This section is about high-level methods of Terminal instances.
NOTE: In the following code sample, term is always a Terminal instance.
This is where Terminal-Kit becomes really shiny: you can really build a feature-rich terminal application using this.
You can handle keyboard inputs, change the terminal color palette, create menu, get text input (similar to readline), create nice progress bars, or display some special effects.
- .fullscreen()
- .processExit()
- .grabInput()
- .getCursorLocation()
- .getColor()
- .setColor()
- .getPalette()
- .setPalette()
- .wrapColumn()
- .table()
- .yesOrNo()
- .inputField()
- .fileInput()
- .singleLineMenu()
- .singleRowMenu()
- .singleColumnMenu()
- .gridMenu()
- .spinner()
- .progressBar()
- .bar()
- .slowTyping()
- .drawImage()
Advanced methods are high-level library functions.
- options: true/false/object: if truthy it activates the fullscreen mode, if falsy it returns to normal mode,
if it is an object it supports those properties:
- noAlternate
booleantrue if the alternate screen buffer should not be used
- noAlternate
Basically, this method try to achieve the same goal than the native terminal capability alternate screen buffer. If alternate screen buffer is disabled on your terminal, it will provide a clean fallback, clearing the screen and positionning the cursor at the upper-left corner.
- code
numberthe exit code
This method should be used instead of calling process.exit() directly. The code argument will be transmitted to
process.exit() as it is.
It helps quitting cleanly your application without leaving the terminal in a bad state, so the user get a working shell back.
- options: false/true/Object, false disable input grabbing, true or an Object turn it on,
if it is an Object then those properties are supported:
- mouse: if defined, it activate mouse event, those values are supported for 'mouse':
- 'button': report only button-event
- 'drag': report button-event and report motion-event only when a button is pressed (i.e. a mouse drag)
- 'motion': report button-event and all motion-event, use it only when needed, many escape sequences are sent from the terminal (e.g. you may consider it for script running over SSH)
- focus: true/false: if defined and true, focus event will be reported (if your terminal support it - xterm does)
- mouse: if defined, it activate mouse event, those values are supported for 'mouse':
- safe
boolean(optional), when set and when options is set tofalse, it returns a promise that resolve when input grabbing is safely turned off, avoiding extra junks to be echoed when the terminal left the raw mode. It is mostly useful after grabbing mouse motion.
This function turns input grabbing on, key will not be echoed anymore, and every input will generate an event
on the term object.
Each key pressed will generate a key event and mouse motion and button (if enabled) will generate a mouse event.
Quick example:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
function terminate() {
term.grabInput( false ) ;
setTimeout( function() { process.exit() } , 100 ) ;
}
term.bold.cyan( 'Type anything on the keyboard...\n' ) ;
term.green( 'Hit CTRL-C to quit.\n\n' ) ;
term.grabInput( { mouse: 'button' } ) ;
term.on( 'key' , function( name , matches , data ) {
console.log( "'key' event:" , name ) ;
if ( name === 'CTRL_C' ) { terminate() ; }
} ) ;
term.on( 'terminal' , function( name , data ) {
console.log( "'terminal' event:" , name , data ) ;
} ) ;
term.on( 'mouse' , function( name , data ) {
console.log( "'mouse' event:" , name , data ) ;
} ) ;- callback( error , x , y ) (optional)
- error
mixedtruthy if an underlying error occurs - x
integerthe x coordinate of the cursor - y
integerthe y coordinate of the cursor
- error
Get the cursor location.
Without a callback argument, it returns a Promise that resolve to an object with a x and y properties.
- register
numberthe register number in the 0..255 range - callback( error , rgb ) (optional)
- error
mixedtruthy if an underlying error occurs - rgb
Objectwhere:- r
numberin the 0..255 range, the red value - g
numberin the 0..255 range, the green value - b
numberin the 0..255 range, the blue value
- r
- error
Get the RGB values of a color register.
Without a callback argument, it returns a Promise that resolve to that same rgb object.
- register
numberthe register number in the 0..255 range - r
numberin the 0..255 range, the red value - g
numberin the 0..255 range, the green value - b
numberin the 0..255 range, the blue value - rgb
Objectwhere:- r
numberin the 0..255 range, the red value - g
numberin the 0..255 range, the green value - b
numberin the 0..255 range, the blue value
- r
- names
Arrayofstring: names for that color, it default to an empty array
Set the RGB values for a color indexed by the integer register.
- callback( error , palette ) (optional)
- error
mixedtruthy if an underlying error occurs - palette
Arrayof 16Objectwhere:- r
numberin the 0..255 range, the red value - g
numberin the 0..255 range, the green value - b
numberin the 0..255 range, the blue value - names
Arrayofstring, names for this color
- r
- error
Request from the terminal the 16-colors palette in use.
If the terminal does not support the feature, then the default palette for this terminal is provided, and each color that was modified by the lib replace it.
Without a callback argument, it returns a Promise that resolve to that same palette array.
- palette, is either:
Arrayof 16Objectwhere:- r
numberin the 0..255 range, the red value - g
numberin the 0..255 range, the green value - b
numberin the 0..255 range, the blue value - names
Arrayofstring, names for this color
- r
- OR
stringone of the built-in palette (default, gnome, konsole, linux, solarized, vga, xterm)
If the terminal supports it, it will reset the 16-colors palette to the provided one.
- options
Objectwhere:- width
integerornullthe width of the column, ornullfor the terminal's width - x
integerthe x-coordinate of the left side of the column - continue
booleantrue if it would continue a previous output (mostly for insternal lib usage) - offset
integerthe offset of the next/first line (used for continuing text, mostly for insternal lib usage)
- width
This method change the behavior of the .wrap modifier. It defines the column setup used for word-wrapping.
