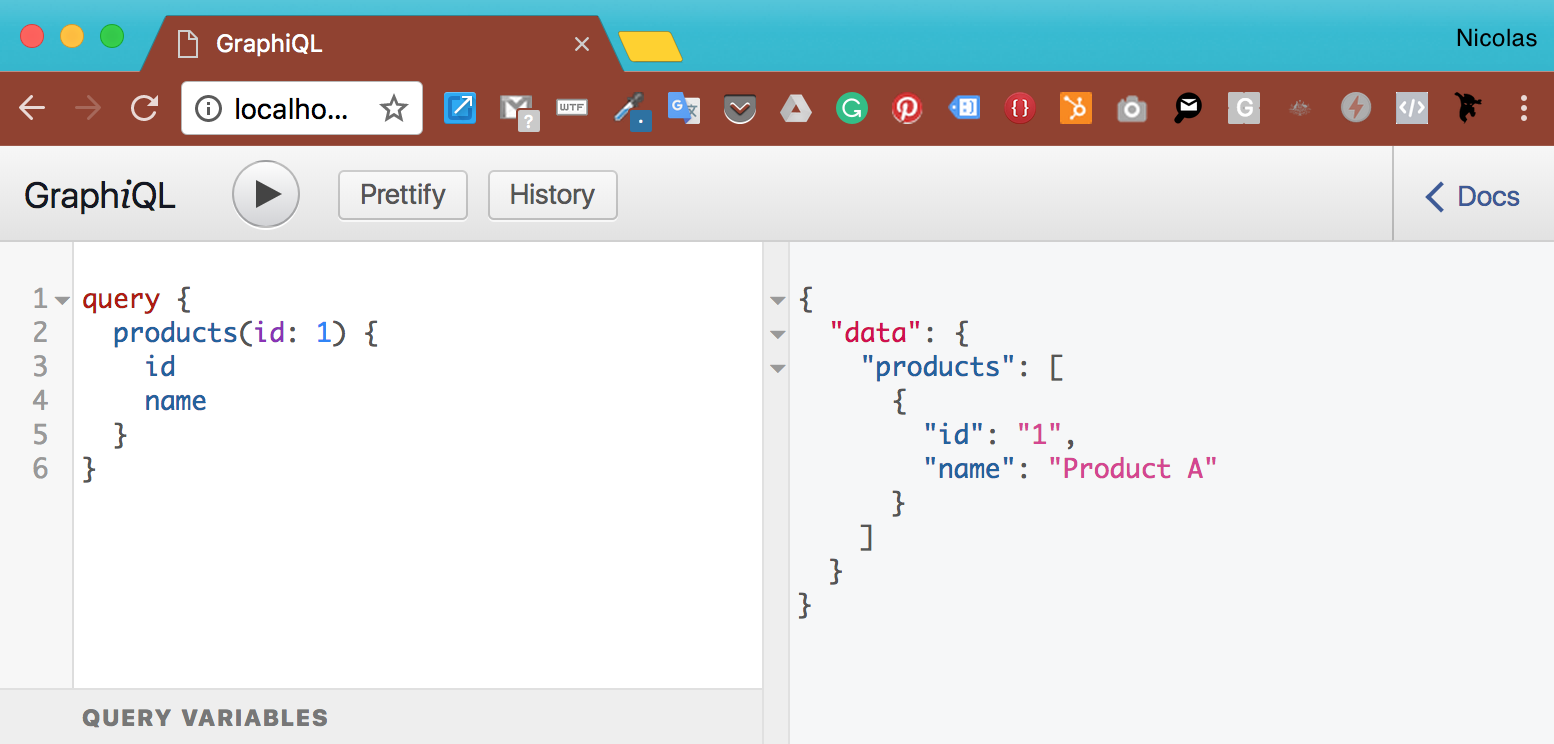
graphql-serverless is a middleware for webfunc, that allows to deploy GraphQL apis (including an optional GraphiQL interface) to the most popular serverless platforms. GraphQl Subscriptions over websocket are also supported out-of-the-box (also supported in GraphiQL). Without changing a single line of code, seamlessly deploy to:
- Zeit Now (using express under the hood)
- Google Cloud Functions (incl. Firebase Function)
- AWS Lambdas
- Azure Functions (COMING SOON...)
