-
成员 苏炜杰 031802228 苏炜杰的 github 仓库
-
成员 沈 帅 031802226 沈帅的 github 仓库
| 分工 | 原型设计 | AI 与原型设计实现 |
|---|---|---|
| 苏炜杰 | 20% | 80% |
| 沈帅 | 80% | 20% |
-
设计说明:首页是两个按钮,一个可以查看战绩,一个可以开始游戏。战绩页有两种,第一种是没有战绩,就显示无战绩,第二种是有战绩。游戏页上面显示原图、步数和计时,下面游戏九宫图,最下面是重新游戏和回到首页按钮。
-
游戏开始界面,可以开始游戏,也可以查看战绩
-
战绩页,没有战绩时的战绩展示
-
战绩页
-
游戏开始页,左上角是原图
- 采用Axure工具
- 我们两个人是室友,就一起组队了
首先就是导入 ico 图标,我们想要将它变个颜色,原本打算用 PS 但是尝试失败之后,通过查询百度,最后选择导入 svg 图片 ,修改了它的颜色。
-
收获
感触比较深的是人多力量大 ,一个人想不出来的或者找不出来的,两个人可以很好地互相帮助,解决问题
因为使用 python 来 编写 ai,所以网络接口的实现就十分简单
使用了业界最流行的 requests 库
from typing import List
import requests
def get_not_answer_list() -> List:
url = 'http://47.102.118.1:8089/api/team/problem/xx'
r = requests.get(url)
return r.json()类似这样就获取了 xx 小组未答的题了
类似这样写了五个比较重要的网络接口函数
这个代码一共设计了四个类,五个网络访问函数,三个工具函数
五个网络函数在 网络接口使用 中就已介绍, 三个工具函数和与计算九容道答案的类将在 算法的关键实现部分
剩下两个图片类是用来匹配获取的题目图片和给的原始图片,并获取题目图片的打乱顺序传给算法相关的类进行解答
设计了图片基类和题目图片类,题目图片类继承了图片基类,图片基类获取九个被切割后的小图片
题目图片类获取了 uuid 并自动得到图片数据,然后和原始图片比较获取打乱顺序
切割图片用了 opencv 库,判断小图片相等使用了
(numpy.ndarray==numpy.ndarray).all()来判断两个图片的矩阵数据是否相等
以下是实现代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
from typing import List
class MyImage(object):
def __init__(self, img_bytes: bytes):
self.img_data: np.ndarray = cv2.imdecode(
np.frombuffer(img_bytes, np.uint8), cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
self.cut_image: List[np.ndarray] = []
self.cut()
def cut(self):
h_3: int = int(self.img_data.shape[0] / 3)
w_3: int = int(self.img_data.shape[1] / 3)
for h_i in range(3):
for w_i in range(3):
self.cut_image.append(
self.img_data[h_i * h_3:(h_i + 1) * h_3, w_i * w_3:(w_i + 1) * w_3])
def draw(self):
cv2.namedWindow("Image")
cv2.imshow("Image", self.img_data)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()from base64 import b64decode
from typing import List
from ai.image import image
import os
from ai.util import http_api
def read_source_image() -> List[image.MyImage]:
path = '../source'
path_list = os.listdir(path)
src_list: List[image.MyImage] = []
for i in path_list:
image_path = f'{path}/{i}'
with open(image_path, 'rb') as f:
src_list.append(image.MyImage(f.read()))
return src_list
source_list = read_source_image()
class MainImage(image.MyImage):
def __init__(self, uuid: str):
res = http_api.post_start(uuid)
self.swap_step: int = res['data']['step']
self.swap: List[int] = res['data']['swap']
self.uuid: str = res['uuid']
super(MainImage, self).__init__(b64decode(res['data']['img']))
self.serial_number: List[int] = []
for i in source_list:
serial_number = self.get_serial_number(i)
if serial_number:
self.serial_number = serial_number
def get_serial_number(self, other_image: image.MyImage) -> [List[int]]:
flag_list: List[int] = [0] * len(self.cut_image)
flag = 0
for i, self_cuy_image in enumerate(self.cut_image):
for j, other_cut_image in enumerate(other_image.cut_image):
if (self_cuy_image == other_cut_image).all():
flag_list[i] = j + 1
flag += 1
break
return flag_list if flag == len(self.cut_image) - 1 else []以下是 bsf 的核心算法
from typing import List, Set
from collections import deque
from copy import deepcopy
from ai.util import http_api
allow_swap: List = [
[-1, 1, 3, -1],
[-1, 2, 4, 0],
[-1, -1, 5, 1],
[0, 4, 6, -1],
[1, 5, 7, 3],
[2, -1, 8, 4],
[3, 7, -1, -1],
[4, 8, -1, 6],
[5, -1, -1, 7]
]
allow_dict: List[str] = ['w', 'd', 's', 'a']
def swap_str(source_str: str, index1: int, index2: int) -> str:
