Before we move on with other tasks it is necessary to install Nginx Ingress. It's also handy to install cert-manager for managing SSL certificates.
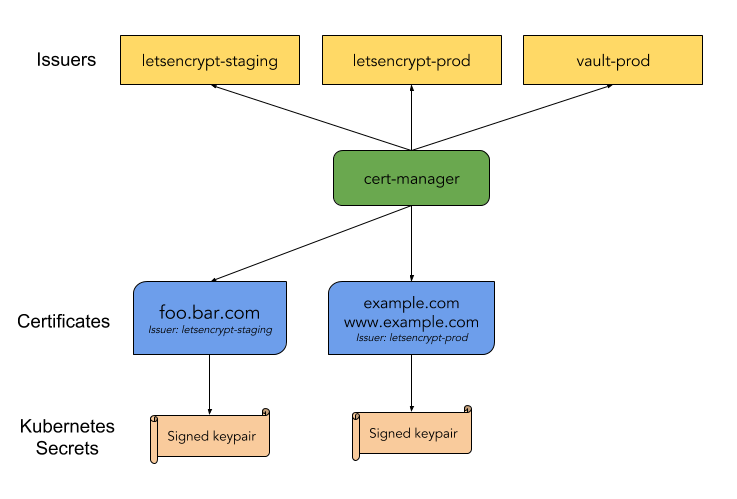
cert-manager architecture:
Install the CRDs resources separately:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jetstack/cert-manager/release-0.10/deploy/manifests/00-crds.yamlOutput:
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/certificates.certmanager.k8s.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/challenges.certmanager.k8s.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/clusterissuers.certmanager.k8s.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/issuers.certmanager.k8s.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/orders.certmanager.k8s.io created
Create the namespace for cert-manager and label it to disable resource validation:
kubectl create namespace cert-manager
kubectl label namespace cert-manager certmanager.k8s.io/disable-validation=trueOutput:
namespace/cert-manager created
namespace/cert-manager labeled
Install the cert-manager Helm chart:
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm install --name cert-manager --namespace cert-manager --wait jetstack/cert-manager --version v0.10.0Output:
"jetstack" has been added to your repositories
NAME: cert-manager
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jul 19 11:47:58 2019
NAMESPACE: cert-manager
STATUS: DEPLOYED
RESOURCES:
==> v1/ClusterRole
NAME AGE
cert-manager-edit 10s
cert-manager-view 10s
==> v1/Pod(related)
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cert-manager-578fc6ff6-qjvrr 1/1 Running 0 10s
cert-manager-cainjector-5975fd64c5-82c8x 1/1 Running 0 10s
==> v1/ServiceAccount
NAME SECRETS AGE
cert-manager 1 10s
cert-manager-cainjector 1 10s
==> v1beta1/ClusterRole
NAME AGE
cert-manager 10s
cert-manager-cainjector 10s
==> v1beta1/ClusterRoleBinding
NAME AGE
cert-manager 10s
cert-manager-cainjector 10s
==> v1beta1/Deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
cert-manager 1/1 1 1 10s
cert-manager-cainjector 1/1 1 1 10s
NOTES:
cert-manager has been deployed successfully!
In order to begin issuing certificates, you will need to set up a ClusterIssuer
or Issuer resource (for example, by creating a 'letsencrypt-staging' issuer).
More information on the different types of issuers and how to configure them
can be found in our documentation:
https://docs.cert-manager.io/en/latest/reference/issuers.html
For information on how to configure cert-manager to automatically provision
Certificates for Ingress resources, take a look at the `ingress-shim`
documentation:
https://docs.cert-manager.io/en/latest/reference/ingress-shim.html
Create ClusterIssuer for Route53 used by cert-manager. It will allow Let's
Encrypt to generate certificate. Route53 (DNS) method of requesting certificate
from Let's Encrypt must be used to create wildcard certificate *.mylabs.dev
(details here).
