- Listening on multiple ports
- Multi-level forward proxy - proxy chain
- Standard HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4(A)/SOCKS5 proxy protocols support
- TLS encryption via negotiation support for SOCKS5 proxy
- Tunnel UDP over TCP
- Permission control
- Local/remote TCP/UDP port forwarding (2.1+)
- Shadowsocks protocol (UDP: 2.4+)
- KCP protocol (2.3+)
- Transparent TCP proxy (2.3+)
- HTTP2 tunnel (2.4+)
- SSH tunnel (2.4+)
- QUIC tunnel (2.4+)
- obfs4 tunnel (2.4+)
Binary file download:https://github.com/ginuerzh/gost/releases
Google group: https://groups.google.com/d/forum/go-gost
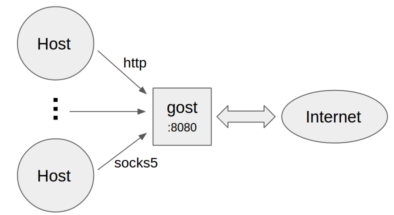
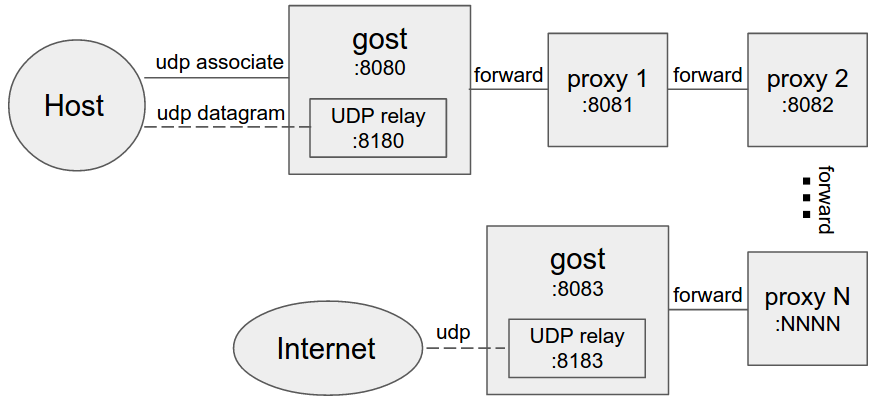
Gost and other proxy services are considered to be proxy nodes, gost can handle the request itself, or forward the request to any one or more proxy nodes.
Gost has been released in ubuntu store, and can be installed directly through the snap in ubuntu 16.04:
$ sudo snap install gostEffective for the -L and -F parameters
[scheme://][user:pass@host]:portscheme can be divided into two parts: protocol+transport
protocol: proxy protocol types (http, socks4(a), socks5, ss), transport: data transmission mode (ws, wss, tls, quic, kcp, ssh, h2, h2c, obfs4), may be used in any combination or individually:
http - standard HTTP proxy: http://:8080
https - standard HTTPS proxy (may need to provide a trusted certificate): http+tls://:443 or https://:443
http2 - HTTP2 proxy and backwards-compatible with HTTPS proxy: http2://:443
h2 - HTTP2 h2 tunnel: h2://:443
h2c - HTTP2 h2c tunnel: h2c://:443
socks4(a) - standard SOCKS4(A) proxy: socks4://:1080 or socks4a://:1080
socks5 - standard SOCKS5 proxy: socks5://:1080
socks5+wss - SOCKS5 over websocket: socks5+wss://:1080
tls - HTTPS/SOCKS5 over TLS: tls://:443
ss - standard shadowsocks proxy: ss://chacha20:123456@:8338
ssu - shadowsocks UDP relay server: ssu://chacha20:123456@:8338
quic - QUIC tunnel: quic://:6121
kcp - KCP tunnel: kcp://:8388
redirect - transparent proxy: redirect://:12345
ssh - SSH proxy tunnel: ssh://:2222, SSH forward tunnel: forward+ssh://:2222
obfs4 - obfs4 tunnel: obfs4://:8080
Effective for the -L parameter
scheme://[bind_address]:port/[host]:hostportscheme - forward mode, local: tcp, udp; remote: rtcp, rudp
bind_address:port - local/remote binding address
host:hostport - target address
Contributed by @septs.
-C : specifies the configuration file path
The configuration file is in standard JSON format:
{
"ServeNodes": [
":8080",
"ss://chacha20:12345678@:8338"
],
"ChainNodes": [
"http://192.168.1.1:8080",
"https://10.0.2.1:443"
],
"Debug": true
}ServeNodes is equivalent to the -L parameter, ChainNodes is equivalent to the -F parameter, Debug is equivalent to the -D parameter.