target_str = deepcopy(source_str)
target_str = target_str[:index1] + source_str[index2] + target_str[index1 + 1:]
target_str = target_str[:index2] + source_str[index1] + target_str[index2 + 1:]
return target_str
def is_solution(source_str: str) -> bool:
num = 0
test: List[int] = [int(i) for i in source_str]
test = list(filter(lambda x: x != 0, test))
for i, v1 in enumerate(test[:-1]):
for v2 in test[i + 1:]:
if v2 < v1:
num += 1
return True if num % 2 == 0 else False
def get_not_zero_index_list(source_str: str) -> List[int]:
l: List[int] = []
for i, j in enumerate(source_str):
if j != "0":
l.append(i + 1)
if len(l) == 2:
break
return l
class QueueItem(object):
def __init__(self, now_str: str, operations: str, swap: List[int]):
self.now_str: str = now_str
self.operations: str = operations
self.swap: List[int] = swap
def get_next(self) -> List:
zero_index = self.now_str.find("0")
new_item_list: List[QueueItem] = []
for i, other_index in enumerate(allow_swap[zero_index]):
if other_index != -1:
now_str = deepcopy(self.now_str)
now_str = now_str[:zero_index] + now_str[other_index] + now_str[zero_index + 1:]
now_str = now_str[:other_index] + '0' + now_str[other_index + 1:]
operations = deepcopy(self.operations)
operations += allow_dict[i]
new_item_list.append(QueueItem(now_str, operations, deepcopy(self.swap)))
return new_item_list
class Ai(object):
def __init__(self, serial_number: List[int], swap_step: int, swap: List[int], uuid: str):
self.serial_number: List[int] = serial_number
self.swap_step: int = swap_step
self.swap: List[int] = swap
self.my_swap: List[int] = []
self.operations: str = ''
self.uuid: str = uuid
def get_steps(self):
self.operations = self.bfs()
def post(self) -> bool:
return http_api.post_submit(self.uuid, self.operations, self.my_swap)
def bfs(self) -> str:
now_str = ''.join(str(i) for i in self.serial_number)
target_str = ''.join(str(i) if i in self.serial_number else "0" for i in range(1, 10))
q = deque()
q.append(QueueItem(now_str, '', []))
seen_str: Set[str] = set(now_str)
while q:
q_item: QueueItem = q.popleft()
if q_item.now_str == target_str:
self.my_swap = q_item.swap
return q_item.operations
if self.swap_step == len(q_item.operations):
q_item.now_str = swap_str(q_item.now_str, self.swap[0] - 1, self.swap[1] - 1)
if not is_solution(q_item.now_str):
if self.swap[1] != self.swap[0] and q_item.now_str[self.swap[0] - 1] != "0" and \
q_item.now_str[self.swap[1] - 1] != "0":
q_item.swap = deepcopy(self.swap)
q_item.now_str = swap_str(q_item.now_str, q_item.swap[0] - 1, q_item.swap[1] - 1)
else:
q_item.swap = get_not_zero_index_list(q_item.now_str)
q_item.now_str = swap_str(q_item.now_str, q_item.swap[0] - 1, q_item.swap[1] - 1)
new_item_list: List[QueueItem] = q_item.get_next()
for new_item in new_item_list:
if new_item.now_str not in seen_str:
seen_str.add(new_item.now_str)
q.append(new_item)get_not_zero_index_list is_solution swap_str 这三个工具函数的作用分别是获取两个非零下标进行交换 返回当前情况是否有解 交换字符串两个下标的值
QueueItem 是用来储存每个 bsf 遍历的每个情况 now_str 是当前情况,operations 是操作字符串,swap是这个情况下玩家的交换情况,get_next 用于获取当前情况的接下来的一步之内所有情况
Ai 是核心类,用于运算结果,它接受四个参数 初始情况数组, 强制交换步数和列表,和 uuid
类自动添加两个参数: my_swap 用于储存用户交换的下标, operations 用于储存最终操作字符串, post 用于提交答案,bsf 函数是核心算法
bsf 函数是广度优先算法,每一重大循环都先判断当前是否符合要求,若符合则直接返回答案;接着判断是否达到交换的步数,若达到则先交换要求的,再判断当前是否有解,若无解则判断强制交换的是否能改变有无解情况,若可以则交换回去,不可以,则获取可能改变有无解情况的交换.
