- SpringBoot - 3.4.1
- Spring Security - 6.4.2
- Jakarta EE - 10
- Java - 21+
- Open API Swagger Docs - 2.7.0
- Google Gson - 2.11.0
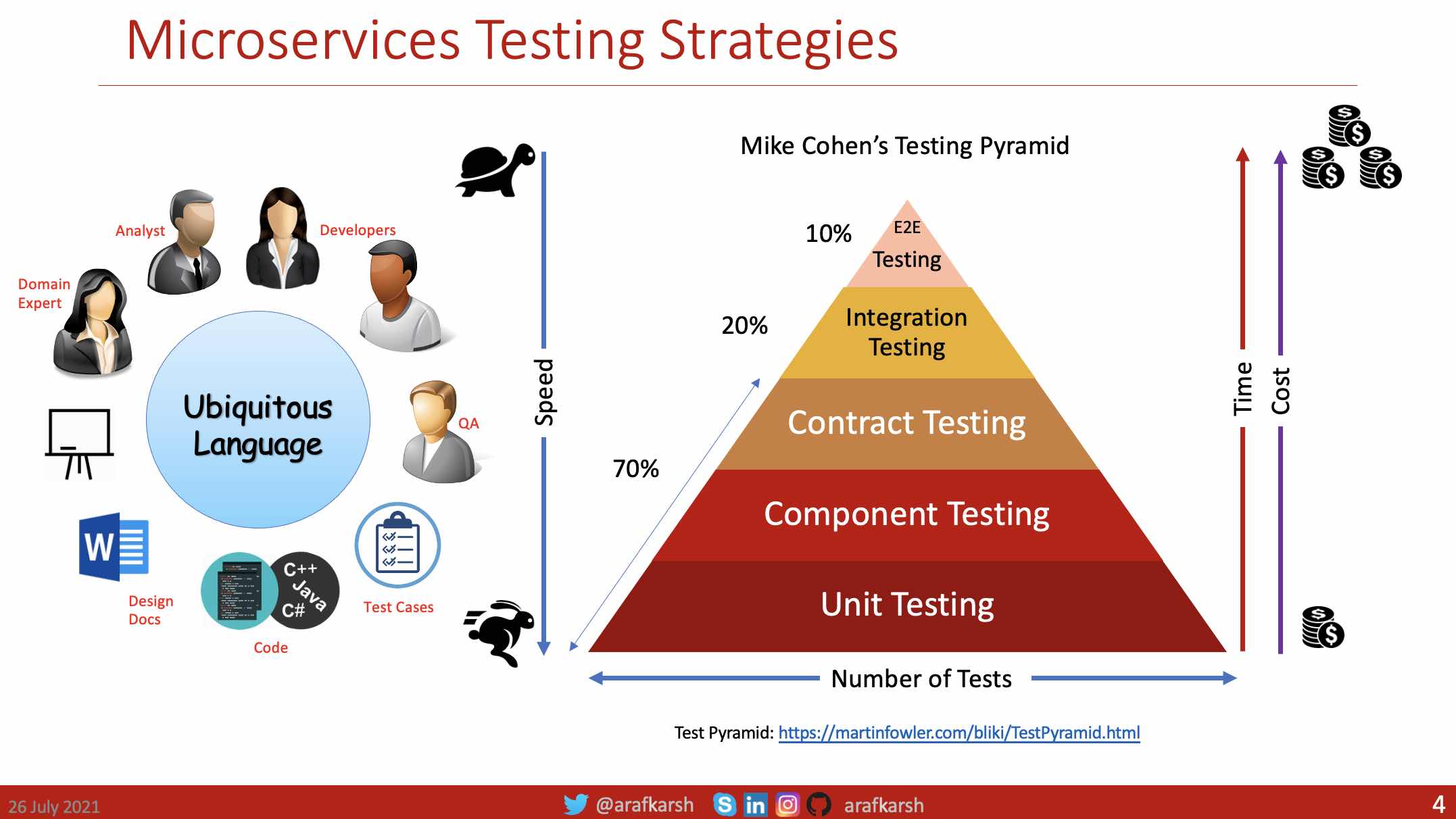
Thorough automation in application testing is crucial for guaranteeing the dependability and optimal performance of cloud-native applications, particularly when prioritizing a rapid time-to-market approach through Continuous Deployment.
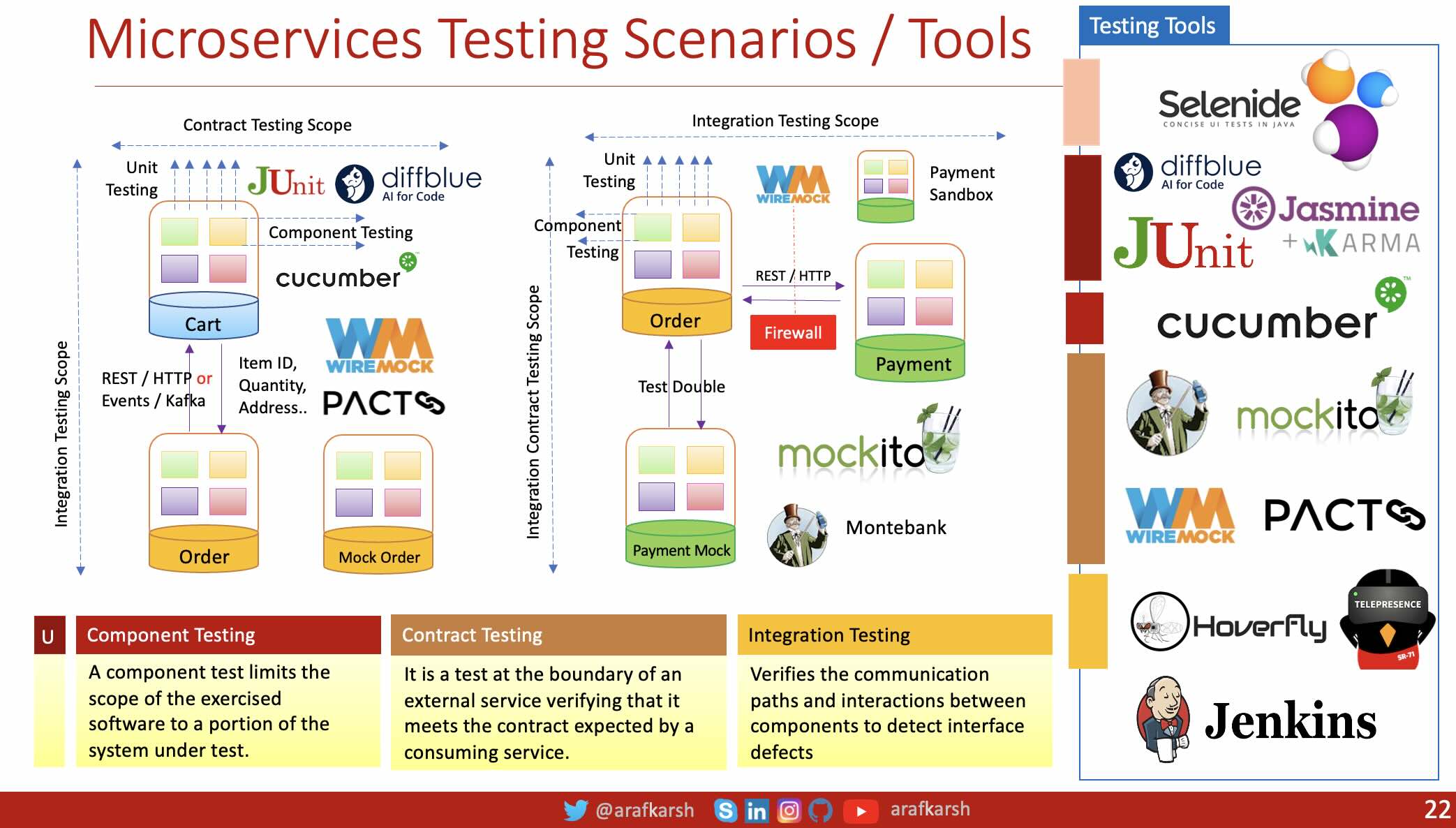
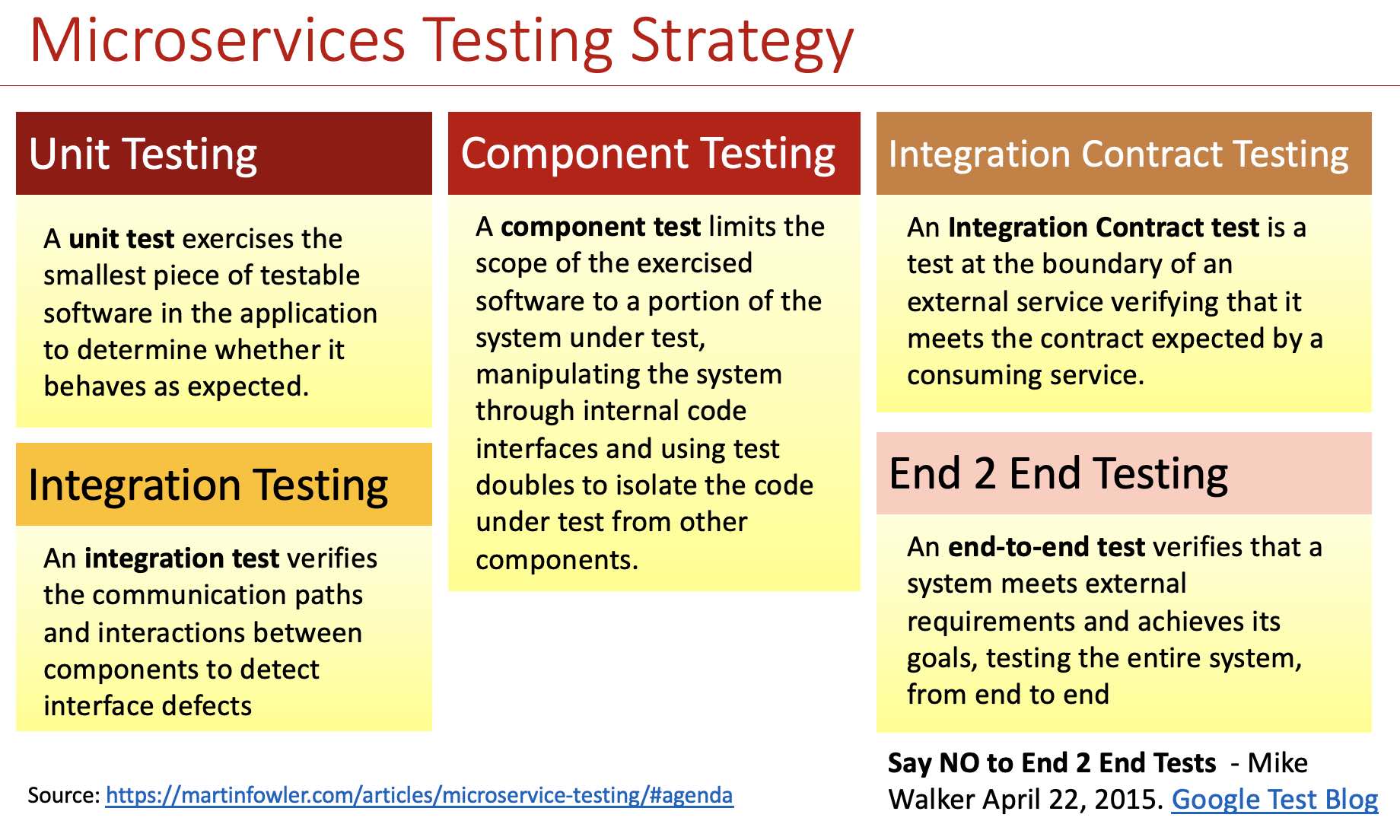
The approach includes unit testing, integration testing, contract testing, and end-to-end testing.
- Unit testing: A unit test exercises the smallest piece of testable software in the application to determine whether it behaves as expected.
- Component Testing: A component test limits the scope of the exercised software to a portion of the system under test, manipulating the system through internal code interfaces and using test doubles to isolate the code under test from other components.
- Contract testing, facilitated by tools like Pact, ensures that services adhere to the agreed-upon API contracts.
- Integration testing: An Integration Contract test is a test at the boundary of an external service verifying that it meets the contract expected by a consuming service.
- End-to-end testing: An end-to-end test verifies that a system meets external requirements and achieves its goals, testing the entire system from end to end.
| Testing Category | Tools | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Testing Platforms | Junit, Spock, TestNG |
| 1 | Unit Testing | Junit, Spock, TestNG |
| 2 | Component Testing | SpringBoot, Cucumber, RestAssured, Mockito |
| 3 | Integration Contract Testing | SpringBoot, Mockito, WireMock, Pact |
| 4 | Integration Testing | SpringBoot, WireMock |
| 5 | UI Testing / E2E Testing | Selenium + Cucumber |
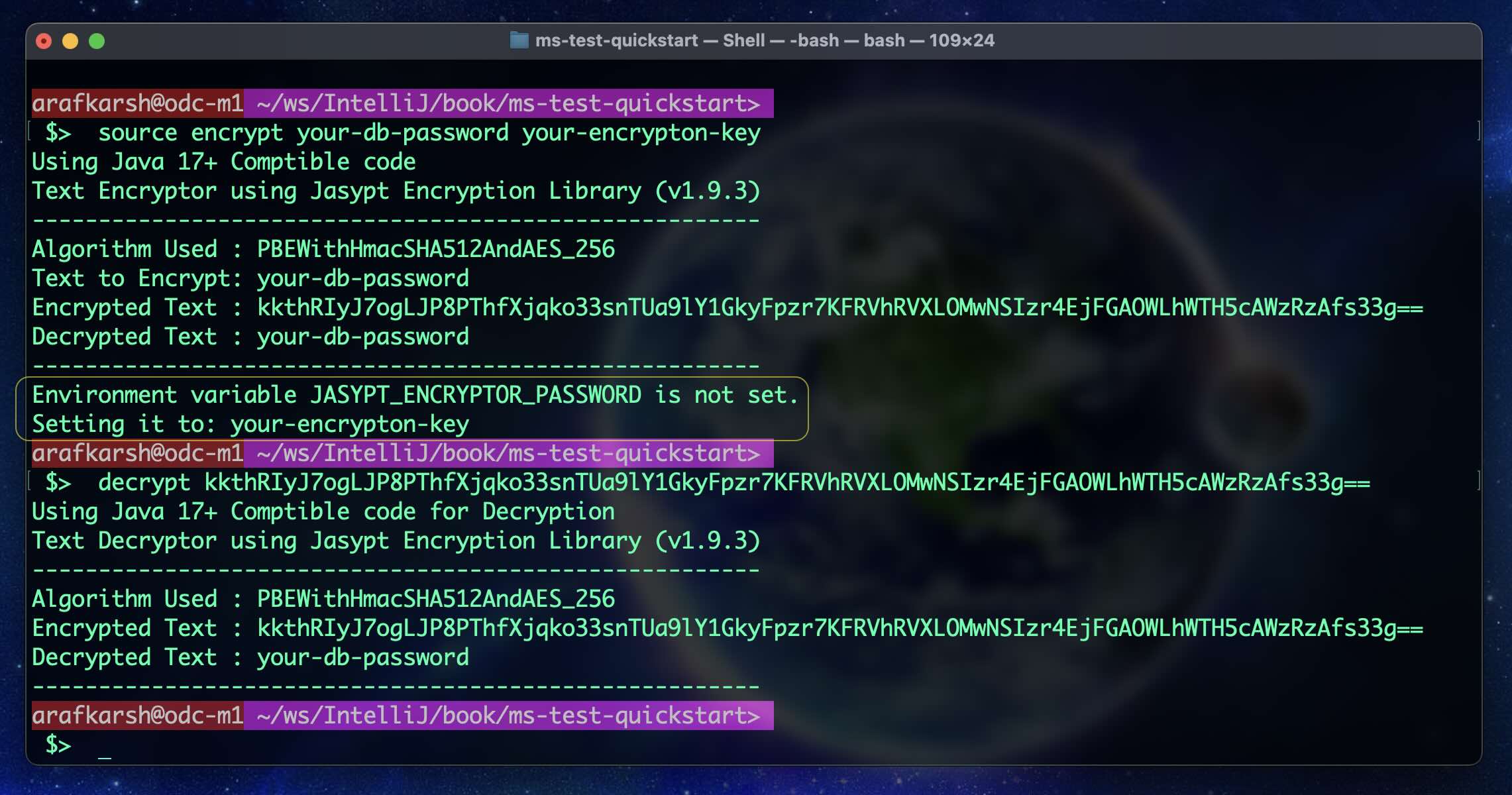
Run the follwing command line option
$ source encrypt your-db-password your-encrypton-key
Your encryption key will be set in the following Environment variable. SpringBoot Will automatically pickup the encryption key from this environment variable.
