Raphael Gottardo
January 14, 2014
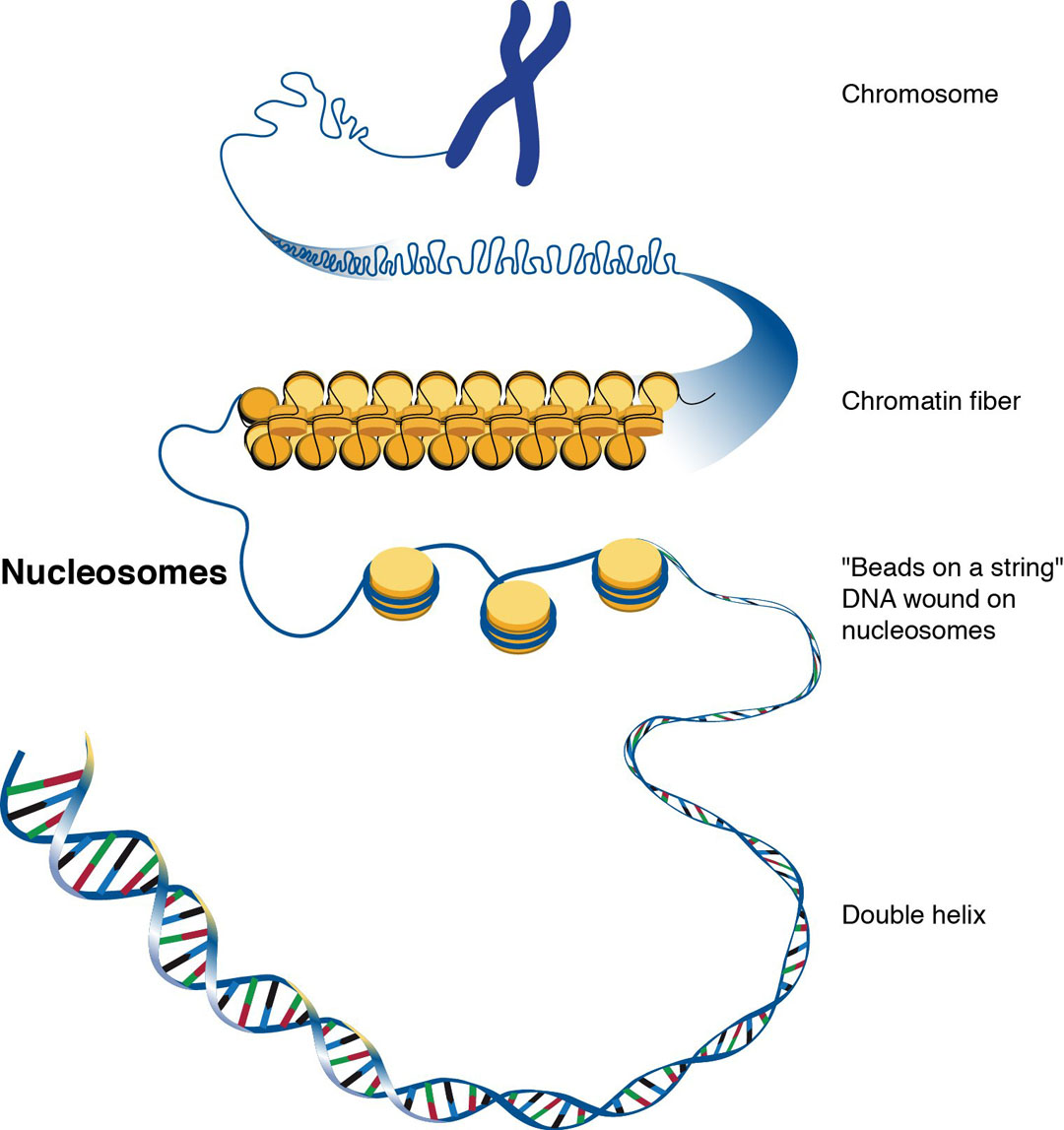
- Cells and genomes
- DNA, RNA, proteins
- Central dogma of molecular biology
- A T-cell
(Source: Wikipedia)
- A Neuron
(Source: thetechjournal.com)
-
DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) contains the genetic instructions (A, G, C,T).
-
Double stranded (complementary) G-C, A-T
- RNA (Ribonucleic acid) ressembles DNA
- Single stranded, much shorter than DNA
- Four bases A, C, G and U.
(Source: Wikipedia)
- Organic compounds (amino acids joined by peptide bonds)
- Essential to the structure and function of all living cells and viruses
- 20 possible amino acids (Lysine, Leucine, etc.)
- Folding → Function
- How do they interact?
- How do we get from DNA to proteins?
(Source: http://darwinview.blogspot.com/)
- Certain pieces (genes) are transcribed
- Gene ≈ piece of DNA coding for a protein
- Gene → Protein (Gene is expressed)
- DNA → RNA → Proteins
- Can measure proteins directly but measuring
- mRNA levels is easier
- mRNA levels (gene expression levels) tell us something about proteins
- How do we measure gene expression levels? Microarrays → Gene expression and more!
- Understanding gene regulation requires a lot more than just gene expression: Chromatin, miRNA, alternative splicing, methylation, etc.