Calling .wrapColumn() without argument simply reset the continue and offset value.
It is useful since issuing multiple term.wrap( "some text" ) would continue the text one after the other.
That would stop that continuation behavior.
Any call to .wrapColumn(), with or without arguments, reset the offset, except if the user defines its own value.
The offset is also reset everytime some text is written without the wrap mode turned on.
Examples:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
// Word-wrap this along the full terminal width
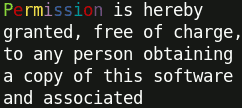
term.wrap.yellow( 'Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish' ) ;
// Word-wrap this inside a column starting at x=10 with a width of 25 terminal cells
term.wrapColumn( { x: 10 , width: 25 } ) ;
term.wrap.green( 'Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish' ) ;
// This reset the offset
term( '\n' ) ;
//term.wrapColumn() could be used as well, but the next text would overwrite the last line
// Text continuation: the second text start at the end of line of the first text
term.wrap.blue( '^GP^re^Yr^um^Mi^bs^bs^ci^ro^mn^ is ' )
term.wrap.red( 'hereby granted' ) ;It produces:
- tableCells
arrayofarrayofstringdescribing the text content of each cells - options
object, see TextTable
This creates a table of text.
Behind the scene, this method uses the inlinized variant of the TextTable widget of the document-model, so for more details, you will have to read the TextTable doc.
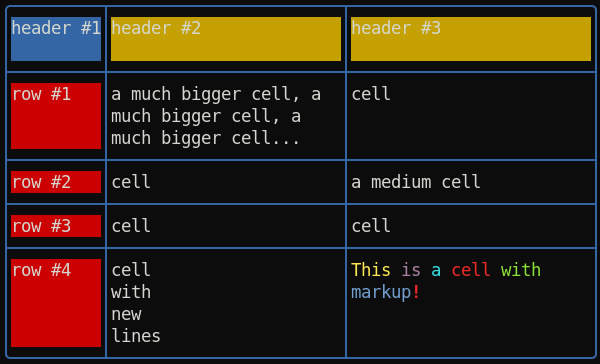
Example of a table with border:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
term.table( [
[ 'header #1' , 'header #2' , 'header #3' ] ,
[ 'row #1' , 'a much bigger cell, a much bigger cell, a much bigger cell... ' , 'cell' ] ,
[ 'row #2' , 'cell' , 'a medium cell' ] ,
[ 'row #3' , 'cell' , 'cell' ] ,
[ 'row #4' , 'cell\nwith\nnew\nlines' , '^YThis ^Mis ^Ca ^Rcell ^Gwith ^Bmarkup^R^+!' ]
] , {
hasBorder: true ,
contentHasMarkup: true ,
borderChars: 'lightRounded' ,
borderAttr: { color: 'blue' } ,
textAttr: { bgColor: 'default' } ,
firstCellTextAttr: { bgColor: 'blue' } ,
firstRowTextAttr: { bgColor: 'yellow' } ,
firstColumnTextAttr: { bgColor: 'red' } ,
width: 60 ,
fit: true // Activate all expand/shrink + wordWrap
}
) ;It produces:
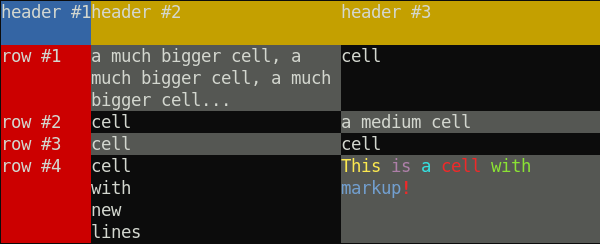
Example of a table without a border, with checkered cells:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
term.table( [
[ 'header #1' , 'header #2' , 'header #3' ] ,
[ 'row #1' , 'a much bigger cell, a much bigger cell, a much bigger cell... ' , 'cell' ] ,
[ 'row #2' , 'cell' , 'a medium cell' ] ,
[ 'row #3' , 'cell' , 'cell' ] ,
[ 'row #4' , 'cell\nwith\nnew\nlines' , '^YThis ^Mis ^Ca ^Rcell ^Gwith ^Bmarkup^R^+!' ]
] , {
hasBorder: false ,
contentHasMarkup: true ,
textAttr: { bgColor: 'default' } ,
firstCellTextAttr: { bgColor: 'blue' } ,
firstRowTextAttr: { bgColor: 'yellow' } ,
firstColumnTextAttr: { bgColor: 'red' } ,
checkerEvenCellTextAttr: { bgColor: 'gray' } ,
width: 60 ,
fit: true // Activate all expand/shrink + wordWrap
}
) ;It produces:
- options
Objectwhere:- yes
stringorArraycontains a key code or an array of key code that will trigger the yes - no
stringorArraycontains a key code or an array of key code that will trigger the - echoYes
Stringcontains what to write on yes, default 'yes' - echoNo
Stringcontains what to write on no, default 'no'
- yes
- callback( error , result ) (optional)
- error
mixedtruthy if an underlying error occurs - result
booleantrue for 'yes' or false for 'no'
- error
Wait for user input, call the completion callback when the user hit the 'y' key or the 'n' key, result will be true if the user hit any yes keys or false if the user hit any no keys. Other keys do not do anything.
Turn input grabbing on if necessary.
We can specify the keys for yes and no by providing a string or an array of string.
