You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Data is one of the core components of engineering software, so the stability of data reading, writing, conversion, and manipulation is vital for the performance of engineering software. General-purpose engineering simulation CAE software is no exception, it also places high demands on maintainability, due to its long research and development cycle. Simulation software covers a wide range of fields, such as data persistence commonly used in software engineering and computational results such as node and element data solved using finite element and finite volume methods. For this reason, various data formats are needed to implement different features.
Choosing the right data format can greatly improve product performance and maintainability, while also benefiting developers by saving development time and resources. Based on years of authentic experience in developing WELSIM, this article discusses data formats and application concepts in general-purpose engineering simulation software.
Geometric shape data
The entry point for general-purpose simulation software is geometric models, commonly referred to as CAD models by engineers. Since the core of CAE simulation software mainly lies in computation and analysis, the primary method to obtain geometric data is to read CAD models rather than generate them from scratch.
Currently, the most suitable geometric data format for simulation software is STEP. Although introduced in the 1980s, it is still widely used today. The STEP format provides a clear and precise representation of the entire 3D model, including not only the basic geometric shape but also the topology, allowing for high-precision reading and storage. It supports length units and can meet the requirements of the majority of CAE applications. The well-known cloud-based CAD vendor OnShape exports CAD data in the STEP format, and the popular open-source geometry engine OpenCascade also provides excellent support for STEP, facilitating its application and compatibility. Currently, STEP is the primary CAD file import format for WELSIM.
There are also other well-known geometric data formats such as JT, ACIS, and Parasolid. These data formats may be discussed in future articles due to space limitations.
In addition to complete geometric data formats, there is another category that contains only surface information, represented by STL. This type of data does not include topological information but consists of triangular mesh data representing the surface. With the recent rise of 3D printing, such data formats as STL have become popular. However, their application in general CAE analysis is somewhat limited due to the lack of topological and volumetric information.
Mesh data
Mesh data is the most important input data for engineering simulation software, characterized by its large volume and diverse types. Balancing performance and versatility is the main criteria for selecting a mesh data format. After years of quality development and customer feedback, WELSIM considers UNV and PVTU two exceptional formats for mesh data.
UNV is a general-purpose neutral mesh data format proposed by I-DEAS. It has clear and easily understandable field definitions, and it's easy to implement in programming. UNV supports a wide range of element types and includes a group module that allows the definition of various boundary conditions and contacts. In the industry, UNV is largely accepted and effective. In practical applications, the default format is ASCII text, but developers can also use tools, like gzstream, to convert it to binary files.
PVTU, proposed by Kitware, is an unstructured mesh format based on VTU. Its distinctive feature is that it can support multi-core parallel reading and writing, greatly improving the speed of mesh file operations. The underlying version, VTU, is an XML-based data format, and the core data can be stored in either ASCII or binary formats, meeting different usage scenarios.