- Standard HTTP/SOCKS5 proxy
gost -L=:8080- Proxy authentication
gost -L=admin:123456@localhost:8080- Multiple sets of authentication information
gost -L=localhost:8080?secrets=secrets.txtThe secrets parameter allows you to set multiple authentication information for HTTP/SOCKS5 proxies, the format is:
# username password
test001 123456
test002 12345678
- Listen on multiple ports
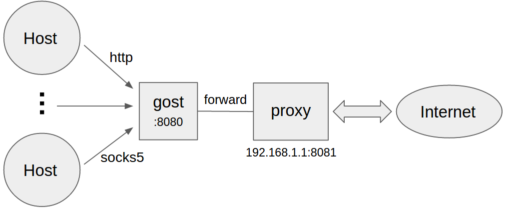
gost -L=http2://:443 -L=socks5://:1080 -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338gost -L=:8080 -F=192.168.1.1:8081- Forward proxy authentication
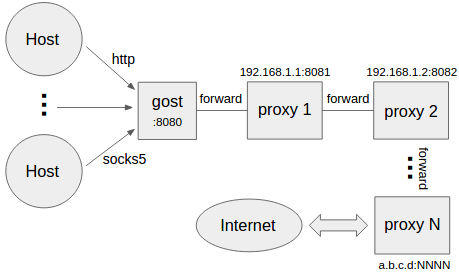
gost -L=:8080 -F=http://admin:123456@192.168.1.1:8081gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://192.168.1.1:6121 -F=socks5+wss://192.168.1.2:1080 -F=http2://192.168.1.3:443 ... -F=a.b.c.d:NNNNGost forwards the request to a.b.c.d:NNNN through the proxy chain in the order set by -F, each forward proxy can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 [-F=...]The data on the local TCP port 2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain). If the last node of the chain (the last -F parameter) is a SSH forwad tunnel, then gost will use the local port forwarding function of SSH directly:
gost -L=tcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F forward+ssh://:2222gost -L=udp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53?ttl=60 [-F=...]The data on the local UDP port 5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and there is no data interaction during this time period, the channel will be closed. The timeout value can be set by the ttl parameter. The default value is 60 seconds.
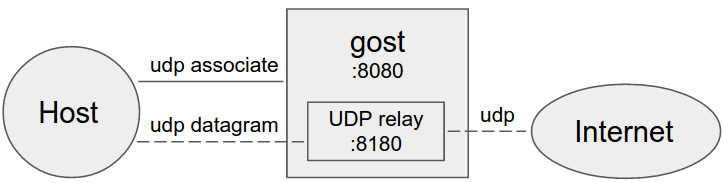
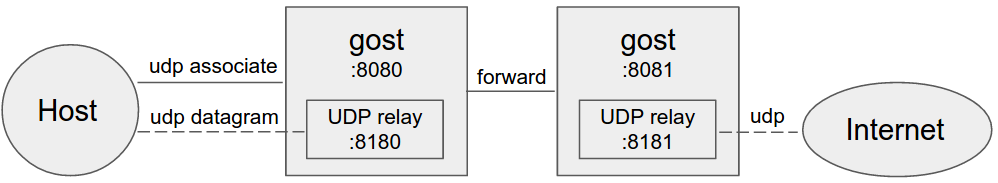
NOTE: When forwarding UDP data, if there is a proxy chain, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy, gost will use UDP-over-TCP to forward data.
gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 [-F=... -F=socks5://172.24.10.1:1080]The data on 172.24.10.1:2222 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:22 (through the proxy chain). If the last node of the chain (the last -F parameter) is a SSH tunnel, then gost will use the remote port forwarding function of SSH directly:
gost -L=rtcp://:2222/192.168.1.1:22 -F forward+ssh://:2222gost -L=rudp://:5353/192.168.1.1:53?ttl=60 [-F=... -F=socks5://172.24.10.1:1080]The data on 172.24.10.1:5353 is forwarded to 192.168.1.1:53 (through the proxy chain).
Each forwarding channel has a timeout period. When this time is exceeded and there is no data interaction during this time period, the channel will be closed. The timeout value can be set by the ttl parameter. The default value is 60 seconds.
NOTE: When forwarding UDP data, if there is a proxy chain, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be gost SOCKS5 proxy, gost will use UDP-over-TCP to forward data.
Gost HTTP2 supports two modes:
- As a standard HTTP2 proxy, and backwards-compatible with the HTTPS proxy.
- As a transport tunnel.
Server:
gost -L=http2://:443Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=http2://server_ip:443?ping=30服务端:
gost -L=h2://:443客户端:
gost -L=:8080 -F=h2://server_ip:443Support for QUIC is based on library quic-go.
Server:
gost -L=quic://:6121Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=quic://server_ip:6121NOTE: QUIC node can only be used as the first node of the proxy chain.
Support for KCP is based on libraries kcp-go and kcptun.
Server:
gost -L=kcp://:8388Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=kcp://server_ip:8388Gost will automatically load kcp.json configuration file from current working directory if exists, or you can use the parameter to specify the path to the file.
gost -L=kcp://:8388?c=/path/to/conf/fileNOTE: KCP node can only be used as the first node of the proxy chain.
Gost SSH supports two modes:
- As a forward tunnel, used by local/remote TCP port forwarding.
- As a transport tunnel.
Server:
gost -L=forward+ssh://:2222Client:
gost -L=rtcp://:1222/:22 -F=forward+ssh://server_ip:2222Server:
gost -L=ssh://:2222Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=ssh://server_ip:2222?ping=60The client supports the ping parameter to enable heartbeat detection (which is disabled by default). Parameter value represents heartbeat interval seconds.
Iptables-based transparent proxy
gost -L=redirect://:12345 -F=http2://server_ip:443Contributed by @isofew.
Server:
gost -L=obfs4://:443When the server is running normally, the console prints out the connection address for the client to use:
obfs4://:443/?cert=4UbQjIfjJEQHPOs8vs5sagrSXx1gfrDCGdVh2hpIPSKH0nklv1e4f29r7jb91VIrq4q5Jw&iat-mode=0
Client:
gost -L=:8888 -F='obfs4://server_ip:443?cert=4UbQjIfjJEQHPOs8vs5sagrSXx1gfrDCGdVh2hpIPSKH0nklv1e4f29r7jb91VIrq4q5Jw&iat-mode=0'
For HTTP, you can use TLS to encrypt the entire communication process, the HTTPS proxy:
Server:
gost -L=http+tls://:443Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=http+tls://server_ip:443Gost HTTP2 proxy mode only supports the use of TLS encrypted HTTP2 protocol, does not support plaintext HTTP2.
Gost HTTP2 tunnel mode supports both encryption (h2) and plaintext (h2c) modes.
Gost supports the standard SOCKS5 protocol methods: no-auth (0x00) and user/pass (0x02), and extends two methods for data encryption: tls(0x80) and tls-auth(0x82).
Server:
gost -L=socks://:1080Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=socks://server_ip:1080If both ends are gosts (as example above), the data transfer will be encrypted (using tls or tls-auth). Otherwise, use standard SOCKS5 for communication (no-auth or user/pass).
Support for shadowsocks is based on library shadowsocks-go.
Server:
gost -L=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338Client:
gost -L=:8080 -F=ss://aes-128-cfb:123456@server_ip:8338Currently, only the server supports UDP Relay.
Server:
gost -L=ssu://aes-128-cfb:123456@:8338There is built-in TLS certificate in gost, if you need to use other TLS certificate, there are two ways:
- Place two files cert.pem (public key) and key.pem (private key) in the current working directory, gost will automatically load them.
- Use the parameter to specify the path to the certificate file:
gost -L="http2://:443?cert=/path/to/my/cert/file&key=/path/to/my/key/file"Client can specify secure parameter to perform server's certificate chain and host name verification:
gost -L=:8080 -F="http2://server_domain_name:443?secure=true"Client can specify a CA certificate to allow for Certificate Pinning:
gost -L=:8080 -F="http2://:443?ca=ca.pem"Certificate Pinning is contributed by @sheerun.
Gost acts as the standard SOCKS5 proxy for UDP relay.
When forward proxies are set, gost uses UDP-over-TCP to forward UDP data, proxy1 to proxyN can be any HTTP/HTTPS/HTTP2/SOCKS4/SOCKS5/Shadowsocks type.
Contributed by @sheerun.
One can pass available permissions with whitelist and blacklist values when starting a socks and ssh server. The format for each rule is as follows: [actions]:[hosts]:[ports].
[actions] are comma-separted list of allowed actions: rtcp, rudp, tcp, udp. can be * to encompass all actions.
[hosts] are comma-separated list of allowed hosts that one can bind on (in case of rtcp and rudp), or forward to (incase of tcp and udp). hosts support globs, like *.google.com. can be * to encompass all hosts.
[ports] are comma-separated list of ports that one can bind to (in case of rtcp and rudp), or forward to (incase of tcp and udp), can be * to encompass all ports.
Multiple permissions can be passed if seperated with +:
rtcp,rudp:localhost,127.0.0.1:2222,8000-9000+udp:8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4:53 (allow for reverse tcp and udp binding on localhost and 127.0.0.1 on ports 2222 and 8000-9000 port range, plus allow for udp forwarding to 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 on port 53)
SSH remote port forwarding can only bind on 127.0.0.1:8000
gost -L=forward+ssh://localhost:8389?whitelist=rtcp:127.0.0.1:8000SOCKS5 TCP/UDP remote port forwarding can only bind on ports greater than 1000
gost -L=socks://localhost:8389?blacklist=rtcp,rudp:*:0-1000SOCKS5 UDP forwading can only forward to 8.8.8.8:53
gost -L=socks://localhost:8389?whitelist=udp:8.8.8.8:53The HTTP proxy node in the proxy chain must support the CONNECT method.
If the BIND and UDP requests for SOCKS5 are to be forwarded, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be the gost SOCKS5 proxy.