Copy/paste the following in your terminal if you want to run your first GraphQL api (http://localhost:4000) including a GraphiQL interface (http://localhost:4000/graphiql) on your local machine in less than 30 seconds:
git clone https://github.com/nicolasdao/graphql-universal-server.git
cd graphql-universal-server
npm install
npm start
This will serve 2 endpoints:
- http://localhost:4000: This is the GraphQL endpoint that your client can start querying.
- http://localhost:4000/graphiql: This is the GraphiQL Web UI that you can use to test and query your GraphQL server.
Deploying that api to Zeit Now will take between 15 seconds to 1.5 minute (depending on whether you need to login/creating a free Zeit account or not).
If you haven't installed Zeit now-CLI yet or you need to login/create an account, then copy/paste this in your terminal:
npm install now -g
now login
npm run deploy:prod
The above will work the exact same way whether you have an account or not. This is free, so don't worry about it.
If you're already logged in, then simply run this:
npm run deploy:prod
npm install webfunc graphql-serverless --save
Using the template above (i.e. graphql-universal-server) is the easiest way to start a new GraphQL project from scratch.
However, if you really want to start on a blank page:
- Create a new npm project:
npm init - Install the following:
npm install graphql-serverless webfunc --save - Create an index.js as follow:
const { graphqlHandler, graphqlError } = require('graphql-serverless')
const { makeExecutableSchema } = require('graphql-tools') // this dependency is automatically included in 'graphql-serverless'
const { app } = require('webfunc')
// STEP 1. Mock some data for this demo.
const productMocks = [
{ id: 1, name: 'Product A', shortDescription: 'First product.' },
{ id: 2, name: 'Product B', shortDescription: 'Second product.' }]
// STEP 2. Creating a basic GraphQl Schema.
const schema = `
type Product {
id: ID!
name: String!
shortDescription: String
}
type Query {
products(id: Int): [Product]
}
schema {
query: Query
}`
const productResolver = {
Query: {
products(root, { id }, context) {
const results = id ? productMocks.filter(p => p.id == id) : productMocks
if (results.length > 0)
return results
else
throw graphqlError(404, `Product with id ${id} does not exist.`)
}
}
}
const executableSchema = makeExecutableSchema({
typeDefs: schema,
resolvers: productResolver
})
// STEP 3. Creating a GraphQL and a GraphiQl endpoint
const graphqlOptions = {
schema: executableSchema,
graphiql: { // If you do not want to host any GraphiQl web interface, leave this property undefined.
endpoint: '/graphiql'
},
context: {
someVar: 'This variable is passed in the "context" object in each resolver.'
}
}
// Host a GraphQl API on 2 endpoints: '/' and '/graphiql'. '/graphiql' is used to host the GraphiQL web interface.
// If you're not interested in the GraphiQl web interface, leave the above 'graphqlOptions.graphiql' undefined and
// replace the path following ['/', '/graphiql'] with '/'.
app.all(['/', '/graphiql'], graphqlHandler(graphqlOptions))
// STEP 4. Starting the server
eval(app.listen('app', 4000))- Then simply run:
node index.js
This will serve 2 endpoints:
- http://localhost:4000: This is the GraphQL endpoint that your client can start querying.
- http://localhost:4000/graphiql: This is the GraphiQL Web UI that you can use to test and query your GraphQL server.
If you need best practices on how to structure your GraphQL project, clone the graphql-universal-server project and see by yourself.
WARNING: This feature is only available on Zeit Now serverless or on localhost. Even though graphql-serverless relies on webfunc to deploy on FaaS solutions like AWS Lambdas or Google Functions, because those hosting platforms do not natively support websocket, GraphQl Subscriptions can't be deployed there.
graphql-serverless exposes a helper method setupSubscriptions that can host a websocket endpoint for GraphQl Subscriptions. In the following example, we will slightly modify the code above to:
- (MODIFICATION A) Configure a new websocket endpoint for all subscriptions.
- (MODIFICATION B) Add a PubSub queue so that publisher can publish messages onto topics and subscribers can listen to certain topics so that clients using websocket can receive updates.
- (MODIFICATION C) Add a new GraphQl Mutation to insert a new product. This insert will act as a publisher. It will add a message to the PubSub topic once the product has been successfully inserted.
- (MODIFICATION D) Add a new GraphQl Subscription that listen to a specific topic on the PubSub queue and uses websocket to inform the client that a new product has been inserted.