(https://b3n.org/intranet-ssl-certificates-using-lets-encrypt-dns-01/)
export EKS_CERT_MANAGER_ROUTE53_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY_BASE64=$(echo -n "$EKS_CERT_MANAGER_ROUTE53_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY" | base64)
envsubst < files/cert-manager-letsencrypt-aws-route53-clusterissuer.yaml | kubectl apply -f -
cat files/cert-manager-letsencrypt-aws-route53-clusterissuer.yamlOutput:
secret/aws-route53-secret-access-key-secret created
clusterissuer.certmanager.k8s.io/selfsigning-issuer created
clusterissuer.certmanager.k8s.io/letsencrypt-staging-dns created
clusterissuer.certmanager.k8s.io/letsencrypt-production-dns created
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: aws-route53-secret-access-key-secret
namespace: cert-manager
data:
secret-access-key: $EKS_CERT_MANAGER_ROUTE53_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY_BASE64
---
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: selfsigning-issuer
spec:
selfSigned: {}
---
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
acme:
# The ACME server URL
server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
# Email address used for ACME registration
email: petr.ruzicka@gmail.com
# Name of a secret used to store the ACME account private key
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
dns01:
# Here we define a list of DNS-01 providers that can solve DNS challenges
providers:
- name: aws-route53
route53:
accessKeyID: ${EKS_CERT_MANAGER_ROUTE53_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID}
region: eu-central-1
secretAccessKeySecretRef:
name: aws-route53-secret-access-key-secret
key: secret-access-key
---
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-production-dns
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
acme:
# The ACME server URL
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
# Email address used for ACME registration
email: petr.ruzicka@gmail.com
# Name of a secret used to store the ACME account private key
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-production-dns
dns01:
# Here we define a list of DNS-01 providers that can solve DNS challenges
providers:
- name: aws-route53
route53:
accessKeyID: ${EKS_CERT_MANAGER_ROUTE53_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID}
region: eu-central-1
secretAccessKeySecretRef:
name: aws-route53-secret-access-key-secret
key: secret-access-key
Create certificate using cert-manager:
envsubst < files/cert-manager-letsencrypt-aws-route53-certificate.yaml | kubectl apply -f -
envsubst < files/cert-manager-letsencrypt-aws-route53-certificate.yamlOutput:
certificate.certmanager.k8s.io/ingress-cert-production created
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: ingress-cert-production
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
secretName: ingress-cert-production
issuerRef:
kind: ClusterIssuer
name: letsencrypt-production-dns
commonName: "*.mylabs.dev"
dnsNames:
- "*.mylabs.dev"
acme:
config:
- dns01:
provider: aws-route53
domains:
- "*.mylabs.dev"
It's necessary to copy the wildcard certificate across all "future" namespaces and that's the reason why kubed needs to be installed (for now). kubed can synchronize ConfigMaps/Secrets across Kubernetes namespaces/clusters.
Kubed - synchronize secret diagram:
Add kubed helm repository:
helm repo add appscode https://charts.appscode.com/stable/Output:
"appscode" has been added to your repositories
Install kubed:
helm install appscode/kubed --name kubed --version 0.11.0 --namespace kube-system --wait \
--set config.clusterName=my_k8s_cluster \
--set apiserver.enabled=falseOutput:
NAME: kubed
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jul 19 11:48:10 2019
NAMESPACE: kube-system
STATUS: DEPLOYED
RESOURCES:
==> v1/ClusterRole
NAME AGE
kubed-kubed 4s
==> v1/ClusterRoleBinding
NAME AGE
kubed-kubed 4s
kubed-kubed-apiserver-auth-delegator 4s
==> v1/Pod(related)
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kubed-kubed-75789b6cc6-6zrst 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 4s
==> v1/RoleBinding
NAME AGE
kubed-kubed-apiserver-extension-server-authentication-reader 4s
==> v1/Secret
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
kubed-kubed Opaque 1 4s
kubed-kubed-apiserver-cert Opaque 2 4s
==> v1/Service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubed-kubed ClusterIP 10.100.193.123 <none> 443/TCP 4s
==> v1/ServiceAccount
NAME SECRETS AGE
kubed-kubed 1 4s
==> v1beta1/Deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
kubed-kubed 0/1 1 0 4s
NOTES:
To verify that Kubed has started, run:
kubectl --namespace=kube-system get deployments -l "release=kubed, app=kubed"
