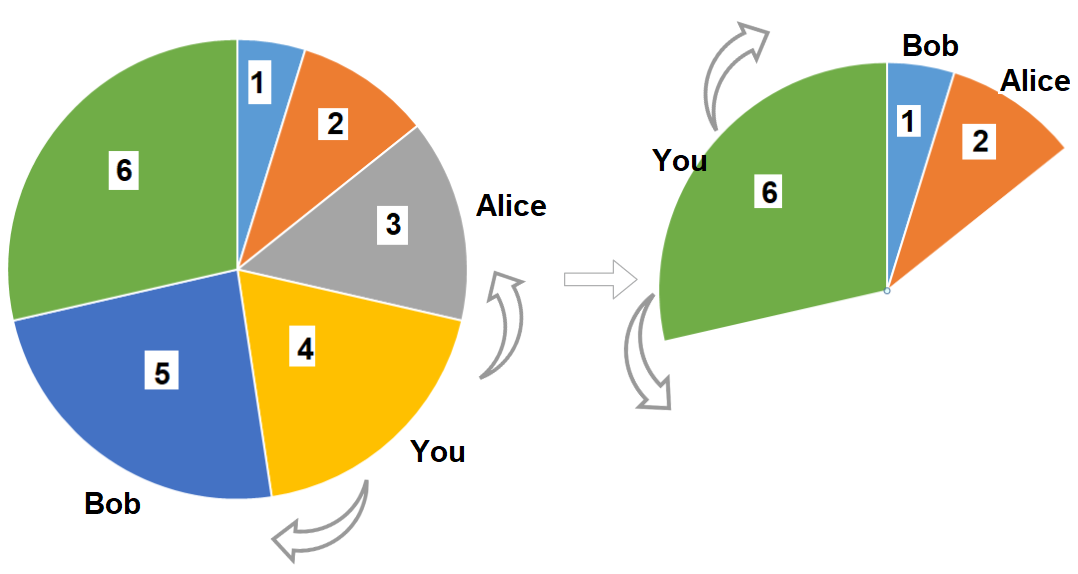
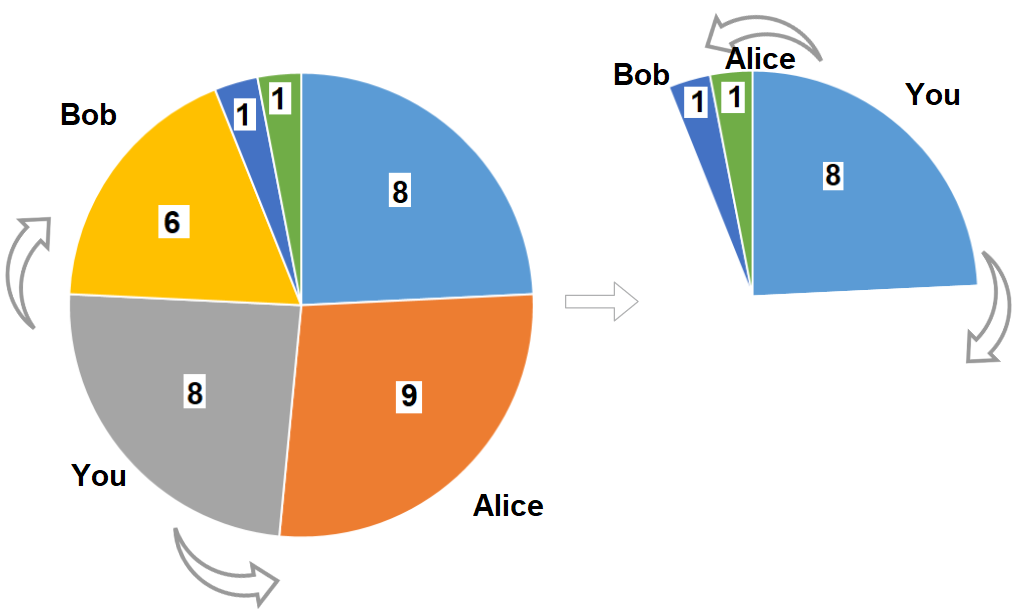
There is a pizza with 3n slices of varying size, you and your friends will take slices of pizza as follows:
- You will pick any pizza slice.
