You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
GDS is a universal 2D CAD electronic layout format widely used in the integrated circuit and chip industry. The simple syntax and broad ecosystem makes it one of the main file formats in the chip and EDA industry. Since engineering simulation CAE software deals with various file formats, supporting GDS files is a necessary feature of modern simulation software. Imported GDS files can be directly applied to thermal and electromagnetic analysis, expanding the application ecosystem of CAE software and enhancing user experience.
The structure of GDS files can include seven elements: Boundary, Path, SREF, AREF, Text, Node, and Box. Details can be found in the article "GDSII, the data format for chip and integrated circuit design." Among them, Text, Node, and Box do not contain actual geometric information. Therefore, when reading GDS files, the focus is on Boundary, Path, SREF, and AREF content. This information is then converted into geometric models. WELSIM can quickly read GDS files and generate models for simulation analysis.
Import GDS file
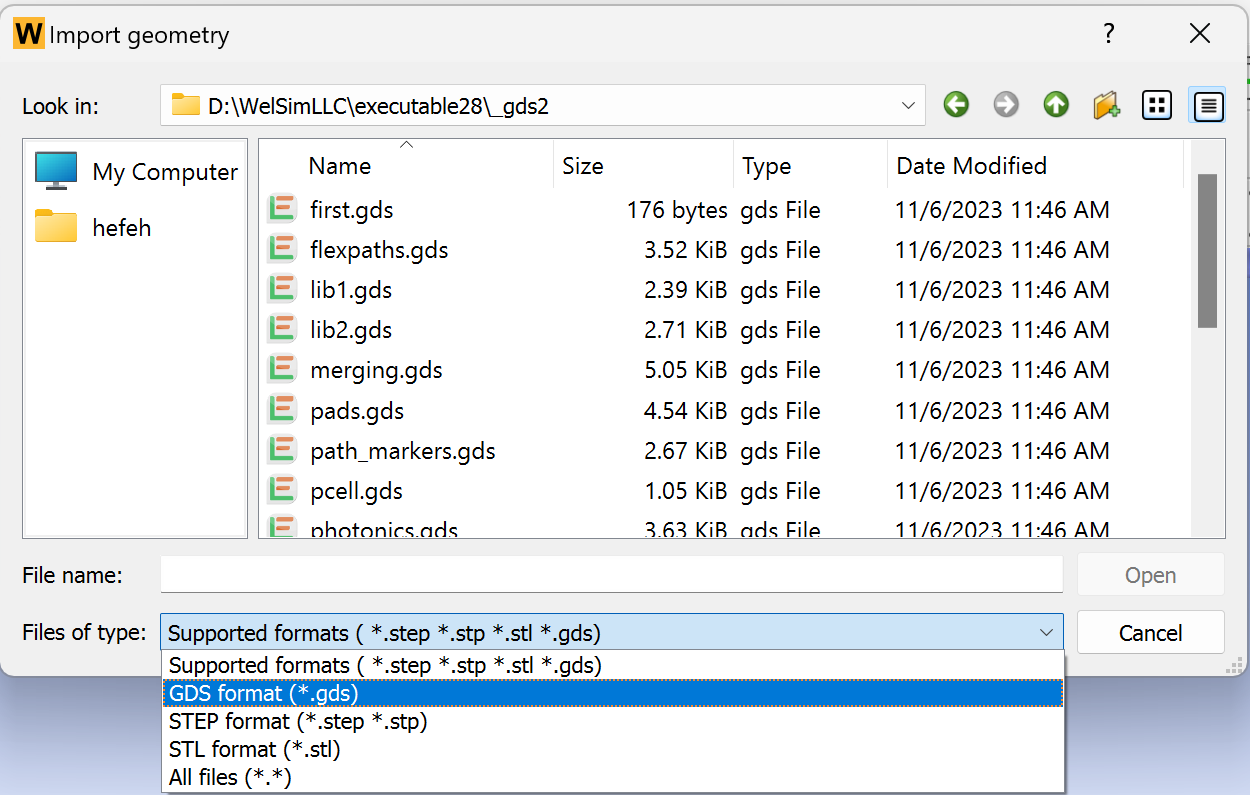
In WELSIM, after opening the software and creating a new project, click on "Import Geometry" to open the file dialog.