Install graphql-subscriptions:
npm install graphql-subscriptions --save
Update the previous index.js as follow:
// MODIFICATION A - Import the 'setupSubscriptions' helper
const { graphqlHandler, graphqlError, setupSubscriptions } = require('graphql-serverless')
...
// MODIFICATION B - Create a simple local pub/sub (not scalable option, but good enough for a demo)
const { PubSub } = require('graphql-subscriptions')
const pubsub = new PubSub()
...
// MODIFICATION C/D - Add an 'insert product' MUTATION and a 'product inserted' SUBSCRIPTION in the GraphQl schema
const schema = `
input NewProductInput {
name: String!
shortDescription: String
}
type Mutation {
productInsert(product: NewProductInput!): Product
}
type Subscription {
productInserted: Product
}
schema {
query: Query
mutation: Mutation
subscription: Subscription
}`
...
// MODIFICATION C/D - Add an 'insert product' MUTATION and a 'product inserted' SUBSCRIPTION in the GraphQl product resolver
const productResolver = {
Query: {...},
Mutation: {
productInsert(root, { product }, context) {
if (!product || !product.name)
throw context.graphqlError('Missing required argument \'product.name\'.')
const newId = productMocks.sort((a,b) => a.id < b.id)[0].id + 1
const newProduct = Object.assign({ id: newId }, product)
productMocks.push(newProduct)
pubsub.publish('productInserted', { productInserted: newProduct })
return newProduct
}
},
Subscription: {
productInserted: {
subscribe: () => pubsub.asyncIterator('productInserted')
}
}
}
...
// MODIFICATION A - Define the location of the subscriptions endpoint
const graphqlOptions = {
schema: executableSchema,
graphiql: {
endpoint: '/graphiql'
},
subscriptionsEndpoint: '/subscriptions' // this means that the subscription endpoint is 'ws://localhost:4000/subscriptions' if you're deploying locally
}
...
// MODIFICATION A - Start the websocket endpoint after the server as started.
// WARNING: This only works for localhost, serverless Zeit Now, but not
// for FaaS like AWS Lambdas, Google Functions, ...
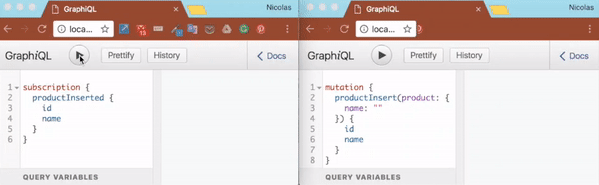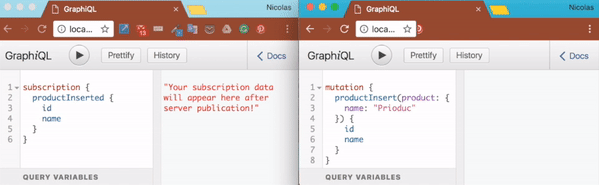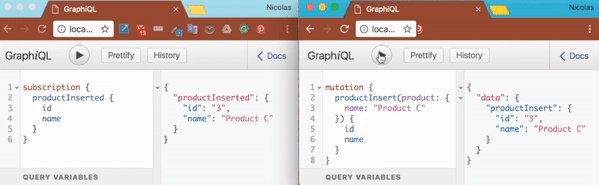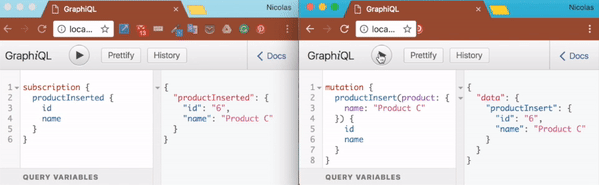
eval(app.listen('app', 4000, () => setupSubscriptions(app.server, graphqlOptions)))Execute node index.js and then browse to http://localhost:4000/graphiql. Start a subscription as follow:
subscription {
productInserted {
id
name
}
}At that point, the client is simply listening to any new messages on the 'productInserted' topic. Time to publish a new messages on that topic. Open a new tab and browse again to http://localhost:4000/graphiql. There insert a new product as follow:
mutation {
productInsert(product: {
name: "Product C"
}) {
id
name
}
}Once the product has been inserted, you should be able to observe that your subscription client has noticed it.