Material data
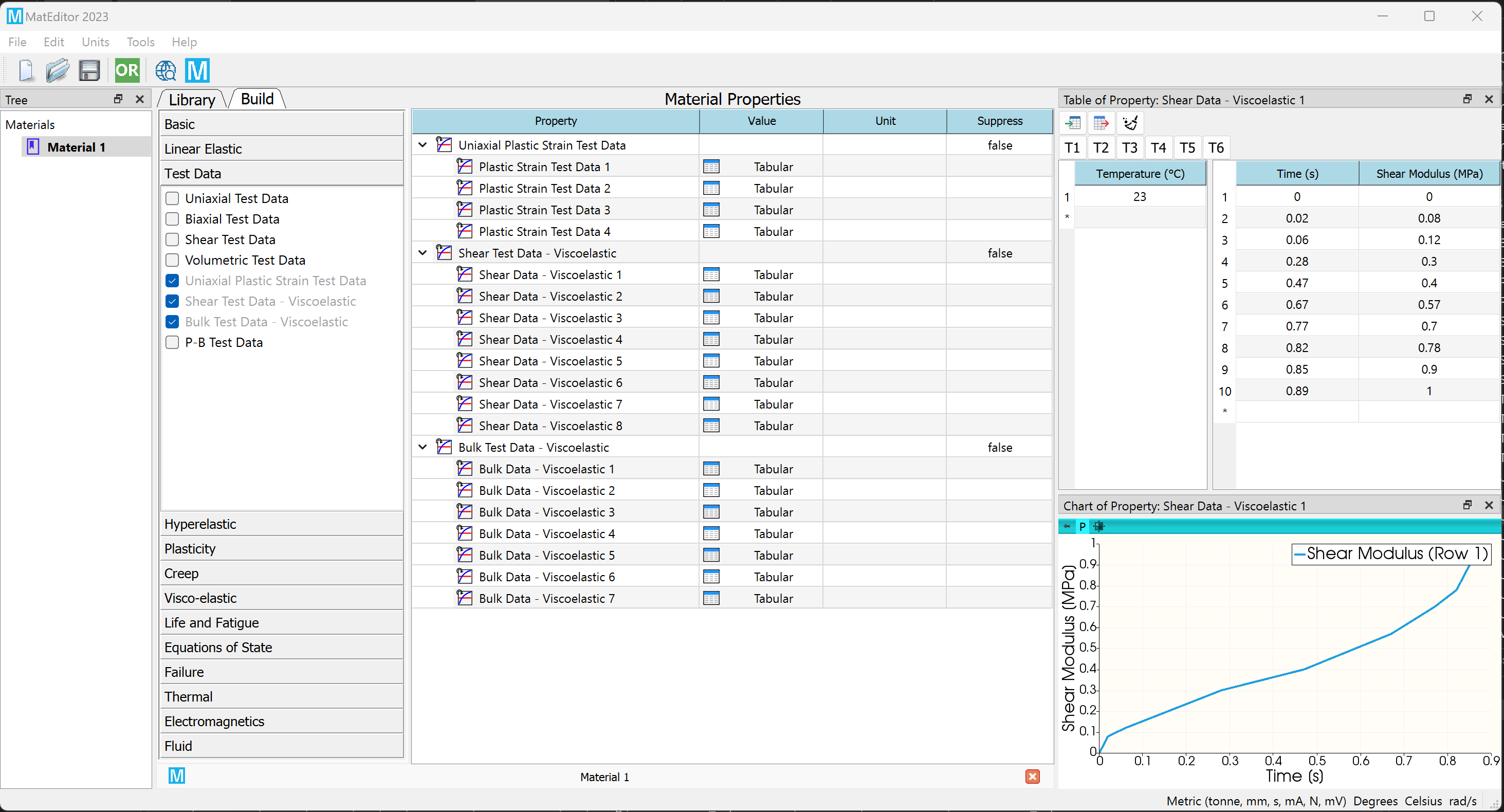
Engineering software involves a vast amount of material data. Although the data volume is not nearly as large as mesh or result data, the volume for material data is a medium amount because it could potentially include test data and other content. XML is a good format choice as it balances readability, read/write efficiency, and support for web-based applications. There is currently no universal data format standard for materials due to their many diverse types, and most software vendors design their own formats. Both WELSIM and MatEditor software uses XML format as their text data format, and it demonstrates stellar performance. It is worth noting that material data often includes numerous units. When designing the format, it's advised to reuse existing units as much as possible to reduce file size and improve read/write efficiency.
Solver input data
Solver control input data, referred to as solver files, typically separate the mesh data from the control commands. As a result, solver files are not large in size, so ASCII text format is suitable for this purpose. The format of solver files primarily depends on the specifications of the solver. If it is a customized solver, using JSON can quickly implement the reading and writing of solver files, making it a good choice. Additionally, JSON inherently supports RPC communication, providing a foundation for remote invocation of the solver and reducing maintenance costs. Some traditional solver formats can also be used widely, such as the Abaqus format Calculix uses, additionally, Dyna and Nastran formats are commonly applied as well.