After importing, the 3D graphics window will display the geometry, and the project window will show the geometry objects.
Since GDS does not contain color information, WELSIM colors the imported geometry randomly; users can modify the colors afterward. All graphics are default on the XY plane, and users can export the model as a STEP file, achieving the conversion from GDSII to STEP format.
Since it is a 2D model, it's recommended to set the project to 2D and define relevant properties according to the analysis type. Here, we set the model for electromagnetic analysis.
In finite element simulation calculations, the geometry needs to be meshed. Simply click the meshing button to quickly generate the mesh.
Then, proceed with relevant analysis settings, such as adding boundary conditions. After completing the settings, export the solver's input scripts.
You will see the generated solver scripts in the specified directory.
As GDS is fundamentally a 2D CAD file format, the imported model belongs to the XY plane's 3D surface model. In future versions, there may be an option to set the thickness of components, generating 3D modeling. The imported GDS model does not consider hierarchy and is uniformly placed under the geometry group object. Users can identify hierarchy through object names. Future versions may reflect hierarchy in the tree structure. Additionally, GDS often uses multiple straight-line segments to define curves, resulting in the imported geometric model having curved boundaries represented by multiple line segments. When applying boundary conditions, users need to select multiple line segments simultaneously.
Conclusion
GDSII is a widely used data format in the chip and integrated circuit industry, and it's one of the CAD formats modern general-purpose engineering simulation software needs to support. WELSIM supports the import of GDS files, automatically generates geometric models, and provides support for subsequent meshing and analysis.
WelSim is not affiliated with GDSII. The development team and organization behind GDSII have no connection to WelSim. This reference is used here solely for the purpose of a technical blog article and software usage.
