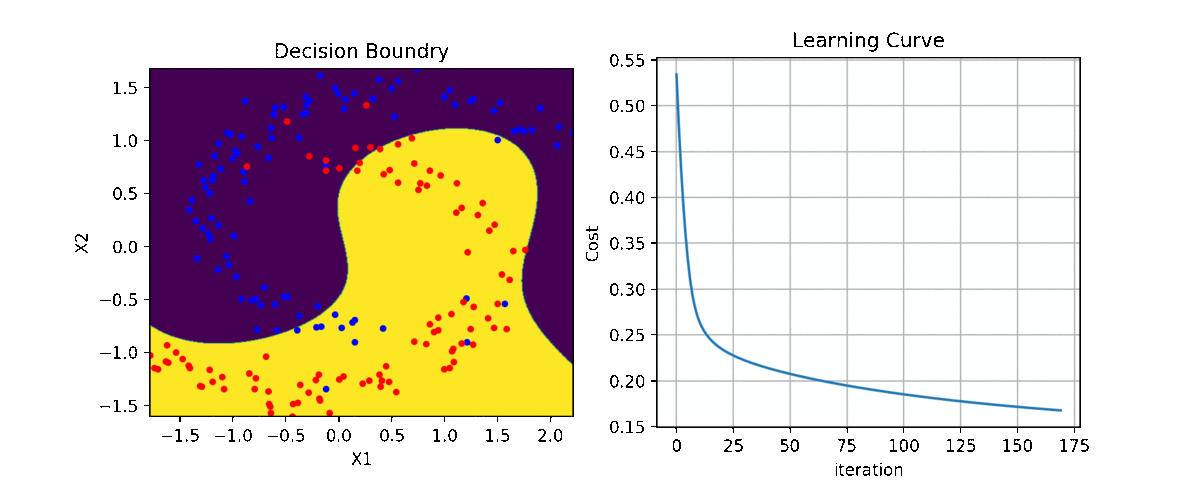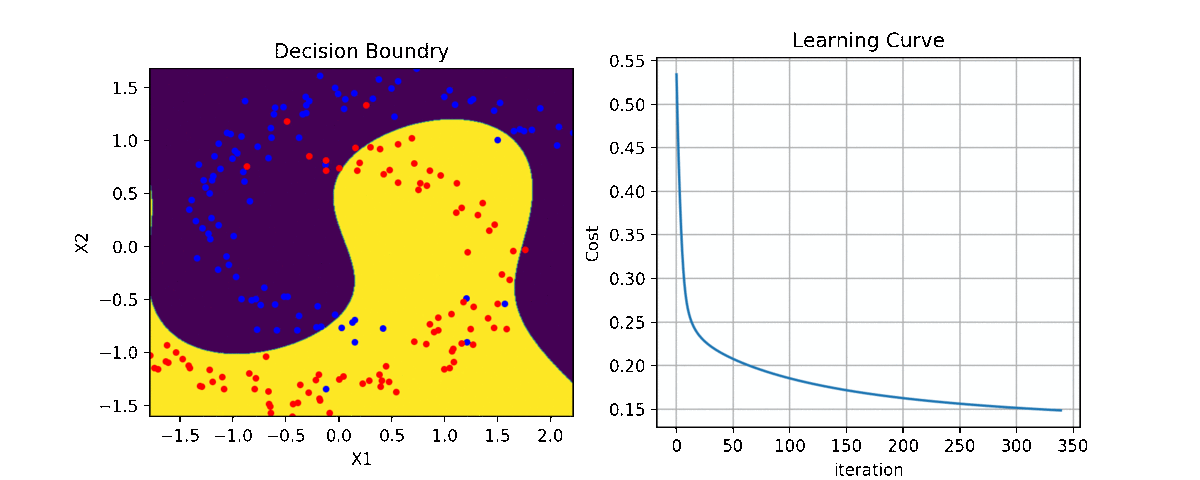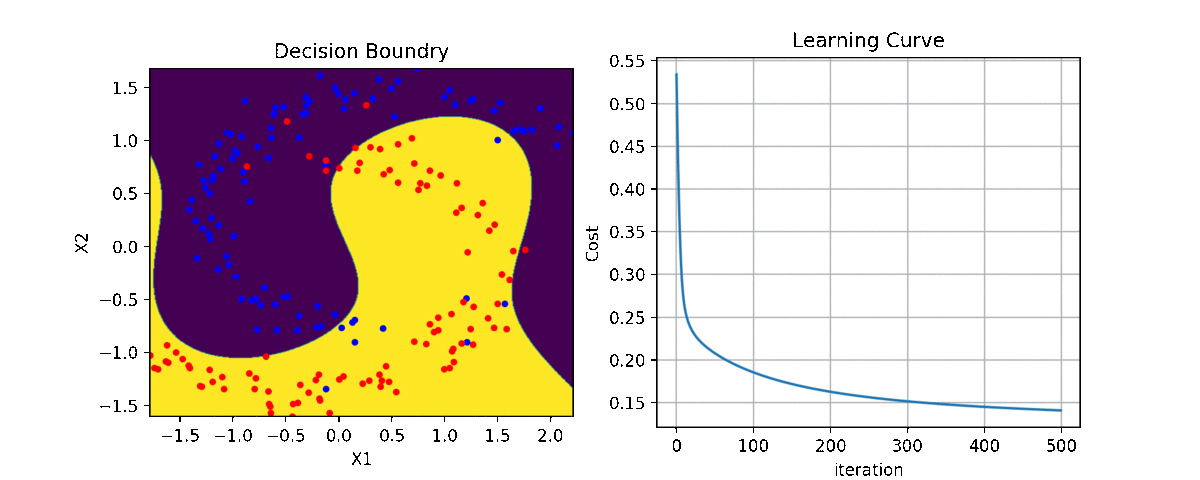
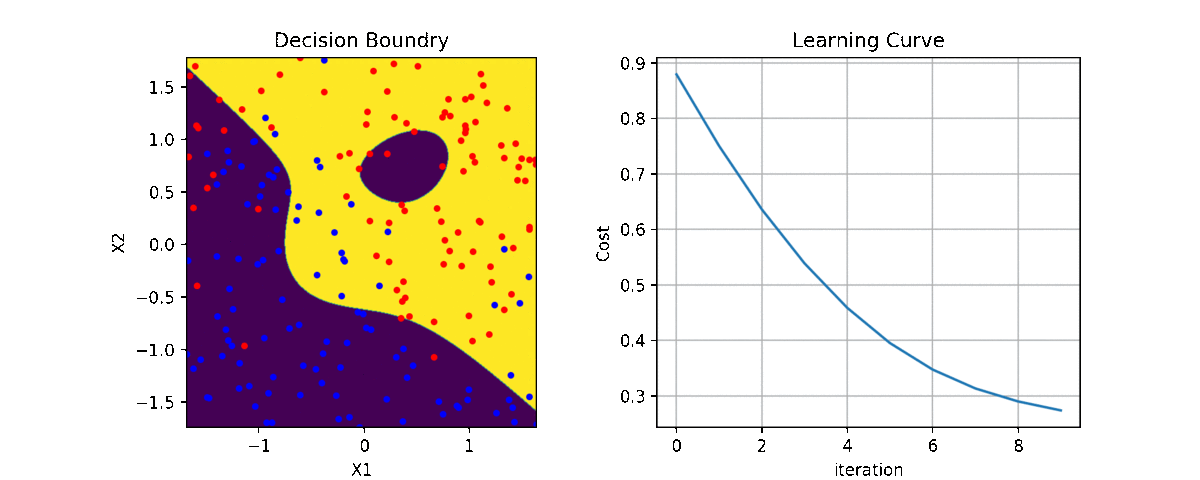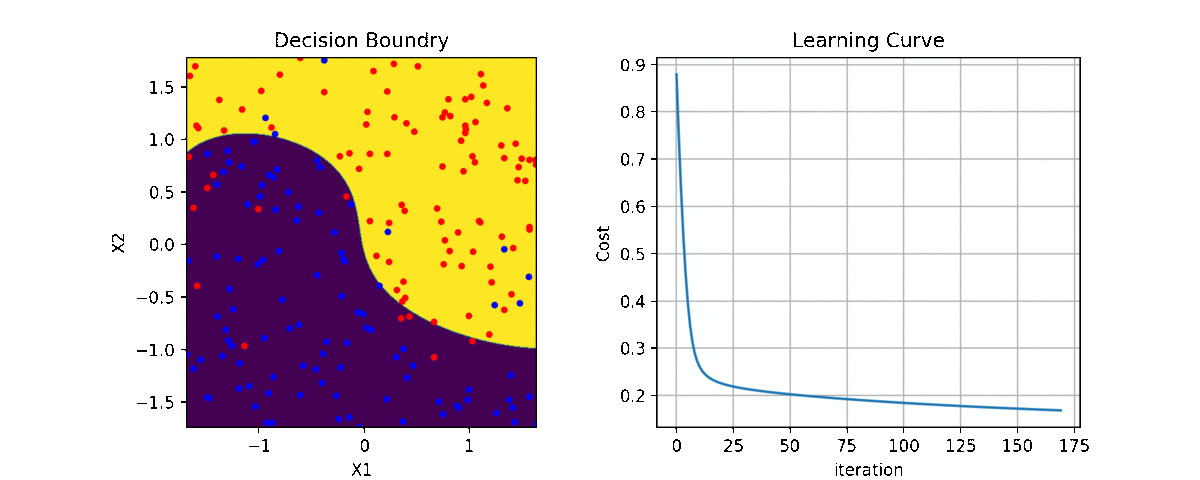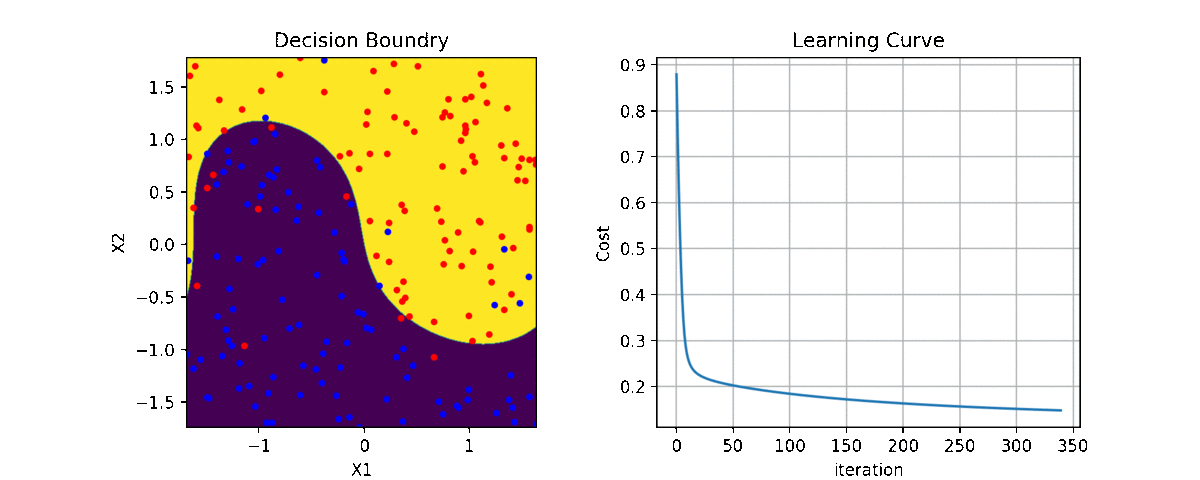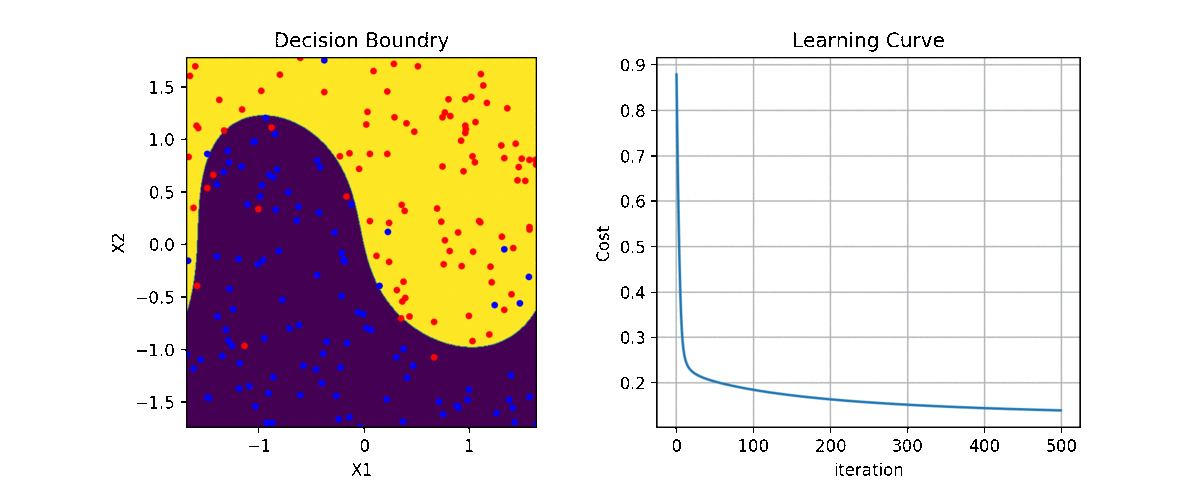
clf = LR(X,y,alpha=0.003,polyfit=True,degree=5,lambd=2)
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(8,4))
gs=GridSpec(1,2)
ax1=fig.add_subplot(gs[0,0])
ax2=fig.add_subplot(gs[0,1])
for i in range(100):
Clf.fit(X,y,itr=10)
ax1.clear()
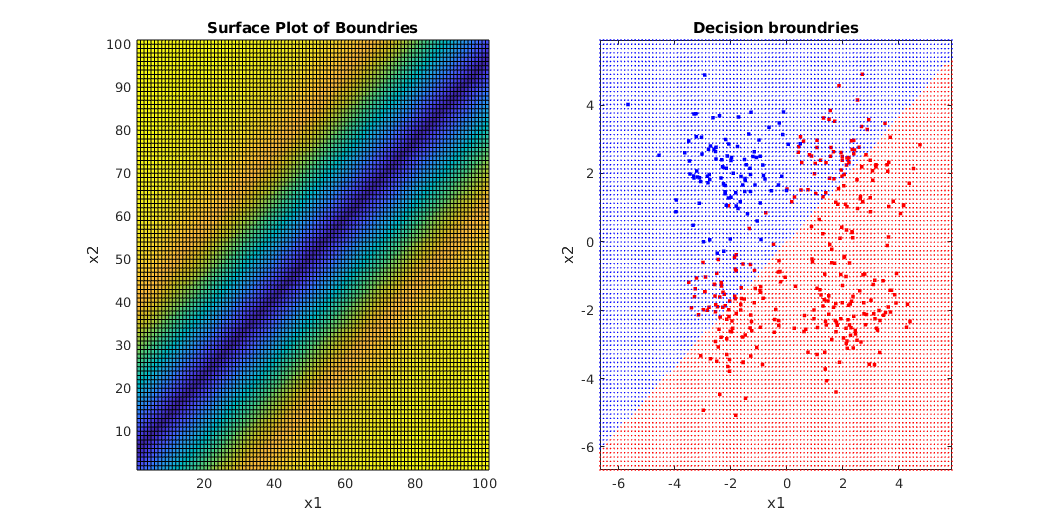
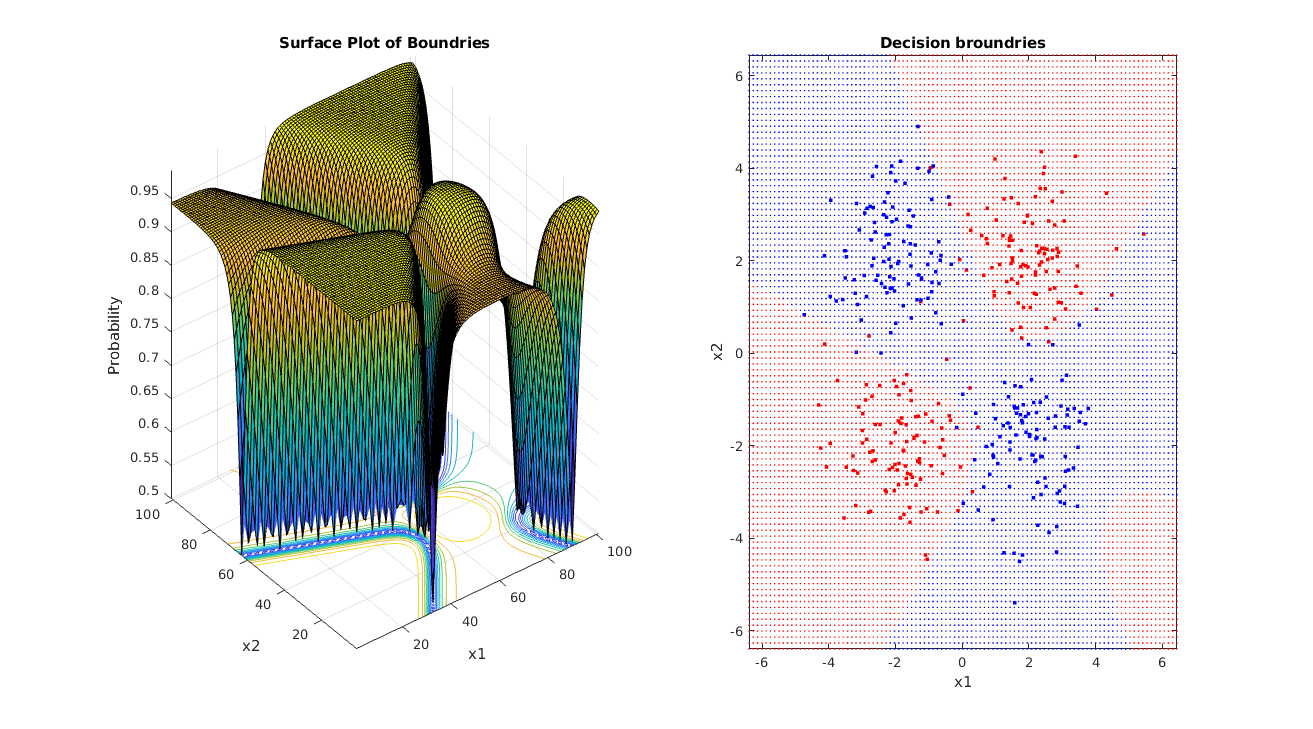
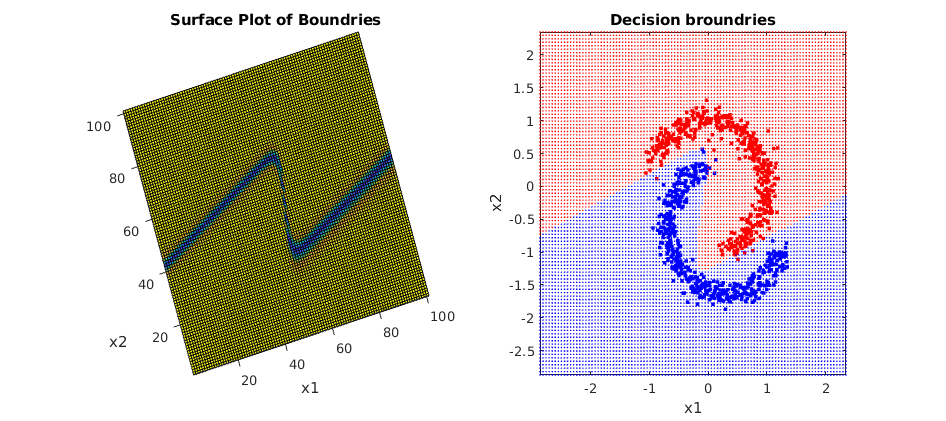
Clf.Bplot(ax1,hardbound=False)
ax2.clear()