Result data
Result data is the most essential and voluminous data in simulation software. Depending on the solution, result files may or may not include mesh data. Therefore, solving processes that involve adaptive mesh will have a significantly increased result file size because of the containing mesh.
Similar to mesh data, VTU is currently the best format for result data. It has an open-source library and friendly licensing, enabling quick reading and writing of VTU result files. Although it is based on XML data format, it also supports saving large data portions in binary format. PVTU supports parallel result files, effectively utilizing multi-core hardware resources and increasing read/write efficiency. For multi-step analysis, result files can be read and written using the PVD format, which is based on VTU. PVD is the default file format of the open-source software Paraview. For more details, refer to the article "(ParaView Data (pvd) file format and writing)[https://welsim.com/2022/10/04/paraview-data-file-format-and-writing.html]." Thanks to the system of VTK and Paraview, VTU result files are very compatible.
Cache data
Caching is widely used in operating systems and various software applications. In the CAE simulation, caching methods are used at various stages to store temporary computational results, user operations, and other data. Caches can be stored in project or computing directories, as well as in the temporary folder of the operating system.
SQLite can be used for some cache files, such as cache during meshing generation, cache at solving, GPU computing cache, local storage cache, etc. SQLite offers fast read/write speeds and is easily scalable. Cache files can be designed in a specific format according to requirements.
RPC interaction data
Modern general-purpose simulation software requires higher flexibility. Using both RPC communication and process management mechanisms is undoubtedly the best approach to implementing flexibility. For more details, refer to the article "(Design and architecture of modern general-purpose engineering simulation software)[https://welsim.com/2023/06/23/design-and-architecture-of-modern-general-purpose-engineering-simulation-software.html]." In RPC communication, TLS is inevitably needed to ensure security. This includes certificates and key files (containing public and private keys) encrypted with RSA, usually in ASCII text format. Other types of files required for RPC may be in YAML format and the content in JSON format.
Project persistence data
Project persistence is an essential feature for engineering software to be a complete set. The quality of the project persistence data design directly affects the product's development efficiency and how stable the backward compatibility with previous versions will be. The core of project persistence data in CAE software is the tree objects and their property data. WELSIM utilizes the HDF5 format, which exhibits excellent performance and maintainability. The compression feature of HDF5 can also handle large data within projects. HDF5 provides a rich set of open-source packages for reading and writing H5 files, and the official HDFView tool is available in order to open and browse H5 files.
Configuration data
A mature software product should have various configuration files that can be customized or modified for different settings, and it should be persistently stored for GUI settings. Configuration files are expected to have strong readability and be easy to understand because they need to allow users from different areas to modify the files. YAML (Yet Another Markup Language) is a highly readable and expressive data interchange format that uses a concise and easy-to-read syntax to represent data. It supports features such as comments and multi-line strings, making configuration files easier to write and maintain. YAML is a very suitable configuration data file format.
Some large framework software also provides the automatic generation of configuration files. For example, the QSettings provided by QT can write to different locations based on the operating system without developer intervention, which is an innovative way to handle configuration data.
Log
There are various types of log files, including user operation logs, solver logs, and even logs for software defects. Generally, ASCII-formatted TXT files are used for ease of reading. It is important to include timestamps in log files. Additionally, when log files become too large, it is necessary to automatically create a new log file with a different name to store new log data.
Conclusion
The development of general-purpose engineering simulation (CAE) software is a massive undertaking. Developers need to optimize development resources to deliver products and features as quickly and efficiently as possible while also ensuring maintainability. The data formats summarized in this article have been successfully applied in the development of WELSIM, demonstrating outstanding performance, low maintenance costs, and ease of expansion. They serve as a good reference for software development and data format selection. The data formats discussed in this article are summarized as follows:
Due to space limitations, this article focuses on narrowing down the discussion of data formats, specifically for CAE software. For startup software, it's advised to choose neutral file formats that offer high versatility. Some neutral formats may also have open-source packages available, which can expedite product development.