It returns an object featuring some functions to control things during the input process:
- abort(): abort the input process and do not even call the yesOrNo()'s callback
- promise: without a callback argument, this will be a promise that resolve with the result value
Quick example:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
function question() {
term( 'Do you like javascript? [Y|n]\n' ) ;
// Exit on y and ENTER key
// Ask again on n
term.yesOrNo( { yes: [ 'y' , 'ENTER' ] , no: [ 'n' ] } , function( error , result ) {
if ( result ) {
term.green( "'Yes' detected! Good bye!\n" ) ;
process.exit() ;
}
else {
term.red( "'No' detected, are you sure?\n" ) ;
question() ;
}
} ) ;
}
question() ;It produces:
- options
Objectwhere:- y
number(optional) if set, this is the y coordinate (the row) of the beginning of the inputField - x
number(optional) if set, this is the x coordinate (the column) of the beginning of the inputField - echo
booleanif true (the default), input are displayed on the terminal - echoChar
stringortrueif set, all characters are replaced by this one (useful for password fields), if true, it is replaced by a dot: • - default
stringdefault input/placeholder - cursorPosition
integer(default: -1, end of input) set the cursor position/offset in the input, negative value starts from the end - cancelable
booleanif true (default: false), it is cancelable by user using the cancel key (default: ESC), thus will returnundefined. - style
Functionstyle used, default to the terminal instance (no style) - hintStyle
Functionstyle used for hint (auto-completion preview), default toterminal.brightBlack(gray) - maxLength
numbermaximum length of the input - minLength
numberminimum length of the input - history
Array(optional) an history array, so UP and DOWN keys move up and down in the history - maxLength
number(optional) the maximum length (in characters) of the user input - autoComplete
ArrayorFunction( inputString , [callback] )(optional) an array of possible completion, so the TAB key will auto-complete the input field. If it is a function, it should accept an inputstringand return the completedstring(if no completion can be done, it should return the input string, if multiple candidate are possible, it should return an array of string), if the function accepts 2 arguments (checked using function.length), then the auto-completer will be asynchronous! If it does not accept a callback but returns a thenable (Promise-like), it will be asynchronous too. Also note that if it is an array or the result of the function is an array, and if that array has a special propertyprefix(a string), then this prefix will be prepended to the output of the auto complete menu, and if it has the special propertypostfix(still a string), this will be appended to the output of the auto complete menu. - autoCompleteMenu
booleanorObjectof options, used in conjunction with the 'autoComplete' option, if truthy any auto-complete attempt having many completion candidates will display a menu to let the user choose between each possibilities. If an object is given, it should contain options for the .singleLineMenu() that is used for the completion (notice: some options are overwritten: 'y' and 'exitOnUnexpectedKey') - autoCompleteHint
booleanif true (default: false) use the hintStyle to write the auto-completion preview at the right of the input - keyBindings
Objectoveride default key bindings, object's keys are Terminal-kit key names, the value is the action (string). See below for the list of available actions. - tokenHook
Function( token , isEndOfInput , previousTokens , term , config )this is a hook called for each token of the input, where:- token
Stringis the current token * isEndOfInputbooleantrue if this is the last token and if it ends the input string (e.g. it is possible for the last token to be followed by some blank char, in that case isEndOfInput would be false) - previousTokens
ArrayofStringis a array containing all tokens before the current one - term is a Terminal instance
- config
Objectis an object containing dynamic settings that can be altered by the hook, where:- style
Functionstyle in use (see the style option) - hintStyle
Functionstyle in use for hint (see the hintStyle option) - tokenRegExp
RegExpthe regexp in use for tokenization (see the tokenRegExp option) - autoComplete
ArrayorFunction( inputString , [callback] )(see the autoComplete option) - autoCompleteMenu
booleanorObject(see the autoCompleteMenu option) - autoCompleteHint
booleanenable/disable the auto-completion preview (see the autoCompleteHint option) The config settings are always reset on new input, on new tokenization pass. The hook can return a style (Function, like the style option) that will be used to print that token. Used together, this can achieve syntax hilighting, as well as dynamic behavior suitable for a shell. Finally, it can return a string, styled or not, that will be displayed in place of that token, useful if the token should have multiple styles (but that string MUST contains the same number of printable character, or it would lead hazardous behavior).
- style
- token
- tokenResetHook
Function( term , config )this is a hook called before the first token - tokenRegExp
RegExpthis is the regex used to tokenize the input, by default a token is space-delimited, so "one two three" would be tokenized as [ "one" , "two" , "three" ]. NOTE: thisRegExpMUST have thegflag, or it will throw an error.
- y
- callback( error , input ): an optional completion callback, for promise, use the returnValue's
.promisepreperty. Arguments:- error
mixedtruthy if an underlying error occurs - input
stringthe user input
- error
Wait for user input, call the completion callback when the user hit the ENTER key and pass the user input to the callback.
It turns input grabbing on if necessary.
Special keys are supported by the input field:
- ENTER, KP_ENTER: end the input process and return the current user input
- DELETE: delete
- BACKSPACE: backward delete
- LEFT/RIGHT: move the cursor one character left/right
- CTRL_LEFT/CTRL_RIGHT: move the cursor to the previous/next word
- HOME: move the cursor at the beginning of the input field
- END: move the cursor at the end of the input field
- DOWN, UP: use the history feature (if
options.historyis set) - TAB: use the auto-completion feature (if
options.autoCompleteis set) - CTRL_R: use the auto-completion feature, using the provided history array (
options.history) - CTRL_U/CTRL_K: delete all characters before/after the cursor
Additional keys are used when the auto-completion displays its menu (see .singleLineMenu() for details).