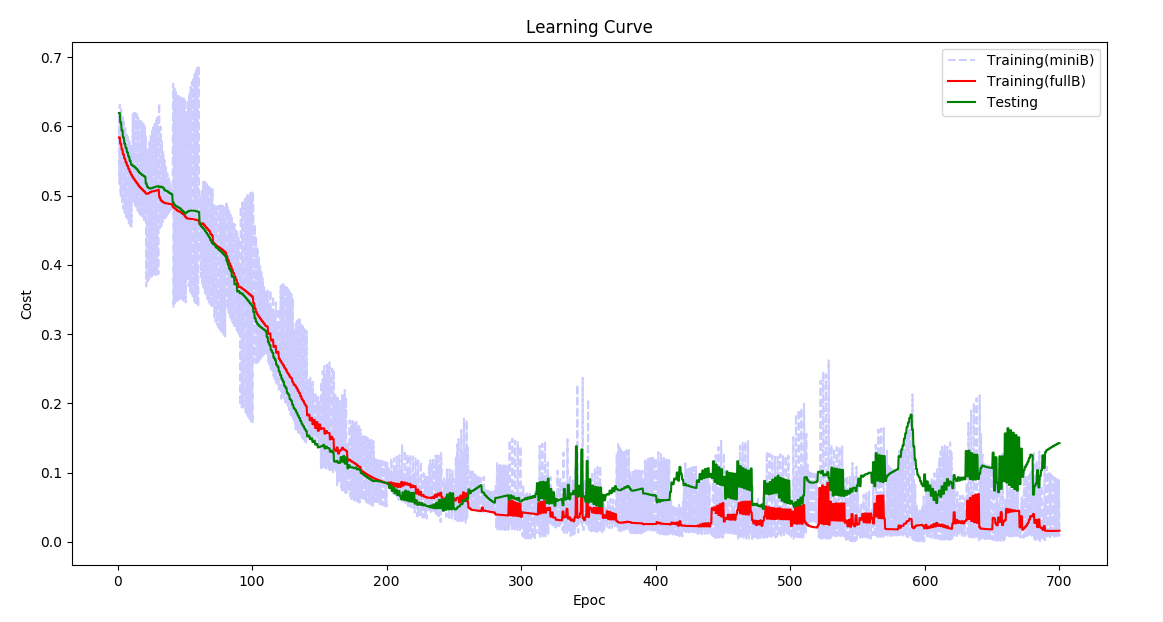
Clf.LCurvePlot(ax2)
fig.canvas.draw()
plt.pause(0.001)
clf.predict(X)
W,b =clf.getWeight()
Code and examples are here
Full detail of implementation and use of code is describe here
- Download the reposatory
- Jupyter-Notebook
- Class file:: DeepNet.py
- example1.py
- example2.py
- example3.py
Code and examples here
Network can be created and trained as for example
W= NeuralNet(X,y,HL,Iterations,alpha,verbose);
% For 2 hidden layers with 5 and 3 neurons, 500 iteration and 0.1 alpha(learning rate)
% input and output layers are chosen according to data X,y provided
W= NeuralNet(X,y,[5,3],500,0.1,1);
% for 8 hidden layers
W= NeuralNet(X,y,[15,10,10,10,5,5,5,3],100,0.1,1);