WELSIM is the #1 engineering simulation software for the open-source community.
reacted with thumbs up emoji reacted with thumbs down emoji reacted with laugh emoji reacted with hooray emoji reacted with confused emoji reacted with heart emoji reacted with rocket emoji reacted with eyes emoji
-
Data is one of the core components of engineering software, so the stability of data reading, writing, conversion, and manipulation is vital for the performance of engineering software. General-purpose engineering simulation CAE software is no exception, it also places high demands on maintainability, due to its long research and development cycle. Simulation software covers a wide range of fields, such as data persistence commonly used in software engineering and computational results such as node and element data solved using finite element and finite volume methods. For this reason, various data formats are needed to implement different features.
Choosing the right data format can greatly improve product performance and maintainability, while also benefiting developers by saving development time and resources. Based on years of authentic experience in developing WELSIM, this article discusses data formats and application concepts in general-purpose engineering simulation software.
Geometric shape data
The entry point for general-purpose simulation software is geometric models, commonly referred to as CAD models by engineers. Since the core of CAE simulation software mainly lies in computation and analysis, the primary method to obtain geometric data is to read CAD models rather than generate them from scratch.
Currently, the most suitable geometric data format for simulation software is STEP. Although introduced in the 1980s, it is still widely used today. The STEP format provides a clear and precise representation of the entire 3D model, including not only the basic geometric shape but also the topology, allowing for high-precision reading and storage. It supports length units and can meet the requirements of the majority of CAE applications. The well-known cloud-based CAD vendor OnShape exports CAD data in the STEP format, and the popular open-source geometry engine OpenCascade also provides excellent support for STEP, facilitating its application and compatibility. Currently, STEP is the primary CAD file import format for WELSIM.
There are also other well-known geometric data formats such as JT, ACIS, and Parasolid. These data formats may be discussed in future articles due to space limitations.
In addition to complete geometric data formats, there is another category that contains only surface information, represented by STL. This type of data does not include topological information but consists of triangular mesh data representing the surface. With the recent rise of 3D printing, such data formats as STL have become popular. However, their application in general CAE analysis is somewhat limited due to the lack of topological and volumetric information.
Mesh data
Mesh data is the most important input data for engineering simulation software, characterized by its large volume and diverse types. Balancing performance and versatility is the main criteria for selecting a mesh data format. After years of quality development and customer feedback, WELSIM considers UNV and PVTU two exceptional formats for mesh data.
UNV is a general-purpose neutral mesh data format proposed by I-DEAS. It has clear and easily understandable field definitions, and it's easy to implement in programming. UNV supports a wide range of element types and includes a group module that allows the definition of various boundary conditions and contacts. In the industry, UNV is largely accepted and effective. In practical applications, the default format is ASCII text, but developers can also use tools, like gzstream, to convert it to binary files.
PVTU, proposed by Kitware, is an unstructured mesh format based on VTU. Its distinctive feature is that it can support multi-core parallel reading and writing, greatly improving the speed of mesh file operations. The underlying version, VTU, is an XML-based data format, and the core data can be stored in either ASCII or binary formats, meeting different usage scenarios.
Material data
Engineering software involves a vast amount of material data. Although the data volume is not nearly as large as mesh or result data, the volume for material data is a medium amount because it could potentially include test data and other content. XML is a good format choice as it balances readability, read/write efficiency, and support for web-based applications. There is currently no universal data format standard for materials due to their many diverse types, and most software vendors design their own formats. Both WELSIM and MatEditor software uses XML format as their text data format, and it demonstrates stellar performance. It is worth noting that material data often includes numerous units. When designing the format, it's advised to reuse existing units as much as possible to reduce file size and improve read/write efficiency.
Solver input data
Solver control input data, referred to as solver files, typically separate the mesh data from the control commands. As a result, solver files are not large in size, so ASCII text format is suitable for this purpose. The format of solver files primarily depends on the specifications of the solver. If it is a customized solver, using JSON can quickly implement the reading and writing of solver files, making it a good choice. Additionally, JSON inherently supports RPC communication, providing a foundation for remote invocation of the solver and reducing maintenance costs. Some traditional solver formats can also be used widely, such as the Abaqus format Calculix uses, additionally, Dyna and Nastran formats are commonly applied as well.