All those keys are customizable through the keyBindings options. Available actions are:
- submit: submit the input field (default: ENTER and KP_ENTER)
- cancel: cancel the input field (default: ESC, the input field should be cancelable)
- backDelete: delete one character backward (default: BACKSPACE)
- delete: delete one character (default: DELETE)
- deleteAllBefore: delete all characters before the cursor (default: CTRL_U)
- deleteAllAfter: delete all characters from the cursor to the end of input (default: DELETE)
- backward: move the cursor one character backward (default: LEFT)
- forward: move the cursor one character forward (default: RIGHT)
- previousWord: move the cursor to the begining of the previous word (default: CTRL_LEFT)
- nextWord: move the cursor to the end of the next word (default: CTRL_RIGHT)
- historyPrevious: use the previous history entry (default: UP)
- historyNext: use the next history entry (default: DOWN)
- startOfInput: move the cursor at the begining of input (default: HOME)
- endOfInput: move the cursor at the end of input (default: END)
- autoComplete: auto-complete the input (default: TAB)
- autoCompleteUsingHistory: auto-complete the input, using the provided history (
options.historyarray instead ofoptions.autoComplete) - meta: if bound to ESCAPE, allows for two-key combos like ESC-D to generate an ALT_D (useful for terminals that do not have a modifier key assigned to alt/meta)
It returns an EventEmitter object featuring some functions to control things during the input process:
- abort(): abort the input process and do not even call the inputField()'s callback
- stop(): stop the input process now, call the inputField()'s callback (same behavior than a regular 'ENTER' key pressed)
- getInput(): get the current input string
- getPosition(): return an object containing 'x' and 'y' properties, the coordinates where the input field starts
- getCursorPosition(): return the cursor position/offset in the input
- setCursorPosition( offset ): set the cursor position/offset in the input
- redraw(): redraw the input field, useful if you had echo'ed something that can mess it
- hide(): hide the input field, it still records keystrokes
- show(): show the input field again
- rebase( [x] , [y] ): rebase the input field to the current cursor position. Please note: it does NOT erase the previously entered text, you have to use hide() before. It works this way because you may want to modify the screen in between, and it needs some I/O with the terminal to works accordingly. If x and y are given, it use those coordinates instead of an internal asynchronous call to .getCursorLocation(), so it makes .rebase() synchronous.
- promise: without a callback argument, this will be a promise that resolve with the input string
It emits:
- ready: when the input field is ready (rarely useful)
- rebased: when the input field has been rebased (rarely useful)
- highlight: when an underlying auto-complete single-line-menu emit an 'hightlight' event, it is re-emitted by the input-field
Quick example, featuring history and auto-completion:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
var history = [ 'John' , 'Jack' , 'Joey' , 'Billy' , 'Bob' ] ;
var autoComplete = [
'Barack Obama' , 'George W. Bush' , 'Bill Clinton' , 'George Bush' ,
'Ronald W. Reagan' , 'Jimmy Carter' , 'Gerald Ford' , 'Richard Nixon' ,
'Lyndon Johnson' , 'John F. Kennedy' , 'Dwight Eisenhower' ,
'Harry Truman' , 'Franklin Roosevelt'
] ;
term( 'Please enter your name: ' ) ;
term.inputField(
{ history: history , autoComplete: autoComplete , autoCompleteMenu: true } ,
function( error , input ) {
term.green( "\nYour name is '%s'\n" , input ) ;
process.exit() ;
}
) ;It produces:
The same, with Promise:
async function func() {
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
var history = [ 'John' , 'Jack' , 'Joey' , 'Billy' , 'Bob' ] ;
var autoComplete = [
'Barack Obama' , 'George W. Bush' , 'Bill Clinton' , 'George Bush' ,
'Ronald W. Reagan' , 'Jimmy Carter' , 'Gerald Ford' , 'Richard Nixon' ,
'Lyndon Johnson' , 'John F. Kennedy' , 'Dwight Eisenhower' ,
'Harry Truman' , 'Franklin Roosevelt'
] ;
term( 'Please enter your name: ' ) ;
var input = await term.inputField(
{ history: history , autoComplete: autoComplete , autoCompleteMenu: true }
).promise ;
term.green( "\nYour name is '%s'\n" , input ) ;
process.exit() ;
}If we need our own auto-completer, we might take advantage of the built-in static method termkit.autoComplete().
Custom auto-completer can be asynchronous, if the function's length is exactly 2.
This is an example of a file selector that exposes the async behavior of auto-completer and the usage of
the static termkit.autoComplete() method:
var fs = require( 'fs' ) ;
var termkit = require( 'terminal-kit' ) ;
var term = termkit.terminal ;
var autoCompleter = function autoCompleter( inputString , callback )
{
fs.readdir( __dirname , function( error , files ) {
callback( undefined , termkit.autoComplete( files , inputString , true ) ) ;
} ) ;
} ;
term( 'Choose a file: ' ) ;
term.inputField(
{ autoComplete: autoCompleter , autoCompleteMenu: true } ,
function( error , input ) {
if ( error )
{
term.red.bold( "\nAn error occurs: " + error + "\n" ) ;
}
else
{
term.green( "\nYour file is '%s'\n" , input ) ;
}
process.exit() ;
}
) ;It produces:
Note: In this example, we created a simple file selector to demonstrate custom auto-completion in action. However, such simple file selectors already exists in the lib: see .fileInput().
Also note that if the autoComplete options is an array or if it is a function whose output is an array,
a special property prefix (a string) can be set on it: this prefix will be prepended to the output of the auto complete menu.
Here an example featuring tokenHook to achive a very basic syntax hilighting:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
term( 'shell> ' ) ;
var autoComplete = [
'dnf install' ,
'dnf install nodejs' ,
'dnf search' ,
'sudo' ,
'sudo dnf install' ,
'sudo dnf install nodejs' ,
'sudo dnf search' ,
] ;
term.inputField(
{
autoComplete: autoComplete ,
autoCompleteHint: true ,
autoCompleteMenu: true ,
tokenHook: function( token , isEndOfInput , previousTokens , term , config ) {
var previousText = previousTokens.join( ' ' ) ;
switch ( token )
{
case 'sudo' :
config.style = term.red ;
return previousTokens.length ? null : term.bold.red ;
case 'dnf' :
return previousText === '' || previousText === 'sudo' ?
term.brightMagenta : null ;
case 'install' :
config.style = term.brightBlue ;
config.hintStyle = term.brightBlack.italic ;
return previousText === 'dnf' || previousText === 'sudo dnf' ?
term.brightYellow : null ;
case 'search' :
config.style = term.brightBlue ;
return previousText === 'dnf' || previousText === 'sudo dnf' ?
term.brightCyan : null ;
}
}
} ,
function( error , input ) {
term.green( "\nYour command is: '%s'\n" , input ) ;
process.exit() ;
}
) ;It produces:
If you want to see an advanced usage of inputField in action, have a look to ngsh, a node.js shell in early alpha stage, featuring auto-completion and syntax hilighting.
- options
Objectwhere:- baseDir
string(optional, default: process.cwd()) the base directory path - ... as well as all .inputField() options
- baseDir
- callback( error , input ) (optional)
- error
mixedtruthy if an underlying error occurs - input
stringthe user input
- error
This is a variant of .inputField() that auto-complete file paths relative to the baseDir path.
Without a callback argument, it returns a promise that resolve to the input.
Example featuring the fileInput:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
term( 'Choose a file: ' ) ;
term.fileInput(
{ baseDir: '../' } ,
function( error , input ) {
if ( error )
{
term.red.bold( "\nAn error occurs: " + error + "\n" ) ;
}
else
{
term.green( "\nYour file is '%s'\n" , input ) ;
}
process.exit() ;
}
) ;- menuItems
arrayof menu item text - options
object(optional) of options, where:- y
numberthe line where the menu will be displayed, default to the next line - separator
string(default: ' ') the string separating each menu item - nextPageHint
string(default: ' » ') string indicator for a next page - previousPageHint
string(default: ' « ') string indicator for a previous page - style
functionthe style of unselected items, default to the currentterm - selectedStyle
functionthe style of the selected item, default toterm.dim.blue.bgGreen - selectedIndex
numberselected index at initialization (default: 0) - align
stringone of 'left' (default), 'right' or 'center', align the menu accordingly - fillIn
booleanif true (default: false), the menu will fill in the whole line with white chars - keyBindings
Objectoveride default key bindings, object's keys are Terminal-kit key names, the value is the action (string) - cancelable
booleanif ESCAPE is pressed, it exits, calling the callback with undefined values - exitOnUnexpectedKey
booleanif an unexpected key is pressed, it exits, calling the callback with undefined values
- y
- callback( error , response ) (optional), where:
- error
mixedtruthy if an underlying error occurs - response
Objectwhere- selectedIndex
numberthe user-selected menu item index - selectedText
stringthe user-selected menu item text - x
numberthe x coordinate of the selected menu item (the first character) - y
numberthe y coordinate of the selected menu item (same coordinate for all items since it's a single line menu) - canceled
truewhen 'cancelable' option is set and the ESCAPE key is pressed - unexpectedKey
stringwhen 'exitOnUnexpectedKey' option is set and an unexpected key is pressed, this contains the key that produced the exit
- selectedIndex
- error
It creates an interactive menu that uses only a single line.
It supports the mouse if the mouse has been activated by .grabInput()'s mouse option.
It features paging if items oversize the line length, and supports the following keys:
- ENTER, KP_ENTER: end the process and return the currently selected menu item
- LEFT, RIGHT: move and select the previous or the next item in the menu
- SHIFT_TAB, TAB: cycle backward or forward and select the item
- UP, DOWN: go to the previous or the next page of items (if paging is used)
- HOME, END: move and select the first or the last item of the menu
- ESCAPE: exit from the menu, if the 'cancelable' option is set
All those keys are customizable through the keyBindings options. Available actions are:
- submit: submit the menu (default: ENTER and KP_ENTER)
- previous: move and select the previous item in the menu (default: LEFT)
- next: move and select the next item in the menu (default: RIGHT)
- cyclePrevious: cycle backward and select the item (default: SHIFT_TAB)
- cycleNext: cycle forward and select the item (default: TAB)
- previousPage: go to the previous page of items, if paging is used (default: UP)
- nextPage: go to the next page of items, if paging is used (default: DOWN)
- first: move and select the first item in the menu (default: HOME)
- last: move and select the last item in the menu (default: END)
- escape: exit from the menu, if the 'cancelable' option is set (default: ESCAPE)
If the 'exitOnUnexpectedKey' option is set, any other keys will exit the menu, the callback's response argument does not contain any property except 'unexpectedKey', that will contain the key having triggered the exit.
It returns an EventEmitter object with those properties:
- promise: without a callback argument, this will be a promise that resolve with the response object.