returns weights W of each layer
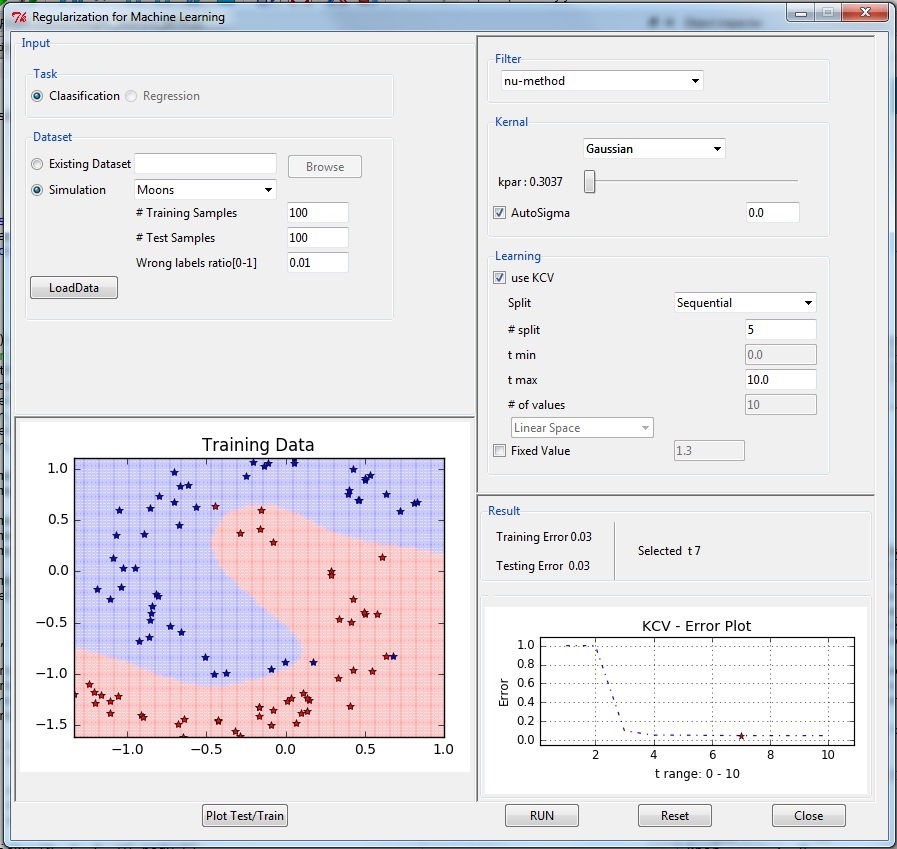
- Regularized Least Squares -RLS Referance
- Nu-Method Referance
- Iterative Landweber Method Referance
- Singular Value Decomposition Reference
- Trunctated SVD Referance 1 Referance 2
- Spectral cut-off
(Linear, Polynomial, Gaussian)
Code and examples with GUI are given here
pip install regml
import regml
regml.GUI()
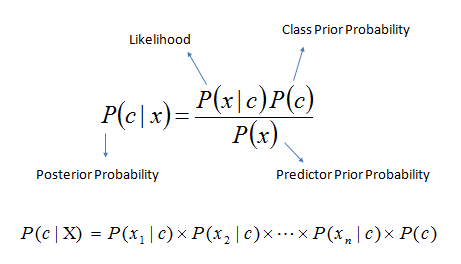
Classifier based on Bayes rule:
Example with jupyter notebook here and Repository
Notebook include example of Iris data, Breast Cancer and Digit classification (MNIST)
here is code snippet
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# For dataset