Result data
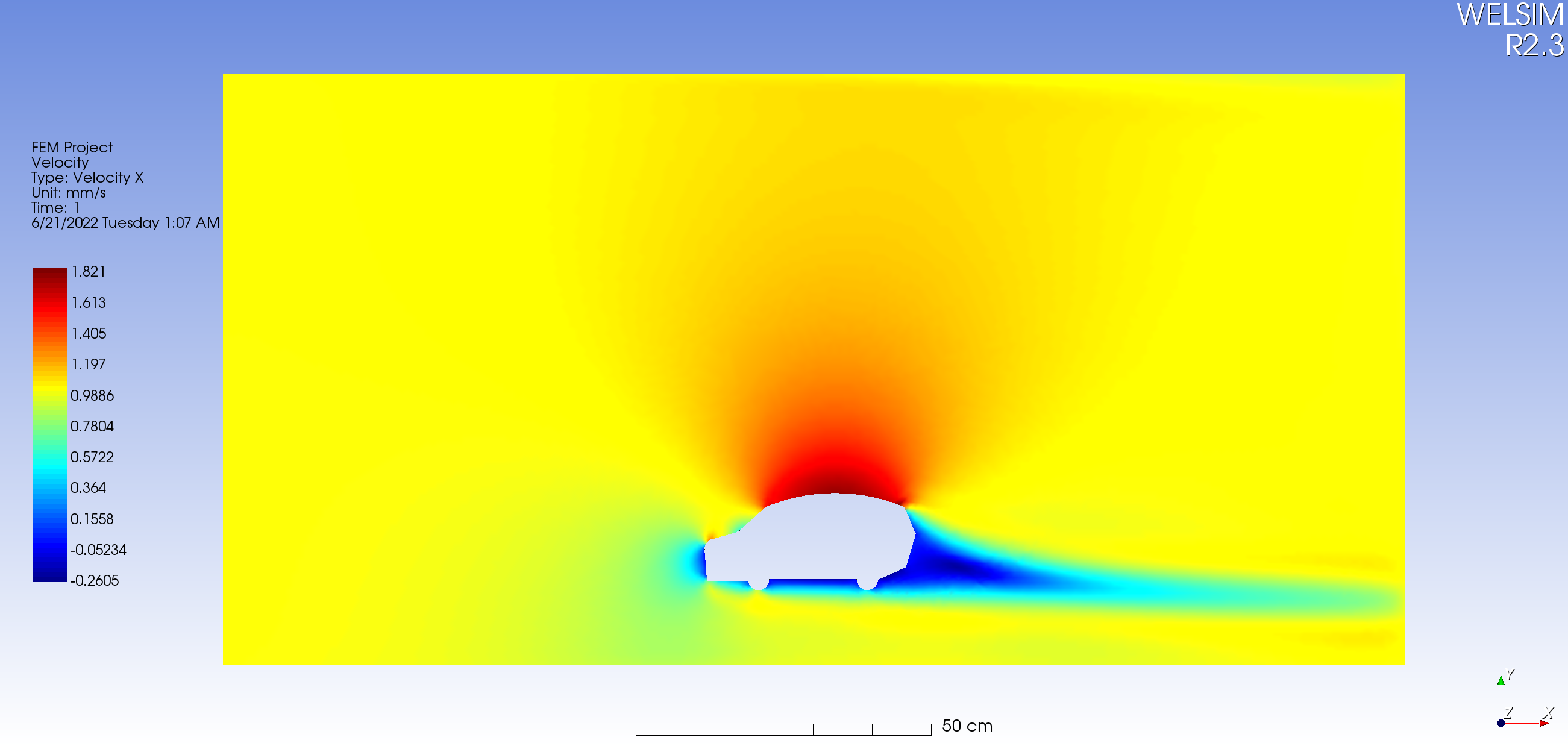
Result data is the most essential and voluminous data in simulation software. Depending on the solution, result files may or may not include mesh data. Therefore, solving processes that involve adaptive mesh will have a significantly increased result file size because of the containing mesh.