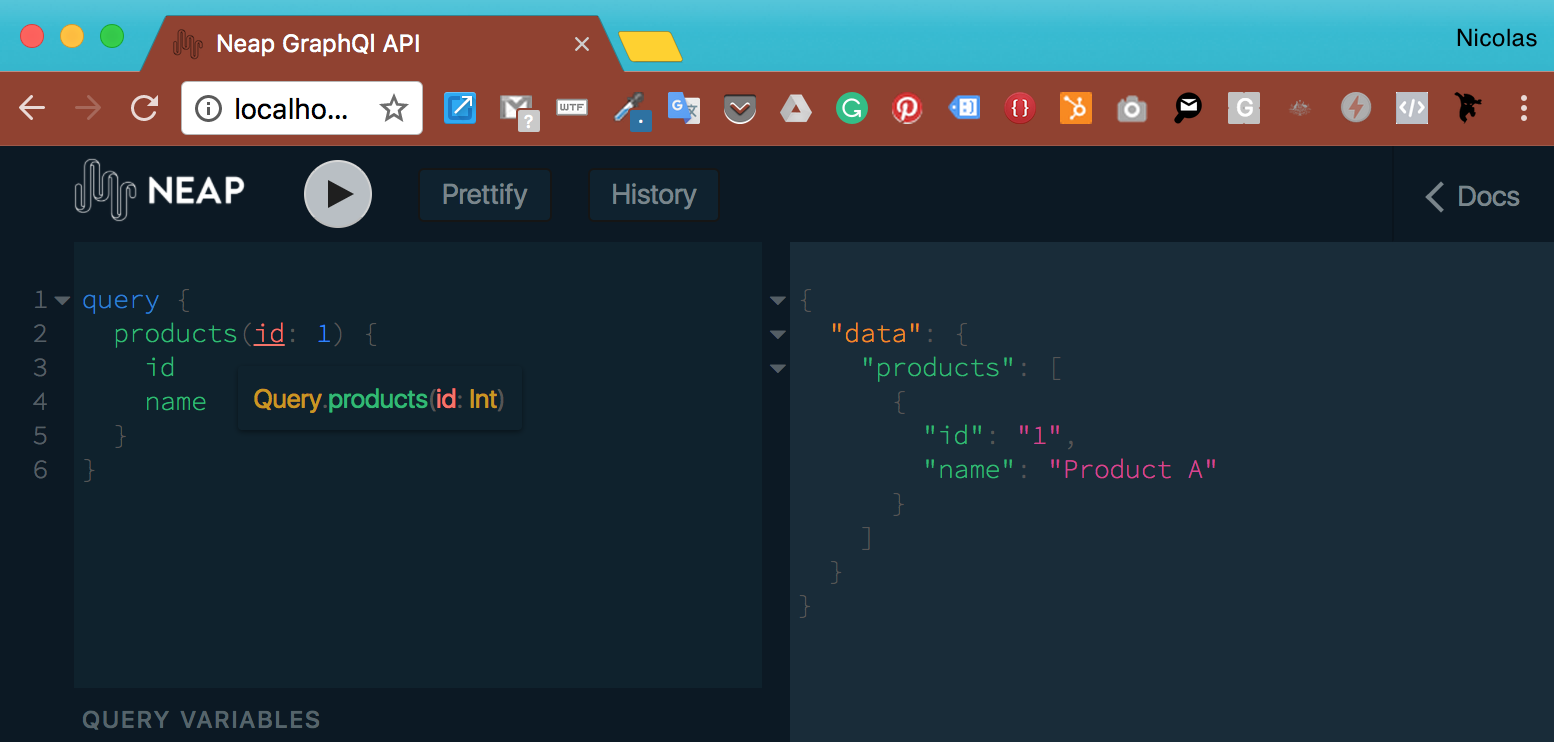
The code sample in the Basics section uses the default GraphiQl settings:
By updating the graphqlOptions in the Basics section example as follow:
const graphqlOptions = {
schema: executableSchema,
graphiql: {
endpoint: '/graphiql',
head: {
title: 'Neap GraphQl API',
// Adding a custom Favicon
custom: '<link rel="shortcut icon" href="https://neap.co/favicon.ico">',
// Change the default 'light' theme to a dark one.
theme: 'dark',
// Replace the default 'GraphiQl' logo to your own
logo: '<div class="title"><img src="https://neap.co/img/neap_white_small_logo.png" style="width: 88px;z-index: 7;padding-left: 24px;"></div>'
},
// Adding a custom JS script
script: () => {
function getCookie(cname) {
var name = cname + '='
var decodedCookie = decodeURIComponent(document.cookie)
var ca = decodedCookie.split(';')
for(var i = 0; i <ca.length; i++) {
var c = ca[i]
while (c.charAt(0) == ' ')
c = c.substring(1)
if (c.indexOf(name) == 0)
return c.substring(name.length, c.length)
}
return ''
}
},
// Executing a custom JS function each time a GraphQL request is made
onRequest: headers => {
var token = getCookie('neap_cookie')
if (token)
headers.Authorization = 'bearer ' + token
}
}
}We can update the GraphiQL interface as follow:
The differences are:
- Custom page name
- Custom favicon
- Changing from the default 'light' theme to a dark one
- Custom logo
- Custom javascript
- Custom function running each time a GraphQl request is made. In our case, we're updating the HTTP headers to add a bearer token stored in a 'neap_cookie' cookie.
To use a custom CSS rather than relying on the 'light' or 'dark' theme, you can use the css property:
const graphqlOptions = {
schema: executableSchema,
graphiql: {
endpoint: '/graphiql',
head: {
// Adding a dark theme
css: [
'https://neap.co/resources/css/graphiql/0.0.1/dark_style.css',
'https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Open+Sans:300,400,600,700|Source+Code+Pro:200,400,700']
}
}
}WARNING: Using the
cssproperty will override completely any other out-of-the-box css.
By default, any uncaught errors are marshalled to the graphql response similar to this:
{
"errors": [
{
"message": "Product with id 20 does not exist.",
"locations": [
{
"line": 2,
"column": 3
}
],
"path": [
"products"
]
}
],
"data": {
"products": null
}
}This type of uncaught error also yield a 500 HTTP code. A piece of code that could produce the error above could be:
const productResolver = {
Query: {
products(root, { id }, context) {
const results = id ? productMocks.filter(p => p.id == id) : productMocks
if (results.length > 0)
return results
else
throw new Error(`Product with id ${id} does not exist.`)
}
}
}However, there are situation where you may want to control the error being returned in one of the following ways:
- Controlling the HTTP code based on the type of error.
- Hide the details of the error (e.g. the full stack trace) in certain conditions (e.g. production environment).
This can be achieved thanks to the graphqlError helper method.
const { graphqlHandler, graphqlError } = require('graphql-serverless')
const productResolver = {
Query: {
products(root, { id }, context) {
const results = id ? productMocks.filter(p => p.id == id) : productMocks
if (results.length > 0)
return results
else
throw graphqlError({ code: 404, text: `Product with id ${id} does not exist.` })
}
}
}In case of errors, the response will look like this:
{
"errors": [
{
"message": "Product with id 123 does not exist."
}
],
"data": {
"products": null
}
}The graphqlError function also supports serializing errors:
throw graphqlError({ code: 422, errors:[error] })The output in case of errors is similar to:
{
"errors": [
{
"message": "Some error message",
"locations": [
{
"line": 382,
"col": 17,
"method": "wrapErrors",
"path": "/Users/nicolasdao/Documents/myproject/src/services/_utils.js"
},
{
"line": 65,
"col": 19,
"method": "onFulfilled",
"path": "/Users/nicolasdao/Documents/myproject/src/services/core/node_modules/co/index.js"
}
]
}
],
"data": {
"products": null
}
}If the stack information in the locations field are sensitive, they can be turned off as follow:
throw graphqlError({ code: 422, errors:[error], noStack:true })graphqlError('Oops, the product does not exist.')
Returns a GraphQL error response with the above error message and a HTTP 500.
graphqlError('Oops, the product does not exist.', { alternateMessage: 'Internal Server Error', hide: true })
Returns a GraphQL error response with error message 'Internal Server Error' (if the hide property is set to true) and a HTTP 500.
graphqlError(404, 'Oops, the product does not exist.')
Returns a GraphQL error response with the above error message and a HTTP 404.
graphqlError(404, 'Oops, the product does not exist.', { alternateMessage: 'Internal Server Error', hide: true })
Returns a GraphQL error response with error message 'Internal Server Error' (if the hide property is set to true) and a HTTP 404.
This section is broken down in 3 parts:
At the end, graphql-serverless is simply another Express-like middleware, and as such, we've added the ability to react differently based on other middleware that may have manipulated the request object previously. Those early middleware can affect the behavior of graphql-serverless thanks to the graphql property of the request object.
Let's take the index.js code from the previous Basics section and add this to it:
// index.js
const customMiddleware = (req, res, next) => {
req.graphql = {
query: `query { products(id:1){ id name shortDescription } }`
}
next()
}
// app.all(['/', '/graphiql'], graphqlHandler(graphqlOptions))
app.all(['/', '/graphiql'], customMiddleware, graphqlHandler(graphqlOptions))
// STEP 4. Starting the server
eval(app.listen('app', 4000))Start your server with node index.js
Browse to http://localhost:4000/graphiql
Execute the following GraphQl query:
query{
products(id:2){
id
name
}
}Normally, you would expect teh following response based on the logic of the code demoed in the Basics section:
{
"data": {
"products": [
{
"id": "2",
"name": "Product B"
}
]
}
}But instead, you will receive:
{
"data": {
"products": [
{
"id": "1",
"name": "Product A",
"shortDescription": "First product."
}
]
}
}As you can see, the customMiddleware we created has allowed us to spoof the original query and replace it with query { products(id:1){ id name shortDescription } }.
This ability is one of the key feature allowing a middleware like graphql-authorize which can remove certain fields from the response based on the user's rights.
Another usefull capability is the modification of any GraphQl response. Let's modify the customMiddleware function we defined previously:
const customMiddleware = (req, res, next) => {
req.graphql = {
// query: `query { products(id:1){ id name shortDescription } }`
transform: graphQlresponse => Object.assign({ magicProperty: { message: 'Magic', creator: 'Nicolas Dao' } }, graphQlresponse)
}
next()
}Executing the previous GraphQl query will yield the following response:
{
"magicProperty": {
"message": "Magic",
"creator": "Nicolas Dao"
},
"data": {
"products": [
{
"id": "2",
"name": "Product B"
}
]
}
}Two other properties that are very usefull allow to add warning or error messages:
const customMiddleware = (req, res, next) => {
req.graphql = {
// query: `query { products(id:1){ id name shortDescription } }`
transform: graphQlresponse => Object.assign({ magicProperty: { message: 'Magic', creator: 'Nicolas Dao' } }, graphQlresponse),
warnings: [{ message: 'Hello, I am a warning.' }],
errors: [{ message: 'Hello, I am an error.' }]
}
next()
}Executing the previous GraphQl query will yield the following response:
{
"magicProperty": {
"message": "Magic",
"creator": "Nicolas Dao"
},
"data": {
"products": [
{
"id": "2",
"name": "Product B"
}
]
},
"errors": [
{
"message": "Hello, I am an error."
}
],
"warnings": [
{
"message": "Hello, I am a warning."
}
]
}| Properties | type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| query | String | Valid GraphQl query. |
| variables | Object | Valid GraphQl variable object. |
| operationName | String | GraphQl query operation. |
| transform | Function | Function accepting a single argument representing the original GraphQl object. This function can affect that result by either mutating it, or returning a new object. |
| warnings | Array | Array of objects representing a warning. The conventional structure is as follow: { message:String, location: String, path:String } |
| errors | Array | Array of objects representing an error. The conventional structure is as follow: { message:String, location: String, path:String } |
npm test
We are Neap, an Australian Technology consultancy powering the startup ecosystem in Sydney. We simply love building Tech and also meeting new people, so don't hesitate to connect with us at https://neap.co.
Our other open-sourced projects:
- webfunc: Write code for serverless similar to Express once, deploy everywhere.
- now-flow: Automate your Zeit Now Deployments.
- graphql-serverless: GraphQL (incl. a GraphiQL interface) middleware for webfunc.
- schemaglue: Naturally breaks down your monolithic graphql schema into bits and pieces and then glue them back together.
- graphql-s2s: Add GraphQL Schema support for type inheritance, generic typing, metadata decoration. Transpile the enriched GraphQL string schema into the standard string schema understood by graphql.js and the Apollo server client.
- graphql-authorize: Authorization middleware for graphql-serverless. Add inline authorization straight into your GraphQl schema to restrict access to certain fields based on your user's rights.
- react-native-game-engine: A lightweight game engine for react native.
- react-native-game-engine-handbook: A React Native app showcasing some examples using react-native-game-engine.
- aws-cloudwatch-logger: Promise based logger for AWS CloudWatch LogStream.
Copyright (c) 2018, Neap Pty Ltd. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
- Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
- Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
- Neither the name of Neap Pty Ltd nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL NEAP PTY LTD BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.