It emits:
- highlight: every-time the hightlighted menu item changes, this event is emitted, with an object as its unique argument:
- highlightedIndex: the index of the highlighted item
- highlightedText: the text of the highlighted item
Example:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
var items = [ 'File' , 'Edit' , 'View' , 'History' , 'Bookmarks' , 'Tools' , 'Help' ] ;
var options = {
y: 1 , // the menu will be on the top of the terminal
style: term.inverse ,
selectedStyle: term.dim.blue.bgGreen
} ;
term.clear() ;
term.singleLineMenu( items , options , function( error , response ) {
term( '\n' ).eraseLineAfter.green(
"#%s selected: %s (%s,%s)\n" ,
response.selectedIndex ,
response.selectedText ,
response.x ,
response.y
) ;
process.exit() ;
} ) ;It produces:
It creates a menu on the top of the terminal, with unselected items using inverted foreground/background colors, and the selected item using blue on green. When the user press RETURN/ENTER, it displays the index, text and coordinates of the selected menu item.
This is an alias of .singleLineMenu().
- menuItems
arrayof menu item text - options
object(optional) of options, where:- y
numberthe line where the menu will be displayed, default to the next line - style
functionthe style of unselected items, default to the currentterm - selectedStyle
functionthe style of the selected item, default toterm.inverse - submittedStyle
functionthe style of the submitted item, default toterm.bgGray.bold - leftPadding
stringthe text to put before a menu item, default to ' ' - selectedLeftPadding
stringthe text to put before a selected menu item, default to ' ' - submittedLeftPadding
stringthe text to put before a submitted menu item, default to ' ' - extraLines
number(default: 1) the number of lines to create (if needed) between the end of the menu and the bottom of the terminal - oneLineItem
booleanif true (default: false), big items do not span multiple lines, instead they are truncated and ended with an ellipsis char - itemMaxWidth
numberthe max width for an item, default to the terminal width - continueOnSubmit
booleanif true, the submit action does not end the menu, the callback argument is ignored. The 'submit' event should be listened instead. - selectedIndex
numberselected index at initialization (default: 0) - keyBindings
Objectoveride default key bindings, object's keys are Terminal-kit key names, the value is the action (string) - cancelable
booleanif ESCAPE is pressed, it exits, calling the callback with undefined values - exitOnUnexpectedKey
booleanif an unexpected key is pressed, it exits, calling the callback with undefined values
- y
- callback( error , response ) (optional), where:
- error
mixedtruthy if an underlying error occurs - response
Objectwhere:- selectedIndex
numberthe user-selected menu item index - selectedText
stringthe user-selected menu item text - submitted
booleanif true, theselectedIndexwas submitted (rarely false, except when stopped) - x
numberthe x coordinate of the selected menu item (the first character) - y
numberthe y coordinate of the selected menu item - canceled
truewhen 'cancelable' option is set and the ESCAPE key is pressed - unexpectedKey
stringwhen 'exitOnUnexpectedKey' option is set and an unexpected key is pressed, this contains the key that produced the exit
- selectedIndex
- error
It creates an interactive menu over multiple lines.
It supports the mouse if the mouse has been activated by .grabInput()'s mouse option.
- ENTER, KP_ENTER: end the process and return the currently selected menu item
- UP, DOWN: move and select the previous or the next item in the menu
- SHIFT_TAB, TAB: cycle backward or forward and select the item
- HOME, END: move and select the first or the last item of the menu
- ESCAPE: exit from the menu, if the 'cancelable' option is set
All those keys are customizable through the keyBindings options. Available actions are:
- submit: submit the menu (default: ENTER and KP_ENTER)
- previous: move and select the previous item in the menu (default: UP)
- next: move and select the next item in the menu (default: DOWN)
- cyclePrevious: cycle backward and select the item (default: SHIFT_TAB)
- cycleNext: cycle forward and select the item (default: TAB)
- first: move and select the first item in the menu (default: HOME)
- last: move and select the last item in the menu (default: END)
- escape: exit from the menu, if the 'cancelable' option is set (default: ESCAPE)
If the 'exitOnUnexpectedKey' option is set, any other keys will exit the menu, the callback's response argument does not contain any property except 'unexpectedKey', that will contain the key having triggered the exit.
It returns an EventEmitter object with those properties:
- promise: without a callback argument, this will be a promise that resolve with the response object.
It emits:
- highlight: every-time the hightlighted menu item changes, this event is emitted, with an object as its unique argument:
- highlightedIndex: the index of the highlighted item
- highlightedText: the text of the highlighted item
Example:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
term.cyan( 'The hall is spacious. Someone lighted few chandeliers.\n' ) ;
term.cyan( 'There are doorways south and west.\n' ) ;
var items = [
'a. Go south' ,
'b. Go west' ,
'c. Go back to the street'
] ;
term.singleColumnMenu( items , function( error , response ) {
term( '\n' ).eraseLineAfter.green(
"#%s selected: %s (%s,%s)\n" ,
response.selectedIndex ,
response.selectedText ,
response.x ,
response.y
) ;
process.exit() ;
} ) ;It produces:
It creates a menu, when the user press RETURN/ENTER, it displays the index, text and coordinates of the selected menu item.
- menuItems
arrayof menu item text - options
object(optional) of options, where:- y
numberthe line where the menu will be displayed, default to the next line - x
numberthe column where the menu will be displayed (default: 1) - width
numberthe maximum width of the grid menu (default: terminal's width) - style
functionthe style of unselected items, default to the currentterm - selectedStyle
functionthe style of the selected item, default toterm.inverse - leftPadding
stringthe text to put before a menu item, default to ' ' - selectedLeftPadding
stringthe text to put before a selected menu item, default to ' ' - rightPadding
stringthe text to put after a menu item, default to ' ' - selectedRightPadding
stringthe text to put after a selected menu item, default to ' ' - itemMaxWidth
numberthe max width for an item, default to the 1/3 of the terminal width or of the specified width option - keyBindings
Objectoveride default key bindings, object's keys are Terminal-kit key names, the value is the action (string) - exitOnUnexpectedKey
booleanif an unexpected key is pressed, it exits, calling the callback with undefined values
- y
- callback( error , response ) (optional), where:
- error
mixedtruthy if an underlying error occurs - response
Objectwhere- selectedIndex
numberthe user-selected menu item index - selectedText
stringthe user-selected menu item text - x
numberthe x coordinate of the selected menu item (the first character) - y
numberthe y coordinate of the selected menu item - unexpectedKey
stringwhen 'exitOnUnexpectedKey' option is set and an unexpected key is pressed, this contains the key that produced the exit
- selectedIndex
- error
It creates an interactive menu, items are organized in multiple rows and columns, as a grid/table.