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Library provided
#from probabilistic import NaiveBayes (NO NEED OF THIS)
##NOW USE spkit library (pip intall spkit)
from spkit.ml import NaiveBayes
data = datasets.load_iris()
X = data.data
y = data.target
Xt,Xs,yt,ys = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3)
print(Xt.shape,yt.shape,Xs.shape,ys.shape)
# Fitting model (estimating the parameters)
clf = NaiveBayes()
clf.fit(Xt,yt)
# Prediction
ytp = clf.predict(Xt)
ysp = clf.predict(Xs)
print('Training Accuracy : ',np.mean(ytp==yt))
print('Testing Accuracy : ',np.mean(ysp==ys))
print(clf.parameters)
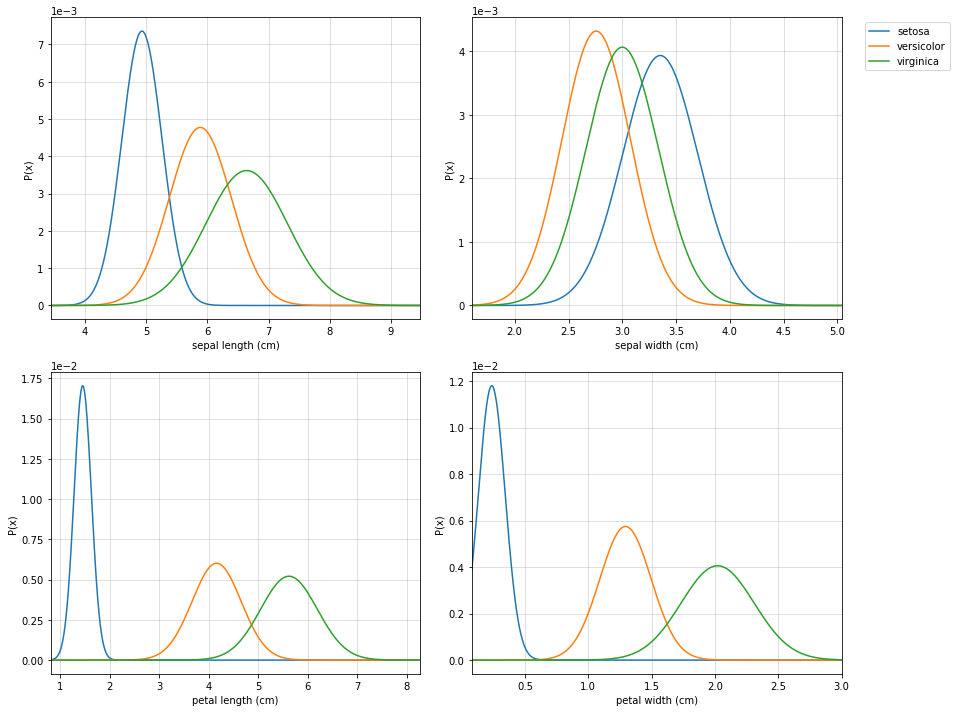
# Visualization
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,10))
clf.VizPx()
pip install spkit
See the examples in Jupyter-Notebook or Repository for more details
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#(NO NEED OF THIS)
#Download trees.py and keep in current directory or give a path (if you know how to)
#from trees import ClassificationTree, RegressionTree
##NOW USE spkit library (pip intall spkit)
from spkit.ml import ClassificationTree, RegressionTree
# For examples
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
data = datasets.load_iris()
X = data.data
y = data.target
feature_names = data.feature_names #Optional
Xt,Xs, yt, ys = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3)
clf = ClassificationTree()
# verbose 0 for no progress, 1 for short and 2 for detailed.
# feature_names is you know, else leave it or set it to None
clf.fit(Xt,yt,verbose=2,feature_names=feature_names)
# Plot Tree that has been learned
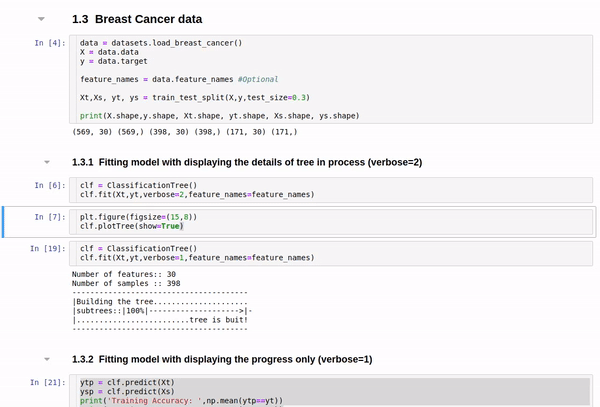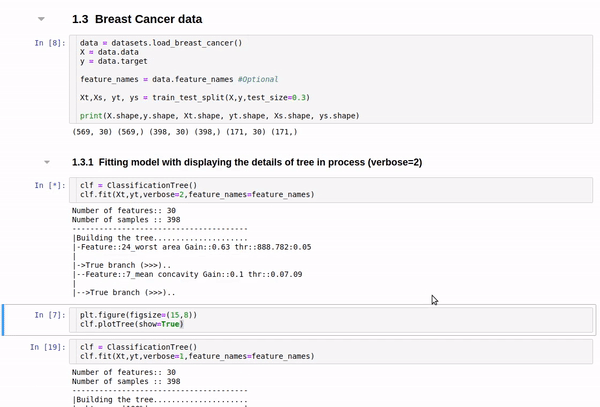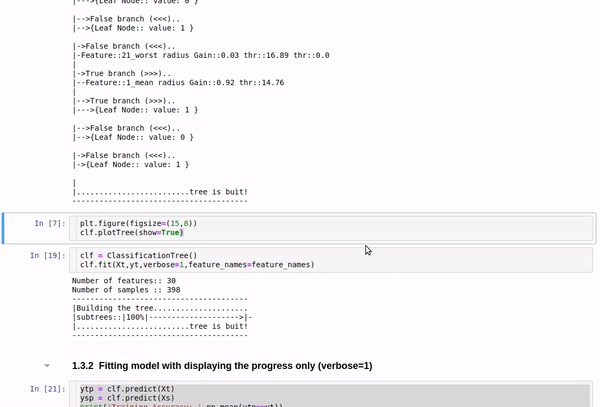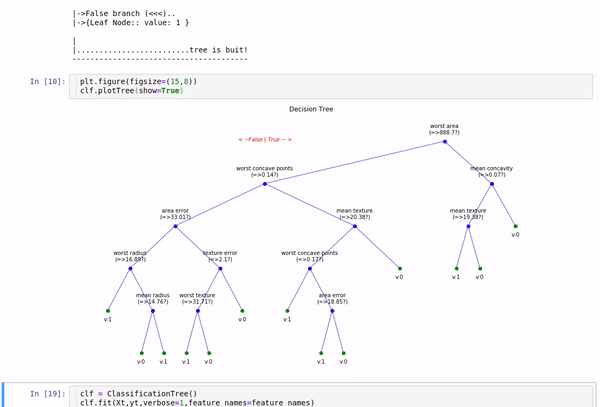
plt.figure(figsize=(15,8))
