-
Set Up Index Lifecycle Management (ILM): Use ILM policies to automate data retention and index rollover. This ensures that old data is properly archived or deleted, preventing index bloat and resource consumption.
-
Consider Shard Sizing: Properly size your Elasticsearch shards to balance performance and resource usage. Avoid overly small or large shards. Monitor shard sizes and adjust as needed.
-
Implement Monitoring: Use monitoring tools like Elasticsearch's built-in monitoring features or third-party solutions to keep an eye on cluster health, performance, and resource utilization.
-
Set Up Alerts: Configure alerts for critical cluster metrics such as disk space, CPU usage, and memory utilization. Be proactive in addressing potential issues.
-
Enable Authentication and Authorization: Implement security features like Elasticsearch's native security or integration with external authentication systems to control access to your ELK Stack.
-
Encrypt Data in Transit and at Rest: Secure data by enabling encryption for communication between nodes and by encrypting data at rest using tools like Elasticsearch's SSL/TLS features and encryption plugins.
-
Regular Backups: Implement a backup strategy to ensure data resilience. Regularly back up both Elasticsearch data and Kibana configurations.
-
Test Disaster Recovery: Periodically test your disaster recovery plan to verify that you can restore data and configurations in case of a failure.
-
Structured Logging: Whenever possible, log in structured formats like JSON. This makes log parsing and analysis more efficient.
-
Log Shipping: Use log shippers (e.g., Filebeat, Logstash) to send logs to Elasticsearch. Ensure that log shipping is reliable and that logs are not lost during transit.
-
Use Query Filters: Apply filters to queries to limit the scope of the search. Filters are faster than queries and can significantly improve performance.
-
Index Optimization: Optimize index mappings and analyzer settings to improve search efficiency and relevance.
-
Plan for Growth: Design your ELK Stack deployment to scale horizontally as your data and query load increases. Add more nodes or resources as needed.
-
Load Balancing: Use load balancers to evenly distribute incoming requests across Elasticsearch nodes to prevent overloading specific nodes.
-
Documentation: Maintain up-to-date documentation for your ELK Stack deployment, including configurations, policies, and procedures.
-
Training: Ensure that your team is well-trained in using and troubleshooting the ELK Stack. Invest in training resources and workshops.
-
Patch and Upgrade: Keep your ELK Stack components up-to-date by applying patches and performing regular upgrades. New versions often include performance improvements and security fixes.
-
Clean Up: Regularly review and clean up old indices, configurations, and obsolete data to maintain optimal performance and resource utilization.
By following these best practices, you can ensure the reliability, security, and performance of your ELK Stack deployment, making it a valuable tool for log management and data analysis in your DevOps and monitoring workflows.
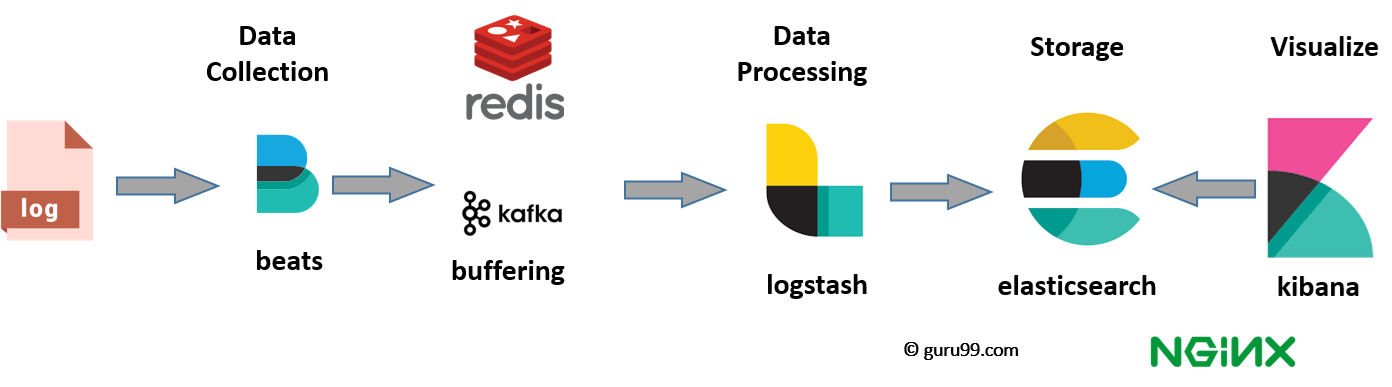
The ELK Stack, consists of three core components: Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana. To enhance its capabilities, lightweight data shippers known as "Beats" were introduced by Elastic (the company behind the ELK Stack). This led Elastic to rename ELK as the Elastic Stack. Beats simplify data collection and transfer from various sources to Elasticsearch or Logstash for indexing and analysis. Some popular Beats include:
-
Filebeat: Designed for log file shipping, Filebeat efficiently collects log data from various sources and ships it to Elasticsearch or Logstash.
-
Metricbeat: Focuses on collecting system and application metrics from servers and services, providing insights into system performance.
-
Packetbeat: Monitors network traffic, capturing packet-level data and analyzing it for network and application insights.
-
Auditbeat: Collects system audit data and security-related events for monitoring and threat detection.
-
Heartbeat: Monitors the availability and response times of services and applications.
By introducing Beats into the ELK Stack, you can streamline data collection and ensure that various types of data, including logs, metrics, and network traffic, are efficiently ingested into the Elastic Stack for analysis.
While dealing with very large amounts of data, you may need Kafka, RabbitMQ for buffering and resilience. For security, nginx can be used.