It supports the mouse if the mouse has been activated by .grabInput()'s mouse option.
- ENTER, KP_ENTER: end the process and return the currently selected menu item
- UP, DOWN: move and select the previous or the next item in the menu
- LEFT, RIGHT: move and select the item on the left or on the right (previous or next column)
- SHIFT_TAB, TAB: cycle backward or forward and select the item
- HOME, END: move and select the first or the last item of the menu
All those keys are customizable through the keyBindings options. Available actions are:
- submit: submit the menu (default: ENTER and KP_ENTER)
- previous: move and select the previous item in the menu (default: UP)
- next: move and select the next item in the menu (default: DOWN)
- previousColumn: move and select the item on the previous column/on the left (default: LEFT)
- nextColumn: move and select the item on the next column/on the right (default: RIGHT)
- cyclePrevious: cycle backward and select the item (default: SHIFT_TAB)
- cycleNext: cycle forward and select the item (default: TAB)
- first: move and select the first item in the menu (default: HOME)
- last: move and select the last item in the menu (default: END)
If the 'exitOnUnexpectedKey' option is set, any other keys will exit the menu, the callback's response argument does not contain any property except 'unexpectedKey', that will contain the key having triggered the exit.
It returns an object with those properties:
- promise: without a callback argument, this will be a promise that resolve with the response object.
Example:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
var fs = require( 'fs' ) ;
term.cyan( 'Choose a file:\n' ) ;
var items = fs.readdirSync( process.cwd() ) ;
term.gridMenu( items , function( error , response ) {
term( '\n' ).eraseLineAfter.green(
"#%s selected: %s (%s,%s)\n" ,
response.selectedIndex ,
response.selectedText ,
response.x ,
response.y
) ;
process.exit() ;
} ) ;It produces:
It reads the current directory and creates a menu with all files and folder, displayed using a table layout. When the user press RETURN/ENTER, it displays the index, text and coordinates of the selected menu item.
- animation
stringorarraywhen using this shorthand ariant, the argument is turned into an object having an animation property set to this value, if it is a string, it should be one of those built-in animations, if it is an array, it should comply with this format those built-in animations. - options
object, see AnimatedText
This creates a spinner.
Behind the scene, this method uses the inlinized variant of the AnimatedText widget of the document-model, so for more details, you will have to read the AnimatedText doc.
Example of the classic line spinner:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
term.spinner() ;It produces:
Example of a colorful unboxing spinner with a text appended after it:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
async function test() {
var spinner = await term.spinner( 'unboxing-color' ) ;
term( ' Loading... ' ) ;
}
test() ;It produces:
Internally, since the spinner is animated, the lib needs to get the cursor location from the terminal before starting spinning, that's why we await it before writing after. Without await, it would write ' Loading...' first, then overwrite it with the spinner.
Here is the list of all built-in animations and for custom animation, follow this format.
- options
objectof options, all of them are OPTIONAL, where:- width:
numberthe total width of the progress bar, default to the max available width - percent:
booleanif true, it shows the progress in percent alongside with the progress bar - eta:
booleanif true, it shows the Estimated Time of Arrival alongside with the progress bar - items
numberthe number of items that should be completed, turns the item mode on - title
stringthe title of the current progress bar, turns the title mode on - barStyle
functionthe style of the progress bar items, default toterm.cyan - barBracketStyle
functionthe style of the progress bar bracket character, default to options.barStyle if given orterm.blue - percentStyle
functionthe style of percent value string, default toterm.yellow - etaStyle
functionthe style of the ETA display, default toterm.bold - itemStyle
functionthe style of the item display, default toterm.dim - titleStyle
functionthe style of the title display, default toterm.bold - itemSize
numberthe size of the item status, default to 33% of width - titleSize
numberthe size of the title, default to 33% of width or title.length depending on context - barChar
stringthe char used for the bar, default to '=' - barHeadChar
stringthe char used for the bar, default to '>' - maxRefreshTime
numberthe maximum time between two refresh in ms, default to 500ms - minRefreshTime
numberthe minimum time between two refresh in ms, default to 100ms - inline
boolean- when false (the default), the progressBar is locked in-place, it always redraws itself on the same place
- when true, the progressBar is redrawn on the beginning of the current line
- syncMode
boolean- when false (the default), the progressBar works asynchronously, every few milliseconds it is redrawn. Note that it will fail for CPU bound tasks, if the tasks do not let the event loop breathes
- when true, the progressBar works in synchronous mode: it only redraws itself synchronously in those cases:
- at startup when
progressBar()is called - each time
progressBar.startItem()is called - each time
progressBar.itemDone()is called - each time
progressBar.update()is called - each time
progressBar.resume()is called
- at startup when
- y
integerif set (and non-zero), the progressBar will be on the yth line - x
integerif set (and non-zero) and the 'y' option is set (and non-zero), the progressBar will start on the xth row
- width:
It creates a nice progress bar and returns a controller object to interact with it.