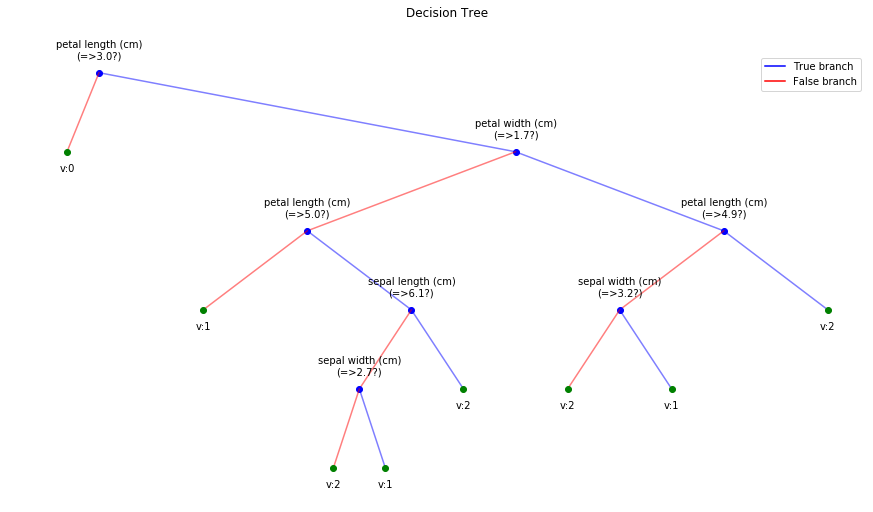
clf.plotTree(show=True)
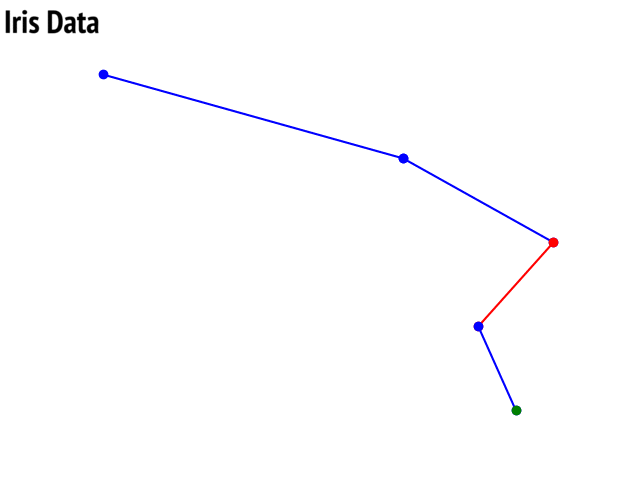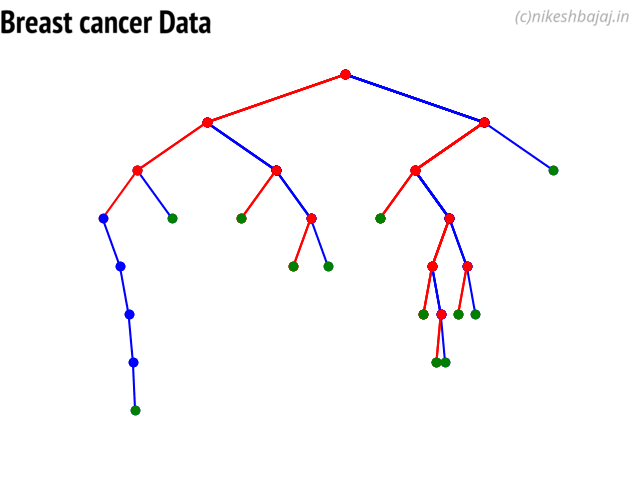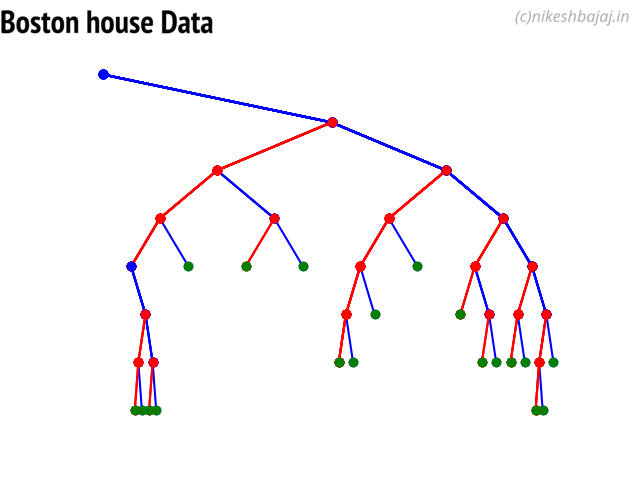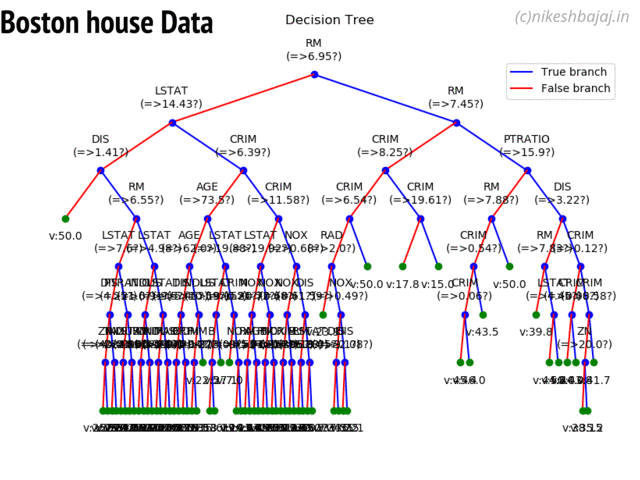
Option to show colored branch: Blue for True and Red for False Or just show all branches as blue with direction to indicate True and False branch