接着再获取下一步的所有非重复情况,加入队列,知道找出答案
一开始测试的时候发现计算一个测试就要花费 230s 左右,用 idea 自带的 profile 工具查看,发现是 bsf 这个函数花了太多时间,仔细检查发现是一下代码花费的最多的时间
for new_item in new_item_list:
if new_item.now_str not in seen_str:
seen_str.add(new_item.now_str)
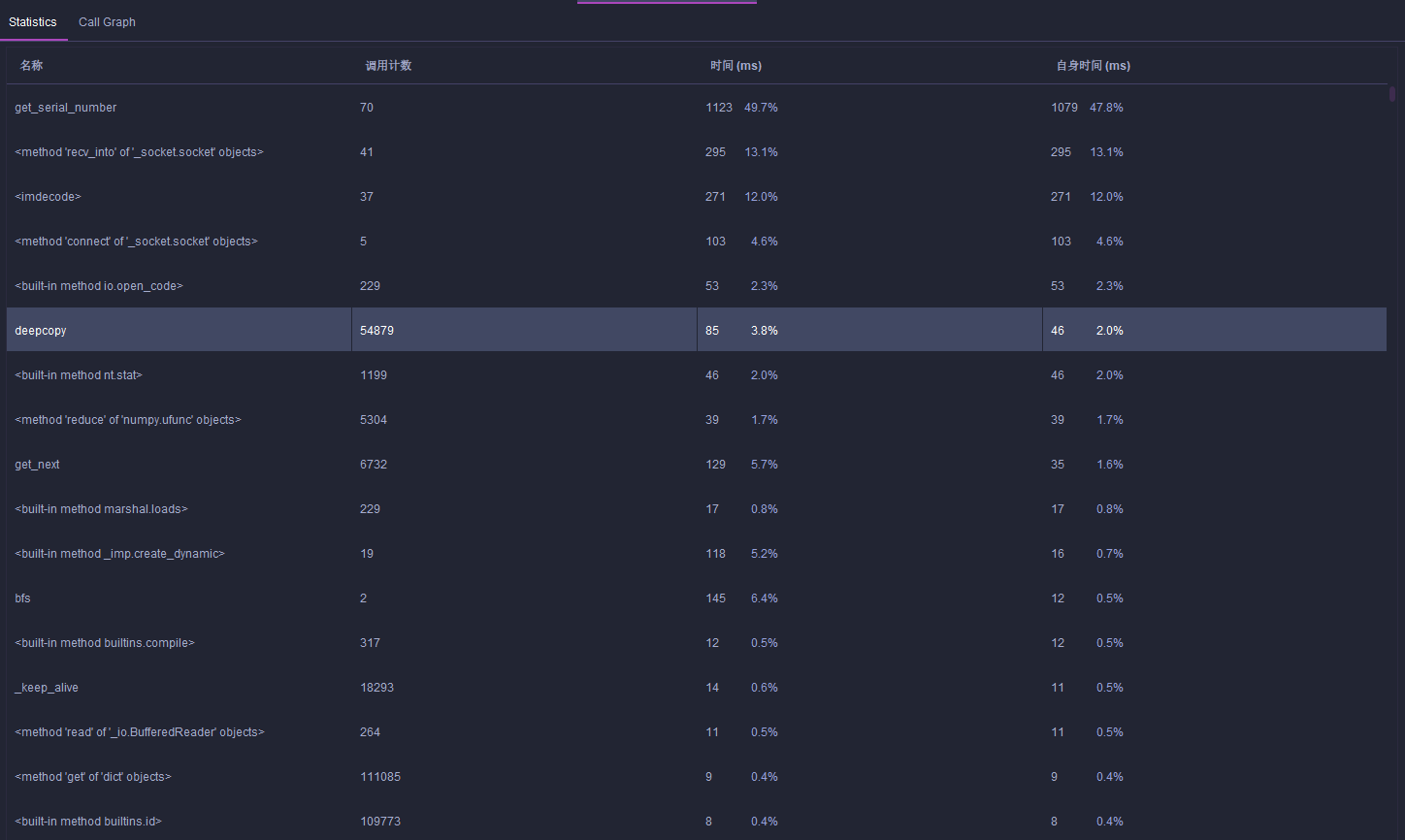
q.append(new_item)发现是因为一开始我使用 list 来储存 seen_str,这样的查找效率为 log(2,n),应该是要使用 set 来储存才对,改过之后测试 5 个数据的性能图如下
可以看出现在 bsf 再也不是最耗资源的函数了,5 个测试点也在几秒钟之内完成
get_serial_number 这个函数耗费了最多的时间,这个是用来从照片数据中获取九宫格当前的乱序情况,因为要和全部的实例图片比较所以耗费挺多的资源,不过内部是使用 numpy.ndarray 比较的,这个库是使用 c++ 编写的,性能已经是最好的了
最早使用 http://47.102.118.1:8089/api/problem?stuid=031802228 这个接口来测试,主要测试代码如下
from ai.image import main_image, image
import os
from typing import List
from ai.util import get_swaps
import json
import time
def read_source_image() -> List[image.MyImage]:
path = '../source'
path_list = os.listdir(path)
source_list: List[image.MyImage] = []
for i in path_list:
image_path = f'{path}/{i}'
with open(image_path, 'rb') as f:
source_list.append(image.MyImage(f.read()))
return source_list
def test():
info_data = main_image.MainImage()
source_list = read_source_image()
serial_number: List[int] = []
for i in source_list:
serial_number = info_data.get_serial_number(i)
if serial_number:
break
ai = get_swaps.Ai(serial_number, info_data.swap_step, info_data.swap, info_data.uuid)
ai.get_steps()
if not ai.post():
with open('test.txt', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f:
result = {
"serial_number": serial_number,
"swap_step": info_data.swap_step,
"swap": info_data.swap,
"uuid": info_data.uuid
}
f.write(json.dumps(result) + '\n')
return False
else:
return True
def main():
test_num = 200
true_num = 0
for i in range(test_num):
time.sleep(3)
if test():
true_num += 1
print(f'{true_num} / {i+1}')
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()通过每次访问执行一次全过程,未通过的实例保存在 test.txt 文件中由以下代码分析
import json
from typing import List, Dict
from ai.util import get_swaps
def test(serial_number: List[int], swap_step: int, swap: List[int], operations: str, my_swap: List[int]):
pass
def main():
fail_list: List[Dict] = []
with open('test.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
while s:=f.readline():
print(s)
fail_list.append(json.loads(s))
# for fail in fail_list:
# ai = get_swaps.Ai(fail['serial_number'], fail['swap_step'], fail['swap'], fail['uuid'])
# ai.get_steps()
# print(ai.operations, ai.is_solution, ai.my_swap)
fail = fail_list[0]
ai = get_swaps.Ai(fail['serial_number'], fail['swap_step'], fail['swap'], fail['uuid'])
ai.get_steps()
print(ai.operations, ai.my_swap, fail)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()因为在 commit:add ai 6 and success rate : 100% 后成功率达到了100%,所以在接下来的提交中两个测试文件被删除
以下是 git commit 记录
-
代码运行时间过长
解出一个华容道的时间要 200s, 一开始以为是算法问题, 后来仔细检查发现是 bfs 算法中储存以遍历的情况使用 list 储存,查找的时间复杂度为 n, 应该使用 set 储存:查找的时间复杂度为 log(2,n), 最后算法的时间为 1.7s
-
算法通过率不高
一开始完成算法,发现通过率不是很高,然后我把未通过的情况记录下来,在 bfs 代码里调试, 发现是我没有考虑清楚代码的所有情况,后来成功解决,代码测试通过率也达到 100%
-
原型实现时前端图片跨域问题
因为我是使用前端技术来完成原型实现,一开始用 webpack 的开发环境下是使用 http 协议打开网页的,没有跨域问题,后来打包后是使用 file 协议打开, 切割图片时使用了 getImageData api ,因为这个时候图片是文件,违法了浏览器的跨域政策.后来设置 webpack 图片在小于 80k 时以 base64 字符串储,无需跨域,存就解决了这个问题.
-
沈帅的回答
苏炜杰是一个实力强大 并且很努力的队友 他学习的态度值得我学习
-
苏炜杰的回答
沈帅会认真完成自己的任务
-
沈帅的回答
苏炜杰表达能力有待提高
-
苏炜杰的回答
沈帅学习能力有待提高
| 第 N 周 | 新增代码 | 累计代码(行) | 本周学习耗时(小时) | 累计学习耗时(小时) | 重要成长 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一周 | 20 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 1. 学习 git 2.学习 github 的 fork 同步等知识 建立了项目仓库 |
| 第二周 | 2929 | 2949 | 11 | 21 | 1.opencv/python 2.bfs 实践 |
| 第三周 | 1915 | 4855 | 3 | 24 | 游戏的实际编写 |
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 60 | 60 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 40 |
| Development | 开发 | 120 | 120 |
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 120 | 100 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 30 | 60 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 10 | 10 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 30 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 120 | 180 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 120 | 120 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 30 | 30 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 30 | 30 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 30 | 40 |
| Test Repor | 测试报告 | 30 | 20 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 10 | 20 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 30 |
| -- | 合计 | 760 | 890 |