JASYPT_ENCRYPTOR_PASSWORD=your-encrypton-key
Update the property file in the local file
spring.datasource.password=ENC(kkthRIyJ7ogLJP8PThfXjqko33snTUa9lY1GkyFpzr7KFRVhRVXLOMwNSIzr4EjFGAOWLhWTH5cAWzRzAfs33g==)
AND the property template in src/main/resources/app.props.tmpl
spring.datasource.password=ENC(kkthRIyJ7ogLJP8PThfXjqko33snTUa9lY1GkyFpzr7KFRVhRVXLOMwNSIzr4EjFGAOWLhWTH5cAWzRzAfs33g==)
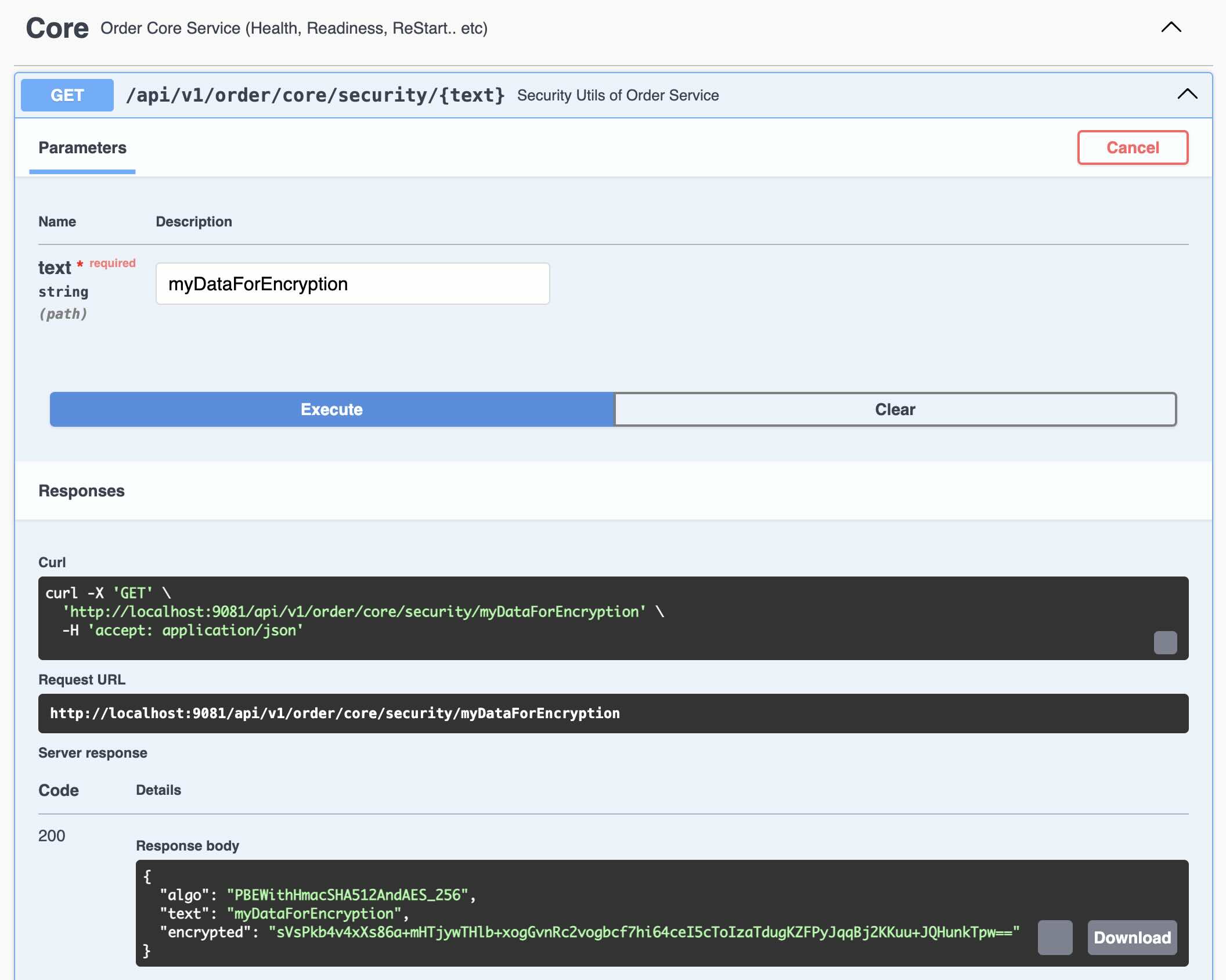
You can use the following REST Endpoint to encrypt the sensitive data. This will work only after setting
the environment variable JASYPT_ENCRYPTOR_PASSWORD and creating the first DB password
using the command line options.
| 1 | Testing Framework | Version | Test Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | JUnit 5 | 5.10.2 | 62 |
| 1.2 | SpringBootTest 3 | 3.3.4 | 01 |
| 1.3 | RestAssured 5 | 5.4.0 | 29 |
| 1.4 | Mockito 5 | 5.12.0 | 21 |
| 1.5 | WireMock 3 | 3.6.0 | 12 |
| 1.6 | Cucumber 7 | 7.18.0 | 03 |
| 1.7 | Selenium 4 | 4.12.0 | 02 |
| 1.8 | Pact 4 | 4.0.10 | 03 |
| 2 | Testing Framework | Version | Test Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | Spock 2 | 2.4.0 | 21 |
| 2.2 | SpringBootTest 3 | 3.3.4 | 02 |
| 2.3 | RestAssured 5 | 5.4.0 | 08 |
| 2.4 | Mockito 5 | 5.12.0 | 02 |
| 2.5 | WireMock 3 | 3.6.0 | 07 |
| 2.6 | Cucumber 7 | 7.18.0 | 03 |
| 2.7 | Selenium 4 | 4.12.0 | 02 |
| 2.8 | Pact 4 | 4.0.10 | 00 |
| 3 | Testing Framework | Version | Test Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.1 | TestNG 7 | 7.10.2 | 18 |
| 3.2 | SpringBootTest 3 | 3.3.4 | 02 |
| 3.3 | RestAssured 5 | 5.4.0 | 05 |
| 3.4 | Mockito 5 | 5.12.0 | 02 |
| 3.5 | WireMock 3 | 3.6.0 | 03 |
| 3.6 | Cucumber 7 | 7.18.0 | 03 |
| 3.7 | Selenium 4 | 4.12.0 | 02 |
| 3.8 | Pact | NA | No Support |
| 4 | Testing Framework | Version |
|---|---|---|
| 4.1 | Hamcrest 2 | 2.2.0 |
| 4.2 | Google Truth | 1.0.1 |
| 4.3 | AssertJ 3 | 3.26.3 |
| 5 | Other Libraries | Version |
|---|---|---|
| 5.1 | Apache Commons | 3.17.0 |
| 5.2 | Apache Http Client | 5.4.1 |
| 5.3 | Apache Http Core | 5.3.1 |
| 5.2 | Google GSON | 2.8.7 |
| 5.3 | Google Guava | 33.3.1.1-jre |
| 5.4 | Faster XML | 2.18.0 |
| 6 | Logging Libraries | Version |
|---|---|---|
| 6.1 | SL4J | 2.0.16 |
| 6.2 | Logback | 1.5.8 |
| 6.3 | Log stash | 8.0 |
| 7 | Open API Libraries | Version |
|---|---|---|
| 7.1 | Open API Webmvc | 2.6.0 |
| 7.2 | Open API Common | 1.8.0 |
Order Microservice is part of an eCommerce Application. The objective of selecting this Microservice is to demonstrate various testing frameworks. As Order is a complex service with internal (Ex. Inventory, Warhouse, Shipping etc) and external (Payment) service integration and it has all the requirements to use various testing frameworks. The objective is to demonstrate various testing frameworks.