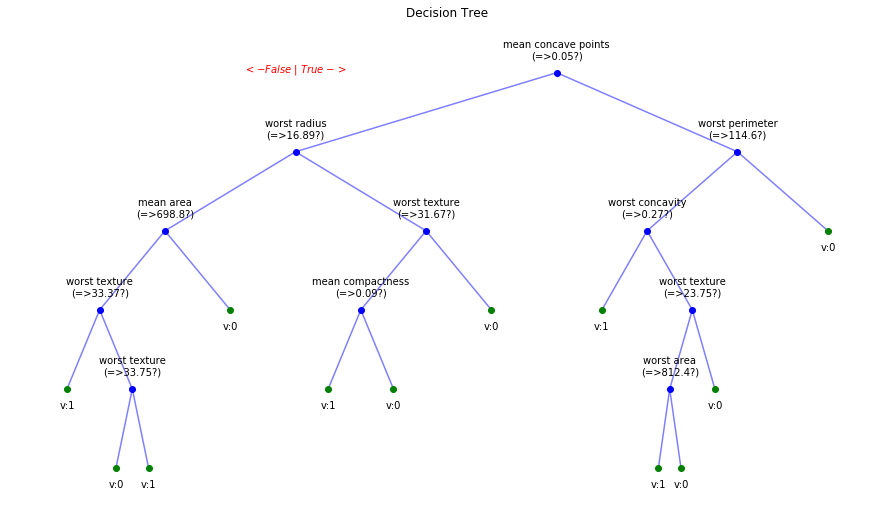
Iris data: Decesion Tree | Cancer data: Decesion Tree
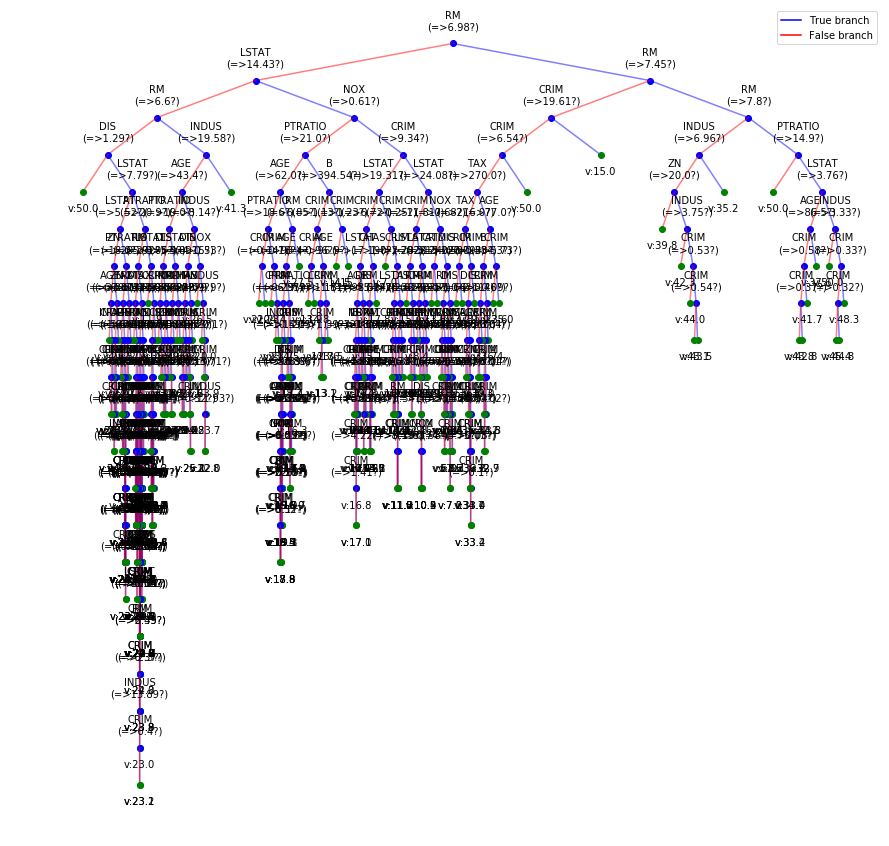
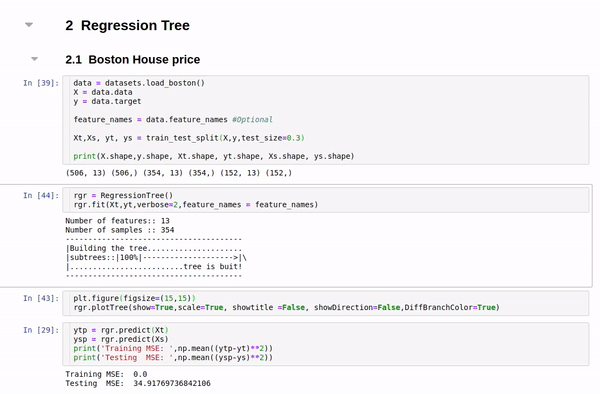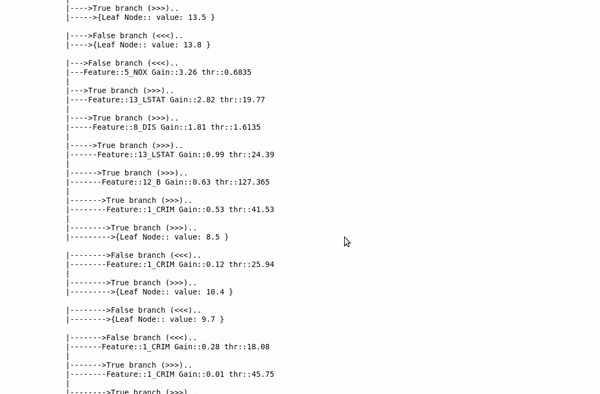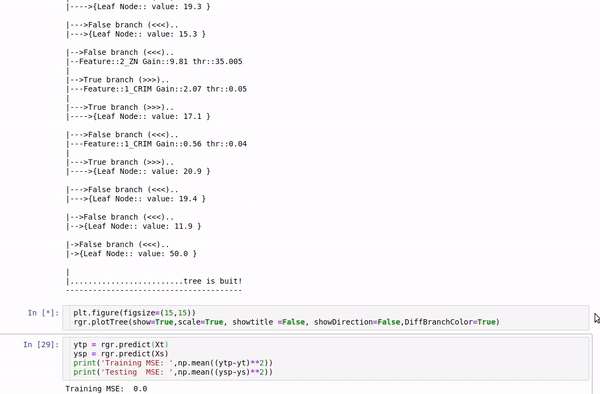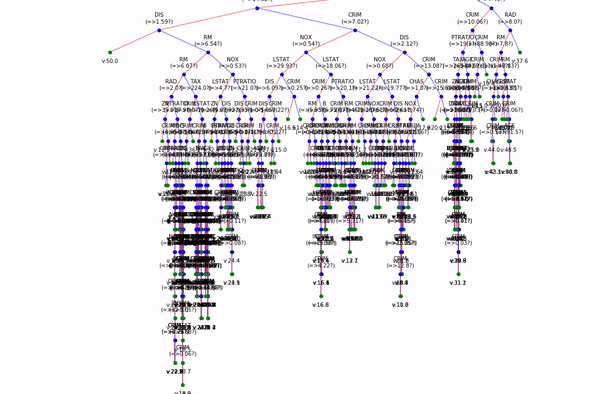
Boston data: Decesion Tree
Tree building for Cancer Data (Classification)
Detailed view
Short view