Similar to mesh data, VTU is currently the best format for result data. It has an open-source library and friendly licensing, enabling quick reading and writing of VTU result files. Although it is based on XML data format, it also supports saving large data portions in binary format. PVTU supports parallel result files, effectively utilizing multi-core hardware resources and increasing read/write efficiency. For multi-step analysis, result files can be read and written using the PVD format, which is based on VTU. PVD is the default file format of the open-source software Paraview. For more details, refer to the article "(ParaView Data (pvd) file format and writing)[https://welsim.com/2022/10/04/paraview-data-file-format-and-writing.html]." Thanks to the system of VTK and Paraview, VTU result files are very compatible.
Cache data
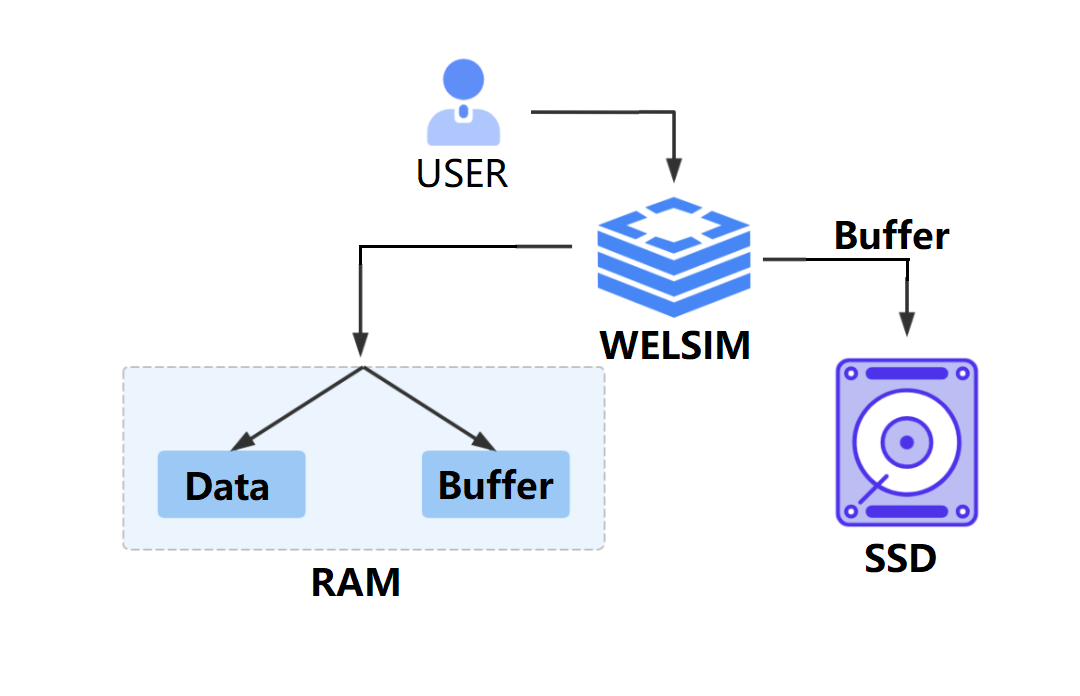
Caching is widely used in operating systems and various software applications. In the CAE simulation, caching methods are used at various stages to store temporary computational results, user operations, and other data. Caches can be stored in project or computing directories, as well as in the temporary folder of the operating system.
SQLite can be used for some cache files, such as cache during meshing generation, cache at solving, GPU computing cache, local storage cache, etc. SQLite offers fast read/write speeds and is easily scalable. Cache files can be designed in a specific format according to requirements.