Annotate (mark) the cert-manager secret to be copied to other namespaces if necessary:
kubectl annotate secret ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT} -n cert-manager kubed.appscode.com/sync="app=kubed"Output:
secret/ingress-cert-production annotated
Install nginx-ingress which will also create a new loadbalancer:
helm install stable/nginx-ingress --wait --name nginx-ingress --namespace nginx-ingress-system --version 1.24.3 \
--set rbac.create=true \
--set controller.extraArgs.default-ssl-certificate=cert-manager/ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}Output:
NAME: nginx-ingress
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jul 19 11:48:17 2019
NAMESPACE: nginx-ingress-system
STATUS: DEPLOYED
RESOURCES:
==> v1/ConfigMap
NAME DATA AGE
nginx-ingress-controller 1 8s
==> v1/Pod(related)
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-ingress-controller-7b59c7c7bc-nhmq8 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 8s
nginx-ingress-default-backend-6d489448cb-d9brb 1/1 Running 0 8s
==> v1/Service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-ingress-controller LoadBalancer 10.100.37.102 a55fd2fadaa0a... 80:30958/TCP,443:31932/TCP 8s
nginx-ingress-default-backend ClusterIP 10.100.15.87 <none> 80/TCP 8s
==> v1/ServiceAccount
NAME SECRETS AGE
nginx-ingress 1 8s
==> v1beta1/ClusterRole
NAME AGE
nginx-ingress 8s
==> v1beta1/ClusterRoleBinding
NAME AGE
nginx-ingress 8s
==> v1beta1/Deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-ingress-controller 0/1 1 0 8s
nginx-ingress-default-backend 1/1 1 1 8s
==> v1beta1/Role
NAME AGE
nginx-ingress 8s
==> v1beta1/RoleBinding
NAME AGE
nginx-ingress 8s
NOTES:
The nginx-ingress controller has been installed.
It may take a few minutes for the LoadBalancer IP to be available.
You can watch the status by running 'kubectl --namespace nginx-ingress-system get services -o wide -w nginx-ingress-controller'
An example Ingress that makes use of the controller:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
name: example
namespace: foo
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: exampleService
servicePort: 80
path: /
# This section is only required if TLS is to be enabled for the Ingress
tls:
- hosts:
- www.example.com
secretName: example-tls
If TLS is enabled for the Ingress, a Secret containing the certificate and key must also be provided:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: example-tls
namespace: foo
data:
tls.crt: <base64 encoded cert>
tls.key: <base64 encoded key>
type: kubernetes.io/tls
nginx-ingress created the loadbalancer service. In case of AWS it is Classic Elastic Loadbalancer:
kubectl get service -n nginx-ingress-systemOutput:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-ingress-controller LoadBalancer 10.100.37.102 a55fd2fadaa0a11e9bcf2026dca96845-1478956562.eu-central-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:30958/TCP,443:31932/TCP 8s
nginx-ingress-default-backend ClusterIP 10.100.15.87 <none> 80/TCP 8s
Create DNS record mylabs.dev for the loadbalancer created by nginx-ingress:
export LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME=$(kubectl get svc nginx-ingress-controller -n nginx-ingress-system -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname}")
export CANONICAL_HOSTED_ZONE_NAME_ID=$(aws elb describe-load-balancers --query "LoadBalancerDescriptions[?DNSName==\`$LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME\`].CanonicalHostedZoneNameID" --output text)
export HOSTED_ZONE_ID=$(aws route53 list-hosted-zones --query "HostedZones[?Name==\`${MY_DOMAIN}.\`].Id" --output text)
envsubst < files/aws_route53-dns_change.json | aws route53 change-resource-record-sets --hosted-zone-id ${HOSTED_ZONE_ID} --change-batch=file:///dev/stdin | jqOutput:
{
"ChangeInfo": {
"Id": "/change/C2YV79SSX0CS95",
"Status": "PENDING",
"SubmittedAt": "2019-07-19T09:48:29.092Z",
"Comment": "A new record set for the zone."
}
}Wait for completion of certificate create process:
COUNT=0; OUTPUT=""; while [ "${OUTPUT}" != "True" ] && [ "${COUNT}" -lt 100 ]; do COUNT=$((COUNT+1)); OUTPUT=$(kubectl get certificate ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT} -n cert-manager -o jsonpath="{.status.conditions[0].status}"); sleep 1; echo -n "${COUNT} "; doneYou should see the following output form cert-manager when looking at certificates:
kubectl describe certificates -n cert-manager ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}Output
Name: ingress-cert-production
Namespace: cert-manager
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1","kind":"Certificate","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"ingress-cert-production","namespace"...
