More often than not, rather than starting a new project from scratch, you would either join a company and start working on an existing project, or you would contribute to an already established open source project. So in this case, in order to get the repository from GitHub to your local machine, you would need to use the git clone command.
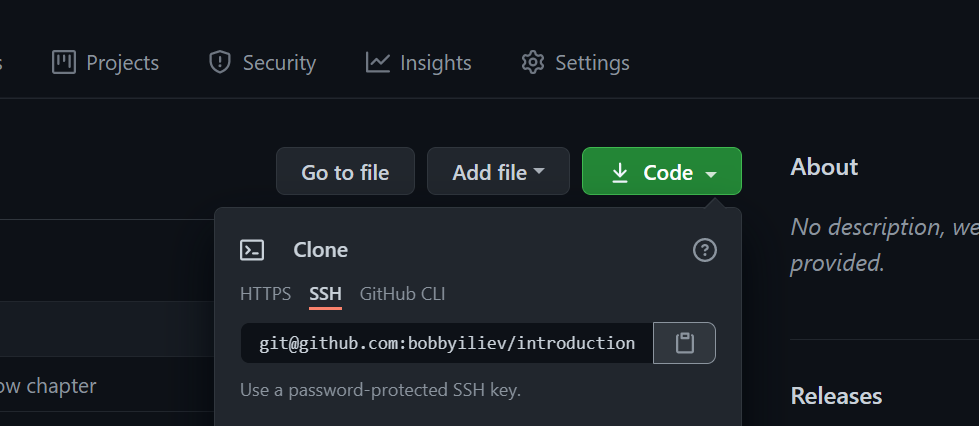
The most straightforward way to clone your GitHub repository is to first visit the repository in your browser, and then click on the green Code button and choose the method that you want to use to clone the repository:
In my case, I would go for the SSH method as I already have my SSH keys configured as per chapter 14.
As I am cloning this repository here, the URL would look like this:
git@github.com:bobbyiliev/introduction-to-bash-scripting.git
Once you have this in my clipboard, head back to your terminal, go to a directory where you would like to clone the repository to and then run the following command:
git clone git@github.com:bobbyiliev/introduction-to-bash-scripting.gitThe output that you would get will look like this:
Cloning into 'introduction-to-bash-scripting'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 21, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (21/21), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (16/16), done.
remote: Total 215 (delta 7), reused 14 (delta 4), pack-reused 194
Receiving objects: 100% (215/215), 3.08 MiB | 5.38 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (114/114), done.
Essentially what the git clone command does is to more or less download the repository from GitHub to your local folder.
Now you can start making the changes to the project by creating a new branch, writing some code, and finally committing and pushing your changes!
One important thing to keep in mind is that in case that you are not the maintainer of the repository and do not have the right to push to the repository, you would need to first fork the original repository and then clone the forked repository from your account. In the next chapter, we will go through the full process of forking a repository!