The controller provides those functions:
-
update( updateObject ): update the progress bar, having the arguments:
- updateObject
objectornumberornull. If updateObject is not an object, it's a shorthand for{ progress: value }. It supports those properties:- progress
numberornullthe progress value:- if it's a float between 0 and 1, it's the actual progress value to be displayed
- if
nullthen it will display a spinning wheel: something is in progress, but cannot be quantified
- items
numberchange the number of items that should be completed, turns the item mode on - title
stringchange the title of the current progress bar, turns the title mode on
- progress
- updateObject
-
startItem( name ): in item mode, it informs the progress bar that a new item is processing, having arguments:
- name
stringthe name of the item that will be displayed in the item status part of the progress bar
- name
-
itemDone( name ): in item mode, it informs the progress bar that an item is now done, if that item was started using
.startItem(), it will be removed from the running item list. When the number of finished item reaches theitemsparameter (see the.progressBar()'s 'items' option or.update()method's 'items' option), the progressBar reaches 100% and stop. It has the arguments:- name
stringthe name of the item that just finished.
- name
-
stop(): stop the progress bar, no redraw will occurs
-
resume(): resume a previously stopped progress bar, it will be redrawn again
-
reset(): reset the progress bar, removing progress value, items done, time elapsed and so on...
Example of a progress bar using fake progress values:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
var progressBar , progress = 0 ;
function doProgress()
{
// Add random progress
progress += Math.random() / 10 ;
progressBar.update( progress ) ;
if ( progress >= 1 )
{
// Cleanup and exit
setTimeout( function() { term( '\n' ) ; process.exit() ; } , 200 ) ;
}
else
{
setTimeout( doProgress , 100 + Math.random() * 400 ) ;
}
}
progressBar = term.progressBar( {
width: 80 ,
title: 'Serious stuff in progress:' ,
eta: true ,
percent: true
} ) ;
doProgress() ;It produces:
It creates a progress bar and feeds it with a random progress value, then quit when it reaches 100%.
Example of a progress bar in item mode:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
var progressBar ;
var thingsToDo = [
'update my lib' ,
'data analyzing' ,
'serious business' ,
'decrunching data' ,
'do my laundry' ,
'optimizing'
] ;
var countDown = thingsToDo.length ;
function start()
{
if ( ! thingsToDo.length ) { return ; }
var task = thingsToDo.shift() ;
progressBar.startItem( task ) ;
// Finish the task in...
setTimeout( done.bind( null , task ) , 500 + Math.random() * 1200 ) ;
// Start another parallel task in...
setTimeout( start , 400 + Math.random() * 400 ) ;
}
function done( task )
{
progressBar.itemDone( task ) ;
countDown -- ;
// Cleanup and exit
if ( ! countDown )
{
setTimeout( function() { term( '\n' ) ; process.exit() ; } , 200 ) ;
}
}
progressBar = term.progressBar( {
width: 80 ,
title: 'Daily tasks:' ,
eta: true ,
percent: true ,
items: thingsToDo.length
} ) ;
start() ;It produces:
It creates a progress bar and start and finish task with a random time, then quit when everything is done.
- value
numbera number between 0 and 1 - options
objectof options, all of them are OPTIONAL, where:- innerSize:
integerinner width of the bar in characters (default: 10) - barStyle
functionthe style of the bar, default to term.blue
- innerSize:
It displays a bar representing the value. It uses unicode characters to improve the precision.
- str
stringthe text to display - options
objectof options, where:- style
functionthe style of text, default toterm.green - flashStyle
functionorfalsyif afunctionis given, then this is the style of the text for the flash effect, iffalsythen the flash effect is turn off, default toterm.bold.brightGreen - delay
numberaverage delay before printing the next char, default to 150 ms - flashDelay
numberfixed delay before theflashStyleof the last printed char is replaced by the regularstyle, default to 100 ms
- style
- callback
function(optional) that will be called on completion
It outputs some text with an old-fashioned slow-typing effect.
Without a callback argument, it returns a promise that resolve on completion.
Example:
var term = require( 'terminal-kit' ).terminal ;
term.slowTyping(
'What a wonderful world!\n' ,
{ flashStyle: term.brightWhite } ,
function() { process.exit() ; }
) ;It produces:
- url
stringfilepath, or URL if the originalget-pixelsmodule is installed - options
objectof options, where:- shrink
object(optional, but recommanded) if set, the image may be shrinked to conform to the max width and height. When shrinking, aspect ratio is always preserved. It has those properties:- width
integerthe max width of the image - height
integerthe max height of the image
- width
- shrink
- callback
Function( error )(optional) that will be called on completion, where:- error: truthy if an error occured
Without a callback argument, it returns a promise that resolve on completion.
This get an image (using a filepath or an URL) and draw it directly into the terminal. Support all format supported by get-pixels, namely PNG, JPEG and GIF. Only the first frame of GIF are used ATM.
NOTE: Terminal Kit does not support loading over HTTP out of the box.
Terminal Kit aims to have a good balance between features and lightweight, and loading images over HTTP adds tons of dependencies,
which of course are only useful in very rare use-cases.
If you need such feature, just add the original get-pixels module (npm install get-pixels), it has precedence
over the get-pixels fork which has HTTP support striped.
It uses the upper half block UTF-8 character (▀) to double the height resolution and produces the correct aspect ratio: the upper half having a foreground color and the lower half having the background color.
The shrink object option can be used to reduce the size of the image.
It is suggested to set it to { width: term.width, height: term.height * 2 } to avoid creating a 2000 lines image.
Example of rendering: