Automated netboot&provisioning server, Foreman and Salt based.
Any setup takes time, practically it is never one-time action.
Maintaining multi-node environments is cumbersome (configuration synchronization, duplicated installation process).
Sometimes it would also be useful to keep your favourite os hacks/tips/tricks in structured manner (like in some configuration management solution)
Moreover updates sometimes break, anything breaks at some point - then it may be better to wipe everything/some part out
and start over. Unfortunately as some setup work had already been done such solution may be too radical.
Setup any environment: dev, prod, work, home using Salt and PXE booting (the Foreman's).
Will aim to be both Linux&Windows friendly.
As the best way of documenting things is writing automation scripts, this automation server's installation process is also automated.
The "installation" process ends up with LXC container containing foreman&salt fully setup and configured.
Simply follow:
git clone https://github.com/kiemlicz/ambassador.git- Optionally provide
ambassador-installer.override.confto override any Salt masterless settings, e.g. add your own pillar:
ext_pillar:
- git:
- branch git@bitbucket.org:someone/pillar_repo.git:
- root: pillar
- env: base
sudo apt install lxc bridge-utils debootstrap python3-lxcsudo SHELL=/bin/bash python3 installer/install.py --to lxc --name ambassador --ifc [ifc] [--kdbx the.db.kdbx] [--kdbx-pass thepassword] [--kdbx-key the.key] [--secrets https://secrets.server.com/path]
Since foreman still doesn't support 'dockerized' deployment (cannot specify plugins for Foreman Docker images, no official foreman-proxy image).
The provided docker-compose.yml can be used only to setup external DB or any other services. Use docker-compose.override.yml for any overrides:
version: '3'
services:
db:
environment:
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=realforemanpassword
volumes:
- db:/var/lib/postgresql/data
volumes:
db:
driver: local
driver_opts:
type: none
o: bind
device: /tmp/foreman
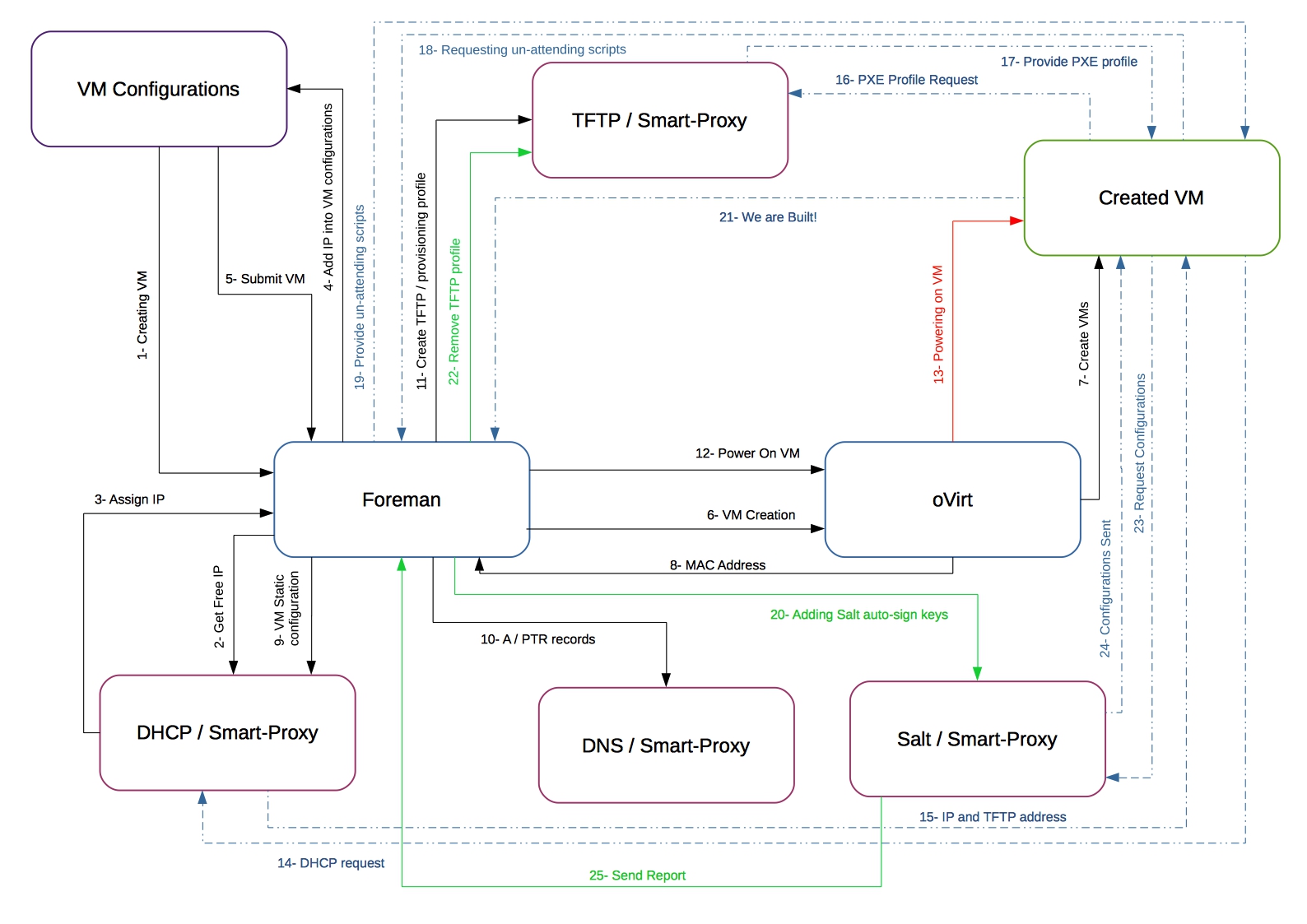
Foreman&Salt workflow is best depicted using this (Foreman's) diagram:
For State Tree and custom extensions documentation, find the State's Tree README.md
Provisioning of OSes involves many technologies and tools, it is very likely that something may not always works "as expected"
- Many BIOS/UEFI TFTP clients are of very low quality and fail on option negotiation. Thus it may be needed to disable negotiation for
some options like blksize. Example for tftp-hpa server: /etc/default/tftpd-hpa append:
TFTP_OPTIONS="--secure --refuse blksize"
- https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/utils/boot/syslinux/Testing/6.04/ (latest stable totally doesn't work for UEFI)