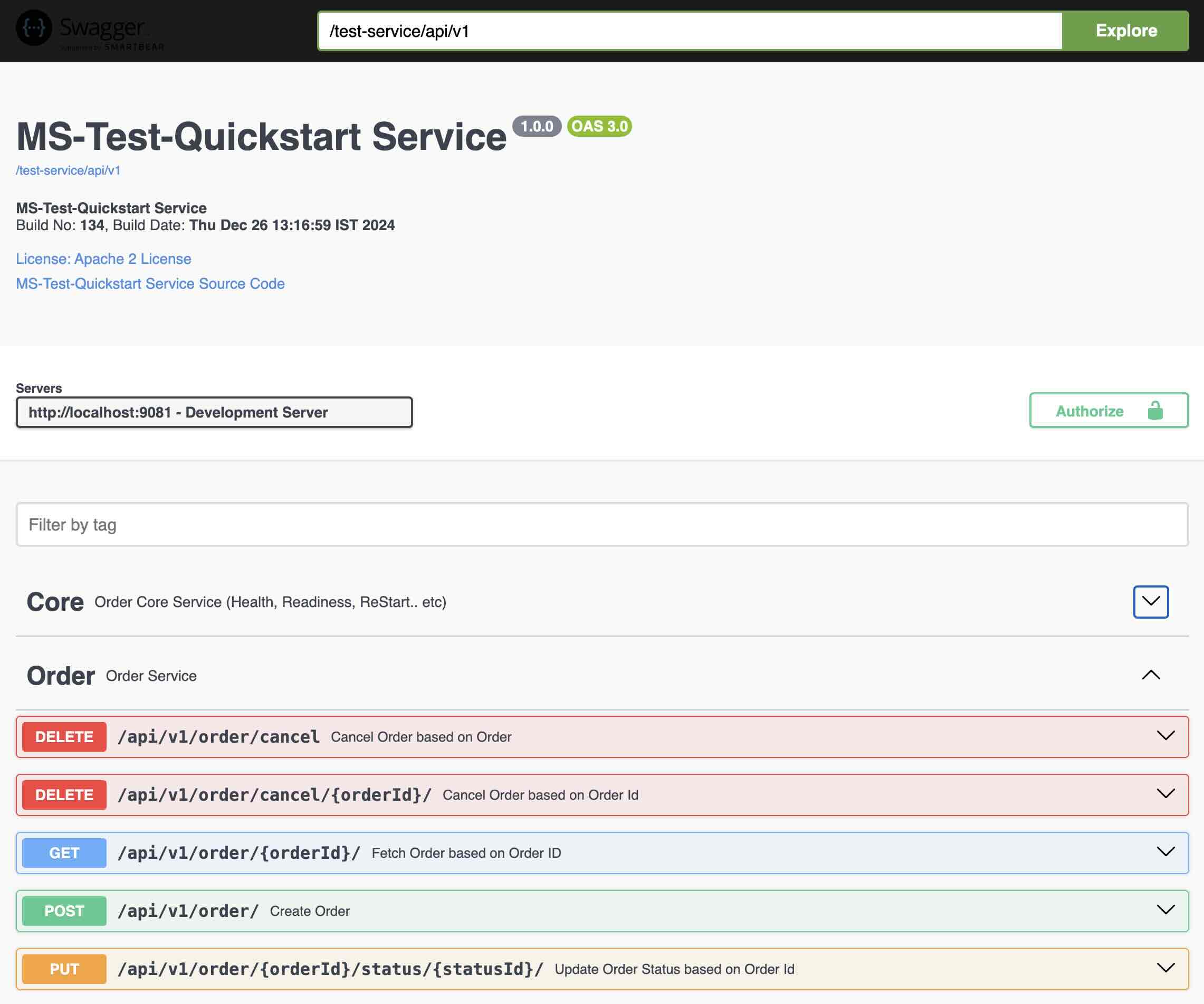
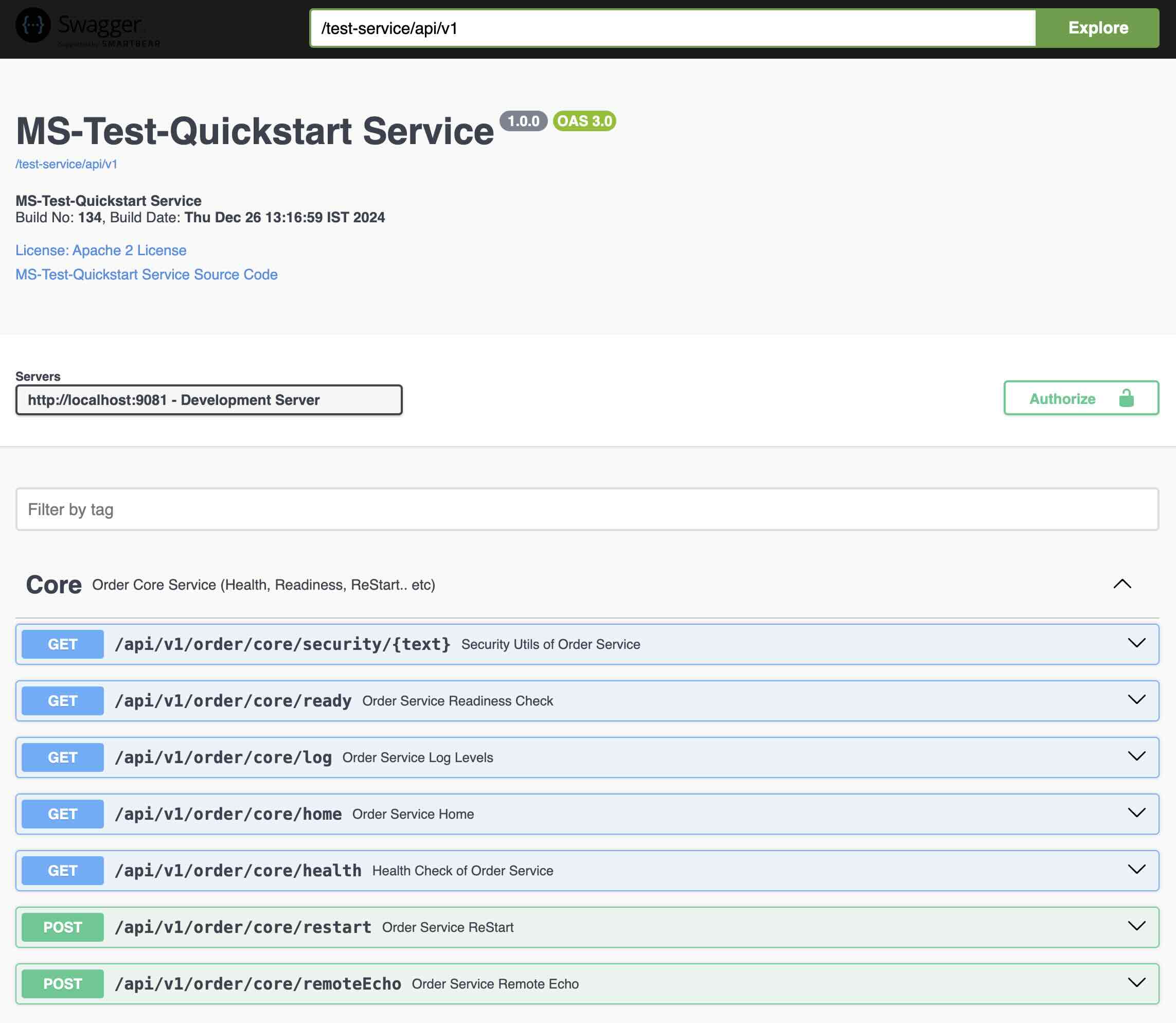
Order Service REST Endpoints are documented using Open API v3. You can access the API's using http://localhost:9081/test-service/api/v1/swagger-ui.html
Other Services
- Payment External Service
- Shipping Service
- Inventory Service
- Warehouse Service
Currently Order Service has a Mock Implementation of these services.
Now let us focus on Microservices Testing Strategies.
The following Test Categories helps you to automate the testing for Microservices based development resulting in ZERO End-2-End Testing.
All the tests will be fully automated as part of your CI/CD pipeline.
- Spring Boot 3 (3.3.4)
- Maven SureFire Plugin 2 (3.0.0-M7)
Copyright (c) 2021-25, Apache 2.0 License, Author: Araf Karsh Hamid