The JDT is an ORM implementation of the current Thing Description model standardised by the W3C Web of Things group. The current features are:
- Serialise:
- Serialise any Thing Description as a Java Object, i.e., a JDT
- Serialise a JDT from a JSON-LD framed document
- Serialise a JDT from a set of RDF triples
- Round trip-translation:
- Translate from a JSON-LD framed document into a set of equivalent RDF triples
- Translate a set of RDF triples into its equivalent JSON-LD framed document
- Validation
- Validate a JTD using SHACL shapes
- Validate a JTD using JSON schema (coming soon)
- Validate a JTD according to the restrictions specified in the standard (coming soon)
If you have any feedback or feature suggestion, please let us know posting an issue with the label feedback
- Installation
- Model
- Usage:
- Serialisation of JTDs:
- From JSON-LD framed document
- From RDF triples
- Deserialisation of JTDs:
- To JSON-LD framed
- To RDF triples
- JDT validation:
- Using SHACL shapes
- Using JSON schema (coming soon)
- Using restrictions in the model (coming soon)
- Serialisation of JTDs:
Import the JDTs library as a maven dependency, be sure to specify the latest version:
<dependency>
<groupId>es.upm.fi.oeg</groupId>
<artifactId>wot-jtd</artifactId>
<version>0.2.2</version>
</dependency>
Alternatively, the dependency can be installed manually. First, download the latest jar from the releases section, and then install the dependency as follows (be sure to specify the latest version):
mvn install:install-file -Dfile=wot-jtd.jar -DgroupId=es.upm.fi.oeg -DartifactId=wot-jtd -Dversion=0.2.2 -Dpackaging=jar
Check our Maven Central Repository page to discover other installation options like Gradle Groovy or Kotlin, Scala, and others.
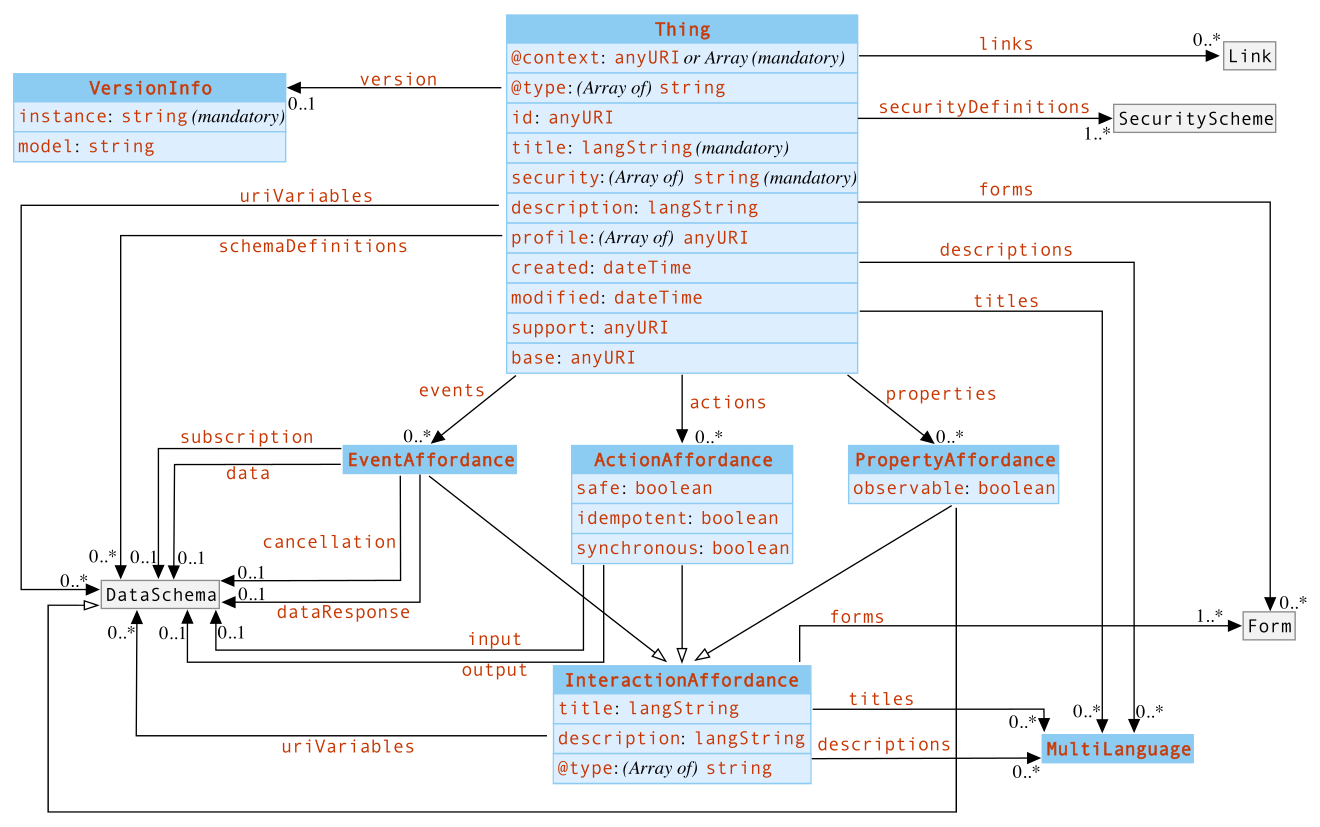
The JDT library implement as Java objects the whole model, and its restrictions, defined in the Thing Description standard. The overview of the model is the following:
For the next examples, let's assume the following java variables containing the same Thing description:
String strJsonTD = "{ \"@context\": \"https://www.w3.org/2019/wot/td/v1\",\n" +
" \"id\": \"urn:dev:ops:32473-WoTLamp-1234\",\n" +
" \"title\": \"MyLampThing\",\n" +
" \"securityDefinitions\": { \"nosec_sc\": { \"scheme\": \"nosec\" }},\n" +
" \"security\": \"nosec_sc\",\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"status\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"string\",\n" +
" \"forms\": [{\"href\": \"https://mylamp.example.com/status\"}]\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
