| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
简单 |
1508 |
第 195 场周赛 Q1 |
|
给你一个字符串 path,其中 path[i] 的值可以是 'N'、'S'、'E' 或者 'W',分别表示向北、向南、向东、向西移动一个单位。
你从二维平面上的原点 (0, 0) 处开始出发,按 path 所指示的路径行走。
如果路径在任何位置上与自身相交,也就是走到之前已经走过的位置,请返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
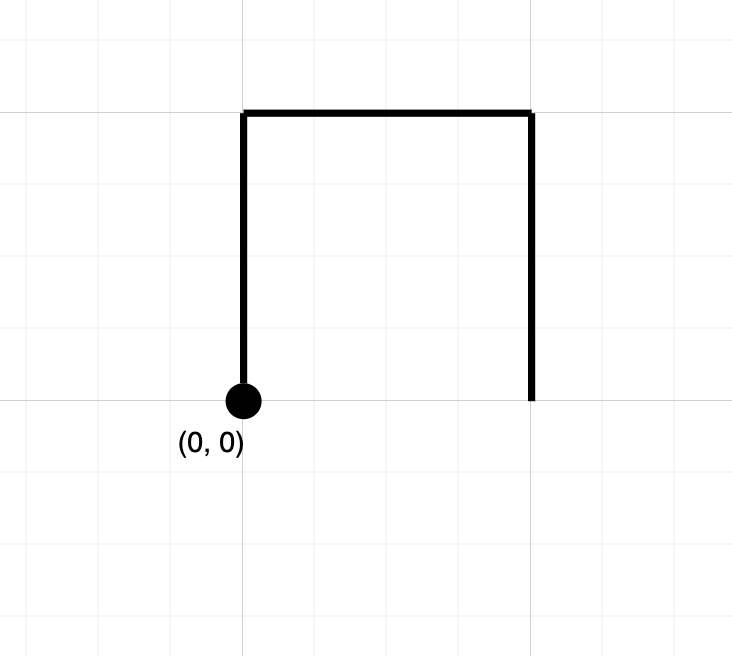
输入:path = "NES" 输出:false 解释:该路径没有在任何位置相交。
示例 2:
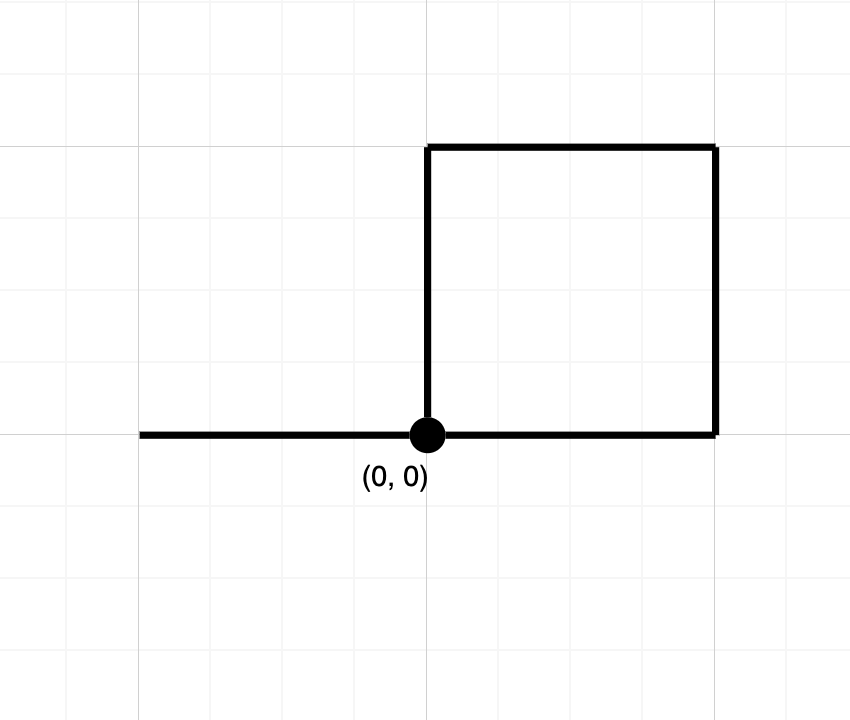
输入:path = "NESWW" 输出:true 解释:该路径经过原点两次。
提示:
1 <= path.length <= 104path[i]为'N'、'S'、'E'或'W'
我们可以用一个哈希表
遍历字符串 true,否则将
遍历结束后,返回 false。
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def isPathCrossing(self, path: str) -> bool:
i = j = 0
vis = {(0, 0)}
for c in path:
match c:
case 'N':
i -= 1
case 'S':
i += 1
case 'E':
j += 1
case 'W':
j -= 1
if (i, j) in vis:
return True
vis.add((i, j))
return Falseclass Solution {
public boolean isPathCrossing(String path) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
Set<Integer> vis = new HashSet<>();
vis.add(0);
for (int k = 0, n = path.length(); k < n; ++k) {
switch (path.charAt(k)) {
case 'N' -> --i;
case 'S' -> ++i;
case 'E' -> ++j;
case 'W' -> --j;
}
int t = i * 20000 + j;
if (!vis.add(t)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}class Solution {
public:
bool isPathCrossing(string path) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
unordered_set<int> s{{0}};
for (char& c : path) {
if (c == 'N') {
--i;
} else if (c == 'S') {
++i;
} else if (c == 'E') {
++j;
} else {
--j;
}
int t = i * 20000 + j;
if (s.count(t)) {
return true;
}
s.insert(t);
}
return false;
}
};func isPathCrossing(path string) bool {
i, j := 0, 0
vis := map[int]bool{0: true}
for _, c := range path {
switch c {
case 'N':
i--
case 'S':
i++
case 'E':
j++
case 'W':
j--
}
if vis[i*20000+j] {
return true
}
vis[i*20000+j] = true
}
return false
}function isPathCrossing(path: string): boolean {
let [i, j] = [0, 0];
const vis: Set<number> = new Set();
vis.add(0);
for (const c of path) {
if (c === 'N') {
--i;
} else if (c === 'S') {
++i;
} else if (c === 'E') {
++j;
} else if (c === 'W') {
--j;
}
const t = i * 20000 + j;
if (vis.has(t)) {
return true;
}
vis.add(t);
}
return false;
}