API Version: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
Kind: Certificate
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2019-07-19T09:48:10Z
Generation: 4
Resource Version: 2919
Self Link: /apis/certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1/namespaces/cert-manager/certificates/ingress-cert-production
UID: 5131721b-aa0a-11e9-bcf2-026dca968456
Spec:
Acme:
Config:
Dns 01:
Provider: aws-route53
Domains:
*.mylabs.dev
Common Name: *.mylabs.dev
Dns Names:
*.mylabs.dev
Issuer Ref:
Kind: ClusterIssuer
Name: letsencrypt-production-dns
Secret Name: ingress-cert-production
Status:
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2019-07-19T09:49:54Z
Message: Certificate is up to date and has not expired
Reason: Ready
Status: True
Type: Ready
Not After: 2019-10-17T08:49:53Z
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Warning IssuerNotReady 105s (x2 over 105s) cert-manager Issuer letsencrypt-production-dns not ready
Normal Generated 105s cert-manager Generated new private key
Normal GenerateSelfSigned 105s cert-manager Generated temporary self signed certificate
Normal OrderCreated 105s cert-manager Created Order resource "ingress-cert-production-20059064"
Normal OrderComplete 1s cert-manager Order "ingress-cert-production-20059064" completed successfully
Normal CertIssued 1s cert-manager Certificate issued successfully
The Kubernetes "secret" in cert-manager namespace should contain the
certificates:
kubectl describe secret -n cert-manager ingress-cert-${LETSENCRYPT_ENVIRONMENT}Output:
Name: ingress-cert-production
Namespace: cert-manager
Labels: certmanager.k8s.io/certificate-name=ingress-cert-production
Annotations: certmanager.k8s.io/alt-names: *.mylabs.dev
certmanager.k8s.io/common-name: *.mylabs.dev
certmanager.k8s.io/ip-sans:
certmanager.k8s.io/issuer-kind: ClusterIssuer
certmanager.k8s.io/issuer-name: letsencrypt-production-dns
kubed.appscode.com/sync: app=kubed
Type: kubernetes.io/tls
Data
====
ca.crt: 0 bytes
tls.crt: 3550 bytes
tls.key: 1675 bytes
Check the SSL certificate:
while ! echo | openssl s_client -showcerts -connect ${MY_DOMAIN}:443 &> /dev/null; do sleep 1; echo -n ". "; done
echo | openssl s_client -showcerts -connect ${MY_DOMAIN}:443 | openssl x509 -inform pem -noout -textOutput:
depth=2 O = Digital Signature Trust Co., CN = DST Root CA X3
verify return:1
depth=1 C = US, O = Let's Encrypt, CN = Let's Encrypt Authority X3
verify return:1
depth=0 CN = *.mylabs.dev
verify return:1
DONE
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
03:cf:14:18:90:0e:c8:7f:c2:39:eb:e5:dc:42:d7:c6:7a:a6
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: C = US, O = Let's Encrypt, CN = Let's Encrypt Authority X3
Validity
Not Before: Jul 19 08:49:53 2019 GMT
Not After : Oct 17 08:49:53 2019 GMT
Subject: CN = *.mylabs.dev
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
RSA Public-Key: (2048 bit)
Modulus:
...
Exponent: 65537 (0x10001)
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Key Usage: critical
Digital Signature, Key Encipherment
X509v3 Extended Key Usage:
TLS Web Server Authentication, TLS Web Client Authentication
X509v3 Basic Constraints: critical
CA:FALSE
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
44:C9:D2:B1:71:D6:94:92:67:DB:8C:C9:7E:0C:68:10:C3:10:41:D9
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
keyid:A8:4A:6A:63:04:7D:DD:BA:E6:D1:39:B7:A6:45:65:EF:F3:A8:EC:A1
Authority Information Access:
OCSP - URI:http://ocsp.int-x3.letsencrypt.org
CA Issuers - URI:http://cert.int-x3.letsencrypt.org/
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
DNS:*.mylabs.dev
X509v3 Certificate Policies:
Policy: 2.23.140.1.2.1
Policy: 1.3.6.1.4.1.44947.1.1.1
CPS: http://cps.letsencrypt.org
...