Model modelTD = ModelFactory.createDefaultModel();
String strRdfTD = "@prefix dc: <http://purl.org/dc/terms/> .\n" +
"@prefix td: <https://www.w3.org/2019/wot/td#> .\n" +
"@prefix jsonschema: <https://www.w3.org/2019/wot/json-schema#> .\n" +
"@prefix hctl: <https://www.w3.org/2019/wot/hypermedia#> .\n" +
"\n" +
"<urn:dev:ops:32473-WoTLamp-1234>\n" +
" dc:title \"MyLampThing\" ;\n" +
" td:hasPropertyAffordance [\n" +
" a <https://www.w3.org/2019/wot/json-schema#StringSchema> ;\n" +
" jsonschema:propertyName \"status\" ;\n" +
" td:hasForm [ hctl:hasTarget <https://mylamp.example.com/status> ]\n" +
" ] ;\n" +
" td:hasSecurityConfiguration <https://json-ld.org/playground/nosec_sc> ;\n" +
" td:securityDefinitions [ td:scheme \"nosec\" ] .";
##### Read the string variable into the jena model
modelTD.read(new ByteArrayInputStream(strRdfTD.getBytes()), null, "Turtle");
The following serialisation operations consists of building a JTD object Thing from either a JSON-LD framed representation or a set of RDF triples.
JsonObject jsonTD = JTD.parseJson(strJsonTD);
Thing thing = Thing.fromJson(jsonTD);
thing = (Thing) JTD.instantiateFromJson(jsonTD, Thing.class); # Alternativelly
Notice that using the method JTD.instantiateFromJson(jsonTD, Thing.class) any other class from the model can be serialised.
In order to build a JTD object from a set of RDF triples there are two main methods:
List<Thing> things = fromRDF(modelTD)
Thing thing = fromRDF(modelTD, "urn:dev:ops:32473-WoTLamp-1234")
JsonObject jsonTD = thing.toJson()
jsonTD = JTD.toJson(thing) # Alternativelly
Notice that using the method JTD.toJson(thing) any other class from the model can be deserialised.
Model modelTD = JTD.toRDF(thing)
# Alternativelly
JsonObject jsonTD = thing.toJson()
modelTD = JTD.toRDF(jsonTD)
Notice that using the method alternative JTD.toRDF(jsonTD) there is actually no need to serialise the JSON-LD framed jsonTD as a Java object, it can be directly translated into RDF.
Currently, the Web of Things provides an official SHACL shape document for validating Thing Descriptions. This shape, or any other, can be used to validate a JTD Thing as follows:
String shapesURI = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/w3c/wot-thing-description/main/validation/td-validation.ttl"
Model shapesGraph = RDFDataMgr.loadModel(shapesURI, Lang.TURTLE);
ValidationReport shapeReport = JTD.validateWithShape(thing, shapesGraph);
WoT-JTD was created by Andrea Cimmino (cimmino@fi.upm.es) and Raúl García Castro (rgarcia@fi.upm.es) at the Universidad Politécnica de Madrid in the research group Ontology Engineering Group.