- Your friend Alice will pick the next slice in the anti-clockwise direction of your pick.
- Your friend Bob will pick the next slice in the clockwise direction of your pick.
- Repeat until there are no more slices of pizzas.
Given an integer array slices that represent the sizes of the pizza slices in a clockwise direction, return the maximum possible sum of slice sizes that you can pick.
Example 1:
Input: slices = [1,2,3,4,5,6] Output: 10 Explanation: Pick pizza slice of size 4, Alice and Bob will pick slices with size 3 and 5 respectively. Then Pick slices with size 6, finally Alice and Bob will pick slice of size 2 and 1 respectively. Total = 4 + 6.
Example 2:
Input: slices = [8,9,8,6,1,1] Output: 16 Explanation: Pick pizza slice of size 8 in each turn. If you pick slice with size 9 your partners will pick slices of size 8.
Constraints:
3 * n == slices.length1 <= slices.length <= 5001 <= slices[i] <= 1000
class Solution:
def maxSizeSlices(self, slices: List[int]) -> int:
def g(nums: List[int]) -> int:
m = len(nums)
f = [[0] * (n + 1) for _ in range(m + 1)]
for i in range(1, m + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], (f[i - 2][j - 1]
if i >= 2 else 0) + nums[i - 1])
return f[m][n]
n = len(slices) // 3
a, b = g(slices[:-1]), g(slices[1:])
return max(a, b)class Solution {
private int n;
public int maxSizeSlices(int[] slices) {
n = slices.length / 3;
int[] nums = new int[slices.length - 1];
System.arraycopy(slices, 1, nums, 0, nums.length);
int a = g(nums);
System.arraycopy(slices, 0, nums, 0, nums.length);
int b = g(nums);
return Math.max(a, b);
}
private int g(int[] nums) {
int m = nums.length;
int[][] f = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i - 1][j], (i >= 2 ? f[i - 2][j - 1] : 0) + nums[i - 1]);
}
}
return f[m][n];
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maxSizeSlices(vector<int>& slices) {
int n = slices.size() / 3;
auto g = [&](vector<int>& nums) -> int {
int m = nums.size();
int f[m + 1][n + 1];
memset(f, 0, sizeof f);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], (i >= 2 ? f[i - 2][j - 1] : 0) + nums[i - 1]);
}
}
return f[m][n];
};
vector<int> nums(slices.begin(), slices.end() - 1);
int a = g(nums);
nums = vector<int>(slices.begin() + 1, slices.end());
int b = g(nums);
return max(a, b);
}
};func maxSizeSlices(slices []int) int {
n := len(slices) / 3
g := func(nums []int) int {
m := len(nums)
f := make([][]int, m+1)
for i := range f {
f[i] = make([]int, n+1)
}
for i := 1; i <= m; i++ {
for j := 1; j <= n; j++ {
f[i][j] = max(f[i-1][j], nums[i-1])
if i >= 2 {
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i-2][j-1]+nums[i-1])
}
}
}
return f[m][n]
}
a, b := g(slices[:len(slices)-1]), g(slices[1:])
return max(a, b)
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}function maxSizeSlices(slices: number[]): number {
const n = Math.floor(slices.length / 3);
const g = (nums: number[]): number => {
const m = nums.length;
const f: number[][] = Array(m + 1)
.fill(0)
.map(() => Array(n + 1).fill(0));
for (let i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (let j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
f[i][j] = Math.max(
f[i - 1][j],
(i > 1 ? f[i - 2][j - 1] : 0) + nums[i - 1],
);
}
}
return f[m][n];
};
const a = g(slices.slice(0, -1));
const b = g(slices.slice(1));
return Math.max(a, b);
}