RPC interaction data
Modern general-purpose simulation software requires higher flexibility. Using both RPC communication and process management mechanisms is undoubtedly the best approach to implementing flexibility. For more details, refer to the article "(Design and architecture of modern general-purpose engineering simulation software)[https://welsim.com/2023/06/23/design-and-architecture-of-modern-general-purpose-engineering-simulation-software.html]." In RPC communication, TLS is inevitably needed to ensure security. This includes certificates and key files (containing public and private keys) encrypted with RSA, usually in ASCII text format. Other types of files required for RPC may be in YAML format and the content in JSON format.
Project persistence data
Project persistence is an essential feature for engineering software to be a complete set. The quality of the project persistence data design directly affects the product's development efficiency and how stable the backward compatibility with previous versions will be. The core of project persistence data in CAE software is the tree objects and their property data. WELSIM utilizes the HDF5 format, which exhibits excellent performance and maintainability. The compression feature of HDF5 can also handle large data within projects. HDF5 provides a rich set of open-source packages for reading and writing H5 files, and the official HDFView tool is available in order to open and browse H5 files.
Configuration data
A mature software product should have various configuration files that can be customized or modified for different settings, and it should be persistently stored for GUI settings. Configuration files are expected to have strong readability and be easy to understand because they need to allow users from different areas to modify the files. YAML (Yet Another Markup Language) is a highly readable and expressive data interchange format that uses a concise and easy-to-read syntax to represent data. It supports features such as comments and multi-line strings, making configuration files easier to write and maintain. YAML is a very suitable configuration data file format.
Some large framework software also provides the automatic generation of configuration files. For example, the QSettings provided by QT can write to different locations based on the operating system without developer intervention, which is an innovative way to handle configuration data.
Log
There are various types of log files, including user operation logs, solver logs, and even logs for software defects. Generally, ASCII-formatted TXT files are used for ease of reading. It is important to include timestamps in log files. Additionally, when log files become too large, it is necessary to automatically create a new log file with a different name to store new log data.
Conclusion
The development of general-purpose engineering simulation (CAE) software is a massive undertaking. Developers need to optimize development resources to deliver products and features as quickly and efficiently as possible while also ensuring maintainability. The data formats summarized in this article have been successfully applied in the development of WELSIM, demonstrating outstanding performance, low maintenance costs, and ease of expansion. They serve as a good reference for software development and data format selection. The data formats discussed in this article are summarized as follows:
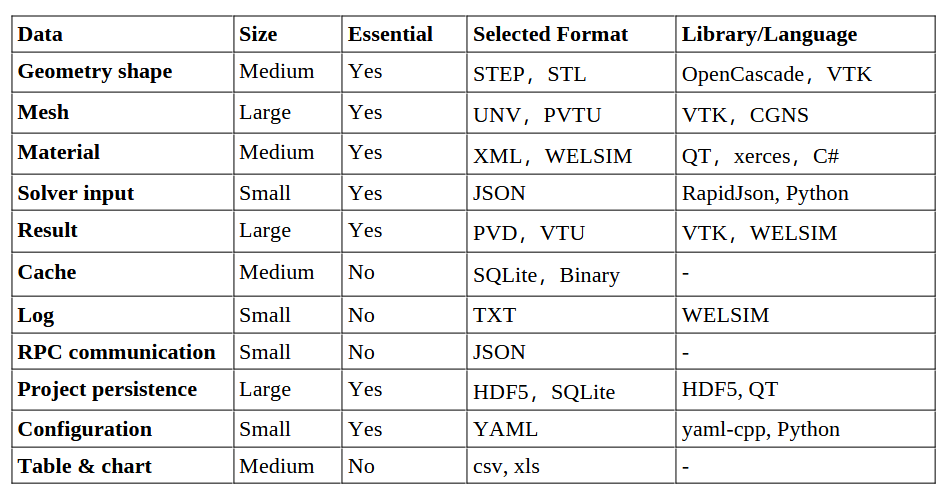
Due to space limitations, this article focuses on narrowing down the discussion of data formats, specifically for CAE software. For startup software, it's advised to choose neutral file formats that offer high versatility. Some neutral formats may also have open-source packages available, which can expedite product development.
WELSIM is the #1 engineering simulation software for the open-source community.
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions