- Basic knowledge of React Native application development.
- A basic knowledge of Javascript or atleast the readiness to pick it up.
- A basic understanding of relational databases.
gitinstalled on your local machine and also a basic knowledge of usinggit
Before you begin, ensure that you have the Hasura CLI installed on your local machine. If not, you can find the instructions to install it here. Once you have the CLI tool installed, login or signup into Hasura by running the following command on your terminal:
$ hasura loginThere are two steps required to get started with Hasura.
Step 1: Get a Hasura project and a Hasura cluster
A hasura project is a folder on your filesystem that contains all the source code and configuration for your application. A hasura project has a particular structure and the best way to create a hasura project is by cloning one from hasura.io/hub. Every project you see on hasura.io/hub is a
Hasura Projectwith particular services or data added to it based on the type of project it is. To know more about a Hasura Project, check out the docs.
We are going to clone the hello-react-native project which consists of:
- Boilerplate code for a nodejs server to handle push notifications and a websocket connection
- A basic React Native application with working code implementing the various backend features covered in this tutorial
To get the project,
$ hasura quickstart hasura/hello-react-nativeThe above command does the following:
- Creates a new directory in your current directory called
hello-react-nativeand clones the content of thehello-react-nativeproject from Hasura Hub into it. - Makes this new directory a
gitrepository and adds a remote calledhasurato it. - It also creates a free
Hasura Clusterfor you andaddsthis cluster to the cloned hasura project.
A Hasura cluster is a cluster of nodes (VMs) on the cloud that can host any Hasura project. It has all the Hasura microservices running and the necessary tooling for you to deploy your Hasura project. Every Hasura cluster comes with a name and a domain attached to it as well. Eg:
awesome45.hasura-app.io. Know more here.
Step 2: Deploy the project to your cluster
$ # cd into the project directory
$ cd hello-react-native
$ # Make your initial commit
$ git add . && git commit -m "Initial Commit"
$ # Push to the hasura remote
$ git push hasura master- Open the
react-native-appdirectory present in the root directory of the project. - Navigate to a file named
Hasura.js. - Replace the value for the variable
clusterNamewith the name of your cluster.
const clusterName = 'yourclustername43';Every Hasura cluster comes with an API Console that you can use to explore the various backend features provided by Hasura. To access the API console,
$ # Run the following inside the project directory
$ hasura api-consoleThis will open up the console on your browser. You can access it at http://localhost:9695. We will be using the API Console extensively during this tutorial.
Most apps require a database to store and retrieve information from. Hasura provides instant GraphQL APIs over Postgres. This means, you can create a table and immediately get an endpoint to make GraphQL queries and mutations.
Let's explore how to do this. Open the API Console and click on the Data tab:
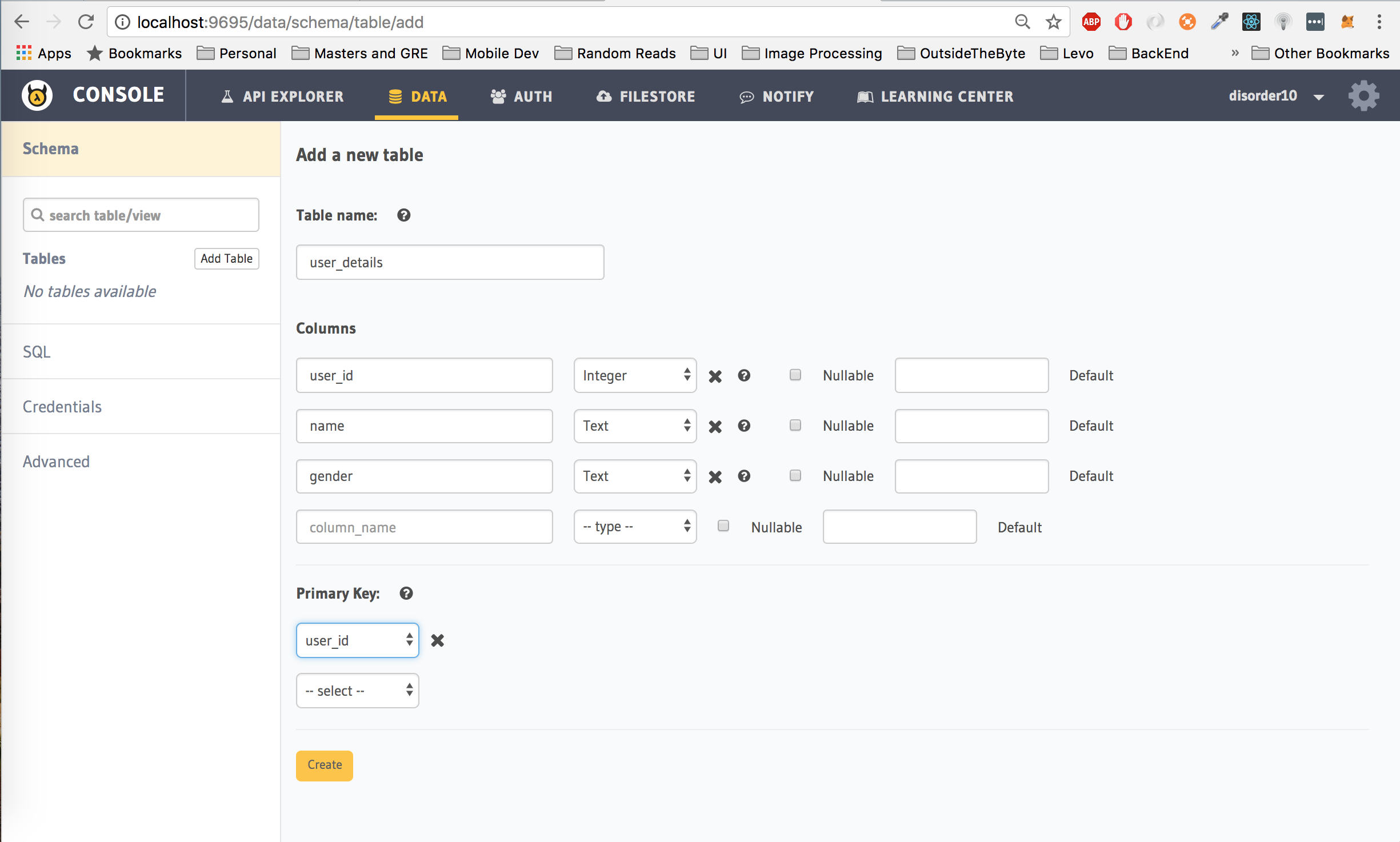
$ hasura api-consoleClick on the Create Table button. Let's start off with a table called user_details which we will use to store extra information about a user, like their name and gender. We will also be adding an additional column user_id to store the hasura_id of the user. user_id will also be our primary key as the hasura_id for every user is always unique.
Click the Create button to create the table.
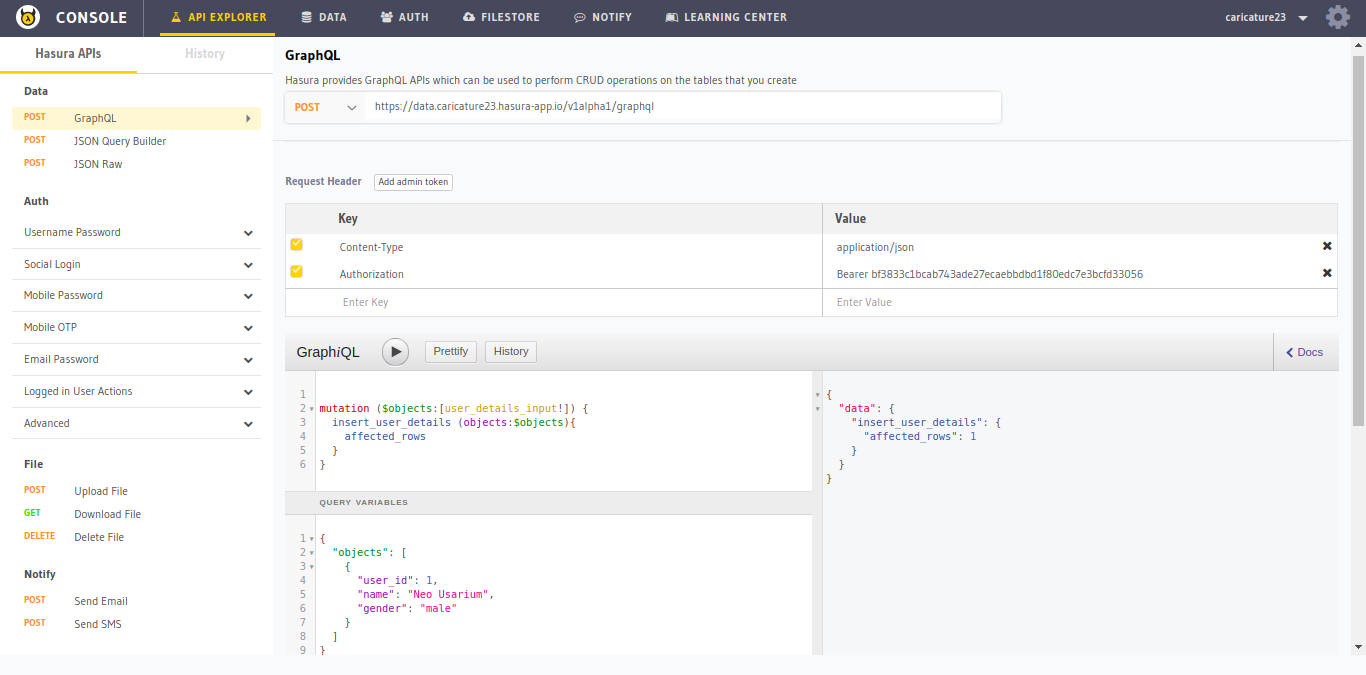
Go to the API-Explorer in the console and select GraphQL in the left panel. Try writing a mutation to insert an entry to the user_details table that we just created.
Please Make sure you add the
Admin tokenin the request headers. By default, onlyAdmincan perform operations on the tables. We will later learn how to enable these operations forlogged in usersandanonymous users.
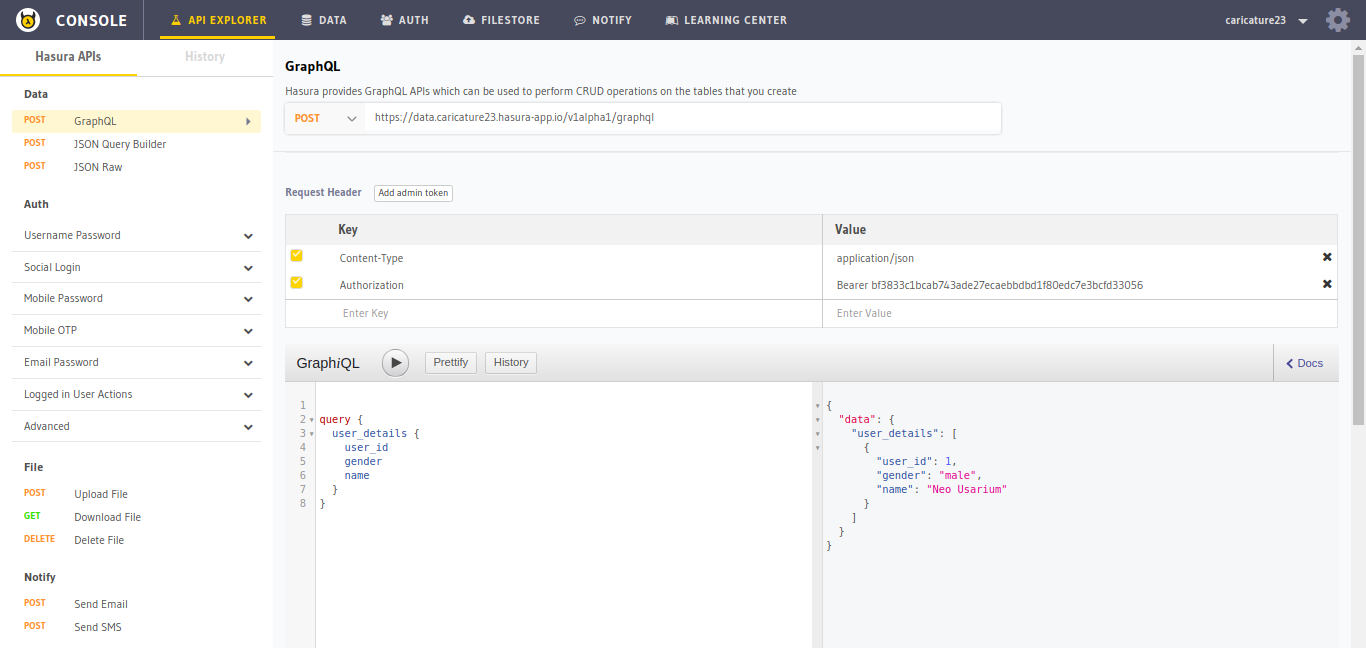
Now that we have inserted data into the table, lets try to fetch this information.
To learn more about using GraphQL with Hasura, check the docs.
This section covers how to set up Apollo client for efficiently using GraphQL in your React Native apps.
- Install the required dependencies
$ npm install apollo-boost react-apollo graphql --save- Create an ApolloClient instance and point it to the Hasura Data GraphQL URL via Apollo Link.
import { ApolloClient } from 'apollo-client';
import { HttpLink } from 'apollo-link-http';
import { InMemoryCache } from 'apollo-cache-inmemory';
const GRAPHQL_URL = "https://data.<cluster-name>.hasura-app.io/v1alpha1/graphql";
const client = new ApolloClient({
link: new HttpLink({uri: GRAPHQL_URL}),
cache: new InMemoryCache({
addTypename: false
})
});Important: You have to configure
addTypenameto false in theInMemoryCacheconstructor.*
- Connect the client to your component tree using the
ApolloProvidercomponent. It is important to putApolloProviderabove every component where you need the GraphQL data. For example, it could be before registering your root component.
import { ApolloProvider } from 'react-apollo';
import { ApolloClient } from 'apollo-client';
import { HttpLink } from 'apollo-link-http';
import { InMemoryCache } from 'apollo-cache-inmemory';
import { App } from './App';
const GRAPHQL_URL = "https://data.<cluster-name>.hasura-app.io/v1alpha1/graphql";
const client = new ApolloClient({
link: new HttpLink({uri: GRAPHQL_URL}),
cache: new InMemoryCache()
});
const AppWithClient= () => (
<ApolloProvider client={client}>
<App/>
</ApolloProvider>
);
AppRegistry.registerComponent('MyApplication', () => AppWithClient);That's it. You can now make queries and mutations in all the children components.
The React Native app in this project uses Apollo client to make GraphQL queries and mutations. You can check the configuration in react-native-app/src/AppScreen.js file.
Every modern app almost always requires some form of authentication. This is useful to identify a user and provide some sort of personalized experience to the user. Hasura provides various types of authentication methods (username/password, mobile/otp, email/password, Google, Facebook etc).
In this tutorial, we are going to take a look at a simple username/password based authentication. Start by opening up the API Console. Ensure that you are on the API Explorer tab.
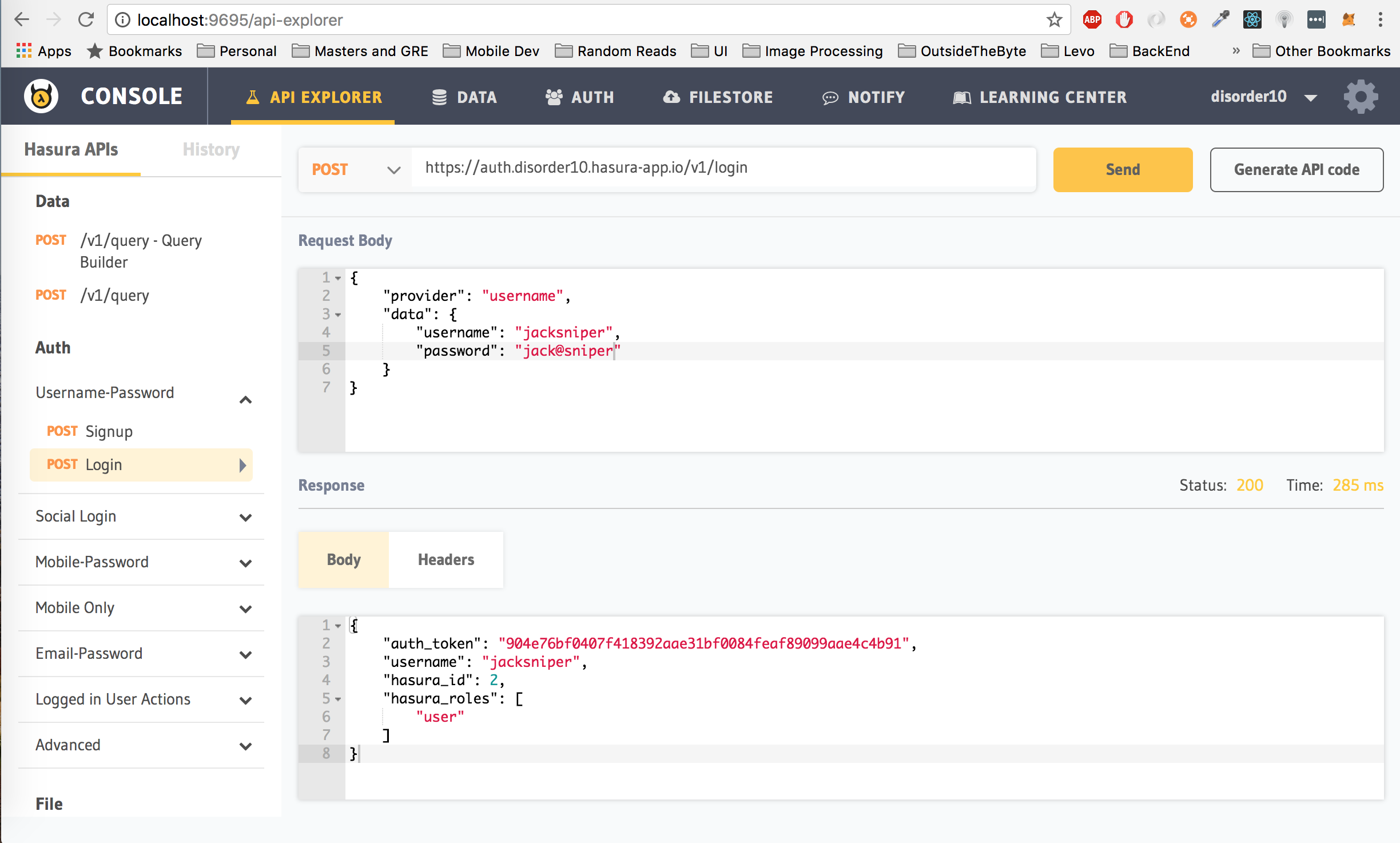
Let's first take a look at the signup endpoint. From the panel on the left, click on SignUp under Username/Password. Next, fill up your required username and password.
We are going with the username "jacksniper" and password "jack@sniper". You can choose any username and password combination. Once you have decided on your username and password, hit on the Send button to Sign Up. Your response would look like:
{
"auth_token": "9cea876c07de13d8336c4a6d80fa9f64648506bc20974fd2",
"username": "jacksniper",
"hasura_id": 2,
"hasura_roles": [
"user"
]
}- auth_token is the authorization token for this particular user, which we will use later to access authorized information. You should save this offline in your app to avoid making your user login each time.
- hasura_id is the id of the user that is automatically assigned by Hasura on signing up. You should save this offline as well.
- hasura_roles are the roles associated with this user. Keep in mind that the role associated with this user is
user. This is default behaviour. We will get to where this comes into play in a bit.
Now that we have created a user using the signup endpoint, we can login with the same credentials. Click on Login under Username/Password. Enter in the same username and password that you used to sign up above and click on Send.
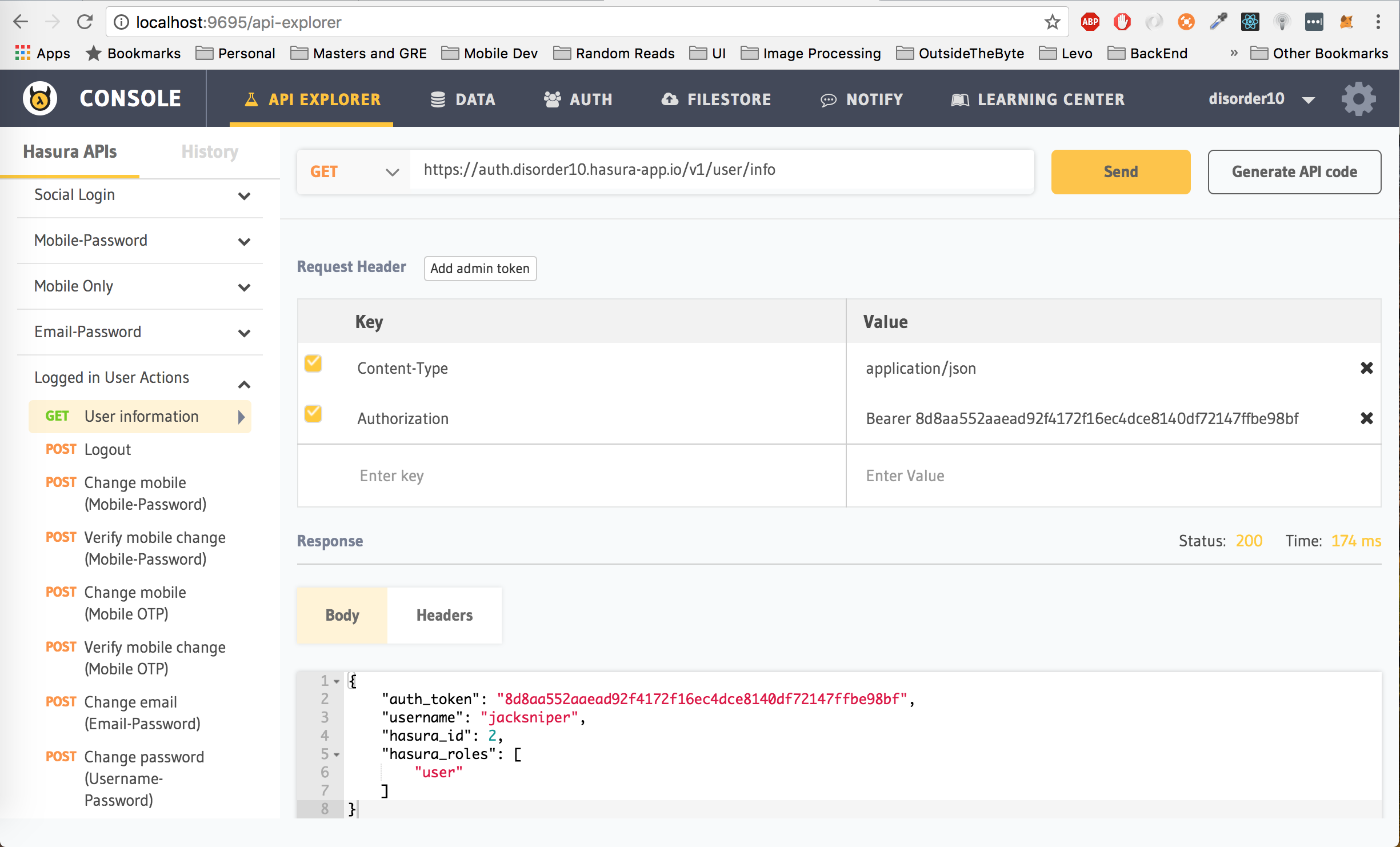
In the response that you get, you will see that the hasura_id key has the same value as the one you got after you signed up. In this case, that value is 2.
To perform any authenticated request, you need the user's authentication token (auth_token from the login/signup endpoint) and pass that as a header.
You can find a list of these APIs under the Logged in User Actions title on the left panel.
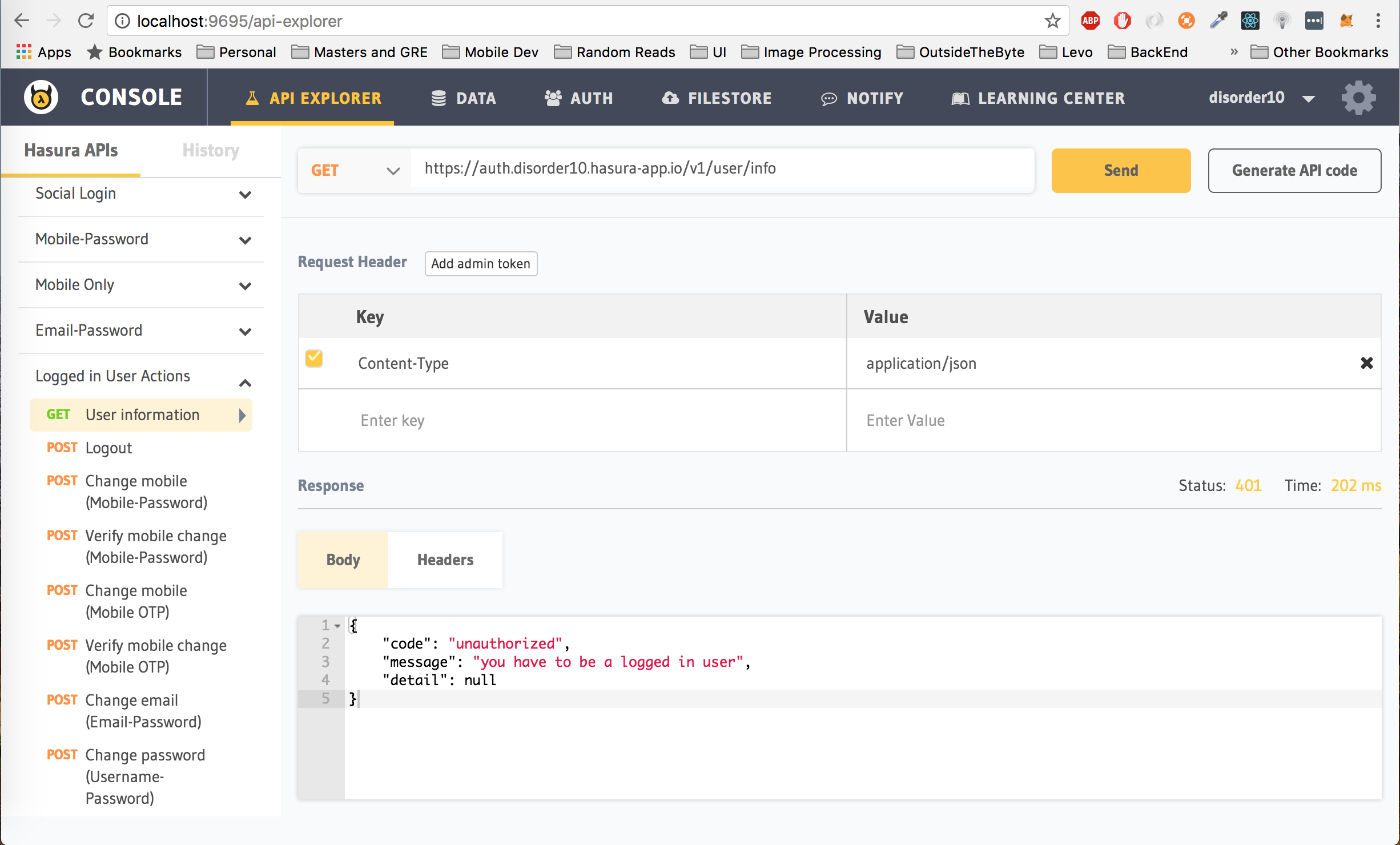
Let's check out one such API. In the API Explorer of the API Console, click on User Information under Logged in User Actions and hit the Send button.
We get the following response:
{
"code": "unauthorized",
"message": "you have to be a logged in user",
"detail": null
}This is because we have not passed the auth_token in the header. Add a new header to the request with key Authorization and value Bearer <auth_token> (replace <auth_token> with the auth_token that you received from your login/signup request. If you did not save it, perform a login request with the same username and password to get an auth_token again)
Hit the Send button after adding the Authorization header. You will receive a response similar to the one you received after login/signup.
To add request headers in ApolloCleint, you have to use a Middleware in Apollo Link.
This has already been implemented in this project. See
react-native-app/src/AppScreen.jsfor reference.
const graphqlUrl = `https://data.${clusterName}.hasura-app.io/v1alpha1/graphql`
const httpLink = new HttpLink({ uri: graphqlUrl });
// adding auth headers
const authMiddleware = new ApolloLink((operation, forward) => {
AsyncStorage.getItem('tokenKey').then((session) => {
operation.setContext({
headers: {
authorization: session ? "Bearer " + session.token : null
}
});
})
return forward(operation);
});
const client = new ApolloClient({
link: concat(authMiddleware, httpLink),
cache: new InMemoryCache({
addTypename: false
})
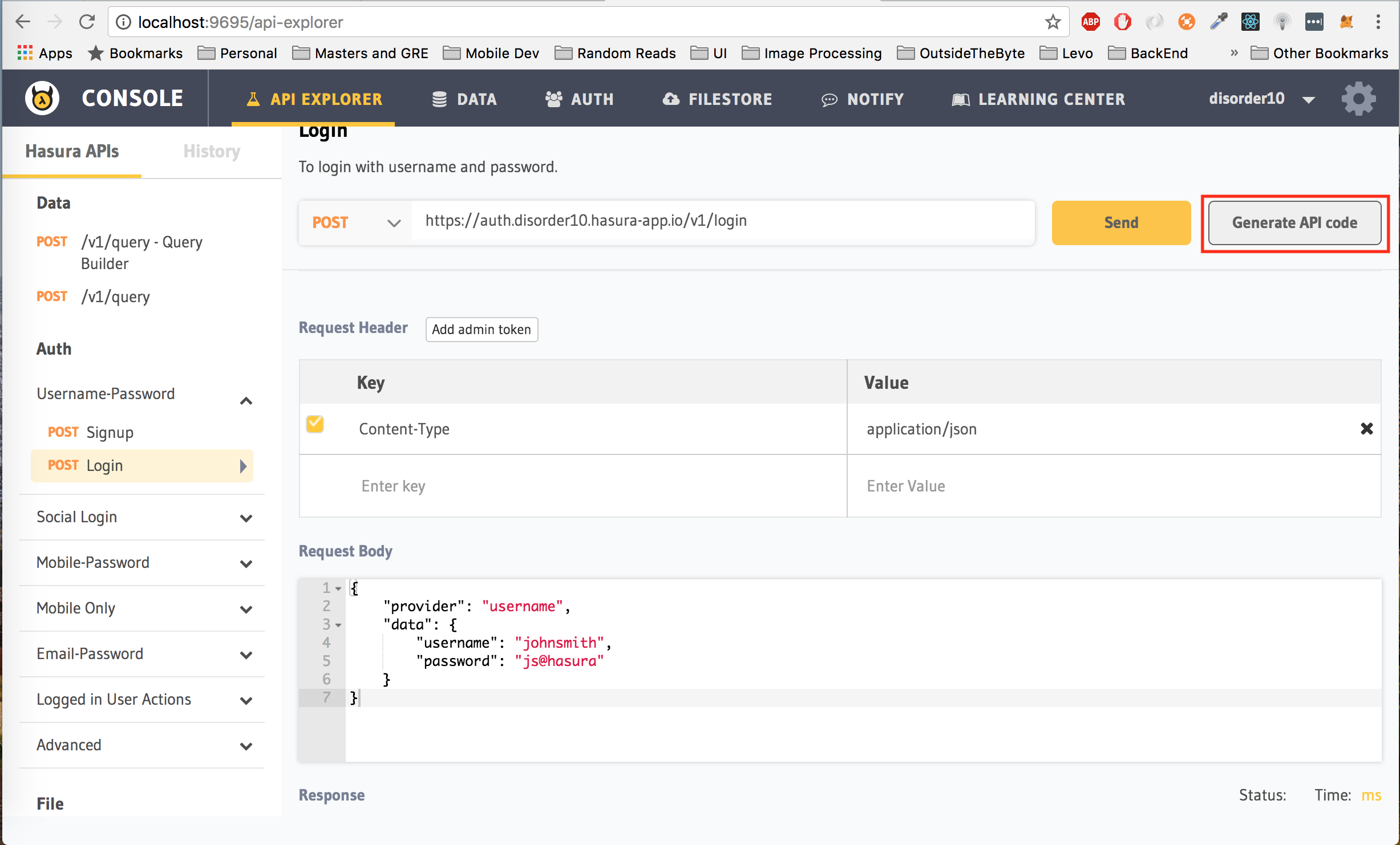
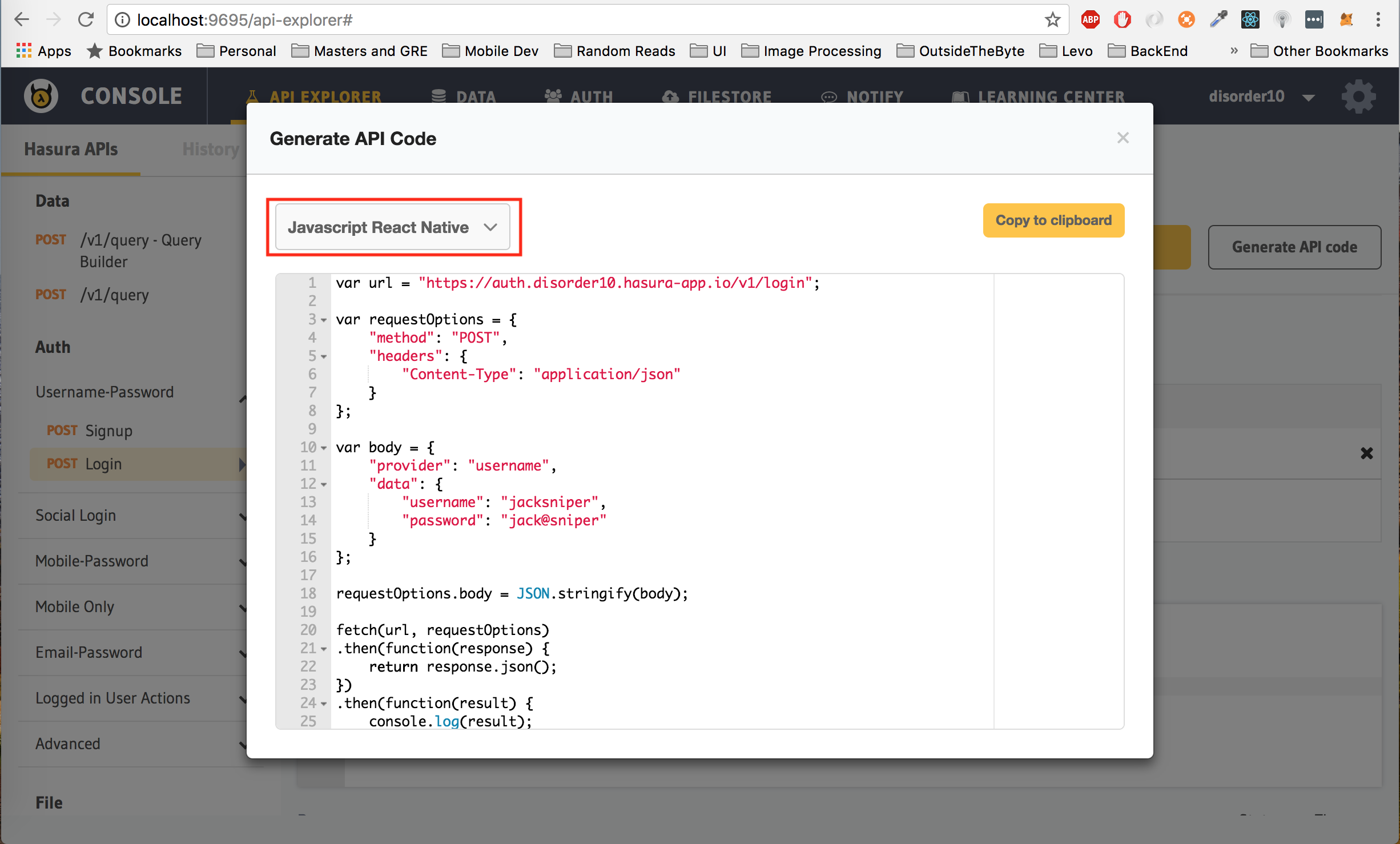
});A nifty feature of the API Console is the Code Generator. For every request that you want to try out on the API Console, you can generate the client side code for it.As an example, let's generate the code to make a login request. Click on the login endpoint and then click on the Generate API Code button the top right corner.
Select your required language and library from the drop down on the left.
- For React Native select
Javascript React Native
You can now copy and paste this into your client.
If you do not wish to write auth code, you can get a headstart by starting with the React Native Auth Boilerplate.
It has authentication using:
- Username/Password
- Mobile OTP
- Add your clusterName in the
Hasura.jsfile in thereact-native-appdirectory. - Authentication for React Native is implemented using the React Native Auth Boilerplate.
- You can find the code in the
authdirectory of thereact-native-app
Advanced use cases:
- Other authentication providers
- Understanding how the auth session works
- Auth Configuration
- Admin user actions
- Authentication user actions
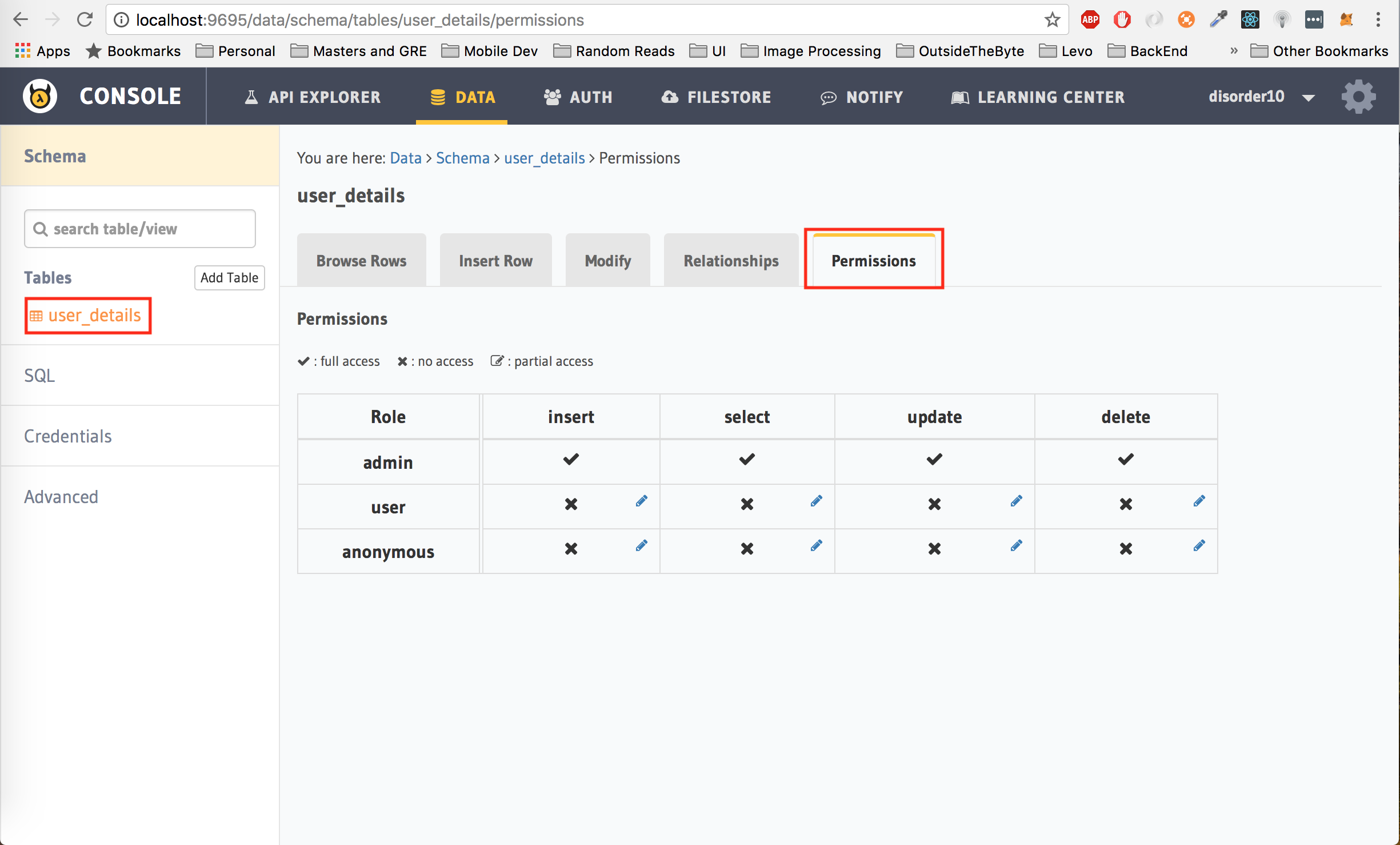
By default, every table created on Hasura can only be accessed by users with an admin role. Ergo, nobody will be able to access the user_details table without have an admin token. This is done to ensure security on all tables, so that nobody can randomly access data from your database unless you specifically allow that.
In our case, user_details table is used to store user specific data. We want to give every logged in user permission to insert and select their own data from the user_details table. Moreover, as an extra security measure, they should not be able to fetch another users data either.
Under the Data tab of the API Console, select user_details from the left panel and then click on the Permissions tab on the right to set permissions for the table. As you can see, an admin role has complete permission over the table. No other role has any permission.
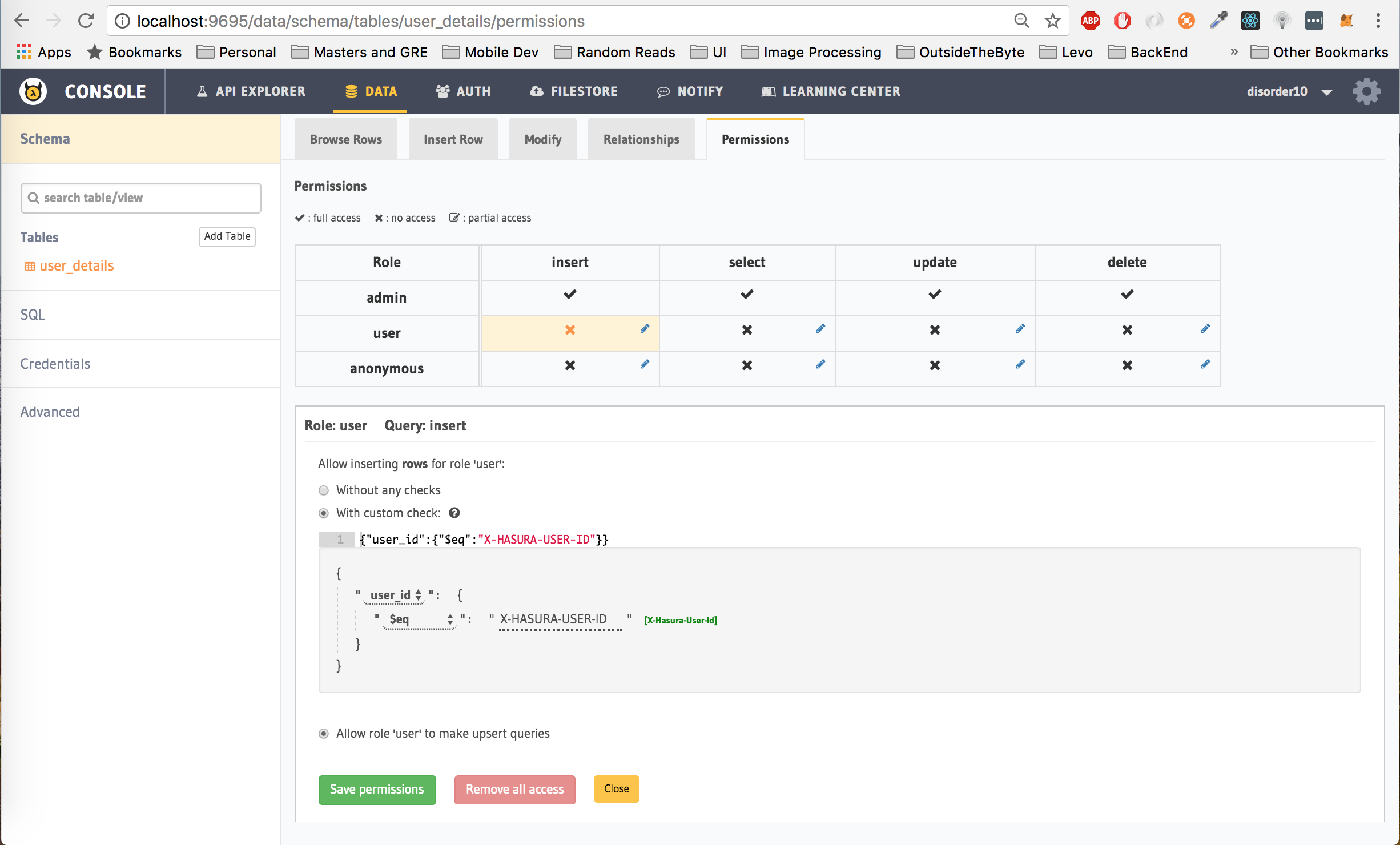
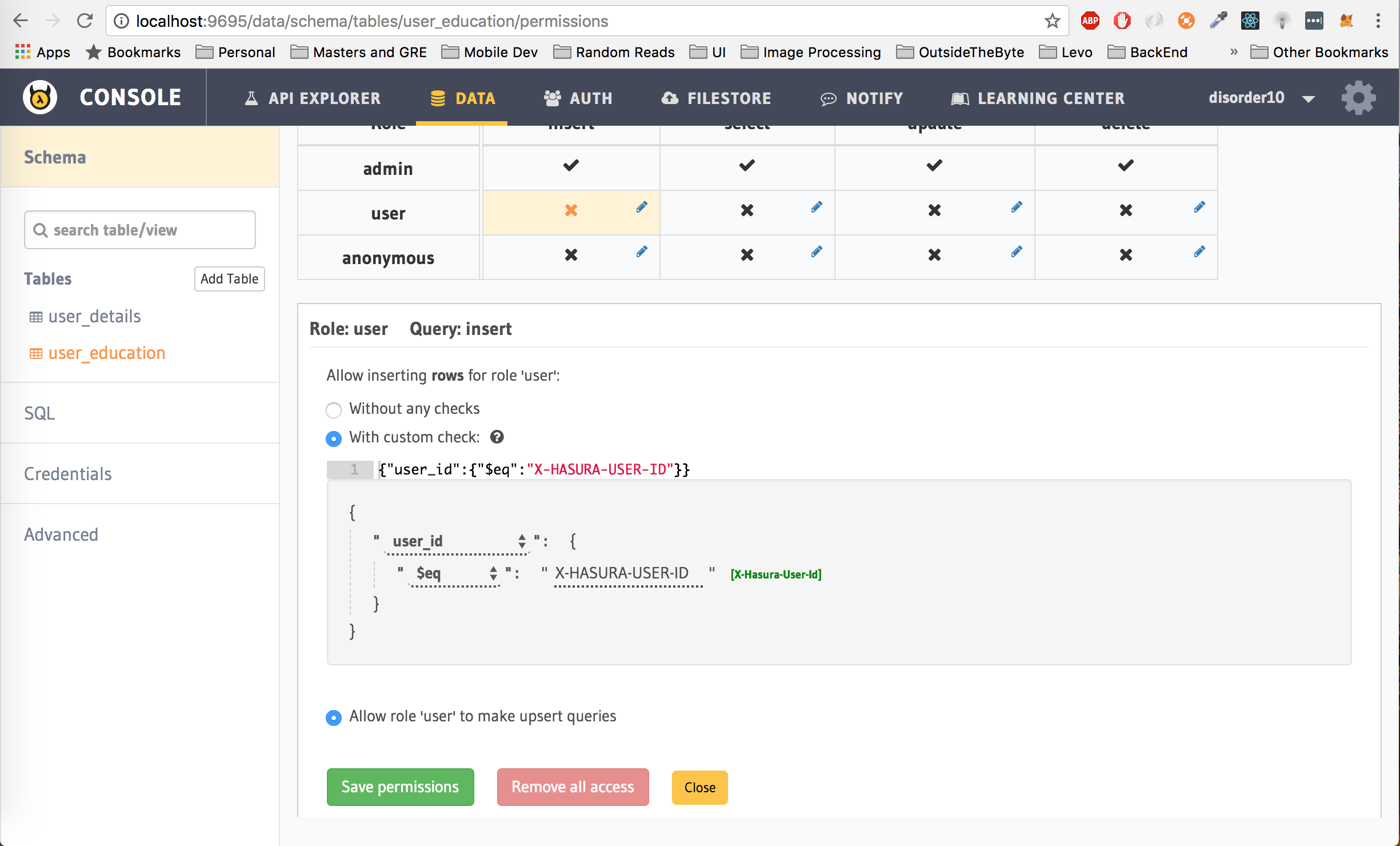
First, lets give the user role permission to insert data into the table. To do this, click on insert next to user row, check the with custom check option, choose user_id from the drop down and then select $eq and finally click on X-Hasura-User-Id. Click on Save Permissions.
The permissions set above translates to: Allow a user to insert into the user_details table only if the user_id being inserted is the same as the hasura_id associated with the user's auth_token which is passed as the Authorization token in the header
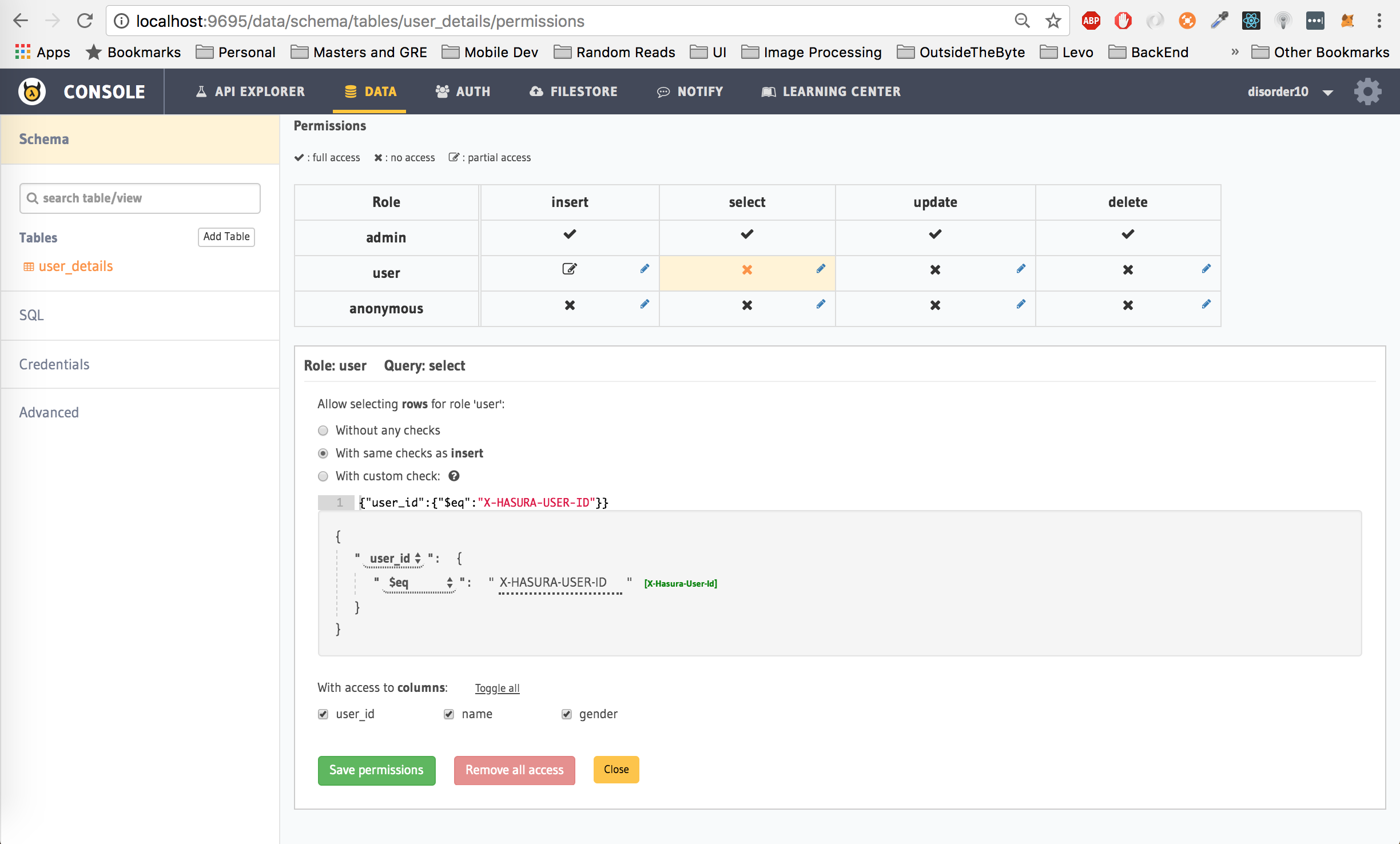
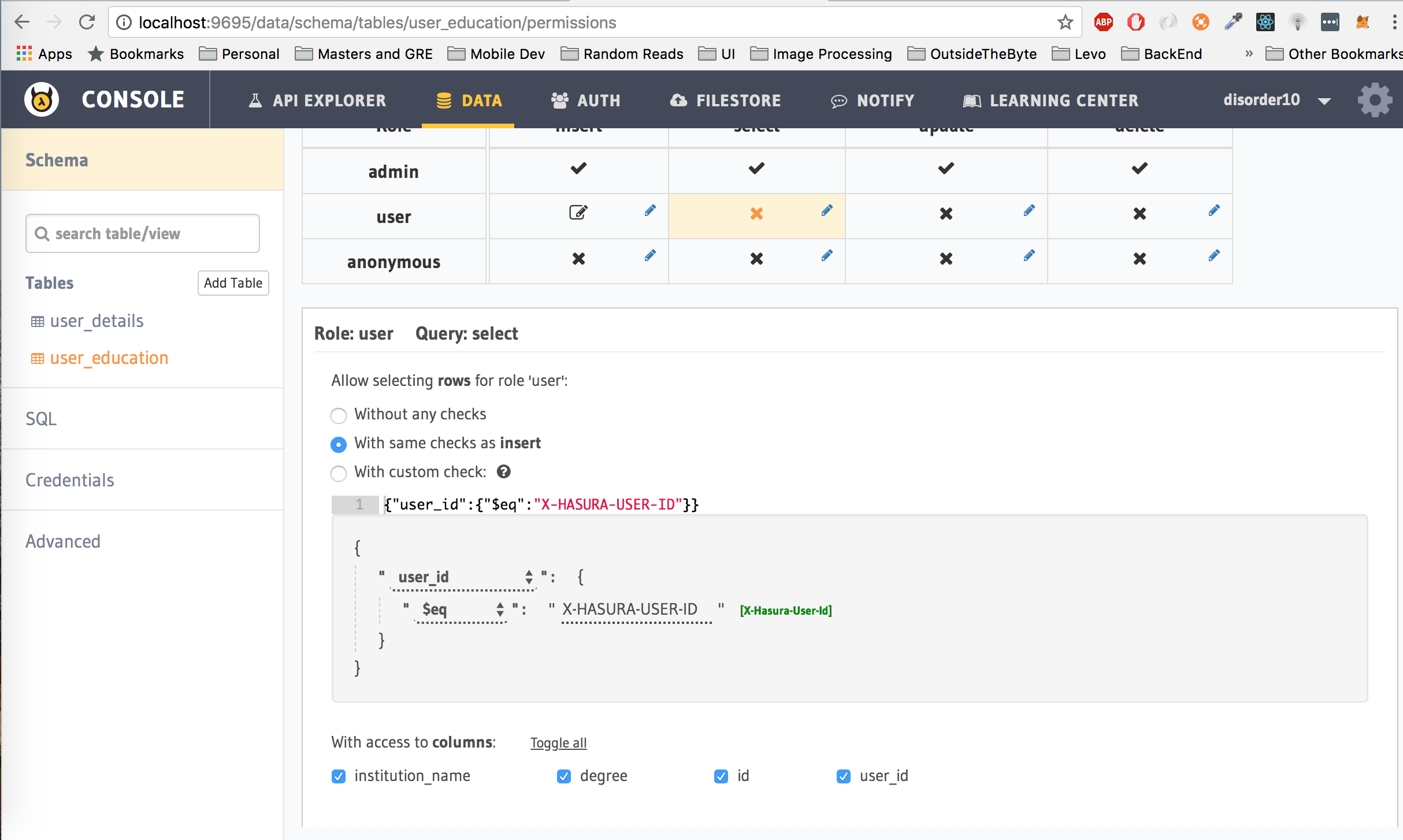
Second, lets give the user role permission to get their data from the table. Click on select next to the user row, check the with same checks as insert, also click on the Toggle All button next to With Access to columns. Click on Save Permissions.
The permissions set above translates to: Let the user only read rows from the user_details table where the user_id is equal to the hasura_id of the user which is passed as the Authorization token in the header. Moreover, allow the user to only read the selected columns, in this case, user_id, name and gender
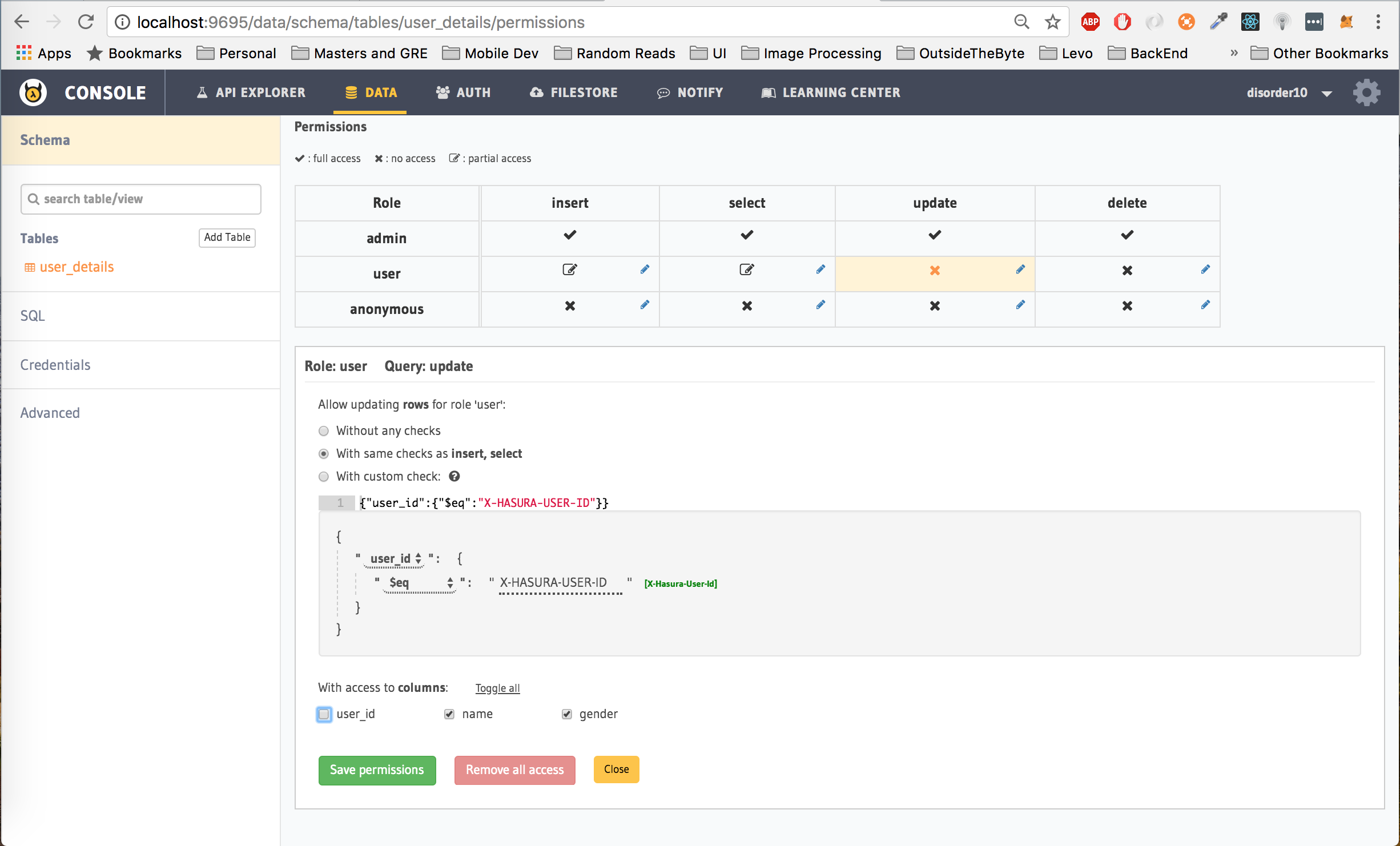
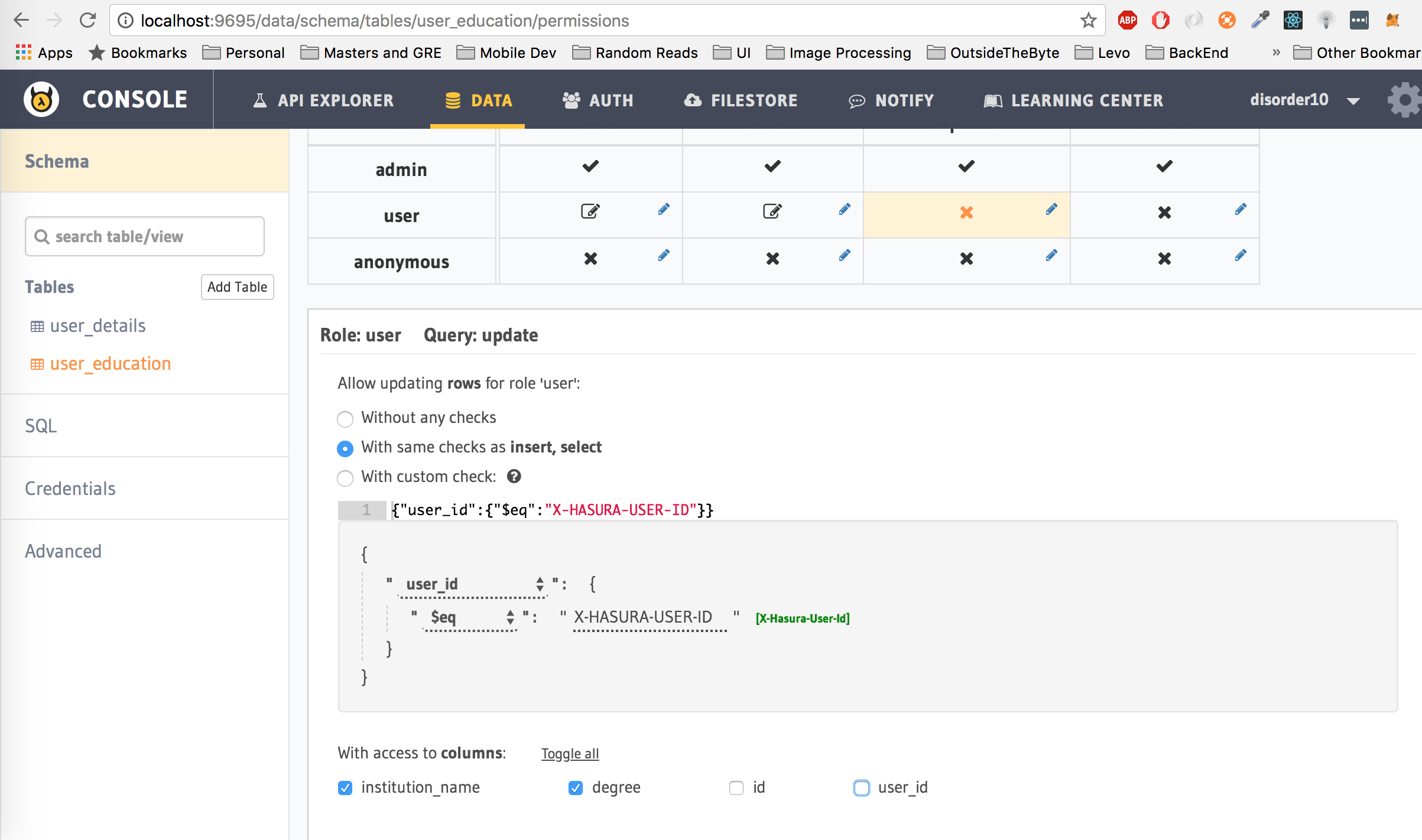
Third, update permissions
Translation: Let the user only update rows from the user_details table where the user_id is equal to the hasura_id of the user which is passed as the Authorization token in the header. Moreover, allow the user to only update the selected columns, in this case, the user cannot modify the user_id
Click on Save Permissions.
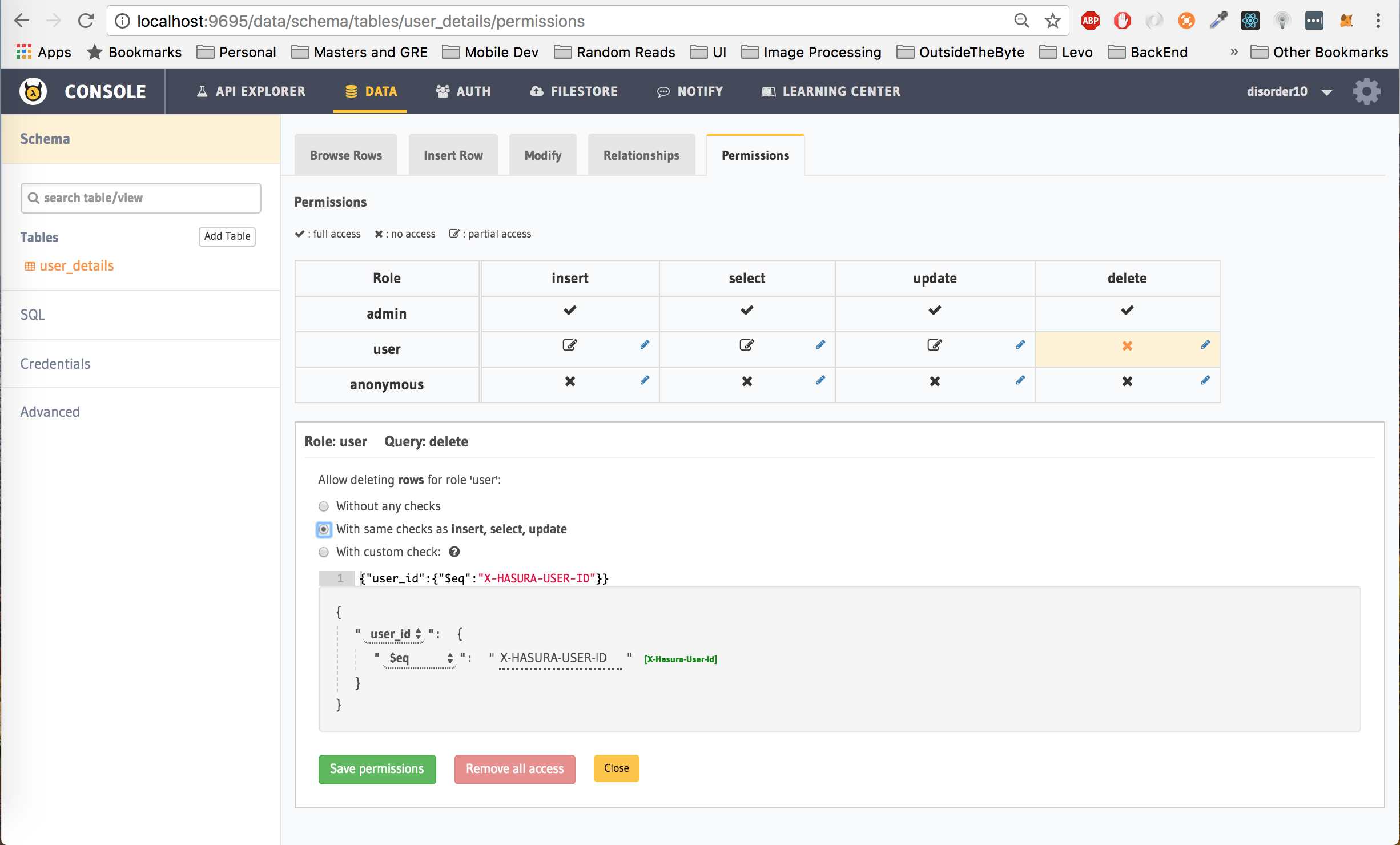
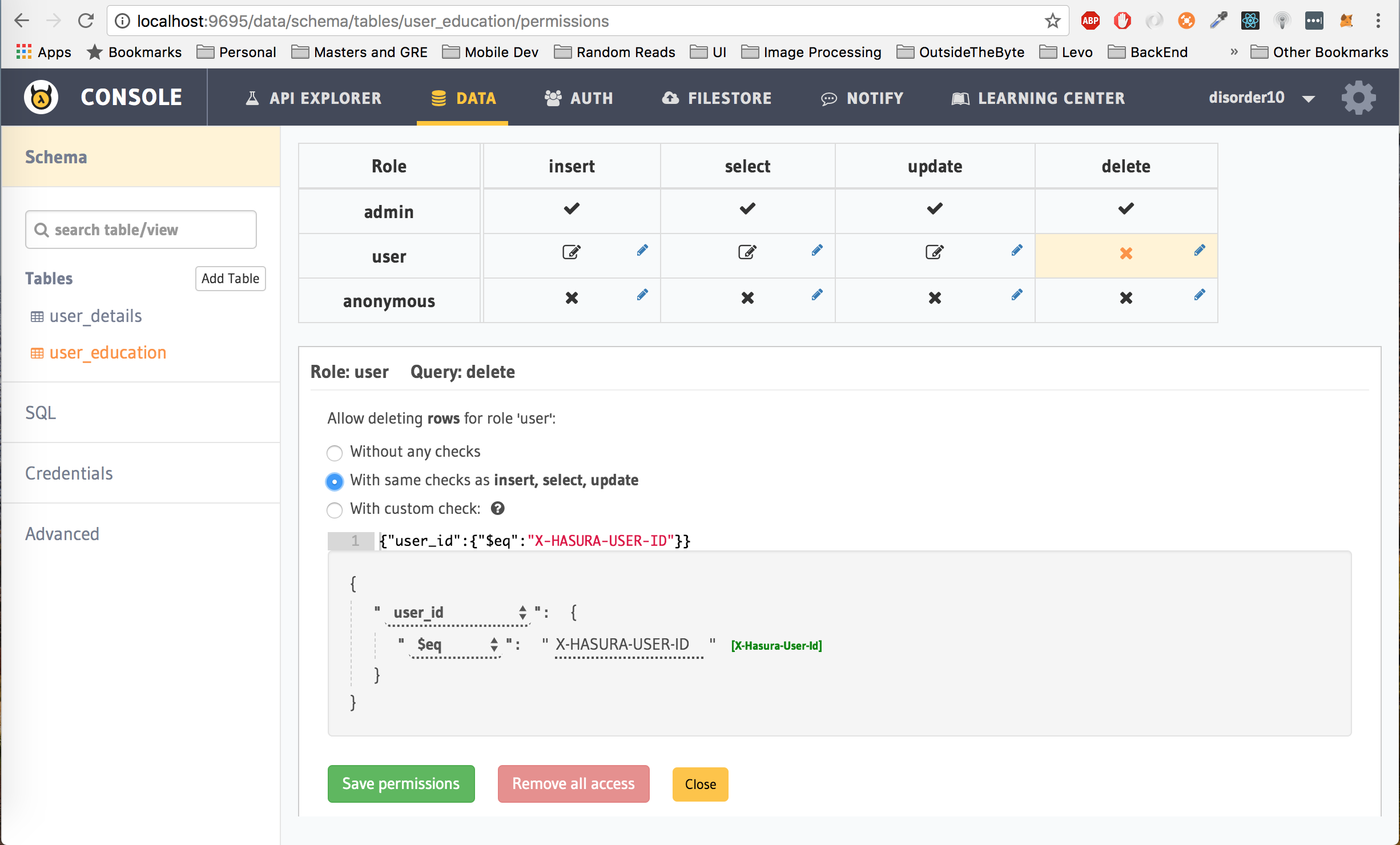
Finally, delete permissions
Translation: Let the user only delete rows from the user_details table where the user_id is equal to the hasura_id of the user which is passed as the Authorization token in the header.
Click on Save Permissions.
Now that we have created user permissions for the user_details table, logged in users will be able to enter their information. Following is an example of a button that inserts user information to user_details table.
const INSERT_USER_DETAILS = gql`
mutation insert_user_details($objects: [user_details_input!]){
insert_user_details(objects: $objects) {
affected_rows
}
}
`;
export default graphql (INSERT_USER_DETAILS)(props => {
return (
<Button
title="Update details"
onPress = {() => {
props.mutate({
variables: {
objects: [{
name: props.name,
gender: props.gender,
user_id: props.userId
}]
}
})
}}
/>
)
})Check react-native-app/src/InputComponent.js for reference.
Following is an example of fetching and rendering this user information
const FETCH_USER_DETAILS = gql`
query fetch_user_details{
user_details {
user_id
name
gender
}
}
`;
export default graphql(FETCH_USER_DETAILS)((props) => {
if (props.data.error) {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text>Unexpected.</Text>
</View>
);
}
if (props.data.loading) {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<ActivityIndicator/>
</View>
)
}
if (props.data.user_details.length === 0) {
return (
<View>No data</View>
)
}
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text>
Name: {props.data.user_details[0].name}
</Text>
<Text>
Gender: {props.data.user_details[0].gender}
</Text>
</View>
)
})The app in this project implements this operation. Check react-native-app/src/components/DataComponent to see the implementation.
You can also create connections between various tables through foreign key constraints. These can be used to build more complex relationships, which can be used to fetch related data alongside the columns queried, as pseudo columns.
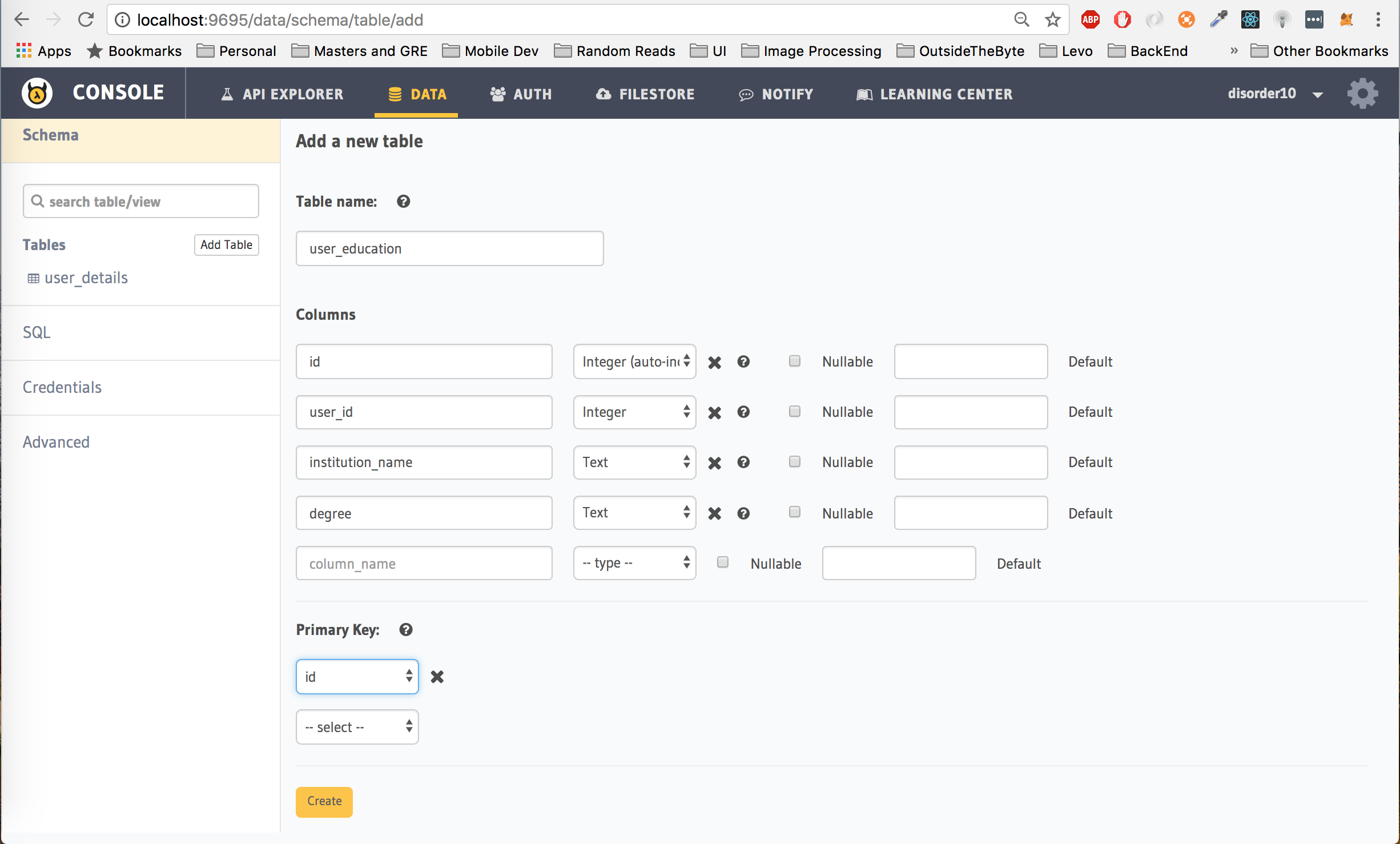
To explore this feature, let's create a new table called user_education to store information about each user's educational background like institution_name and degree. We will also have an additional column id of type Integer (auto increment) and a user_id column to store the hasura_id of the user. id will be the primary key for this table.
It is not a good idea to set
user_idas the primary key as a user can have multiple addresses and settinguser_idas the primary key will not let us enter more than address for a particular user.
Click on the Create button.
Similar to user_details table, add user permissions on the user_education table.
What we want to achieve now is that when we fetch user details from the user_details table, we should also get the respective education data for the user.
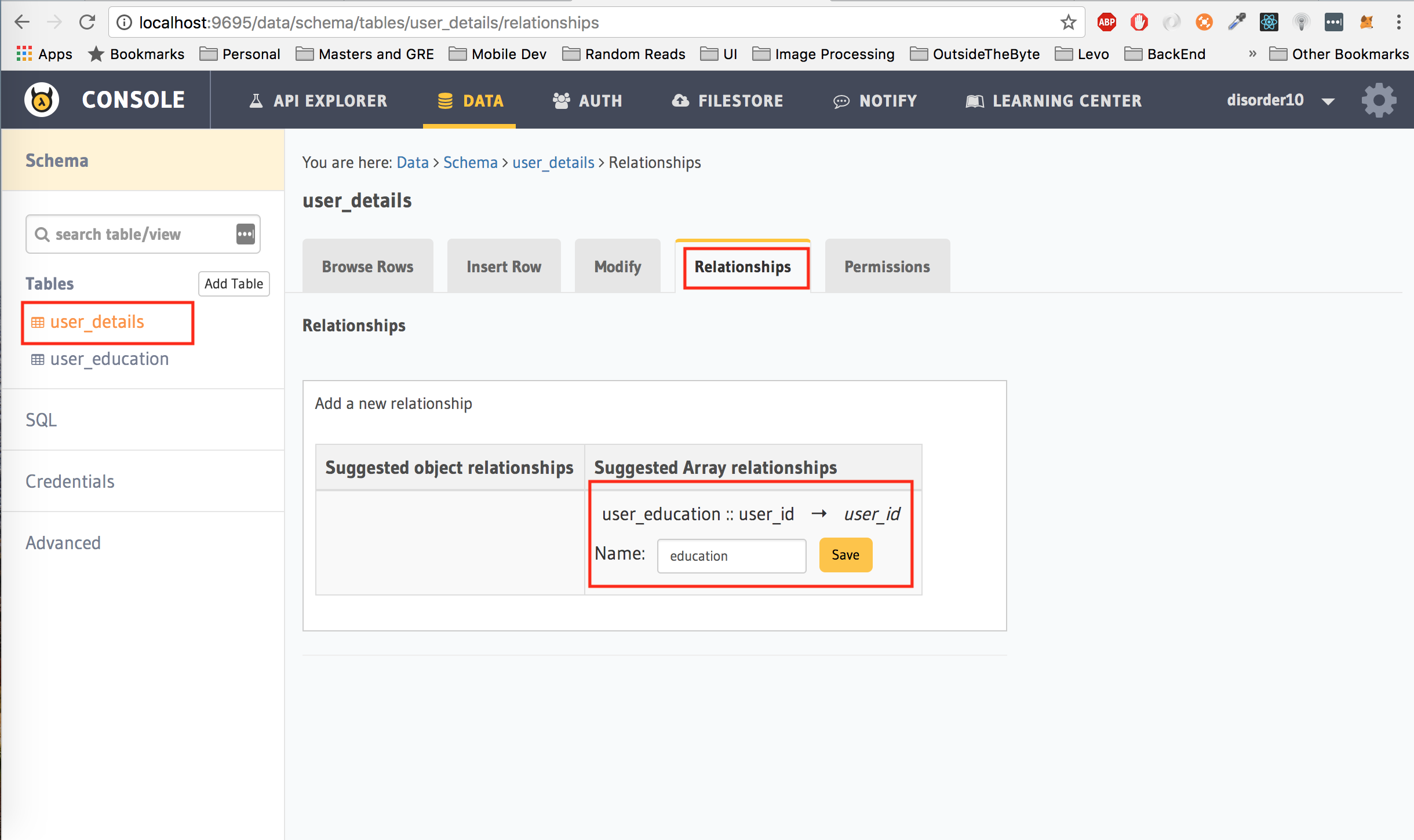
For this, we are going to create an array relationship from the user_details table to the user_education table. To create a relationship:
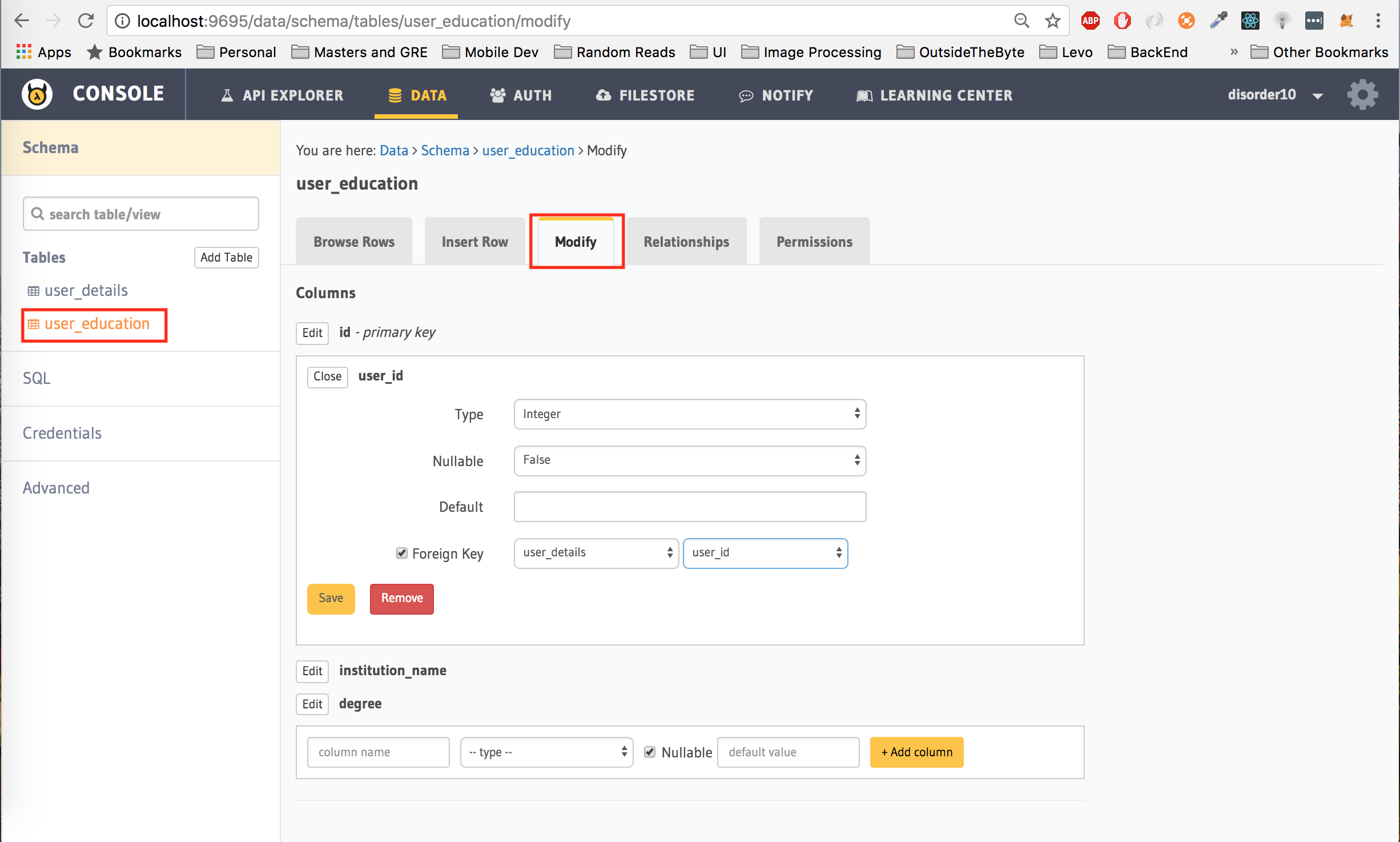
First, add a foreign key constraint from the user_id column of the user_education table to the user_id column of the user_details table. To do this, under the Modify tab, click on edit next to user_id, choose user_details as the reference table and user_id as the reference column. Click on Save to add this foreign key constraint.
Next, open up the user_details table from the left panel and click on the Relationships tab. If you have followed the instructions above correctly, you will now have an entry under the Suggested Array Relationship column. Click on Add and name the relationship education and hit Save.
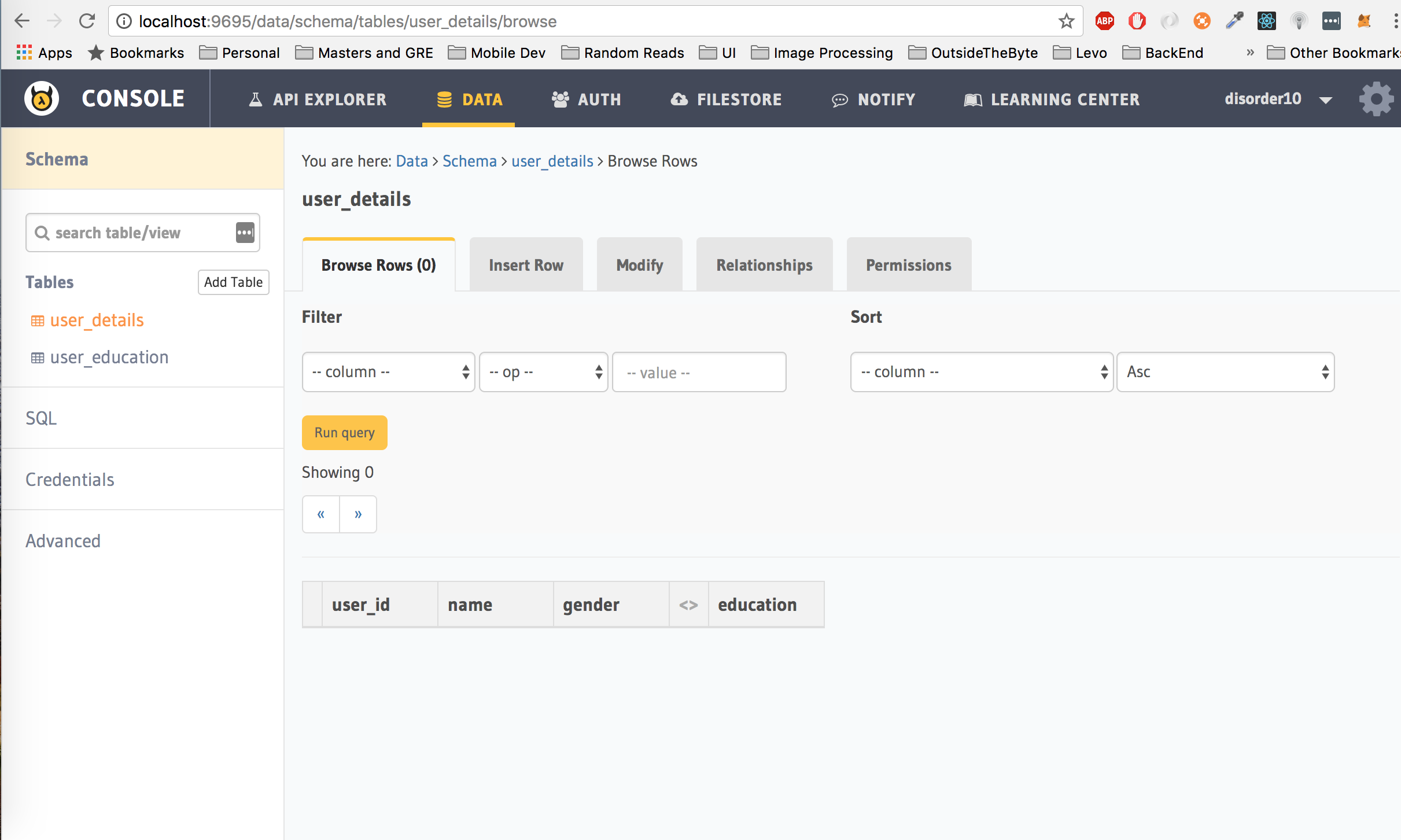
Click on Browse Rows and you will now see another column called education for the user_details table.
educationis not really a column, but a pseudo column. You can now use the Data APIs to fetch data from this table which includes education data as well.
We can now fetch the education details for each user from the user_details table using the following query:
query fetch_user_details{
user_details {
user_id
name
gender
education {
id
institution_name
degree
}
}
}
Your response will look like the following:
[
{
"user_id": 2,
"name": "Jack Sniper",
"gender": "Male",
"education": [
{
"institution_name": "XYZ University",
"degree": "BE",
"id": 1,
"user_id": 2
},
{
"institution_name": "ABC University",
"degree": "MS",
"id": 2,
"user_id": 2
}
]
}
]- Add your clusterName in the
Hasura.jsfile in thereact-native-appdirectory. - Run the app
- Login or signup
- Click on
Datain the landing screen to see a working example of fetching user details. - The code for Data can be found in the
DataComponent.js
For advanced use cases, it is recommended to go through our docs.
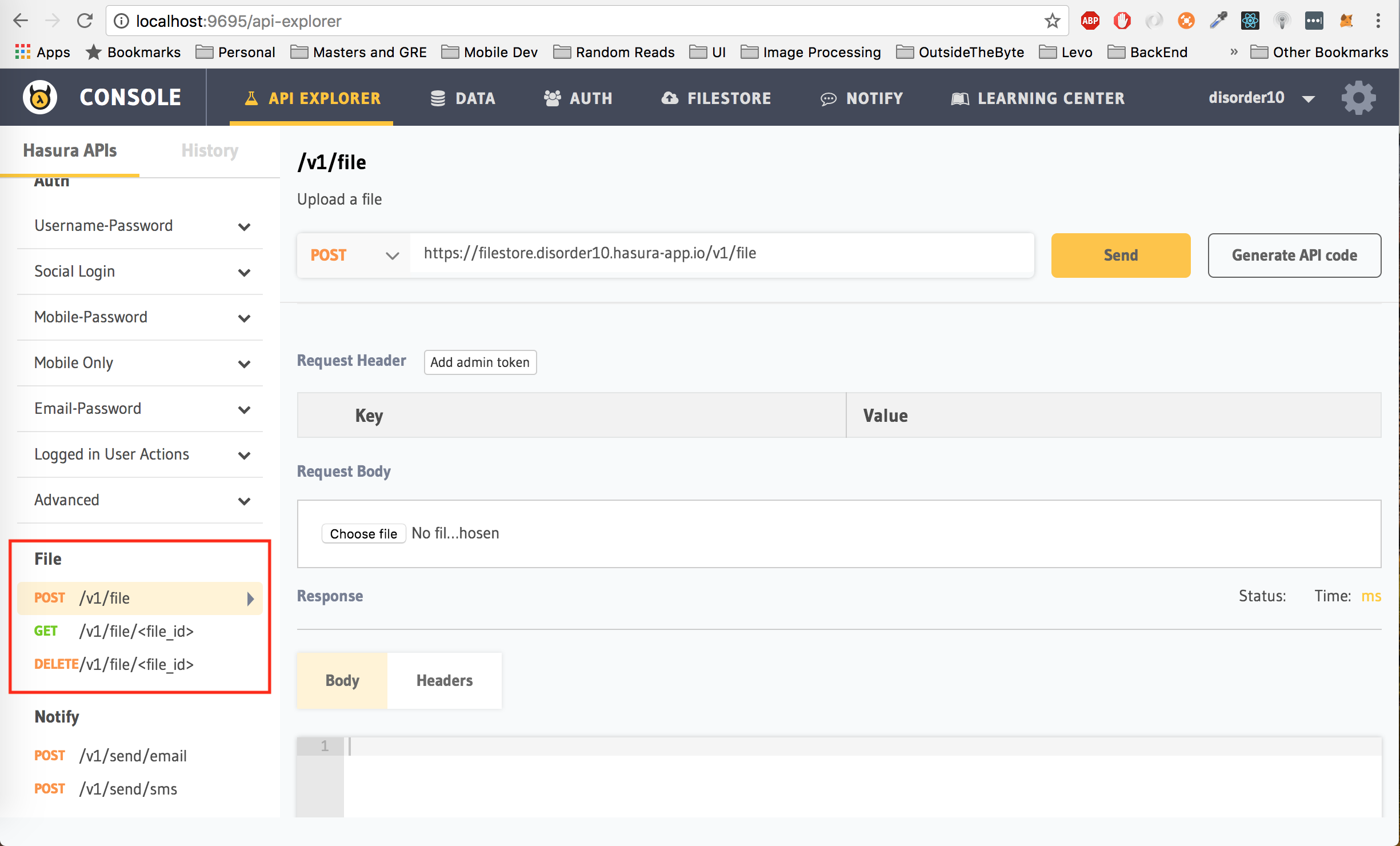
Some apps require the ability to upload and download files, for eg: storing user profile pictures or if you are building an app like google drive. Hasura provides easy to use APIs to upload and download files as well. Under the API Explorer tab, explore the APIs under File
You can test out the filestore APIs on the API Explorer and use the Code Generator to include it in your client side code.
- React Native:
- Add your clusterName in the
Hasura.jsfile in thereact-native-appdirectory. - Run the app
- Login or signup
- Click on
Filesin the landing screen to see a working example of fetching user details. - The code for Data can be found in the
FileComponent.js.
- Add your clusterName in the
Go though the docs, to know more about the filestore and to understand how you can set permissions on it.
Although, Hasura provides backend components, there are times when you might want to write your own custom logic and for this write your own server. Common use cases of this include, sending push notifications to the users mobile device when a certain event happens, doing some sort of calculation or data manipulation for some event.
For this, you would want to create a custom microservice on Hasura. This project comes with one such microservice which runs on the api subdomain. This microservice is a simple Nodejs Express server which includes boilerplate code for the following:
- Writing custom endpoints
- Push notifications
- Websockets
You can open the url to this microservice on your web browser by running the following in your terminal
$ hasura microservice open apiEvery Hasura cluster comes with a few default microservices, all the backend feature we have used until now is a Microservice. Authentication is provided by the
authmicroservice, the data APIS by thedatamicroservice, file upload and download by thefilestoremicroservice. To take a look at the available microservices, run$ hasura microservice liston your terminal, inside the project directory. Hence, it is only natural that if you want additional features, you would simply create a new microservice. All custom microservices can be found inside themicroservicesdirectory. You can learn more about microservices on Hasura here.
The code for this microservice can be found inside the microservices/api/src
Navigate to microservices/api/src/custom-logic/routes.js to see how to define a custom route. There are two examples in it, one is a definition for a GET request at "/" and the other for a POST request at "/echo". The "/" route just returns a "Hello World" and the "/echo" endpoint just returns whatever you send to it.
For React Native, you have to eject the app and configure firebase as given here.
Now, whenever you want to send a push notification to a user, you will fetch the associated fcm_token from the user's user_id and then hit the fcm api to send the push notification.
There is an example of doing this in the
apimicroservice, you can find the code for it atmicroservices/api/src/push-notif/routesdefined as the"/test_push".
Note: You need to set the Web API Key from your Firebase Project Settings on the Firebase Cloud Console and add it to the fcmKey variable at microservices/api/src/push-notif/routes.
Ideally, you should pass the FCM key as an environment variable to the server and not hard code it in the source code. To do this, you need to add the key as a secret into Hasura and then edit the k8s.yaml file inside microservices/api/ to pass that as an environment variable.
Step 1: Add FCM key to Hasura secrets
$ # Replace <WEB API KEY> with the FCM Key
$ $ hasura secret update fcm.key "<WEB API KEY>"Step 2: Edit k8s.yaml file
Run the following from the root directory of the project.
$ cp microservices/api/k8s.fcm.yaml microservices/api/k8s.yamlWebSockets are a technology that makes it possible to open an interactive communication session between a client app and a server. With this API, you can send messages to a server and receive event-driven responses without having to poll the server for a reply.
Chat apps are the most common use cases for Websockets. We are going to use Socket.io, which is basically a Javascript framework implementing the Websockets protocol.
microservices/api/src/server.js has a simple setup done using socket.io.
The socket listens at https:api.<cluster-name>.hasura-app.io (replace <cluster_name> with the name of your cluster). It listens to the topic "message" and responds with an echo of whatever you send.
- Add your clusterName in the
Hasura.jsfile in thereact-native-appdirectory. - Run the React Native app
- Login or signup
- Click on
Socket.IO. Currently, the server will just respond with a "The message your sent is: ". - You can find the code in the
SocketIO.js.
For more information on using socket.io, it is recommended to check their docs.