reacted with thumbs up emoji reacted with thumbs down emoji reacted with laugh emoji reacted with hooray emoji reacted with confused emoji reacted with heart emoji reacted with rocket emoji reacted with eyes emoji
-
GDS is a universal 2D CAD electronic layout format widely used in the integrated circuit and chip industry. The simple syntax and broad ecosystem makes it one of the main file formats in the chip and EDA industry. Since engineering simulation CAE software deals with various file formats, supporting GDS files is a necessary feature of modern simulation software. Imported GDS files can be directly applied to thermal and electromagnetic analysis, expanding the application ecosystem of CAE software and enhancing user experience.

The structure of GDS files can include seven elements: Boundary, Path, SREF, AREF, Text, Node, and Box. Details can be found in the article "GDSII, the data format for chip and integrated circuit design." Among them, Text, Node, and Box do not contain actual geometric information. Therefore, when reading GDS files, the focus is on Boundary, Path, SREF, and AREF content. This information is then converted into geometric models. WELSIM can quickly read GDS files and generate models for simulation analysis.
Import GDS file
In WELSIM, after opening the software and creating a new project, click on "Import Geometry" to open the file dialog.
After importing, the 3D graphics window will display the geometry, and the project window will show the geometry objects.
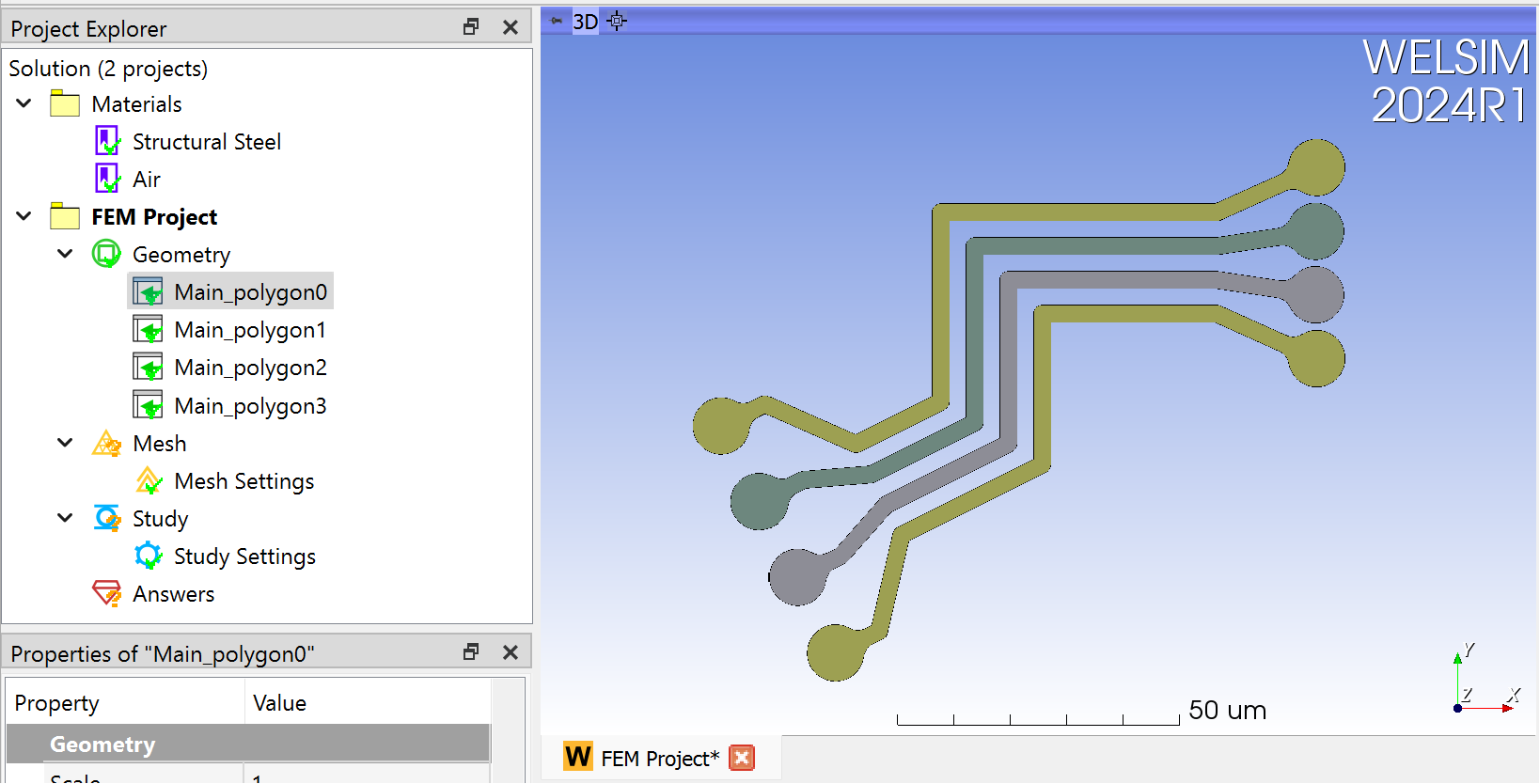
Since GDS does not contain color information, WELSIM colors the imported geometry randomly; users can modify the colors afterward. All graphics are default on the XY plane, and users can export the model as a STEP file, achieving the conversion from GDSII to STEP format.
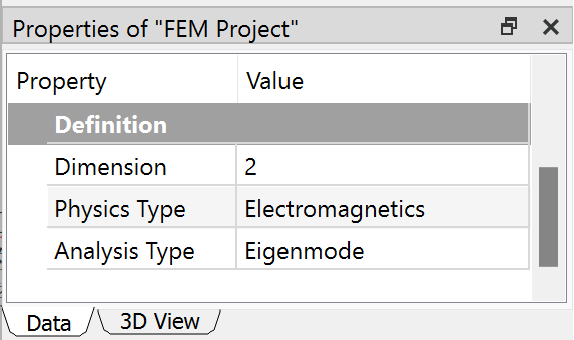
Since it is a 2D model, it's recommended to set the project to 2D and define relevant properties according to the analysis type. Here, we set the model for electromagnetic analysis.
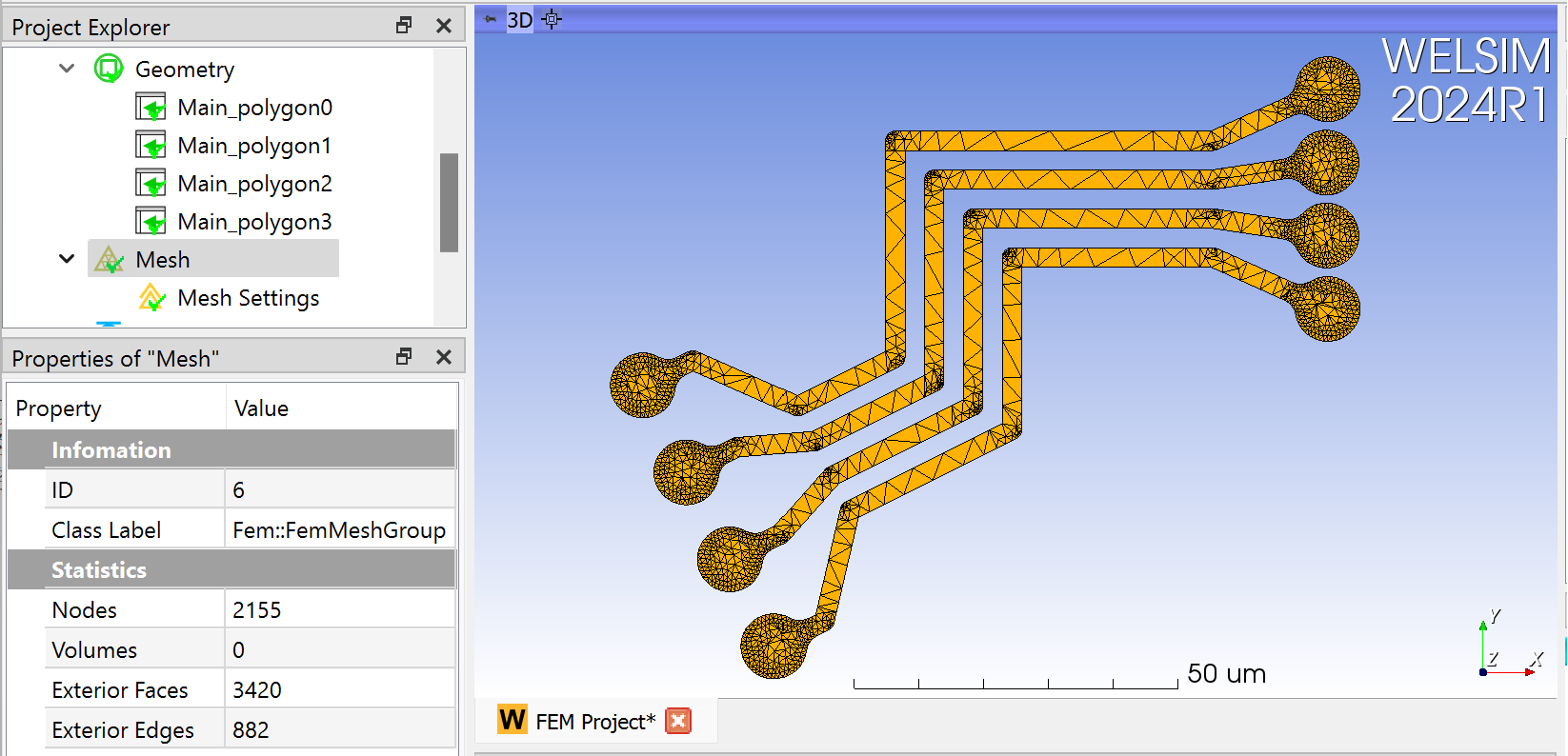
In finite element simulation calculations, the geometry needs to be meshed. Simply click the meshing button to quickly generate the mesh.
Then, proceed with relevant analysis settings, such as adding boundary conditions. After completing the settings, export the solver's input scripts.
You will see the generated solver scripts in the specified directory.
As GDS is fundamentally a 2D CAD file format, the imported model belongs to the XY plane's 3D surface model. In future versions, there may be an option to set the thickness of components, generating 3D modeling. The imported GDS model does not consider hierarchy and is uniformly placed under the geometry group object. Users can identify hierarchy through object names. Future versions may reflect hierarchy in the tree structure. Additionally, GDS often uses multiple straight-line segments to define curves, resulting in the imported geometric model having curved boundaries represented by multiple line segments. When applying boundary conditions, users need to select multiple line segments simultaneously.
Conclusion
GDSII is a widely used data format in the chip and integrated circuit industry, and it's one of the CAD formats modern general-purpose engineering simulation software needs to support. WELSIM supports the import of GDS files, automatically generates geometric models, and provides support for subsequent meshing and analysis.
WelSim is not affiliated with GDSII. The development team and organization behind GDSII have no connection to WelSim. This reference is used here solely for the purpose of a technical blog article and software usage.
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions