Version: 5.4.1 November 12, 2024. Requires MOODLE V4.0 or later. Earlier versions of Moodle must use CodeRunner V4.
Authors: Richard Lobb, University of Canterbury, New Zealand. Tim Hunt, The Open University, UK.
NOTE: A few sample quizzes containing example CodeRunner questions are available at coderunner.org.nz. There's also a forum there, where you can post CodeRunner questions, such as requests for help if things go wrong, or are looking for ideas on how to write some unusual question type.
Table of Contents generated with DocToc
- Introduction
- Installation
- Uninstalling CodeRunner
- The Architecture of CodeRunner
- Question types
- Templates
- Template debugging
- Using the template as a script for more advanced questions
- Template parameters
- Use of the Precheck button
- Randomising questions
- Grading with templates
- Template grader examples
- Customising the result table
- User-interface selection
- User-defined question types
- Supporting or implementing new languages
- Multilanguage questions
- The 'qtype_coderunner_run_in_sandbox' web service
- Administrator scripts
- A note on accessibility
- APPENDIX 1: How questions get marked
- APPENDIX 2: How programming quizzes should work
CodeRunner is a Moodle question type that allows teachers to run a program in order to grade a student's answer. By far the most common use of CodeRunner is in programming courses where students are asked to write program code to some specification and that code is then graded by running it in a series of tests. CodeRunner questions have also been used in other areas of computer science and engineering to grade questions in which a program must be used to assess correctness.
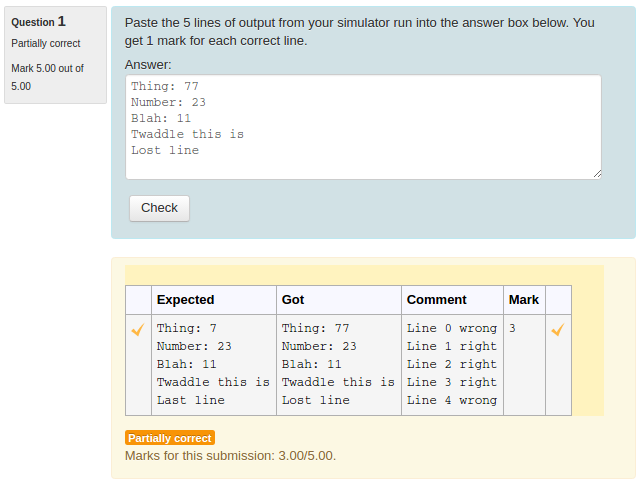
Regardless of the behaviour chosen for a quiz, CodeRunner questions always run in an adaptive mode, in which students can click a Check button to see if their code passes the tests defined in the question. If not, students can resubmit, typically for a small penalty. In the typical 'all-or-nothing' mode, all test cases must pass if the submission is to be awarded any marks. The mark for a set of questions in a quiz is then determined primarily by which questions the student is able to solve successfully and then secondarily by how many submissions the student makes on each question. However, it is also possible to configure CodeRunner questions so that the mark is determined by how many of the tests the code successfully passed.
CodeRunner has been in use at the University of Canterbury for over ten years running many millions of student quiz question submissions in Python, C, JavaScript, PHP, Octave and Matlab. It is used in laboratory work, assignments, tests and exams in multiple courses. In recent years CodeRunner has spread around the world and as of January 2021 is installed on over 1800 Moodle sites worldwide (see here), with at least some of its language strings translated into 19 other languages (see here).
CodeRunner supports the following languages: Python2 (considered obsolete), Python3, C, C++, Java, PHP, Pascal, JavaScript (NodeJS), Octave and Matlab. However, other languages are easily supported without altering the source code of either CodeRunner or the Jobe server just by scripting the execution of the new language within a Python-based question.
CodeRunner can safely be used on an institutional Moodle server, provided that the sandbox software in which code is run ("Jobe") is installed on a separate machine with adequate security and firewalling. However, if CodeRunner-based quizzes are to be used for tests and final exams, a separate Moodle server is recommended, both for load reasons and so that various Moodle communication facilities, like chat and messaging, can be turned off without impacting other classes.
The most recent version of CodeRunner specifies that it requires Moodle version 3.9 or later, but previous releases support Moodle version 3.0 or later. The current version should work with older versions of Moodle 3.0 or later, too, provided they are running PHP V7.2 or later. CodeRunner is developed and tested on Linux only, but Windows-based Moodle sites have also used it.
Submitted jobs are run on a separate Linux-based machine, called the Jobe server, for security purposes. CodeRunner is initially configured to use a small, outward-facing Jobe server at the University of Canterbury, and this server can be used for initial testing; however, the Canterbury server is not suitable for production use. Institutions will need to install and operate their own Jobe server when using CodeRunner in a production capacity. Instructions for installing a Jobe server are provided in the Jobe documentation. Once Jobe is installed, use the Moodle administrator interface for the CodeRunner plug-in to specify the Jobe host name and port number. A Docker Jobe server image is also available.
A modern 8-core Moodle server can handle an average quiz question submission rate of well over 1000 Python quiz questions per minute while maintaining a response time of less than 3 - 4 seconds, assuming the student code itself runs in a fraction of a second. We have run CodeRunner-based exams with nearly 500 students and experienced only light to moderate load factors on our 8-core Moodle server. The Jobe server, which runs student submissions (see below), is even more lightly loaded during such an exam.
Some videos introducing CodeRunner and explaining question authoring are available in this youtube channel.
This chapter describes how to install CodeRunner. It assumes the existence of a working Moodle system, version 3.0 or later.
CodeRunner requires two separate plug-ins, one for the question type and one
for the specialised adaptive behaviour. The plug-ins are in two
different github repositories: github.com/trampgeek/moodle-qbehaviour_adaptive_adapted_for_coderunner
and github.com/trampgeek/moodle-qtype_coderunner. Install the two plugins
using one of the following two methods.
EITHER:
-
Download the zip file of the required branch from the coderunner github repository unzip it into the directory
moodle/question/typeand change the name of the newly-created directory frommoodle-qtype_coderunner-<branchname>to justcoderunner. Similarly download the zip file of the required question behaviour from the behaviour github repository, unzip it into the directorymoodle/question/behaviourand change the newly-created directory name toadaptive_adapted_for_coderunner. OR -
Get the code using git by running the following commands in the top level folder of your Moodle install:
git clone https://github.com/trampgeek/moodle-qtype_coderunner.git question/type/coderunner git clone https://github.com/trampgeek/moodle-qbehaviour_adaptive_adapted_for_coderunner.git question/behaviour/adaptive_adapted_for_coderunner
Either way you may also need to change the ownership and access rights to ensure the directory and its contents are readable by the webserver.
You can then complete the installation by logging onto the server through the web interface as an administrator and following the prompts to upgrade the database as appropriate.
In its initial configuration, CodeRunner is set to use a University of Canterbury Jobe server to run jobs. You are welcome to use this during initial testing, but it is not intended for production use. Authentication and authorisation on that server is via an API-key and the default API-key given with CodeRunner imposes a limit of 100 per hour over all clients using that key, worldwide. If you decide that CodeRunner is useful to you, please set up your own Jobe sandbox as described in Sandbox configuration below.
WARNING: at least a couple of users have broken CodeRunner by duplicating
the prototype questions in the System/CR_PROTOTYPES category. Do not touch
those special questions until you have read this entire manual and
are familiar with the inner workings of CodeRunner. Even then, you should
proceed with caution. These prototypes are not
for normal use - they are akin to base classes in a prototypal inheritance
system like JavaScript's. If you duplicate a prototype question the question
type will become unusable, as CodeRunner doesn't know which version of the
prototype to use.
Upgrading CodeRunner versions from version 2.4 or later onwards should generally be straightforward though, as usual, you should make a database backup before upgrading. To upgrade, simply install the latest code and login to the web interface as an administrator. When Moodle detects the changed version number it will run upgrade code that updates all questions to the latest format.
However, if you have written your own question types
you should be aware that all existing questions in the system
CR_PROTOTYPES category with names containing the
string PROTOTYPE_ are deleted by the installer/upgrader.
The installer then re-loads them from the file
db/questions-CR_PROTOTYPES.xml
Hence if you have developed your own question prototypes and placed them in
the system CR_PROTOTYPES category (not recommended) you must export them
in Moodle XML format before upgrading. You can then re-import them after the
upgrade is complete using the usual question-bank import function in the
web interface. However, it is strongly recommended that you do not put your
own question prototypes in the CR_PROTOTYPES category but create a new
category for your own use.
Once you have installed the CodeRunner question type, you should be able to run CodeRunner questions using the University of Canterbury's Jobe Server as a sandbox. It is recommended that you do this before proceeding to install and configure your own sandbox.
Using the standard Moodle web interface, either as a Moodle administrator or as a teacher in a course you have set up, go to the Question Bank and try creating a new CodeRunner question. A simple Python3 test question is: "Write a function sqr(n) that returns the square of its parameter n.". The introductory quick-start guide in the incomplete Question Authoring Guide gives step-by-step instructions for creating such a question. Alternatively you can just try to create a question using the on-line help in the question authoring form. Test cases for the question might be:
| Test | Expected |
|---|---|
| print(sqr(-7)) | 49 |
| print(sqr(5)) | 25 |
| print(sqr(-1)) | 1 |
| print(sqr(0)) | 0 |
| print(sqr(-100)) | 10000 |
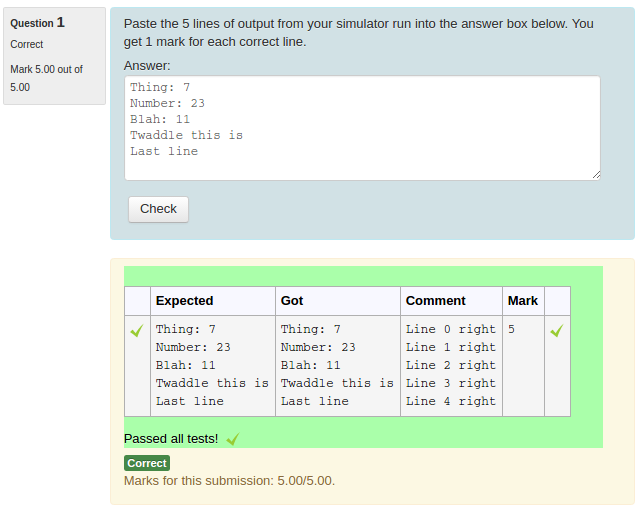
You could check the 'UseAsExample' checkbox on the first two (which results in the student seeing a simple "For example" table) and perhaps make the last case a hidden test case. (It is recommended that all questions have at least one hidden test case to prevent students synthesising code that works just for the known test cases).
Save your new question, then preview it, entering both correct and incorrect answers.
If you want a few more CodeRunner questions to play with, try importing the
files
MoodleHome>/question/type/coderunner/samples/simpledemoquestions.xml and/or
MoodleHome>/question/type/coderunner/samples/python3demoquestions.xml.
These contains
most of the questions from the two tutorial quizzes on the
demo site.
If you wish to run the questions in the file python3demoquestions.xml,
you will also need to import
the file MoodleHome>/question/type/coderunner/samples/uoc_prototypes.xml
or you will receive a "Missing prototype" error.
Also included in the samples folder is a prototype question,
prototype\_c\_via\_python.xml
that defines a new question type, equivalent to the built-in c_program
type, by scripting in Python the process of compiling and running the student
code. This is a useful template for authors who wish to implement their own
question types or who need to support non-built-in languages. It is discussed
in detail in the section "Supporting or implementing new languages".
It is important that students get shown the result table when they click Check. In Moodle quiz question parlance, the result table is called the question's Specific feedback and the quiz review options normally control when that feedback should be displayed to the student. By default, however, CodeRunner always displays this result table; if you wish to have the quiz review options control when it is shown you must change the Feedback drop-down in the question author form from its default Force show to Set by quiz.
Some recommended setting in the "During the attempt" column of the quiz review options are:
-
Right answer. This should be unchecked, at least in the "During the attempt" column and possibly elsewhere, if you don't want your sample answers leaked to the whole class.
-
Whether correct. This should probably be unchecked if the quiz includes any non-coderunner questions. It doesn't appear to affect CodeRunner feedback but if left checked will result in other questions types displaying an excessive amount of help when Check is clicked.
-
Marks and General feedback. These should probably be checked.
Although CodeRunner has a flexible architecture that supports various different ways of running student task in a protected ("sandboxed") environment, only one sandbox - the Jobe sandbox - is supported by the current version. This sandbox makes use of a separate server, developed specifically for use by CodeRunner, called Jobe. As explained at the end of the section on installing CodeRunner from scratch, the initial configuration uses the Jobe server at the University of Canterbury. This is not suitable for production use. Please switch to using your own Jobe server as soon as possible.
To build a Jobe server, follow the instructions at https://github.com/trampgeek/jobe. Then use the Moodle administrator interface for the CodeRunner plug-in to specify the Jobe host name and perhaps port number. Depending on how you've chosen to configure your Jobe server, you may also need to supply an API-Key through the same interface.
A video walkthrough of the process of setting up a Jobe server on a DigitalOcean droplet, and connecting an existing CodeRunner plugin to it, is available here.
An alternative and generally much faster way to set up a Jobe server is to use the Docker image jobeinabox. Because it is containerised, this version of Jobe is even more secure. The only disadvantage is that is is more difficult to manage the code or OS features within the Jobe container, e.g. to install new languages in it.
If you intend running unit tests you
will also need to copy the file tests/fixtures/test-sandbox-config-dist.php
to tests/fixtures/test-sandbox-config.php, then edit it to set the correct
host and any other necessary configuration for the Jobe server.
Assuming you have built Jobe on a separate server, suitably firewalled, the JobeSandbox fully isolates student code from the Moodle server. Some users install Jobe on the Moodle server but this is not recommended for security reasons: a student who manages to break out of the Jobe security might then run code on the Moodle server itself if it is not adequately locked down. If you really want to run Jobe on the Moodle server, please at least use the JobeInAbox docker image, which should adequately protect the Moodle system from direct damage. Do realise, though, that unless the Moodle server is itself carefully firewalled, Jobe tasks are likely to be able to open connections to other machines within your intranet or elsewhere.
If your Moodle installation includes the phpunit system for testing Moodle modules, you might wish to test the CodeRunner installation. Most tests require that at least python2 and python3 are installed.
Before running any tests you first need to copy the file
<moodlehome>/question/type/coderunner/tests/fixtures/test-sandbox-config-dist.php
to <moodlehome>/question/type/coderunner/tests/fixtures/test-sandbox-config.php,
then edit it to set whatever configuration of sandboxes you wish to test,
and to set the jobe host, if appropriate. You should then initialise
the phpunit environment with the commands
cd <moodlehome>
sudo php admin/tool/phpunit/cli/init.php
You can then run the full CodeRunner test suite with one of the following two commands, depending on which version of phpunit you're using:
sudo -u www-data vendor/bin/phpunit --verbose --testsuite="qtype_coderunner test suite"
or
sudo -u www-data vendor/bin/phpunit --verbose --testsuite="qtype_coderunner_testsuite"
If you're on a Red Hat or similar system in which the web server runs as apache, you should replace www-data with *apache.
The unit tests will almost certainly show lots of skipped or failed tests relating to the various sandboxes and languages that you have not installed, e.g. the LiuSandbox, Matlab, Octave and Java. These can all be ignored unless you plan to use those capabilities. The name of the failing tests should be sufficient to tell you if you need be at all worried.
Feel free to email the principal developer if you have problems with the installation.
Like any question-type plugin, CodeRunner can be uninstalled using the Uninstall link in the Moodle Manage plugins page. BUT in order for that link to be present (for any question type), the system checks to see if there are any questions of that type present. If so, the link is silently not displayed.
So, you need to do the following before the Uninstall link is displayed:
-
Backup your server.
-
Find any quizzes that use CodeRunner questions and either delete them or remove the CodeRunner questions from them. If you don't do this, then when you try to delete the questions from the question bank (step 2) they will simply be hidden rather than properly deleted.
-
Remove all the user-defined CodeRunner questions.
-
Delete all the CodeRunner prototypes (which define the set of available question types) from the System > Top for System > CR_PROTOTYPES category. This requires Moodle administrator level privileges.
You should then find the Uninstall link showing for CodeRunner in the Manage plugins page. If not, you must still have some CodeRunner questions hidden away somewhere. If you have admin rights, you should be able to find them with the SQL command:
select id, category, name from mdl_question where qtype='coderunner';
If you have a lot of coderunner questions you may be able to just delete all the coderunner questions SQL but I'd be very reluctant to do that myself as it will break the database integrity and I'm not sure that the subsequent plugin deletion will clean up the mess. Certainly any quizzes referring to deleted questions will break (but of course they're going to break anyway if you uninstall CodeRunner).
Although it's straightforward to write simple questions using the built-in question types, anything more advanced than that requires an understanding of how CodeRunner works.
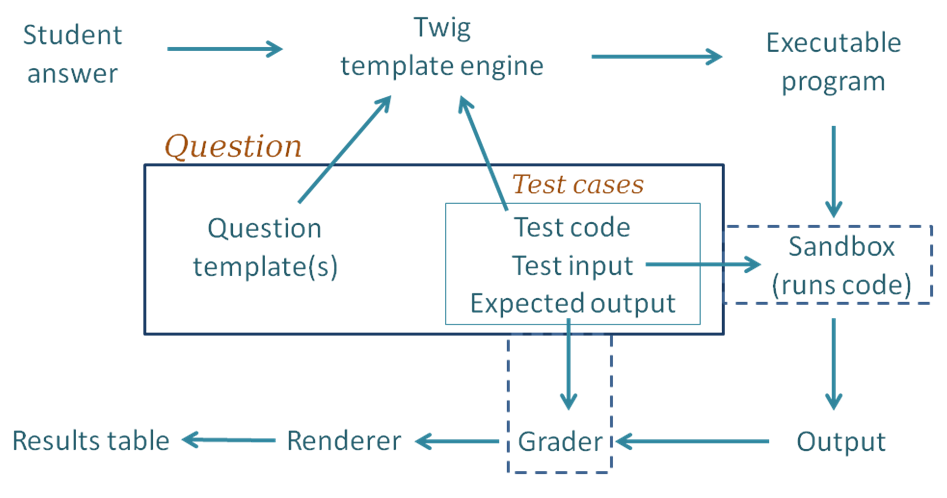
The block diagram below shows the components of CodeRunner and the path taken as a student submission is graded.
Following through the grading process step by step:
- For each of the test cases, the Twig template engine merges the student's submitted answer with the question's template together with code for this particular test case to yield an executable program. By "executable", we mean a program that can be executed, possibly with a preliminary compilation step.
- The executable program is passed to the Jobe sandbox, which compiles the program (if necessary) and runs it, using the standard input supplied by the testcase.
- The output from the run is passed into whatever Grader component is configured, as is the expected output specified for the test case. The most common grader is the "exact match" grader but other types are available.
- The output from the grader is a "test result object" which contains (amongst other things) "Expected" and "Got" attributes.
- The above steps are repeated for all testcases, giving an array of test result objects (not shown explicitly in the figure).
- All the test results are passed to the CodeRunner question renderer, which presents them to the user as the Results Table. Tests that pass are shown with a green tick and failing ones shown with a red cross. Typically the whole table is coloured red if any tests fail or green if all tests pass.
The above description is somewhat simplified, in the following ways:
-
It is not always necessary to run a different job in the sandbox for each test case. Instead, all tests can often be combined into a single executable program. This is achieved by use of what is known as a "combinator template" rather than the simpler "per-test template" described above. Combinator templates are useful with questions of the write-a-function or write-a-class variety. They are not often used with write-a-program questions, which are usually tested with different standard inputs, so multiple execution runs are required. Furthermore, even with write-a-function questions that do have a combinator template, CodeRunner will revert to running tests one-at-a-time (still using the combinator template) if running all tests in the one program gives some form of runtime error, in order that students can be presented with all test results up until the one that failed.
Combinator templates are explained in the Templates section.
-
The question author can pass parameters to the Twig template engine when it merges the question's template with the student answer and the test cases. Such parameters add considerable flexibility to question types, allow question authors to selectively enable features such as style checkers and allowed/disallowed constructs. This functionality is discussed in the Template parameters section.
-
The above description ignores template graders, where the question's template includes code to do grading as well as testing. Template graders support more advanced testing strategies, such as running thousands of tests or awarding marks in more complex ways than is possible with the standard option of either "all-or-nothing" marking or linear summation of individual test marks.
A per-test-case template grader can be used to define each row of the result table, or a combinator template grader can be used to defines the entire feedback panel, with or without a result table. See the section on Grading with templates for more information.
CodeRunner support a wide variety of question types and can easily be extended to support others. A CodeRunner question type is defined by a question prototype, which specifies run time parameters like the execution language and sandbox and also the template that define how a test program is built from the question's test-cases plus the student's submission.
The prototype also defines whether the correctness of the student's submission is assessed by use of an EqualityGrader, a NearEqualityGrader, a RegexGrader or a TemplateGrader.
- The EqualityGrader expects the output from the test execution to exactly match the expected output for the testcase.
- The NearEqualityGrader is similar but is case insensitive and tolerates variations in the amount of white space (e.g. missing or extra blank lines, or multiple spaces where only one was expected).
- The RegexGrader takes the Expected output as a regular expression (which should not have PERL-type delimiters) and tries to find a match anywhere within the output. Thus for example an expected value of 'ab.*z' would match any output that contains the the characters 'ab' anywhere in the output and a 'z' character somewhere later. To force matching of the entire output, start and end the regular expression with '\A' and '\Z' respectively. Regular expression matching uses MULTILINE and DOTALL options.
- Template graders are more complicated but give the question author almost unlimited flexibility in controlling the execution, grading and result display; see the section Grading with templates.
The EqualityGrader is recommended for most normal use, as it encourages students to get their output exactly correct; they should be able to resubmit almost-right answers for a small penalty, which is generally a better approach than trying to award part marks based on regular expression matches.
Test cases are defined by the question author to check the student's code. Each test case defines a fragment of test code, the standard input to be used when the test program is run and the expected output from that run. The author can also add additional files to the execution environment.
The test program is constructed from the test case information plus the student's submission using the template defined by the prototype. The template can be either a per-test template, which defines a different program for each test case or a combinator template, which has the ability to define a program that combines multiple test cases into a single run. Templates are explained in the Templates section.
The C-function question type expects students to submit a C function, plus possible
additional support functions, to some specification. As a trivial example, the question
might ask "Write a C function with signature int sqr(int n) that returns
the square of its parameter n". The author will then provide some test
cases, such as
printf("%d\n", sqr(-11));
and give the expected output from this test.
A per-test template for such a question type would then wrap the submission and the test code into a single program like:
#include <stdio.h>
// --- Student's answer is inserted here ----
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", sqr(-11));
return 0;
}
which would be compiled and run for each test case. The output from the run would then be compared with the specified expected output (121) and the test case would be marked right or wrong accordingly.
That example assumes the use of a per-test template rather than the more complicated combinator template that is actually used by the built-in C function question type. See the section on Templates for more details.
The file <moodlehome>/question/type/coderunner/db/builtin_PROTOTYPES.xml
is a moodle-xml export format file containing the definitions of all the
built-in question types. During installation, and at the end of any version upgrade,
the prototype questions from that file are all loaded into a category
CR_PROTOTYPES in the system context. A system administrator can edit
those prototypes but this is not recommended as the modified versions
will be lost on each upgrade. Instead, a category LOCAL_PROTOTYPES
(or other such name of your choice) should be created and copies of any prototype
questions that need editing should be stored there, with the question-type
name modified accordingly. New prototype question types can also be created
in that category. Editing of prototypes is discussed later in this
document.
Built-in question types include the following:
-
c_function. This is the question type discussed in the above example, except that it uses a combinator template. The student supplies just a function (plus possible support functions) and each test is (typically) of the form
printf(format_string, func(arg1, arg2, ..))
The template for this question type generates some standard includes, followed by the student code followed by a main function that executes the tests one by one. However, if any of the test cases have any standard input defined, the template is expanded and executed separately for each test case separately.
The manner in which a C (or any other) program is executed is not part of the question
type definition: it is defined by the particular sandbox to which the
execution is passed. The architecture of CodeRunner allows for the multiple
different sandboxes but currently only the Jobe sandbox is supported. It
uses the gcc compiler with the language set to
accept C99 and with both -Wall and -Werror options set on the command line
to issue all warnings and reject the code if there are any warnings.
-
cpp_function. This is the C++ version of the previous question type. The student supplies just a function (plus possible support functions) and each test is (typically) of the form
cout << func(arg1, arg2, ..)
The template for this question type generates some standard includes, followed by the line
using namespace std;
followed by the student code followed by a main function that executes the tests one by one.
-
c_program and cpp_program. These two very simple question types require the student to supply a complete working program. For each test case the author usually provides
stdinand specifies the expectedstdout. The program is compiled and run as-is, and in the default all-or-nothing grading mode, must produce the right output for all test cases to be marked correct. -
python3. Used for most Python3 questions. For each test case, the student code is run first, followed by the test code.
-
python3_w_input. A variant of the python3 question in which the
inputfunction is redefined at the start of the program so that the standard input characters that it consumes are echoed to standard output as they are when typed on the keyboard during interactive testing. A slight downside of this question type compared to the python3 type is that the student code is displaced downwards in the file so that line numbers present in any syntax or runtime error messages do not match those in the student's original code. -
python2. Used for most Python2 questions. As for python3, the student code is run first, followed by the sequence of tests. This question type should be considered to be obsolescent due to the widespread move to Python3 through the education community.
-
java_method. This is intended for early Java teaching where students are still learning to write individual methods. The student code is a single method, plus possible support methods, that is wrapped in a class together with a static main method containing the supplied tests (which will generally call the student's method and print the results).
-
java_class. Here the student writes an entire class (or possibly multiple classes in a single file). The test cases are then wrapped in the main method for a separate public test class which is added to the students class and the whole is then executed. The class the student writes may be either private or public; the template replaces any occurrences of
public classin the submission with justclass. While students might construct programs that will not be correctly processed by this simplistic substitution, the outcome will simply be that they fail the tests. They will soon learn to write their classes in the expected manner (i.e. withpublicandclasson the same line, separated by a single space)! -
java_program. Here the student writes a complete program which is compiled then executed once for each test case to see if it generates the expected output for that test. The name of the main class, which is needed for naming the source file, is extracted from the submission by a regular expression search for a public class with a
public static void mainmethod. -
octave_function. This uses the open-source Octave system to process matlab-like student submissions.
-
php. A php question in which the student submission is a normal php file, with PHP code enclosed in tags and the output is the usual PHP output including all HTML content outside the php tags.
Other less commonly used built-in question types are: nodejs, pascal_program and pascal_function.
As discussed later, this base set of question types can be customised or extended in various ways.
The following question types, used by the University
of Canterbury (UOC) are not part of the basic supported question type set.
They can be imported, if desired, from the file
uoc_prototypes.xml, located in the CodeRunner/coderunner/samples folder.
However, they come with no guarantees of correctness or on-going support.
The UOC question types include:
-
python3_cosc121. This is a complex Python3 question type that's used at the University of Canterbury for nearly all questions in the COSC121 course. The student submission is first passed through the pylint source code analyser and the submission is rejected if pylint gives any errors. Otherwise testing proceeds as normal. Obviously, pylint needs to be installed on the sandbox server. This question type takes many different template parameters (see the section entitled Template parameters for an explanation of what these are) to allow it to be used for a wide range of different problems. For example, it can be configured to require or disallow specific language constructs (e.g. when requiring students to rewrite a for loop as a while loop), or to limit function size to a given value, or to strip the main function from the student's code so that the support functions can be tested in isolation. Details on how to use this question type, or any other, can be found by expanding the Question Type Details section in the question editing page.
-
matlab_function. Used for Matlab function questions. Student code must be a function declaration, which is tested with each testcase. The name is actually a lie, as this question type now uses Octave instead, which is much more efficient and easier for the question author to program within the CodeRunner context. However, Octave has many subtle differences from Matlab and some problems are inevitable. Caveat emptor.
-
matlab_script. Like matlab_function, this is a lie as it actually uses Octave. It runs the test code first (which usually sets up a context) and then runs the student's code, which may or may not generate output dependent on the context. Finally the code in Extra Template Data is run (if any). Octave's
dispfunction is replaced with one that emulates Matlab's more closely, but, as above: caveat emptor.
Templates are the key to understanding how a submission is tested. Every question has a template, either imported from the question type or explicitly customised, which defines how the executable program is constructed from the student's answer, the test code and other custom code within the template itself.
The template for a question is by default defined by the CodeRunner question type, which itself is defined by a special "prototype" question, to be explained later. You can inspect the template of any question by clicking the customise box in the question authoring form.
A question's template can be either a per-test template or a combinator template. The first one is the simpler; it is applied once for every test in the question to yield an executable program which is sent to the sandbox. Each such execution defines one row of the result table. Combinator templates, as the name implies, are able to combine multiple test cases into a single execution, provided there is no standard input for any of the test cases. We will discuss the simpler per-test template first.
A per_test_template is essentially a program with "placeholders" into which are inserted the student's answer and the test code for the test case being run. The expanded template is then sent to the sandbox where it is compiled (if necessary) and run with the standard input defined in the testcase. The output returned from the sandbox is then matched against the expected output for the testcase, where a 'match' is defined by the chosen grader: an exact match, a nearly exact match or a regular-expression match. There is also the possibility to perform grading with the the template itself using a 'template grader'; this possibility is discussed later, in the section Grading with templates.
Expansion of the template is done by the Twig template engine. The engine is given both the template to be rendered and a set of pre-defined variables that we will call the Twig Context. The default set of context variables is:
- STUDENT_ANSWER, which is the text that the student entered into the answer box.
- TEST, which is a record containing the testcase. See The Twig TEST variable.
- IS_PRECHECK, which has the value 1 (True) if the template is being evaluated as a result of a student clicking the Precheck button or 0 (False) otherwise.
- ANSWER_LANGUAGE, which is meaningful only for multilanguage questions, for which it contains the language chosen by the student from a drop-down list. See Multilanguage questions.
- ATTACHMENTS, which is a comma-separated list of the names of any files that the student has attached to their submission.
- STUDENT, which is a record describing the current student. See The Twig STUDENT variable.
- QUESTION, which is the entire Moodle
Questionobject. See The Twig QUESTION variable.
Additionally, if the question author has set any template parameters and has checked the Hoist template parameters checkbox, the context will include all the values defined by the template parameters field. This will be explained in the section Template parameters.
The TEST attributes most likely to be used within the template are TEST.testcode (the code to execute for the test) and TEST.extra (the extra test data provided in the question authoring form). The template will typically use just the TEST.testcode field, which is the "test" field of the testcase. It is usually a bit of code to be run to test the student's answer.
When Twig processes the template, it replaces any occurrences of
strings of the form {{ TWIG_VARIABLE }} with the value of the given
TWIG_VARIABLE (e.g. STUDENT_ANSWER). As an example,
the question type c_function, which asks students to write a C function,
might have the following template (if it used a per-test template):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
{{ STUDENT_ANSWER }}
int main() {
{{ TEST.testcode }};
return 0;
}
A typical test (i.e. TEST.testcode) for a question asking students to write a
function that
returns the square of its parameter might be:
printf("%d\n", sqr(-9))
with the expected output of 81. The result of substituting both the student code and the test code into the template might then be the following program (depending on the student's answer, of course):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int sqr(int n) {
return n * n;
}
int main() {
printf("%d\n", sqr(-9));
return 0;
}
When authoring a question you can inspect the template for your chosen question type by temporarily checking the 'Customise' checkbox. Additionally, if you check the Template debugging checkbox you will get to see in the output web page each of the complete programs that gets run during a question submission.
When customising a question you'll also find a checkbox labelled Is combinator. If this checkbox is checked the template is a combinator template. Such templates receive the same Twig Context as per-test templates except that rather than a TEST variable they are given a TESTCASES variable. This is is a list of all the individual TEST objects. A combinator template is expected to iterate through all the tests in a single run, separating the output from the different tests with a special separator string, defined within the question authoring form. The default separator string is
"#<ab@17943918#@>#"
on a line by itself.
The template used by the built-in C function question type is not actually a per-test template as suggested above, but is the following combinator template.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
#define SEPARATOR "#<ab@17943918#@>#"
{{ STUDENT_ANSWER }}
int main() {
{% for TEST in TESTCASES %}
{
{{ TEST.testcode }};
}
{% if not loop.last %}printf("%s\n", SEPARATOR);{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
return 0;
}
The Twig template language control structures are wrapped in {%
and %}. If a C-function question had two three test cases, the above template
might expand to something like the following:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
#define SEPARATOR "#<ab@17943918#@>#"
int sqr(int n) {
return n * n;
}
int main() {
printf("%d\n", sqr(-9));
printf("%s\n", SEPARATOR);
printf("%d\n", sqr(11));
printf("%s\n", SEPARATOR);
printf("%d\n", sqr(-13));
return 0;
}
The output from the execution is then the outputs from the three tests separated by a special separator string, which can be customised for each question if desired. On receiving the output back from the sandbox, CodeRunner then splits the output using the separator into three separate test outputs, exactly as if a per-test template had been used on each test case separately.
The use of a combinator template is problematic with questions that require standard input: if each test has its own standard input, and all tests are combined into a single program, what is the standard input for that program? By default if a question has standard inputs defined for any of the tests but has a combinator template defined, CodeRunner simply runs each test separately on the sandbox. It does that by using the combinator template but feeding it a singleton list of testcases, i.e. the list [test[0]] on the first run, [test[1]] on the second and so on. In each case, the standard input is set to be a file containing the contents of the Standard Input field of the particular testcase being run. The combinator template is then functioning just like a per-test template but using the TESTCASES variable rather than a TEST variable.
However, advanced combinator templates can actually manage the multiple runs themselves, e.g. using Python Subprocesses. To enable this, there is a checkbox "Allow multiple stdins" which, if checked, reverts to the usual combinator mode of passing all testcases to the combinator template in a single run.
The use of a combinator also becomes problematic if the student's code causes a premature abort due to a run error, such as a segmentation fault or a CPU time limit exceeded. In such cases, CodeRunner reruns the tests, using the combinator template in a per-test mode, as described above.
As mentioned above, if a question author clicks in the customise checkbox, the question template is made visible and can be edited by the question author to modify the behaviour for that question.
As a simple example, consider the following question:
"What is the missing line in the sqr function shown below, which returns the square of its parameter n?"
int sqr(int n) {
// What code replaces this line?
}
Suppose further that you wished the test column of the result table to display
just, say, sqr(-11) rather than printf("%d, sqr(-11));
You could set such a question using a template like:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int sqr(int n) {
{{ STUDENT_ANSWER }}
}
int main() {
printf("%d\n", {{ TEST.testcode }});
return 0;
}
The authoring interface allows the author to set the size of the student's answer box, and in a case like the above you'd typically set it to just one or two lines in height and perhaps 30 columns in width.
The above example was chosen to illustrate how template editing works, but it's not a very compelling practical example. It would generally be easier for the author and less confusing for the student if the question were posed as a standard built-in write-a-function question, but using the Preload capability in the question authoring form to pre-load the student answer box with something like
// A function to return the square of its parameter n
int sqr(int n) {
// *** Replace this line with your code
If you're a newcomer to customising templates or developing your own question type (see later), it is recommended that you start with a per-test template, and move to a combinator template only when you're familiar with how things work and need the performance gain offered by a combinator template.
When customising question templates or developing new question types, it is usually helpful to check the Template debugging checkbox and to uncheck the Validate on save checkbox. Save your question, then preview it. Whenever you click the Check (or Precheck button, if it's enabled) you'll be shown the actual code that is sent to the sandbox. You can then copy that into your favourite IDE and test it separately.
If the question results in multiple submissions to the sandbox, as happens by default when there is standard input defined for the tests or when any test gives a runtime error, the submitted code for all runs will be shown.
It may not be obvious from the above that the template mechanism allows for almost any sort of question where the answer can be evaluated by a computer. In all the examples given so far, the student's code is executed as part of the test process but in fact there's no need for this to happen. The student's answer can be treated as data by the template code, which can then execute various tests on that data to determine its correctness. The Python pylint question type mentioned earlier is a simple example: the template code first writes the student's code to a file and runs pylint on that file before proceeding with any tests.
The per-test template for a simple pylint question type might be:
import subprocess
import os
import sys
def code_ok(prog_to_test):
"""Check prog_to_test with pylint. Return True if OK or False if not.
Any output from the pylint check will be displayed by CodeRunner
"""
try:
source = open('source.py', 'w')
source.write(prog_to_test)
source.close()
env = os.environ.copy()
env['HOME'] = os.getcwd()
cmd = ['pylint', 'source.py']
result = subprocess.check_output(cmd,
universal_newlines=True, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, env=env)
except Exception as e:
result = e.output
if result.strip():
print("pylint doesn't approve of your program", file=sys.stderr)
print(result, file=sys.stderr)
print("Submission rejected", file=sys.stderr)
return False
else:
return True
__student_answer__ = """{{ STUDENT_ANSWER | e('py') }}"""
if code_ok(__student_answer__):
__student_answer__ += '\n' + """{{ TEST.testcode | e('py') }}"""
exec(__student_answer__)
The Twig syntax {{ STUDENT_ANSWER | e('py') }} results in the student's submission being filtered by an escape function appropriate for the language Python, which escapes all double quote and backslash characters with an added backslash.
Note that any output written to stderr is interpreted by CodeRunner as a runtime error, which aborts the test sequence, so the student sees the error output only on the first test case.
The full python3_cosc121 question type is much more complex than the
above, because it includes many extra features, enabled by use of
template parameters.
Some other complex question types that we've built using the technique described above include:
-
A Matlab question in which the template code (also Matlab) breaks down the student's code into functions, checking the length of each to make sure it's not too long, before proceeding with marking.
-
Another advanced Matlab question in which the template code, written in Python runs the student's Matlab code, then runs the sample answer supplied within the question, extracts all the floating point numbers is both, and compares the numbers for equality to some given tolerance.
-
A Python question where the student's code is actually a compiler for a simple language. The template code runs the student's compiler, passes its output through an assembler that generates a JVM class file, then runs that class with the JVM to check its correctness.
-
A Python question where the students submission isn't code at all, but is a textual description of a Finite State Automaton for a given transition diagram; the template code evaluates the correctness of the supplied automaton.
The second example above makes use of two additional CodeRunner features not mentioned so far:
-
the ability to set the Ace code editor, which is used to provide syntax highlighting code-entry fields, to use a different language within the student answer box from that used to run the submission in the sandbox.
-
the use of the QUESTION template variable, which contains all the attributes of the question including its question text, sample answer and template parameters.
As explained above, the Twig syntax {{ STUDENT_ANSWER | e('py') }} results in the student's submission being filtered by a Python escape function that escapes all double quote and backslash characters with an added backslash. The python escaper e('py') is just one of the available escapers. Others are:
-
e('java'). This prefixes single and double quote characters with a backslash and replaces newlines, returns, formfeeds, backspaces and tabs with their usual escaped form (\n, \r etc).
-
e('c'). This is an alias for e('java').
-
e('matlab'). This escapes single quotes, percents and newline characters. It must be used in the context of Matlab's sprintf, e.g.
student_answer = sprintf('{{ STUDENT_ANSWER | e('matlab')}}'); -
e('js'), e('html') for use in JavaScript and html respectively. These are Twig built-ins. See the Twig documentation for details.
Escapers are used whenever a Twig variable is being expanded within the template to generate a literal string within the template code. Usually the required escaper is that of the template language, e.g. e('py') for a template written in Python. Escapers must not be used if the Twig variable is to be expanded directly into the template program, to be executed as is.
When Twig is called to render the template it is provided with a set of
variables that we call the Twig context. The default Twig context for
per-test templates is defined in the section Per-test templates;
the default context for combinator templates is exactly the same except that
the TEST variable is replaced by a TESTCASES variable which is just an
array of TEST objects.
The question author can enhance the Twig context for a given question or question type by means of the Template parameters field. This must be either a JSON string or a program in some languages which evaluates to yield a JSON string. The latter option will be explained in the section Preprocessing of template parameters and for now we will assume the author has entered the required JSON string directly, i.e. that the Preprocessor drop-down has been set to None.
The template parameters string is a JSON object and its (key, value) attributes
are added to the QUESTION.parameters field of the QUESTION variable in
the Twig context. Additionally, if the Hoist template parameters checkbox is
checked, each (key, value) pair is added as a separate variable to the Twig context
at the top level.
The template parameters feature is very powerful when you are defining your own question types, as explained in User-defined question types. It allows you to write very general question types whose behaviour is then parameterised via the template parameters. This is much better than customising individual questions because customised questions no longer inherit templates from the base question type, so any changes to that base question type must then be replicated in all customised questions of that type.
For example, suppose we wanted a more advanced version of the python3_pylint question type that allows customisation of the pylint options via template parameters. We might also wish to insert a module docstring for "write a function" questions. Lastly we might want the ability to configure the error message if pylint errors are found.
The template parameters might be:
{
"isfunction": false,
"pylintoptions": ["--disable=missing-final-newline", "--enable=C0236"],
"errormessage": "Pylint is not happy with your program"
}
The template for such a question type might then be:
import subprocess
import os
import sys
import re
def code_ok(prog_to_test):
{% if QUESTION.parameters.isfunction %}
prog_to_test = "'''Dummy module docstring'''\n" + prog_to_test
{% endif %}
try:
source = open('source.py', 'w')
source.write(prog_to_test)
source.close()
env = os.environ.copy()
env['HOME'] = os.getcwd()
pylint_opts = []
{% for option in QUESTION.parameters.pylintoptions %}
pylint_opts.append('{{option}}')
{% endfor %}
cmd = ['pylint', 'source.py'] + pylint_opts
result = subprocess.check_output(cmd,
universal_newlines=True, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, env=env)
except Exception as e:
result = e.output
# Have to remove pylint's annoying config file output message before
# checking for a clean run. [--quiet option in pylint 2.0 fixes this].
result = re.sub('Using config file.*', '', result).strip()
if result:
print("{{QUESTION.parameters.errormessage | e('py')}}", file=sys.stderr)
print(result, file=sys.stderr)
return False
else:
return True
__student_answer__ = """{{ STUDENT_ANSWER | e('py') }}"""
if code_ok(__student_answer__):
__student_answer__ += '\n' + """{{ TEST.testcode | e('py') }}"""
exec(__student_answer__)
If Hoist template parameters is checked, all QUESTION.parameters. prefixes
can be dropped.
Sometimes question authors want to use template parameters to alter not just the template of the question but also its text, or its test case or indeed just about any part of it. This is achieved by use of the Twig all checkbox. If that is checked, all parts of the question can include Twig expressions. For example, if there is a template parameter function name, defined as, say,
{ "functionname": "find_first"}
the body of the question might begin
Write a function {{ functionname }}(items) that takes a list of items as a
parameter and returns the first ...
The test cases would then also need be parameterised, e.g. the test code might be
{{ functionname }}([11, 23, 15, -7])
The Twig all capability is most often used when randomising questions, as explained in the following sections.
As mentioned earlier, the template parameters do not need to be hard coded; they can be procedurally generated when the question is first initialised, allowing for the possibility of random variants of a question or questions customised for a particular student. The question author chooses how to generate the required template parameters using the Preprocessor dropdown in the Template controls section of the question editing form.
The simplest and by far the most efficient option is Twig. Selecting that option results in the template parameters field being passed through Twig to yield the JSON template parameter string. That string is decoded from JSON to PHP, to yield the Twig context for all subsequent Twig operations on the question. When evaluating the template parameters with Twig the only context is the STUDENT variable. The output of that initial Twig run thus provides the context for subsequent evaluations of the question's template, text, test cases, etc.
As a simple example of using Twig as a preprocessor for randomising questions we might have a template parameters field like
{ "functionname": "{{ random(["find_first", "get_first", "pick_first"]) }}" }
which will evaluate to one of
{ "functionname": "find_first"}
or
{ "functionname": "get_first"}
or
{ "functionname": "pick_first"}
If the Twig variable functionname is then used throughout the question (with Twig All checked), students will get to see one of three different variants of the question.
The topic of randomisation of questions, or customising them per student, is discussed in more length in the section Randomising questions.
When randomising questions you usually expect to get different outputs from the various tests. Computing the expected outputs for some given randomised input parameters can be difficult in Twig, especially when numerical calculations are involved. The safest approach is to precompute offline a limited set of variants and encode them, together with the expected outputs, into the twig parameters. Then Twig can simply select a specific variant from a set of variants as shown in the section Miscellaneous tips.
An alternative approach is to compute the template parameters in an alternative language of your choice - one that is supported by the sandbox (Jobe) server, e.g. Python Java etc. You set the template parameter Preprocessor language to your chosen language and fill the template parameters field with a program in that language. The standard output from that program must be a JSON string containing all the required template parameters. This is a very powerful method and makes complex randomisation much easier than in Twig.
However, using a template preprocessor other than Twig suffers from one major disadvantage. The evaluation of the template parameters takes place on the sandbox server, and when a student starts a quiz, all their questions using this form of randomisation initiate a run on the sandbox server and cannot even be displayed until the run completes. If you are running a large test or exam, and students all start at the same time, there can be thousands of jobs hitting the sandbox server within a few seconds. This is almost certain to overload it! Caveat emptor!
Using a template preprocessor other than Twig should be safe for lab and assignment use, when students are not all starting the quiz at the same time. We have also used it cautiously in exams at the University of Canterbury with courses of a few hundred students, but have been careful to ensure that not too many questions in the exam use this randomisation method. We have also mitigated the sandbox server overload risk by spreading the exam start times for students over several minutes. Lastly, we have two separate 8-core sandbox (Jobe) servers to give us a high throughput. Multiple Jobe servers are supported by listing them all, separated by a semicolon, in the CodeRunner settings Jobe server URL field.
If, despite the above warnings, you still wish to use this approach, here's how.
The template parameter program must print to standard output a single valid JSON string, which then is used in exactly the same way as if it had been entered into the template parameter field as pure JSON with no preprocessor. The program is given command line arguments specifying the random number seed that it must use and the various attributes of the student. For example, it should behave as if invoked from a Linux command line of the form:
blah seed=1257134 id=902142 username='amgc001' firstname='Angus' 'lastname=McGurk' email='angus@somewhere.ac'
The command line arguments are
- Seed (int): the random number seed. This must be used for any randomisation and the program must generate the same output when given the same seed.
- Student id number (int)
- Student username (string)
- Student first name (string)
- Student last name (string)
- Student email address (string)
The student parameters can be ignored unless you wish to customise a question differently for different students.
Here, for example, is a Python preprocessor program that could be used to ask a student to write a function that has 3 variant names to print the student's first name:
import sys, json, random
args = {param.split('=')[0]: param.split('=')[1] for param in sys.argv[1:]}
random.seed(args['seed'])
func_name = ['welcome_me', 'hi_to_me', 'hello_me'][random.randint(0, 2)]
first_name = args['firstname']
print(json.dumps({'func_name': func_name, 'first_name': first_name}))
The question text could then say:
Write a function {{ func_name }}() that prints a welcome message of the form "Hello {{ first_name }}!".
Note that this simple example is chosen only to illustrate the technique. It is a very bad example of when to use a preprocessor, as the job is more easily and more efficiently done in Twig, as explained in the section Randomising questions. Use of a non-Twig preprocessor is best suited to complex randomisation that is difficult or impossible in Twig, or when you need to use the same language as that of the question itself to ensure that the evaluation of any expression is exactly correct.
Note, too, that Twig All must be set.
When you select a preprocessor other than Twig, a checkbox 'Evaluate per run' is shown, and is initially unchecked. This controls when the preprocessor gets called. If you are using the template preprocessor for randomisation or for per-student customisation, you must check this option so that the preprocessor is invoked for each student when they start their attempt. As explained above, this can have serious load implications.
However, if you are using the template preprocessor for other purposes, e.g. to compute values within the question text in a non-randomised question without using an offline program you can leave Evaluate per run unchecked. In this case the template parameters will be computed only once, when the question is saved.
Although clumsy, this approach can also be used to compute the expected output values in the "For example" table. However, you then either need to replicate the sample answer within the template parameters program, or have that program define the sample answer as a string which it both uses internally to compute the expected outputs and which it also returns as one of the template parameters. Not recommended!
The template variable TEST, which is defined in the Twig context only when
Twig is rendering a per-test template, contains the following attributes:
TEST.rownumThe sequence number of this test (0, 1, 2 ...).TEST.questionidThe ID of the question being run. Not generally useful.TEST.testtypeThe type of test, relevant only when Precheck is enabled for the question and is set to Selected so that the author has control over which tests get run. 0 denotes "run this test only when Check is clicked, 1 denotes "run this test only when Precheck is clicked" and 2 denotes "always run this test".TEST.testcodeThe code for this test.TEST.extraWhatever text was entered by the author into the Extra field of this test.TEST.stdinThe standard input (as a text string) to be used when running this test. This isn't generally needed by the question author because CodeRunner by default copies it to a file and sets standard input to use that file when running the test.TEST.expectedThe expected output when running this test.TEST.useasexampleTrue (1) if the "Use as example" checkbox is checked for this test.TEST.displayOne of the string values "SHOW", "HIDE", "HIDE_IF_SUCCEED" or "HIDE_IF_FAIL".TEST.hiderestiffailTrue (1) if the "Hide rest if fail" checkbox is checked for this test.TEST.markHow many marks to allocate to this test. Meaningful only if not using "All or nothing" grading.TEST.orderingThe number entered by the question author into the Ordering field of the test.
The template variable TESTCASES, which is defined in the Twig context only when
Twig is rendering a combinator template, is just a list of TEST objects, as
defined in the previous section.
The template variable QUESTION is an object containing a
subset of the fields of the PHP question object.
By far the most import fields are:
QUESTION.idThe unique internal ID of this question.QUESTION.questionidSame asQUESTION.id- deprecated.QUESTION.parametersA Twig object whose (key, value) pairs are the result of merging the evaluated template parameters of the prototype with those of the question itself. These template parameters can either by used in Twig code like {{ QUESTION.parameters.someparam }} or, it hoisttemplateparams was set in the question authoring form, simply as {{ someparam }}.QUESTION.uiparametersA Twig object whose (key, value) pairs are the result of merging the UI parameters of the prototype with those of the question itself. These template parameters must be referenced in Twig code like {{ QUESTION.uiparameters.someparam }}; they are not available as global variables.QUESTION.answerThe supplied sample answer (null if not explicitly set).
Other fields are:
QUESTION.nameThe name of the question.QUESTION.generalfeedbackThe contents of the general feedback field in the question authoring form.QUESTION.generalfeedbackformatThe format of the general feedback. 0 = moodle, 1 = HTML, 2 = Plain, 3 = Wiki, 4 = Markdown.QUESTION.questiontextThe question text itselfQUESTION.answerpreloadThe string that is preloaded into the answer box.QUESTION.stepinfo. An object with info regarding the current step. Attributes are preferredbehaviour, numchecks, numprechecks and fraction being respectively the behaviour set for the quiz in which the question is running, the number of times the user has clicked Check prior to this submission, the number of times the user has clicked Precheck prior to this submission, and the best fraction (0 - 1) the student has achieved so far on this question (not including this submission). Additionally, if a combinator template grader is being used and the question author has chosen to report the grader state in a previous submission, a string-valued attribute graderstate may be present. The use of this is entirely over to the question author. See under Combinator-template grading.QUESTION.languageThe language being used to run the question in the sandbox, e.g. "Python3".QUESTION.precheckThe setting of the precheck dropdown: 0 = no precheck, 1 = empty, 2 = precheck examples, 3 = precheck selected, 4 = all.QUESTION.hidecheckTrue if the Hide check checkbox is set.QUESTION.iscombinatortemplateTrue if this is a combinator question.QUESTION.penaltyregimeThe penalty regime for this question.QUESTION.globalextraExtra data for use by template authors, global to all tests.QUESTION.prototypeextraExtra data for use by prototype or customised code.QUESTION.useace'1'/'0' if the ace editor is/is not in use.QUESTION.acelangThe language for the Ace editor to use for syntax colouring etc.QUESTION.allowmultiplestdinsTrue if the author has requested all tests be run in a single sandbox submission despite the existence of standard input in the questions.QUESTION.sandboxThe sandbox being used, e.g. "jobesandbox".QUESTION.graderThe PHP grader class being used, e.g. "EqualityGrader".QUESTION.allornothingTrue if all-or-nothing grading has been requested.QUESTION.cputimelimitsecsThe allowed CPU time (null unless explicitly set).QUESTION.memlimitmbThe allowed memory in MB (null unless explicitly set).QUESTION.sandboxparamsThe JSON string used to specify the sandbox parameters in the question authoring form (null unless explicitly set).QUESTION.uipluginThe UI plugin in use.QUESTION.resultcolumnsThe JSON string used in the question authoring form to select which columns to display, and how to display them (null unless explicitly set).QUESTION.attachmentsHow many attachments are allowed. -1 means unlimited.QUESTION.attachmentsrequiredThe minimum number of attachments that must be included in a submission.QUESTION.displayfeedbackControls the feedback display (result table). 0 to allow display of specific feedback to be controlled by the quiz's review options, 1 to force display, 2 to force hide.
Most of these are effectively read only - assigning a new value within the
template to the cputimelimitsecs attribute does not alter the actual run time;
the assignment statement is being executed in the sandbox after all resource
limits have been set. The question author can however directly alter all
the above question attributes directly in the question authoring form.
The template variable STUDENT is an object containing a subset of the fields of the
PHP user object. The fields/attributes of STUDENT are:
STUDENT.idThe unique internal id of the current user (an integer).STUDENT.usernameThe unique internal username of the current user.STUDENT.firstnameThe first name of the current user.STUDENT.lastnameThe last name of the current user.STUDENT.emailThe email address of the current user.
Twig has a macro capability that provides something akin to functions in normal programming languages. Macros can be stored in one Twig template and imported from there into another.
In the CodeRunner context there is only a single template available at any time - usually the question's so-called template field, although other question fields are expanded if TwigAll is set. CodeRunner does not provide access to an associated file system from which templates of macros can be loaded or created by question authors. However, CodeRunner does provide a few macros in a support (pseudo) template named "html". These macros are primarily intended for use with the Html UI (q.v.); each one inserts a named HTML element into the template that is being expanded. As an example, if the question author includes the following in a question field
{% from 'html' import input %}
...
{{ input('fieldname', 15) }}
and that question is subject to Twig expansion, the invocation of the input macro will generate the HTML code
<input name="somename" class="coderunner-ui-element" width="15">
All macros name take a mandatory name parameter and additional parameters as follows. Optional parameters and their default values are indicated with an equals sign.
input(name, width=10)generates an input element as in the above example.textarea(name, rows=2, cols=60)to generate an HTML textarea element.select(name, options)generates an HTML select element with a sequence of embeddedoptionelements as defined by the second parameter, which must be an array with elements that are either strings or 2-element string arrays. If a single string is provided as the array elements, it is used as both the value attribute of the option element and its inner HTML. If a 2-element array is provided, the first string is used as the value and the second as the inner HTML.radio(name, items)generates a vertically-aligned sequence of mutually exclusive radio buttons, one for each of the elements of theitemsparameter, which must be an array with elements that are either strings or 2-element string arrays. As with select options, if an element is a single string it is used as both the radio button label and its value. But if a 2-element array is provided, the first element is the value attribute of theinputelement (the radio button) and the second is the label.checkbox(name, label, ischecked=false)generates a checkbox with the given name, and label, which is checked only if ischecked is true.
To reduce the risk that the UI element names conflict with existing UI element
names in the Moodle page, all names are prefixed by crui_.
The question authoring form allows the author to provide students with a Precheck button in addition to the normal Check button. This is intended to allow students to do a penalty-free preliminary sanity check on their submission. The form of the sanity check can be controlled by the question author, but in the simplest case it is just a syntax check on their code.
When the Precheck button is clicked, the answer is submitted for grading in the normal way except:
- A Twig variable IS_PRECHECK is set to True. This is typically used by template graders to control the feedback that is given to the student when prechecking versus when doing a full check.
- The set of testcases to be run is restricted according to the setting of
the Precheck dropdown menu in the authoring form. Options are:
- Empty: The list of testcases is a single empty testcase, which is a hidden test with the empty string for testcode, stdin, expected and extra.
- Examples. The set of testcases is all the ones with the Use as example checkbox checked.
- Selected. If this option has been chosen, each test case has a dropdown menu labelled Precheck test type, with options Check only, Precheck only and Both. The set of cases on a Precheck is then all those marked either Precheck only or Both, while the set of cases on a full Check is all those marked either Check only or Both.
- All. All testcases are included, as with a normal Check. This is meaningful only if the question author has made use of the IS_PRECHECK Twig variable to provide different feedback from the normal.
The feedback presented to the student contains the output from the run, as with a full check, but no marking takes place, so there are no penalties. Additionally the correctness of the Precheck is indicated to the student by a striped background shading that is blue for an OK submission and red for a failed one. There may also be a "Precheck failed" warning message.
The correctness of the precheck is determined as follows.
- If the Empty precheck option has been set, and a combinator template grader has not been used, any output (which is usually compile errors) is taken to denote a failed precheck. In this case, there is also an extra "Precheck failed" or "Precheck passed" message.
- If a combinator template grader is being used, the Precheck is deemed correct if the returned Fraction is 1.
- In all other cases, i.e. when a subset of test cases is being run, the Precheck is correct only if all tests pass.
As explained in the section Preprocessing with Twig, randomisation is achieved through a template parameter pre-process that generates a randomised set of template parameters. The various template parameters are then used throughout the question, by setting the Twig All checkbox.
Although there are many different template parameter preprocessors available, the rest of this discussion will focus only on the use of Twig as the preprocessor. The use of alternative languages as preprocessors is sometimes useful when different template parameters have dependencies that are not easily computed by Twig. However, because preprocessing has to be done on the Jobe sandbox when a question is first instantiated use of a preprocessor other than Twig can have a huge performance impact at the start of a test or exam, so use of non-Twig preprocessors should be used with caution.
As a trivial example of randomisation, consider a generalisation of a Hello world
program that asks students to write a program that prints Hello <name>,
where there are many different values for name. A Python version of the above
example above is easily achieved,
albeit with only four different names, as follows:
-
Set the template parameters field of the question authoring form to
{ "name": "{{ random(["Bob", "Carol", "Ted", "Alice"]) }}" }
-
Turn on the Twig All checkbox, so that all fields of the question will get processed by Twig, once the template parameters have been set up.
-
Turn on the Hoist template parameters checkbox if necessary. It's on by default for new questions but off for old questions.
-
Set the question text to Write a program that prints
Hello {{ name }} -
Set the expected output of the first test case to
Hello {{ name }} -
Set the sample answer to
print("Hello {{name}}")
The underlying mechanism will now be explained in more detail. It assumes the reader already understands the basic workings of CodeRunner, in particular how the Twig template engine is used to convert the question's template into an executable program and how that process can be parameterised by use of CodeRunners template parameters
When a student starts a Moodle quiz, an instance of each quiz question is generated. As each quiz question is instantiated, certain variables need to be defined, such as the order in which shuffled options will be presented in a multichoice question. These variables are essentially "frozen" throughout the lifetime of that particular question instance, including when it is subsequently reviewed or regraded.
When a CodeRunner question is instantiated with the template parameters preprocessor set to Twig, the template parameters field is processed by the Twig template engine. It is assumed that the template parameters field includes some embedded Twig, which will make at least one call to the Twig random function. This results in one or more template parameters having randomised values. The above example shows a case in which the template parameter "name" is assigned a randomly-chosen value from a list of options. Another common variant is
{ "number": {{ 5 + random(7) }} }
which will result in the template parameter number having a uniformly distributed integer value in the range 5 to 12 inclusive.
If the Twig All checkbox for the question is checked, all other text fields of the question, except for the template itself, are processed by Twig directly after the template parameters field has been Twigged. This yields new values for the question text, test cases etc, which are used throughout the question's lifetime. The Twig environment used when processing all these other fields is that defined by the Twigged template parameters field.
It is usual to click the Twig All checkbox with randomised questions, as otherwise only the template will be subject to randomisation, which isn't usually appropriate.
CodeRunner adds a new function set_random_seed(seedvalue) to Twig. This is a call through to the underlying PHP mt_srand function to define the state of the pseudo random number generator. The return value is the empty string. If a call to this function is made from within the Twigged template parameters before any calls are made to the random function, the same sequence of randomisations will be performed every time the question is attempted. If the id field of the Twig STUDENT variable is used as the seed value, the effect is then that a particular student only ever sees one variant of the question, no matter how often they attempt a question. A typical use might be to begin the template parameters with the line
{{- set_random_seed(STUDENT.id) -}}
Tip: don't add this line until you've checked out several variants of the question, because once you've added it, you'll only ever see the one variant yourself.
The above description is a slight simplification. It implies that all the Twig-expanded template parameters are recorded within the question instance and frozen throughout the question lifetime. Such an approach, while technically "correct", creates problems for question authors who, after a quiz has gone live, discover they need to make changes to the non-randomised template parameters. For example, a template parameter that sets a limit on the allowed number of lines of code might turn out to be too restrictive. The author might wish to raise the limit and regrade existing submissions with the changed parameters. If the parameters were strictly frozen, this wouldn't be possible. So instead the implementation records only the random number seed, and rebuilds the set of template parameters whenever the question is reloaded from the database.
However, it is vital that question authors do not make any changes that might alter the randomised template parameters once a quiz has gone live. For example, re-ordering the randomised parameters will result in their being given different values when the question is reloaded. The student will then see a different question, to which their answer is no longer correct. Regrading would then result in their getting zero marks for a question they have already passed. Even if they've submitted and closed the quiz, they will find, if they subsequently review it, that their answer doesn't match the question.
To recap: once a quiz has gone live, you must ensure that any editing of the template parameters does not alter the randomisation behaviour.
Caveat Emptor.
Prior to the implementation of randomisation, template parameters were used
only within the template, where it was standard practice to
refer to template parameters with the syntax {{QUESTION.parameters.x}} where
x is a parameter. However, that syntax becomes very clumsy when the same
parameters is being used in lots of different places within the question.
There is now a checkbox Hoist template parameters, which copies the
template parameters into the Twig global name space, where STUDENT_ANSWER,
TEST etc reside. The variable x can then be inserted into the text simply
by writing {{ x }}.
C++ programmers might wish to think of this as similar to the line
using namespace std;
Hoisting was not done automatically because it might have broken existing questions if the Twig code were using similar variables globally. Hence, when upgrading an older version of CodeRunner to one that has randomisation, the Hoist template parameters checkbox is set to false. However, it is set to true on newly created questions.
-
Read the Twig documentation!
-
Check out the sample questions in the question export file
randomisationexamples.xmlin the CodeRunner samples folder. -
Sometimes you need a set of random variables to be "coupled". For example you might want an
animalto be one ofdog,cat,cowand an associated variablesoundto be respectivelywoof,miaow,moo. Three ways of achieving this are:-
Create a single random
indexvariable and use that to index into separate animal and sound lists. For example:{ {% set index = random(2) %} "animal": "{{ ["Dog", "Cat", "Cow"][index] }}", "sound": "{{ ["Woof", "Miaow", "Moo"][index] }}" -
Select an animal at random from a list of Twig 'hash' objects, then plug each of the animal attributes into the JSON record. For example:
{ {% set obj = random([ {'name': 'Dog', 'sound': 'Woof'}, {'name': 'Cat', 'sound': 'Miaow'}, {'name': 'Cow', 'sound': 'Moo'} ]) %} "animal": "{{ obj.name }}", "sound": "{{ obj.sound }}" } -
Select an animal at random from a list of Twig 'hash' objects as above, but then json_encode the entire object as a single template parameter. For example
{ {% set animal = random([ {'name': 'Dog', 'sound': 'Woof'}, {'name': 'Cat', 'sound': 'Miaow'}, {'name': 'Cow', 'sound': 'Moo'} ]) %} "animal": {{ animal | json_encode }} }
In the last case, the template parameters will need to be referred to as {{ animal.name }} and {{ animal.sound }} instead of {{ animal }} and {{ sound }}.
-
-
Since the Twig output must be JSON, and newlines aren't allowed in JSON strings, you may find the Twig whitespace control modifiers (
{{-and-}}) useful in more complex Twig programs. As an example, the following Twig code uses a recursive macro plus whitespace control modifiers to generate a JSON structure that defines a valueexpression, which is a random fully-parenthesised infix expression.{% macro randomexpr(depth) %} {% from _self import randomexpr as expr %} {% if depth >= 5 %}{# Leaf nodes are random operands #} {{- random(["a", "b", "c", "d"]) -}} {% else %}{# Internal nodes are of the form ( expr op expr ) #} {{- '(' -}} {{- expr(depth + 1 + random(3)) -}} {{- random(['*', '/', '+', '-']) -}} {{- expr(depth + 1 + random(3)) -}} {{- ')' -}} {% endif %} {% endmacro %} {% import _self as exp %} { "expression": "{{ exp.randomexpr(0) }}"}
This generates expressions like
(((c+b)+d)-(a*((c-a)-d)))
and
(((a/(a-d))-(c/b))+(d+(((d/c)/d)*(c+a))))
-
The TwigFiddle web site is useful for debugging Twig code in your template parameters. You can enter your template parameter field, click Run, and see the resulting JSON. Alternatively, you can set up a trivial question that simply prints the values of the QUESTION.parameters Twig variable. For example (in Python)
print("""{{QUESTION.parameters | json_encode}}""")
Grading of student submissions can be problematic in some situations. For example, you may need to ask a question where many different valid program outputs are possible, and the correctness can only be assessed by a special testing program. Or you may wish to subject a student's code to a very large number of tests and award a mark according to how many of the test cases it can handle. The usual exact-match grader cannot handle these situations. For such cases the TemplateGrader option can be selected in the Grading field of the question authoring form, after clicking the Customise checkbox. The template code then has a somewhat different role: the output from running the expanded template program is required to be a JSON string that defines the mark allocated to the student's answer and provides appropriate feedback.
A template grader behaves in two very different ways depending on whether the template is a per-test template or a combinator template.
When the template is a per-test template and a TemplateGrader is selected, the output from the program must be a JSON string that defines one row of the test results table. [Remember that per-test templates are expanded and run once for each test case.] The JSON object must contain at least a 'fraction' field, which is multiplied by TEST.mark to decide how many marks the test case is awarded. It should usually also contain a 'got' field, which is the value displayed in the 'Got' column of the results table. The other columns of the results table (testcode, stdin, expected) can, if desired, also be defined by the template grader and will then be used instead of the values from the test case. As an example, if the output of the program is the string
{"fraction":0.5, "got": "Half the answers were right!"}
half marks would be given for that particular test case and the 'Got' column would display the text "Half the answers were right!".
For even more flexibility the result_columns field in the question editing form can be used to customise the display of the test case in the result table. That field allows the author to define an arbitrary number of arbitrarily named result-table columns and to specify using printf style formatting how the attributes of the grading output object should be formatted into those columns. For more details see the section on result-table customisation.
Writing a grading template that executes the student's code is, however, rather difficult as the generated program needs to be robust against errors in the submitted code. The template-grader should always return a JSON object and should not generate any stderr output.
Although template graders can be written in any language, the developer finds it convenient to write them in Python, regardless of the language in which the student answer is written. Python's subprocess module can be used to execute the student code plus whatever test code is required. This ensures that errors in the syntax or runtime errors in the student code do not break the template program itself, allowing it to output a JSON answer regardless. Some examples of per-test template graders are given in the section Template grader examples.
Sometimes the author of a template grader wishes to abort the testing of the
program after a test case, usually the first, e.g. when pre-checks on the
acceptability of a student submission fail. This can be achieved by defining
in the output JSON object an extra attribute abort, giving it the boolean
value true. If such
an attribute is defined, any supplied fraction value will be ignored, the
test case will be marked wrong (equivalent to fraction = 0) and all further
test cases will be skipped. For example:
{"fraction":0.0, "got":"Invalid submission!", "abort":true}
Note to Python programmers: the Python boolean literals are True and False but the
JSON boolean literals are true and false. The superficial similarity of JSON objects
to Python dictionaries is also confusing. Usually, in Python, you will generate
the JSON objects using the dumps function in the json module, passing it a
Python dictionary, further adding to the confusion!
For example, to generate the above JSON output (with lower case t in true)
you would write
json.dumps({"fraction":0.0, "got":"Invalid submission!", "abort":True})
The ultimate in grading flexibility is achieved by use of a "Combinator
template grader", i.e. a TemplateGrader with the Is combinator checkbox checked.
In this mode, the JSON string output by the template grader
should again contain a 'fraction' field, this time for the total mark,
and may contain zero or more of the following attributes:
- prologuehtml: this is html that is displayed before the (optional) result table.
- epiloguehtml: this is html that is displayed after the (optional) result table.
- introductorhtml: this is like epiloguehtml except that it is visible only to instructors.
- testresults: is a list of lists used to display a result table similar to that displayed by the built-in question types. The first row is the column-header row and all other rows define the table body. Two special column header values exist: 'iscorrect' and 'ishidden'. The 'iscorrect' column(s) are used to display ticks or crosses for 1 or 0 row values respectively. The 'ishidden' column isn't actually displayed but 0 or 1 values in the column can be used to turn on and off row visibility. Students do not see hidden rows but markers and other staff do.
- columnformats: this field is only meaningful if there is a testresults field. It is a list of format specifier strings, one per table column excluding the optional ishidden and iscorrect columns. Each format specifier should either be '%s', in which case all formatting is left to the renderer (which sanitises the field and encloses it in a <pre> element) or '%h' in which case the table cell is displayed directly without further processing. '%s' formatting is the default in the absence of an explicit 'columnformats' field.
- showoutputonly: if set true, this results in the prologuehtml and epiloguehtml fields being displayed against a neutral background with the usual outcome message (e.g. "Passed all tests") suppressed. The mode is intended for use in pseudo-questions that can be used by students to experiment with a given bit of code. The 'fraction' attribute is not required and is ignored if given. Since a mark is still required by the framework when a question is checked, full marks are awarded regardless of the result of the run but questions of this sort would normally not contribute marks towards a student's grade.
- showdifferences: if set true, the standard 'Show differences' button will be displayedafter the result table if full marks were not awarded to the question.
- graderstate: this is a string value that is stored in the database with the question attempt and is passed back to the combinator template grader code on the next attempt of that question as the field 'graderstate' of the 'QUESTION.stepinfo' object. The use of this variable is entirely at the discretion of the question author; the facility is available only to allow question authors to grade a submission differently according to what was previously submitted. It could, for example, be a json-encoded record of the correctness of the different tests.
- files (new, experimental): this allows the question author to return
temporary files that are displayed within the response page. It is
a JSON object mapping filenames to the corresponding
base4 encoded file contents. This parameter is intended primarily for returning image files
that will be displayed in the feedback, but could have other uses. If a 'files'
attribute is present, the files are written to the Moodle file area and
URLs generated to reference those files. The URLs are then used to update any
occurrences of the strings
src="filename"orhref="filename"within the 'prologuehtml', 'testresults', 'epiloguehtml' and 'instructorhtml' attributes to use the full URL instead of just the filename. Unmatched filenames are disregarded. Single quotes instead of double quotes can also be used in the 'src' and 'href' attribute assignments. Files are timestamped so the same filename can be used unambiguously in multiple grade responses. Warning: the files created in this way are temporary in the sense that they will not survive a course backup/restore sequence. They should only be referenced from within the question grading response. If really needed after a course restore they can be regenerated by a regrade.
Combinator-template grading gives the user complete control of the feedback to the student as well as of the grading process. The ability to include HTML in the feedback allows for complex output containing SVG or images.
The combinator-template grader has available to it the full list of all test cases and their attributes (testcode, stdin, expected, mark, display etc) for use in any way the question author sees fit. It is highly likely that many of them will be disregarded or alternatively have some meaning completely unlike their normal meaning in a programming environment. It is also possible that a question using a combinator template grader will not make use of test cases at all. For example it might test the students code with thousands of random tests and display just a few of the failing cases using the result table.
In this section we look at two uses of a per-test-case template grader, both implemented in Python3. The first example shows how we can grade a student submission that isn't actually code to be run but is some text to be graded by a program. The second example, which is a bit more complicated, shows how we can test student code in a more complex manner than simply running tests and matching the output against the expected output.
For a more comprehensive example, inspect the dotnet C# question prototype in the distribution's unsupported question types folder.
A simple case in which one might use a template grader is where the answer supplied by the student isn't actually code to be run, but is some sort of raw text to be graded by computer. For example, the student's answer might be the output of some simulation the student has run. To simplify further, let's assume that the student's answer is expected to be exactly 5 lines of text, which are to be compared with the expected 5 lines, entered as the 'Expected' field of a single test case. One mark is to be awarded for each correct line, and the displayed output should show how each line has been marked (right or wrong).
A template grader for this situation might be the following
import json
got = """{{ STUDENT_ANSWER | e('py') }}"""
expected = """{{ TEST.expected | e('py') }}"""
got_lines = got.split('\n')
expected_lines = expected.split('\n')
mark = 0
if len(got_lines) != 5:
comment = "Expected 5 lines, got {}".format(len(got_lines))
else:
comment = ''
for i in range(5):
if got_lines[i] == expected_lines[i]:
mark += 1
comment += "Line {} right\n".format(i)
else:
comment += "Line {} wrong\n".format(i)
print(json.dumps({'got': got, 'comment': comment, 'fraction': mark / 5}))
Note that in the above program the Python dictionary
{'got': got, 'comment': comment, 'fraction': mark / 5}
gets converted by the call to json.dumps to a JSON object string, which looks syntactically similar but is in fact a different sort of entity altogether. You should always use json.dumps, or its equivalent in other languages, to generate a valid JSON string, handling details like escaping of embedded newlines.
In order to display the comment column in the output JSON, the 'Result columns' field of the question (in the 'customisation' part of the question authoring form) should include that field and its column header, e.g.
[["Expected", "expected"], ["Got", "got"], ["Comment", "comment"], ["Mark", "awarded"]]
Note that the 'awarded' value, which is what is displayed in the 'Mark' column, is by default computed as the product of the faction and the number of marks allocated to the particular test case. You can alternatively include an 'awarded' attribute in the JSON but this is not generally recommended; if you do this, make sure that you award a mark in the range 0 to the number of marks allocated to the test case.
The following two images show the student's result table after submitting a fully correct answer and a partially correct answer, respectively.
A template-grader can also be used to grade programming questions when the usual graders (e.g. exact or regular-expression matching of the program's output) are inadequate.
As a simple example, suppose the student has to write their own Python square root function (perhaps as an exercise in Newton-Raphson iteration?), which is to be named my_sqrt. Their function is required to return an answer that is within an absolute tolerance of 0.000001 of the correct answer. To prevent them from using the math module, any use of an import statement would need to be disallowed but we'll ignore that aspect in order to focus on the grading aspect.
The simplest way to deal with this issue is to write a series of testcases of the form
approx = my_sqrt(2)
right_answer = math.sqrt(2)
if math.abs(approx - right_answer) < 0.00001:
print("OK")
else:
print("Fail (got {}, expected {})".format(approx, right_answer))
where the expected output is "OK". However, if one wishes to test the student's code with a large number of values - say 100 or more - this approach becomes impracticable. For that, we need to write our own tester, which we can do using a template grader.
Template graders that run student-supplied code are somewhat tricky to write correctly, as they need to output a valid JSON record under all situations, handling problems like extraneous output from the student's code, runtime errors or syntax error. The safest approach is usually to run the student's code in a subprocess and then grade the output.
A per-test template grader for the student square root question, which tests the student's my_sqrt function with 1000 random numbers in the range 0 to 1000, might be as follows:
import subprocess, json, sys
student_func = """{{ STUDENT_ANSWER | e('py') }}"""
if 'import' in student_func:
output = 'The word "import" was found in your code!'
result = {'got': output, 'fraction': 0}
print(json.dumps(result))
sys.exit(0)
test_program = """import math
from random import uniform
TOLERANCE = 0.000001
NUM_TESTS = 1000
{{ STUDENT_ANSWER | e('py') }}
ok = True
for i in range(NUM_TESTS):
x = uniform(0, 1000)
stud_answer = my_sqrt(n)
right = math.sqrt(x)
if abs(right - stud_answer) > TOLERANCE:
print("Wrong sqrt for {}. Expected {}, got {}".format(x, right, stud_answer))
ok = False
break
if ok:
print("All good!")
"""
try:
with open('code.py', 'w') as fout:
fout.write(test_program)
output = subprocess.check_output(['python3', 'code.py'],
stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, universal_newlines=True)
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
output = e.output
mark = 1 if output.strip() == 'All good!' else 0
result = {'got': output, 'fraction': mark}
print(json.dumps(result))
The following figures show this question in action.
Obviously, writing questions using template graders is much harder than using the normal built-in equality based grader. It is usually possible to ask the question in a different way that avoids the need for a custom grader. In the above example, you would have to ask yourself if it mightn't have been sufficient to test the function with 10 fixed numbers in the range 0 to 1000 using ten different test cases of the type suggested in the third paragraph of this section.
The output from the standard graders is a list of so-called TestResult objects, each with the following fields (which include the actual test case data):
testcode // The test that was run (trimmed, snipped)
iscorrect // True iff test passed fully (100%)
expected // Expected output (trimmed, snipped)
mark // The max mark awardable for this test
awarded // The mark actually awarded.
got // What the student's code gave (trimmed, snipped)
stdin // The standard input data (trimmed, snipped)
extra // Extra data for use by some templates
A field called result_columns in the question authoring form can be used to control which of these fields are used, how the columns are headed and how the data from the field is formatted into the result table.
By default the result table displays the testcode, stdin, expected and got columns, provided the columns are not empty. Empty columns are dropped from the table. You can change the default, and/or the column headers by entering a value for result_columns (leave blank for the default behaviour). If supplied, the result_columns field must be a JSON-encoded list of column specifiers.
The default value in English is
[["Test", "testcode"], ["Input", "stdin"], ["Expected", "expected"], ["Got", "got"]]
The column headers are language dependent.
Each column specifier is itself a list,
typically with just two or three elements. The first element is the
column header, the second element is usually the field from the TestResult
object being displayed in the column (one of those values listed above) and the optional third
element is an sprintf format string used to display the field.
Per-test template graders can add their
own fields, which can also be selected for display. It is also possible
to combine multiple fields into a column by adding extra fields to the
specifier: these must precede the sprintf format specifier, which then
becomes mandatory. For example, to display a Mark Fraction column in the
form 0.74 out of 1.00, a column format specifier of ["Mark Fraction", "awarded", "mark", "%.2f out of %.2f"] could be used.
As a special case, a format
of %h means that the test result field should be taken as ready-to-output
HTML and should not be subject to further processing; this can be useful
with custom-grader templates that generate HTML output, such as
SVG graphics, and we have also used it in questions where the output from
the student's program was HTML.
NOTE: %h format requires PHP >= 5.4.0 and Libxml >= 2.7.8 in order to
parse and clean the HTML output.
It was stated above that the values to be formatted by the format string (if given) were fields from the TestResult object. This is a slight simplification. The syntax actually allows for expressions of the form:
filter(testResultField [,testResultField]... )
where filter is the name of a built-in filter function that filters the
given testResult field(s) in some way. Currently the only such built-in
filter function is diff. This is (or was) a function
taking two test result fields as parameters and
returning an HTML string that representing the first test field with embedded
HTML <ins> and <del> elements that show the insertions and deletions
necessary
to convert the first field into the second. This was used to provide support
for the Show Differences button, which the user could click in order to
highlight differences between the Expected and Got fields. However that
functionality is now provided by JavaScript; the Show Differences button is
automatically displayed if an answer is being marked wrong and if an
exact-match grader is being used. Hence the diff filter function
is no longer functional but it remains supported syntactically to support
legacy questions that use it.
The default value of result_columns is:
[["Test", "testcode"], ["Input", "stdin"], ["Expected", "expected"], ["Got", "got"]].
For normal programming questions, the Ace editor is used both for author editing of the templates and for the student answer. Ace provides syntax colouring, bracket matching, auto indent and many other programmer-oriented capabilities to make editing of the underlying pure text more user-friendly.
Sometimes question authors ask questions in which the answer is not in fact program code. For example, it might be a textual representation of an FSM (finite state machine). In such questions the Ace editor is often not appropriate. Prior to version 3.3, authors could turn off the Ace editor by unchecking a Use Ace checkbox, but this disabled it both for student answers and for the author's template.
Since version 3.3.0, CodeRunner now supports pluggable user interfaces, although an administrator has to install the plugin. The user interfaces currently built in to CodeRunner are Ace, Ace-gapfiller, Gapfiller, Graph, Scratchpad and Table. The question author selects the required user interface via a dropdown menu in the customisation section of the question author form. The selection controls editing of the sample answer and answer preload fields of the authoring form and the student's answer in the live quiz. The Ace editor is always used for editing the template itself, unless turned off with the Template uses ace checkbox in the authoring form.
The value of the STUDENT_ANSWER variable seen by the template code is different for the various UI plugins. For example, with the Ace editor the STUDENT_ANSWER is simply the raw text edited by Ace, while for the Ace-gapfiller it's a JSON list of the string values that the student entered into the gaps.
Most UI plugins support a few configuration options via a UI parameters entry field in the question authoring form.
All active CodeRunner user interface plugins in both the question authoring form and the student's quiz page can be toggled off and on with a CTRL-ALT-M keypress, alternately exposing and hiding the underlying textarea element.
The general behaviour, serialisation and UI parameters of the supported plugins are as follows.
This is the default UI interface and is the one most-commonly used for programming questions.
The serialisation is simply the raw text that the Ace editor is displaying.
Mostly the default configuration options will be used but a few specialised UI parameters exist:
-
auto_switch_light_dark. If true, this parameter allows a browser or OS colour-scheme preference for a dark theme to override the default Ace theme setting for a question. Default: false.
-
font_size. The font-size for the Ace editor. Default: 14 px.
-
import_from_scratchpad. True to allow the Ace editor to detect that a question appears to have been configured for the scratchpad UI, and extract the actual code from the JSON. Should not be changed from its default of true unless you want students to edit JSON objects with an 'answer_code' key. Default: true.
-
live_autocompletion. Turns on the Ace editor auto-complete function.
-
theme. The theme to be used by the ace editor. Type ctrl + ',' within the Ace editor to see a list of available themes. Default: textmate.
If a user uses the ctrl + ',' option to select a theme, this theme will be used in all Ace editor windows within that browser until changed back.
A UI that presents the user with an Ace editor window containing code with some gaps in it. The user is expected to fill in the gaps. Only simple gaps at most one line in length are supported.
The text to be displayed in the editor window is by default the contents of the globalextra field in the question author form, but can alternatively be set from the code in the first test case (see the ui_source UI parameter below). The text will normally be most of a program but with one or more bits replaced by a gap specifier of the form
{[20-40]}
where the two numbers are the default field width and maximum field width respectively. It the second number (and the preceding '-') is omitted, the field width can expand arbitrarily.
For example (a case in which the source is test0):
The serialisation is a JSON list of strings, which are the values entered by the student into the gaps.
- ui_source. This parameter specifies where to get the source text to be displayed in the editor (with gaps as specified above). The default value is "globalextra" but the alternative is "test0". In the latter case, the contents of the test code field of the first test is used. In this latter case, all other test cases should contain corresponding gap fillers and the result table will substitute the student's gap fillers into all tests with syntax colouring to denote the substitution. In this mode, you can't use the "Use as example" feature because the test code isn't defined until the student has filled in the gaps.
This plugin is an older version of the Ace gapfiller UI and has largely been superseded by it. It does have one advantage over the Ace gapfiller: it allows for multiline HTML text area gaps as well as single line HTML input elements. But the program is displayed as simple non-syntax-coloured text.
This UI replaces the usual textarea answer box with a div consisting of pre-formatted text supplied by the question author in either the "globalextra" field or the testcode field of the first test case, according to the ui parameter ui_source (default: globalextra). HTML entry or textarea elements are then inserted at specified points. It is intended primarily for use with coding questions where the answerbox presents the students with code that has smallish bits missing, but it can also be used in non-coding questions.
The locations within the globalextra text at which the input elements are to be inserted are denoted by "tags" of the form
{[ size ]}
for an HTML input element
or
{[ rows, columns ]}
for a textarea element
where size, rows and column are integer literals. These respectively inject an HTML input element or a textarea element of the specified size.
The serialisation of the answer box contents, i.e. the text that is copied back into the textarea for submission as the answer, is simply a list of all the field values (strings), in order.
As a special case of the serialisation, if the value list is empty, the serialisation itself is the empty string.
-
ui_source. As with the Ace gapfiller, this sets the source for the program source with the inserted gaps. It can be set to "globalextra" to take the HTML from the globalextra field or to "test0" to take if from the test code of the first test case.
-
delimiters. A 2-element array of the strings used to open and close the gap description. Default ["{[", "]}"]
-
sync_interval_secs. The time interval in seconds between calls to sync the UI contents back to the question answer. 0 for no such auto-syncing.
The Graph UI plugin provides simple graph-drawing capabilities to support questions where the student is asked to draw or edit a graph. By default the Graph UI, which was developed for Finite State Machines, draws directed graphs, allows nodes to be marked as Accept states and allows incoming start edges. For example:
Clicking the Help button on the graph canvas displays information on how to draw graphs.
The serialised Graph UI STUDENT_ANSWER is a JSON object with the following attributes:
-
nodes. An array of 2-element arrays [nodelabel, is_acceptor]. The 'is_acceptor' value is a boolean that's true for accept state nodes in FSM graphs, false otherwise.
-
edges. An array of 3-element arrays [from_node_num, to_node_num, edge_label]. Node numbers are indices into the nodes array (0-origin).
-
nodeGeometry. An array of 2-element arrays that are the coordinates of the nodes.
-
edgeGeometry. An array of JSON objects, that define the shape of the in-general-circular arcs connecting two nodes. Hopefully you never need to understand this attribute.
Some limited control of the Graph UI is available to the question author via template parameters as follows:
-
isdirected - defaults to true. Set it to false for a non-directed graph.
-
isfsm - defaults to false. Set it to true to allow edges to enter the graph from space, i.e., without a start node. It also allows nodes to be marked as accept states by double clicking.
-
noderadius - defaults to 26. The radius of nodes, in pixels.
-
fontsize - defaults to 20. The size of the Arial font, in px.
-
textoffset. An offset in pixels used when positioning link label text. Default 4.
-
locknodepositions. True to prevent the user from moving nodes. Useful when the answer box is preloaded with a graph that the student has to annotate by changing node or edge labels or by adding/removing edges. Note, though that nodes can still be added and deleted. See locknodeset. Default false.
-
locknodelabels. True to prevent the user from editing node labels. Also prevents any new nodes having non-empty labels. Default false.
-
locknodeset. True to prevent user from adding or deleting nodes or toggling node types to/from acceptors. Default false.
-
lockedgepositions. True to prevent the user from dragging edges to change their curvature. Possibly useful if the answer box is preloaded with a graph that the student has to annotate by changing node or edge labels or by adding/removing edges. Also ensures that edges added by a student are straight, e.g. to draw a polygon on a set of given points. Note, though that edges can still be added and deleted. See lockedgeset. Default false.
-
lockedgelabels. True to prevent the user from editing edge labels. Also prevents any new edges from having labels. Default false.
-
lockedgeset. True to prevent the user from adding or deleting edges. Default false.
-
helpmenutext - text to replace the default help menu text. Must be a single JSON string written on line using "\n" to separate lines in the menu. For example:
{"helpmenutext": "Line1\nLine2\nLine3"}
The default value, written here in multiple lines for readability, is:
- Double click at a blank space to create a new node/state.
- Double click an existing node to "mark" it e.g. as an accept state for Finite State Machines
(FSMs). Double click again to unmark it.
- Click and drag to move a node.
- Alt click (or Ctrl alt click) and drag on a node to move a (sub)graph.
- Shift click inside one node and drag to another to create a link.
- Shift click on a blank space, drag to a node to create a start link (FSMs only).
- Click and drag a link to alter its curve.
- Click on a link/node to edit its text.
- Typing _ followed by a digit makes that digit a subscript.
- Typing \\epsilon creates an epsilon character (and similarly for \\alpha, \\beta etc).
- Click on a link/node then press the Delete key to remove it (or function-delete on a Mac).
For example, for a non-directed non-fsm graph set the UI parameters field to
{"isdirected": false, "isfsm": false}
Many thanks to Emily Price for the original implementation of the Graph UI.
The Html UI plug-in replaces the answer box with custom HTML provided by the
question author. The HTML will usually include data entry fields such as
html input and text area elements and it is the values that the user enters
into these fields that constitutes the student answer. The HTML can
also include JavaScript in <script> elements.
The HTML to use in the answer area must be provided as the contents of
either the globalextra field or the prototypeextra field (see UI parameters
below) in the question authoring form.
The CodeRunner-relevant HTML elements are required to have a name and the class 'coderunner-ui-element'. They also need to support a call to the jquery val() method to get their values. HTML input, select and textarea elements are the most commonly used. If an element lacks a val method, jquery valHooks can be used to define one.
Care must be taken when using the HTML UI to avoid using field names that conflict
with any other named HTML elements in the page. It is recommended that a prefix
of some sort, such as crui_ (for "CodeRunner UI"), be used with all names.
Although very powerful, and capable of implementing almost any custom user interface, the mechanism is complex and there are several pitfalls. Caveat emptor!
-
enable_in_editor. By default, when editing questions the UI manages both the question answer and answer-preload fields. While this is by far the most user-friendly way to operate, it doesn't allow for the use of Twig in those fields, since Twig processing takes place on the server, not in JavaScript in the client. If you wish to use Twig you must set this UI parameter to false. Default: true.
-
html_src. This parameter specifies where the HTML code comes from. It must be either "globalextra" to get the code from the current question or "prototypeextra" to get it from the question's prototype prototypeextra field.
-
sync_interval_secs. This sests the time interval in seconds between calls to sync the UI contents serialisation back into the question answer. 0 for no such auto-syncing.
The STUDENT_ANSWER is a JSON object with an attribute for every name used by CodeRunner-relevant elements within the HTML. Since multiple HTML elements can have the same name, the value of each named attribute is a list of strings, not a single string. The strings are in DOM order. Each individual value is extracted using the jquery val() method.
As a trivial example, if the HTML supplied by the question author in the globalextra field were simply:
<input type="text" name="crui_input" class="coderunner-ui-element"
placeholder="Enter the word 'floodle' here">
and the student entered 'floodle' in the text area as instructed, the serialisation would be
{"crui_input":["floodle"]}
When authoring a question that uses the HTML UI, the answer and answer preload
fields are by default also controlled by the UI. While this is most user-friendly presentation,
it does not allow you to include Twig code in those fields. If you need
to use Twig there, you must turn off the use of the UI within the question
editing page by setting the UI parameter enable_in_editor to false:
{"enable_in_editor": false}
The underlying serialisation is then displayed as raw JSON text. In this case editing the answer and answer preload text is difficult; the easiest approach is to save the question, preview it, enter the right answers into all fields, type CTRL-ALT-M to switch off the UI and expose the serialisation, then copy that serialisation back into the author form. But this rigmarole is only necessary when you need to use Twig within the answer or sample answer, which is rare.
It is possible that the question author might want a dynamic answer box in which the student can add extra fields. A simple example of this is the Table UI, which is a special case of the Html UI. The Table UI provides an optional Add rows button, plus associated JavaScript, which allows students to add rows to the table. The serialisation then contains more data than can be accommodated in the fields of the original HTML. In the case of the Table UI, where the same name is used for all cells in a table column, the list of values for each name in the serialisation is longer than the number of rows. In other dynamic HTML contexts, new elements with entirely new names may have been added.
When the serialisation is reloaded back into the HTML all such leftover values
from the serialisation are assigned to the data['leftovers']
attribute of the outer html div, as a sub-object of the original object.
This outer div can be located as the 'closest' (in a jQuery sense)
div.qtype-coderunner-html-outer-div. The author-supplied HTML must include
JavaScript to make use of the 'leftovers'.
As a special case of the serialisation, if all values in the serialisation are either empty strings or a list of empty strings, the serialisation is itself the empty string.
A problem arises if the HTML supplied by the question author contains elements with explicit id attributes, as might be required if there is also JavaScript present that needs to refer to the new elements. If the review options allow display of the question author's answer then when the student reviews their quiz, the student answer and the author's answer will both include the new elements, resulting in a conflict of id. Apart from being invalid HTML, this is likely to result in wrong results when any JavaScript code referencing the elements runs.
A workaround for this problem is to include the special macro string
___textareaId___
as part of any new ids. Note the capital-I and that there are THREE (3) underscores at both the start and end of the macro string.
When the Html UI inserts the global extra html into the question, that macro is replaced everywhere by the actual ID of the answer box's text-area, which is different for the student and author answers. This technique can also be used to ensure that the names given to elements like radio buttons are different in the two answers.
Using this macro, it is also possible to include the GraphUI in the HtmlUI. By including a custom grader, it is possible to create a Question with several sub questions. To do this, in the html-code a textarea element needs to be defined:
<textarea class="coderunner-ui-element"
id="graph_target_name____textareaId___"
name="graph_target" spellcheck="false" rows="18" data-params=""
data-globalextra=""></textarea>
This element is hidden, but the graph will be drawn at this position and its contents serialised into that textarea.
Secondly, the amd-script needs to get called using:
M.util.js_pending('qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper');
require(['qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper'], function(amd) {
amd.newUiWrapper("graph", "graph_target_name____textareaId___");
M.util.js_complete('qtype_coderunner/userinterfacewrapper');
});
By using multiple graph elements, keep in mind that the id and name should be unique. For more information, see this CodeRunner author's forum thread where Markus Gafner (who contributed this workaround) shows a HtmlUI question with an embedded GraphUI question, plus other embedded questions.
This UI is an extension of the Ace UI. In addition to the usual Ace code edit window for the question answer, an optional extra "scratchpad" Ace edit window is available. If the student opens the scratchpad, they can add code to test their answer (or any other code they wish to run) and are presented with a Run button that submits the code from the scratchpad to the Jobe server using the CodeRunner webservice (which must be enabled for the UI to be usable). This essentially gives them a mini-IDE for each question. Their test code is saved alongside their answer when they submit ("Check") their question answer.
Prior to opening the scratchpad, the student sees something like the following (where they have already written their answer):
In use, the scratchpad UI looks like this:
Note that the student has the choice of running the scratchpad code in isolation or of running code consisting of their question answer followed by their scratchpad code.
In the simplest use cases, a question author can flip between the Ace-UI and the Scratchpad UI transparently. However, for question types like "Java write a function", the test needs boiler-plate code that is hidden from the student, so simply clicking the Run button won't behave the same as when the Check button is clicked. The question author can customise the behaviour of the scratchpad UI using the UI parameters below, but the process can be complex, particularly for question types that might need to collect images from the Jobe server. Some examples are given here on the CodeRunner demo site.
The serialisation is a JSON object with the following attributes. The values of all attributes are lists of strings, rather than just the strings themselves, for compatibility with the HTML UI, where there can be multiple HTML data-entry elements with the same name. (The original scratchpad question type at the University of Canterbury was implemented with the HTML UI, and we wanted compatibility with that).
-
answer_code: a singleton list containing the contents of the main question answer box. -
test_code: a singleton list containing the contents of the scratchpad. -
show_hide: a singleton list containing either '0' or '1' depending on whether the scratchpad is hidden or shown respectively. -
prefix_ans: a singleton list containing either '0' or '1' depending on whether or not the "Prefix with ans" checkbox is checked or not.
The set of UI parameters for the scratchpad is rather complex and you probably need to study the examples on the CodeRunner demo site (see above link) to understand these.
-
scratchpad_name. The text in the link used to open/close the scratchpad. Default: "scratchpad". -
button_name. The text in the Run button. Default: "Run". -
prefix_name. Prefix with answer check-box label text. Default: "Prefix with answer". -
help_text. The help text to show when a student clicks the help icon. -
run_lang. The language to use when running the code on the Jobe server. Default: null -
wrapper_src. The location of wrapper to be used by the run button: setting to 'globalextra' will use text in global extra field, 'prototypeextra' will use the prototype extra field. The wrapper is code that wraps the student's scratchpad code; it can be used to support additional functionality like boilerplate code for initialising libraries, fetching images, etc. See -
output_display_mode. Control how program output is displayed on runs. There are three modes:-
text: Display the output as text, html escaped. (default) -
json: Display programs that output JSON, useful for capturing stdin and displaying images. (recommended). Accepts JSON in the run output with the fields:returncode: Exit code from program run.stdout: Stdout text from program run.stderr: Error text from program run.files: An object containing filenames mapped to base64 encoded images. These will be displayed below any stdout text. When the returncode is set to 42, an HTML input field will be added after the last stdout received. When the enter key is pressed inside the input, the input's value is added to stdin and the program is run again with this updated stdin. This is repeated until returncode is not set to 42. This allows simulation of interactive keyboard standard input within the run (with considerable effort - see CodeRunner demo website).
-
html: Display program output as raw html inside the output area. (advanced) + This can be used to show images and insert other HTML. + Giving an element the class coderunner-run-input will add an event: when the enter key is pressed inside the input, the input's value is added to stdin and the program is run again with this updated stdin.
-
-
open_delimiter. The opening delimiter to use when inserting answer or Scratchpad code into the wrapper. It will replace the default value '{|'. -
close_delimiter. The closing delimiter to use when inserting answer or Scratchpad code into the wrapper. It will replace the default value '|}'. -
params. Parameter for the sandbox webservice (e.g. to set timelimit). -
disable_scratchpad. Disable the scratchpad, resulting in what looks to the student like the Ace UI. This allows question authors to turn off the scratchpad without having to customise the question (which then becomes disassociated from the original question) or changing the question type altogether. -
invert_prefix. Inverts meaning of prefix_ans serialisation: '1' means un-ticked -- and vice versa. This can be used to swap the default state. -
escape. Escape the JSON ANSWER_CODE and SCRATCHPAD_CODE strings by removing the double quotes from the start and end and escaping all internal double quotes with backslash before insertion into the wrapper. Useful when inserting code into a string. NOTE: single quotes ' are NOT escaped.
The table UI plug-in replaces the usual textarea answer element with an HTML table, into which the student must enter text data. All cells in the table are HTML textarea elements. The question author can enable Add row and Delete row buttons that allow the student to add or delete rows. The configuration of the table is set by the following template parameters, where the first two are required and the rest are optional.
-
num_rows(required): sets the (initial) number of table rows, excluding the header. -
num_columns(required): sets the number of table columns. -
column_headers(optional): a list of strings used for column headers. By default no column headers are used. -
row_labels(optional): a list of strings used for row labels. By default no row labels are used. -
lines_per_cell(optional): the initial number of rows for each of the table text-area cells. Default 2. -
column_width_percents(optional): a list of numeric percentage widths of the different columns. For example, if there are two columns, and the first one is to occupy one-quarter of the available width, the list should be [25, 75]. By default all columns have the same width. -
dynamic_rows(optional): settrueto enable the addition of Add row and Delete row buttons through which the student can alter the number of rows. The number of rows can never be less than the initialnum_rowsvalue. -
locked_cells(optional): an array of 2-element [row, column] cell specifiers. The specified cells are rendered to HTML with the disabled attribute, so cannot be changed by the user. For example"locked_cells": [[0, 0], [1, 0]]to lock the leftmost column of rows 0 and 1. This is primarily for use in conjunction with an answer preload in which some cells are defined by the question author. The preload answer must be defined before the locked_cells template parameter is defined, or the question author will not be able to define the required values in the first place.
For example, the python3\_program\_testing question type uses the following
UI parameter setting:
{
"num_rows": 3,
"num_columns": 2,
"column_headers": ["Test", "Result"],
"dynamic_rows": true
}
The table serialisation is simply a JSON array of arrays containing all the table cells excluding the header row.
As a special case of the serialisation, if all values in the serialisation are empty strings, the serialisation is itself the empty string.
An example of the use of this UI type can be seen in the python3_program_testing prototype in the samples folder.
NOTE: User-defined question types are very powerful but are not for the faint of heart. There are some known pitfalls, so please read the following very carefully. You may also wish to watch the short video introducing user-defined question types.
As explained earlier, each question type is defined by a prototype question, which is just another question in the database from which new questions can inherit. When customising a question, if you open the Advanced customisation panel you'll find the option to save your current question as a prototype. You will have to enter a name for the new question type you're creating. It is strongly recommended that you also change the name of your question to reflect the fact that it's a prototype, in order to make it easier to find. The convention is to start the question name with the string PROTOTYPE_, followed by the type name. For example, PROTOTYPE_python3_OOP. Having a separate PROTOTYPES category for prototype questions is also strongly recommended. Obviously the question type name you use should be unique, at least within the context of the course in which the prototype question is being used.
The question text of a prototype question is displayed in the 'Question type details' panel in the question authoring form.
CodeRunner searches for prototype questions just in the current course context. The search includes parent contexts, typically visible only to an administrator, such as the system context; the built-in prototypes all reside in that system context. Thus if a teacher in one course creates a new question type, it will immediately appear in the question type list for all authors editing questions within that course but it will not be visible to authors in other courses. If you wish to make a new question type available globally you should ask a Moodle administrator to move the question to the system context, such as a LOCAL_PROTOTYPES category.
When you create a question of a particular type, including user-defined types, all the so-called "customisable" fields are inherited from the prototype. This means changes to the prototype will affect all the "children" questions. However, as soon as you customise a child question you copy all the prototype fields and lose that inheritance.
To reduce the UI confusion, customisable fields are subdivided into the basic ones (per-test-template, grader, result-table column selectors etc) and "advanced" ones. The latter include the language, sandbox, timeout, memory limit and the "make this question a prototype" feature.
The following section on supporting or implementing new languages shows in detail the process for creating a new question type.
WARNING #1: if you define your own question type you'd better make sure when you export your question bank that you include the prototype, or all of its children will die on being imported anywhere else! Similarly, if you delete a prototype question that's actually in use, all the children will break, giving "missing prototype" errors. To recover from such screw ups you will need to create a new prototype of the right name (preferably by importing the original correct prototype). To repeat: user-defined question types are not for the faint of heart. Caveat emptor.
WARNING #2: although you can define test cases in a question prototype, e.g. for validation purposes, they are not inherited by the "children" of the prototype.
** TBS **
Most authors seem to assume that if they wish to write CodeRunner questions that use a language not directly supported by the Jobe sandbox, they must first modify the Jobe code to support the new language. That is not the case, although the required language does of course need to be installed on the Jobe server. A much easier, more convenient and more maintainable approach is to use a Python question type that compiles (if necessary) and runs the student code in a Python subprocess. Indeed, in recent years at the University of Canterbury nearly all new question types have been scripted in Python, even those using languages built into Jobe. For example, the question type we now use for all question in the C programming course is a Python3 question type parses the student's C program and performs lots of checks on things like function length and use of various C constructs before compiling and running the submitted code.
The template code below shows a simple example in which a Python question prototype is used to define a new question type c_via_python that mimics the built-in c_program question type but provides more flexibility. To create the new question type using this template:
- Create a new CodeRunner question.
- Choose the question type python3
- Click Customise
- Replace the contents of the Template text area with the template code below.
- Uncheck the Is combinator checkbox
- Enter DEMO_PROTOTYPE_C_using_python as the question name
- Enter whatever text you wish to use to describe the question type in the Question text area. This text will be displayed to any authors using this new question type if they open the Question type details section of the question authoring form.
- Open Advanced Customisation
- Set Is prototype? to Yes (user defined)
- Set Question type to c_via_python.
- Set Ace language to c, so that the students' code will be edited as C even though the prototype is in Python.
- Save the question.
You should now find the new question type c_via_python appearing in the Question type dropdown of the author edit form for a new CodeRunner question. This new question type should behave like the built-in c_program question type but is more flexible; for example, it can easily be extended to perform checks on the submitted C code prior to compilation.
The full question prototype for the c_via_python question type is included in the samples folder of the CodeRunner distribution.
""" The template for a question type that compiles and runs a student-submitted
C program.
"""
import subprocess, sys
# Write the student code to a file prog.c
student_answer = """{{ STUDENT_ANSWER | e('py') }}"""
with open("prog.c", "w") as src:
print(student_answer, file=src)
# Compile
{% if QUESTION.parameters.cflags is defined %}
cflags = """{{ QUESTION.parameters.cflags | e('py') }}"""
{% else %}
cflags = "-std=c99 -Wall -Werror"
{% endif %}
return_code = subprocess.call("gcc {0} -o prog prog.c".format(cflags).split())
if return_code != 0:
print("** Compilation failed. Testing aborted **", file=sys.stderr)
# If compile succeeded, run the code. Since this is a per-test template,
# stdin is already set up for the stdin text specified in the test case,
# so we can run the compiled program directly.
if return_code == 0:
try:
output = subprocess.check_output(["./prog"], universal_newlines=True)
print(output)
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
if e.returncode > 0:
# Ignore non-zero positive return codes
if e.output:
print(e.output)
else:
# But negative return codes are signals - abort
if e.output:
print(e.output, file=sys.stderr)
if e.returncode < 0:
print("Task failed with signal", -e.returncode, file=sys.stderr)
print("** Further testing aborted **", file=sys.stderr)
The above is just a general template and some languages will need additional tweaks, e.g. to set up required environment variables. One user tells me that he had to redirect stderr output to stdout in the call to subprocess.check_output when using R, because it apparently writes some messages and warnings to stderr while still returning a 0 ('SUCCESS') exit code. In another example, the same user reports that Erlang requires the HOME environment variable to be defined and set to be the current working directory.
By extending the above approach it is possible to write questions that can be answered in multiple languages. Multi-language questions are enabled by setting the Ace-language field within the Advanced Customisation section of a question to a comma-separated list of languages. Students are then presented with a drop-down menu which they use to select the language in which their answer is written. If exactly one of the languages has an asterisk ('*') appended, that language is chosen as the default language, selected as the initial state of the drop-down menu. For example, an Ace-language value of "C,C++,Java*,Python3" would allow student to submit in C, C++, Java or Python3 but the drop-down menu would initially show Java which would be the default. If no default is specified the initial state of the drop-down is empty and the student must choose a language. Multilanguage questions require a special template that uses the {{ANSWER_LANGUAGE}} template variable to control how to execute the student code. The {{ANSWER_LANGUAGE}} variable is meaningfully defined only for multilanguage questions; it is the empty string, otherwise.
The template for a multilanguage question is a generalisation of the template shown in the previous section. It is essentially a single large case statement of the following form (assuming the sandbox language is Python3):
import subprocess
import re
student_answer = """{{ STUDENT_ANSWER | e('py') }}"""
language = """{{ ANSWER_LANGUAGE | e('py') }}""".lower()
if language == 'c':
# Code to run a C program, as in the previous section
elif language == 'python3':
# Code to execute student_answer in Python3 directly
elif language == 'java':
# Code to run a Java program, modified from that in the previous section
... etc
For a fully working version of such a question type, see the implementation
of the built-in multilanguage question type, BUILT_IN_PROTOTYPE_multilanguage.
If you're a system administrator, you'll find the question prototype in the
System/CR_PROTOTYPES category. If not, create a new question of
type multilanguage, customise it, and examine its template. You can also
inspect the entire question prototype in XML form within the repository
file db/builtin_PROTOTYPES.xml. Note that the prototype is
a non-combinator question, i.e. it does a separate run for each test case, which
isn't efficient for sluggish languages like Java.
If the author wishes to supply a sample answer to a multilanguage question, they must write it in the default language, if specified, or the first of the allowed languages otherwise.
CodeRunner provides an Ajax-accessible web service that allows JavaScript code to directly run jobs on the Jobe server. (More precisely, it runs jobs on whatever sandbox has been configured for the specified language, but nowadays the only sandbox in production use is the Jobe sandbox). This service was added to support the Ace_inline code Moodle filter plugin in order to display syntax-coloured editable code with a 'Try it!' button in any Moodle content page, but may have other uses.
The web service is not enabled by default, and must be enabled in the CodeRunner settings page by by a moodle system administrator. There are several additional configuration options:
-
Jobe server to use for web services. The sandbox server web service will use whatever sandbox is configured for the specified language. This is virtually always a Jobe server, and the particular Jobe server to use is configured via the admin interface (above). However, for best web service security it is better to use an alternative Jobe server, set by this field. Leave blank to use the default.
-
Enable logging. By default every request made using the web service is logged to the Moodle event log. Only logged-in users can use the service, and the event records simply the name of the user and the date and time at which they made use of the service. It does not record which particular page or script initiated the request Logging can be disabled by unchecking this option, which will reduce the size of user-activity reports if there is heavy usage of the web service. Unless there is a problem with the size of reports, however, it is strongly recommended to leave logging enabled.
-
Maximum hourly submission rate. If logging is enabled (above) the system administrator can set a per-user maximum web service submission rate. This is mostly a security feature to prevent abuse of the service, for example by JavaScripted automatic submissions. The default rate is 200 submissions per hour. The system denies any request that would result in exceeding the specified rate over the preceding hour. The feature works only if event logging is enabled.
-
Maximum allowed CPU time. The maximum CPU time that a web service job can take is configurable by a system administrator. The default value of 5 seconds is sufficient for most short runs but larger values might be appropriate in some environments. The absolute maximum CPU time is set by the Jobe server configuration and is usually about 50 seconds.
The service is intended for use within Moodle content pages, usually within AMD scripts. However, the service can be used from JavaScript directly embedded in a page using an HTML editor. For example:
<h3>A simple demo of the CodeRunner sandbox web service.</h3>
<textarea id="code" rows="4" cols="40"></textarea>
<br>
<button type="button" id="mybutton">Run me!</button>
<script>
var button = document.getElementById('mybutton');
var text = document.getElementById('code');
button.onclick = function() {
require(['core/ajax'], function(ajax) {
ajax.call([{
methodname: 'qtype_coderunner_run_in_sandbox',
args: {
contextid: M.cfg.contextid, // Moodle context ID
sourcecode: text.value,
language: "python3"
},
done: function(responseJson) {
var response = JSON.parse(responseJson);
if (response.error !== 0 || response.result !== 15) {
alert("Oops: " + responseJson);
} else {
alert("Output was: '" + response.output + "'");
}
},
fail: function(error) {
alert(error.message);
}
}]);
});
}
</script>
This page displays a textarea into which a user can enter Python code, which can then be run by clicking the button. The output is displayed in an alert. The ace_inline filter plugin does something similar to this, except it uses the Ace editor to provide code editing, displays the output inline in the page, does much more extensive error analysis and has many more configuration options.
The response object is an object with at least an attribute 'error'. This is one of the values 0 through 9 (OK to SERVER_OVERLOAD) as defined in the CodeRunner source file sandbox.php. Any value other than 0 is a sandbox error of some sort, meaning the run did not take place.
If error is 0 (OK), the job did get run on the sandbox server and the returned
object then has additional attributes
result, output, stderr, signal and cmpinfo as follows:
-
result: one of the result constants defined in sandbox.php. The hoped-for value is 15 ('RESULT_SUCCESS'). Other common values are 11 ('RESULT_COMPILATION_ERROR), 12 ('RESULT_RUNTIME_ERROR') and 13 ('RESULT_TIME_LIMIT'). Other outcomes are more serious (and much more rare) and can be classified as, say, 'Unexpected sandbox error'. -
output: the stdout from the run -
stderr: the stderr output from the run (generally a non-empty string is taken as a runtime error) -
signal: one of the standard Linux signal values (but often not used) -
cmpinfo: the output from the compilation run (usually empty unless the result code is for a compilation error).
If error is anything other than OK, the returned object may optionally include an error message in the stderr field.
Other arguments to the ajax webservice call are:
-
stdin, which prides a fixed string to use as standard input by the code. -
files, which is a JSON-encoded object that provides a map from a so-called 'filename' (the attribute name) to 'file contents' (the attribute value). Each attribute of the files object is used to create a file in the working directory on the Jobe server. -
params, which is a JSON-encoded object that defines parameters to the jobe sandbox. For example the following string value would set the maximum runtime on the sandbox to 10 seconds (although constrained by the system administrator's setting of the maximum allowed CPU time):{"cputime": 10}
There are currently three CodeRunner-related utility scripts available. While initially intended only for administrator use, they are proving useful to teachers as well, particularly the third one. Teachers are able to run the scripts only within courses they can normally access; they must be logged into such a course before attempting to run the scripts.
The three scripts are:
-
<moodle_home>/question/type/coderunner/bulktestindex.phpThis script displays a list of all question categories accessible to the user who is currently logged into Moodle on the machine running the script. Each category is displayed as a clickable link that then runs a script that tests the sample answers on all questions in that category, reporting all successes and failures. -
<moodle_home>/question/type/coderunner/prototypeusageindex.phpThis scripts displays an index like the one above except that the clickable links now run a script that reports on the question prototype usage within that category. -
<moodle_home>/question/type/coderunner/downloadquizattempts.phpThis script displays a list of all quizzes available to the logged in user, allowing them to download a spreadsheet of all submissions to a selected quiz by all students. The downloaded spreadsheet is suitable for off-line analysis, and includes information not available in the exported Moodle responses file, such as all intermediate submisssions and prechecks and the time of each such action.The download can be in either csv or excel format. The exported Excel spreadsheet can then be opened in Excel or Open Office and saved as csv.
The download format is complicated and requires a good understanding of Moodle's database scheme. The following query is used, with each row of the result being output as a single spreadsheet row.
SELECT concat(quiza.uniqueid, qasd.attemptstepid, qasd.id) as uniquekey, quiza.uniqueid as quizattemptid, timestart, timefinish, u.firstname, u.lastname, u.email, qatt.slot, qatt.questionid, quest.name as qname, slot.maxmark as mark, qattsteps.timecreated as timestamp, FROM_UNIXTIME(qattsteps.timecreated,'%Y/%m/%d %H:%i:%s') as datetime, qattsteps.fraction, qattsteps.state, qasd.attemptstepid, qasd.name as qasdname, qasd.value as value FROM {user} u JOIN {quiz_attempts} quiza ON quiza.userid = u.id AND quiza.quiz = :quizid JOIN {question_attempts} qatt ON qatt.questionusageid = quiza.uniqueid JOIN {question_attempt_steps} qattsteps ON qattsteps.questionattemptid = qatt.id JOIN {question_attempt_step_data} qasd on qasd.attemptstepid = qattsteps.id JOIN {question} quest ON quest.id = qatt.questionid JOIN {quiz_slots} slot ON qatt.slot = slot.slot AND slot.quizid = quiza.quiz WHERE quiza.preview = 0 AND (qasd.name NOT RLIKE '^-_' OR qasd.name = '-_rawfraction') AND (qasd.name NOT RLIKE '^_' OR qasd.name = '_testoutcome') AND quest.length > 0 ORDER BY quiza.uniqueid, timestamp;This query gives rise to multiple near-identical rows for a single student action (e.g. answer submission), with different (qasdname, value) pairs. ['qasdname' is the
namecolumn of the question-attempt-step-data table andvalueis the value associated with that name. The set of such (key, value) pairs depends on the question type and the particular user action being recorded.] Currently, so-called "behaviour variables" - those containing an underscore - are not included in the export, except for the '-_rawfraction' variable. This is to restrict the volume of data, but the decision may change in the future.Processing of the raw spreadsheet is somewhat complicated. The file
quizsubmissions.pyincluded in the git repository defines Python classes to simplify the process. The statementsfrom quizsubmissions import QuizSubmissions submission_data = QuizSubmissions(csvfilename)import the exported spreadsheet and gives easy access to data about any particular student and their activities in the quiz.
For example
submission-data['rjl83'].submissions[2].get_answer()returns the final answer submitted by student
rjl83to question 2.Lots of other information, such as the student's name, all intermediate submissions and prechecks and their times etc is available. See
quizsubmissions.pyfor more information.Note the script requires large amounts of memory and you may find it fails with large classes. Increasing the memory_limit setting in php.ini may solve the problem if you have administrative rights on the server to change this.
To assist the use of screen readers for visually impaired students, text area inputs now have two modes:
-
When keyboard focus first enters them via Tab or Shift+TAB, they are in 'non-capturing' mode, and pressing TAB or Shift+TAB moves to the next or previous form control.
-
After you start typing, or if focus enters by way of a click, they go into Tab-capturing mode, and then pressing Tab indents.
-
CTRL+M switches modes (as recommended by https://www.w3.org/TR/wai-aria-practices/#richtext).
-
Esc always switches to non-capturing mode.
CodeRunner is a rather complex system and, being web based, is driven by user-events. In this Appendix we attempt to describe the effective behaviour using pseudocode algorithms.
An understanding of the Twig template engine is assumed in what follows. See the Twig documentation if you are not familiar with Twig. CodeRunner uses standard Twig, except for the addition of a [set_random_seed](https://github.com/trampgeek/moodle-qtype_coderunner#randomising-per-student-rather-than-per-question-attempt] function and some extra escapers.
When a student starts a quiz, an instance of each question in the quiz has be be created. It's at the point that any environmental context, such as the student's name, plus any randomisation, gets established. To ensure that any randomisation done by the template remains locked in to all subsequent views and attempts of the question within this quiz by the current student, a new random number seed is generated and stored in the question at this stage. That seed is used for all subsequent randomisation except that the question author can explicitly call the set_random_seed function to use a different seed, such as the student's ID number.
That initialisation process can be described as follows:
procedure create_question_instance(question):
question.student = get_current_moodle_user_info()
question.prototype = locate_prototype_question(question.prototype_name)
question.random_seed = make_new_random_seed()
set_twig_environment(question.random_seed, question.student)
question.template_params = twig_expand(question.template_params)
if question.prototype has template parameters:
prototype_params = twig_expand(question.prototype.template_params)
question.template_params = merge_json(prototype_params, question.template_params)
if question.twigall:
# Twig expand question text, sample answer, answer preload,
# all test case fields and global extra. The just-computed
# template parameters provide (most of) the twig environment.
set_twig_environment(question.random_seed,
question.student, question.template_params)
for each twiggable attribute of question:
question.attribute = twig_expand(question.attribute)
save question instance
When the user clicks the Check button (or Precheck if turned on), the current answer is graded. The "current answer" comprises:
-
The code in the answer box or, more generally, the serialised text returned by the selected UI (user interface) plug-in. For coding questions, the UI is usually the Ace code-editor so the serialised text is just the raw code without syntax colouring. Other UIs (e.g. GraphUI, TableUI, GapFillerUI) have their own unique serialisations; see the UI plug-in documentation for details.
-
The set of student-supplied attached files, if attachments are enabled.
The grading process involves expanding the question template, executing the code and grading the result. However, the process is complicated by the choice of sandbox, whether the question uses a so-called "combinator" or not (i.e. whether it attempts to combine all test-cases into a single run), whether the question requires that different standard input be set for each test case, whether it's a precheck or a full check and what grading method has been selected (Exact Match, Near Exact Match, Regular Expression, or Template Grader).
Another complication relates to the environment in which the question's template gets expanded by Twig, i.e. the set of "template parameters". In legacy code the template refers to the question's template parameters using a notation like
{{ QUESTION.parameters.sometemplateparam }}
but there is now a checkbox called 'Hoist template parameters', defaulting to true, which adds the template parameters directly to the Twig environment, allowing the question author to refer directly to
{{ sometemplateparam }}
In the following pseudocode, we assume Hoist template parameters is true.
Although CodeRunner is set up to use a variety of different sandboxes, in recent years only the Jobe sandbox has been supported, so we will generally disregard all other sandboxes. However, it sometimes helps to remember that CodeRunner could in principle use different sandboxes, and that not all sandboxes might provide the same functionality as Jobe e.g., setting of maximum memory or maximum runtime.
function grade_response(question, attachments, is_precheck):
# Grade the current submission and return a table of test results
if question.answer plus current set of attachments has already been graded:
return cached results
test_cases = select_subset_of_tests(question.testcases, is_precheck)
run_results = None
if question.is_combinator and (template grader is being used or
question.allow_multiple_stdins or all stdins are empty strings):
# Try running the combinator. If something breaks, e.g. a
# testcase times out, the result will be None.
Set up the Twig environment (templateParams) to consist of all
the variables in question.templateParams plus STUDENT_ANSWER,
IS_PRECHECK, ANSWER_LANGUAGE, and ATTACHMENTS. Additionally
the entire question is made available as the parameter QUESTION.
run_results = run_combinator(question, testcases, templateParams)
if run_result is not None:
run_results = []
for each test in test_cases:
run_results.append(run_single_testcase(question, test, templateParams)
return run_results
The algorithms used in `run_combinator` and `run_single_testcase` are
function run_combinator(question, testcases, templateParams)
*** TBS ***
Historical notes and a diatribe on the use of Adaptive Mode questions ...
The original pycode was inspired by CodingBat, a site where students submit Python or Java code that implements a simple function or method, e.g. a function that returns twice the square of its parameter plus 1. The student code is executed with a series of tests cases and results are displayed immediately after submission in a simple tabular form showing each test case, expected answer and actual answer. Rows where the answer computed by the student's code is correct receive a large green tick; incorrect rows receive a large red cross. The code is deemed correct only if all tests are ticked. If code is incorrect, students can simply correct it and resubmit.
CodingBat proves extraordinarily effective as a student training site. Even experienced programmers receive pleasure from the column of green ticks and all students are highly motivated to fix their code and retry if it fails one or more tests. Some key attributes of this success, to be incorporated into pycode, were:
-
Instant feedback. The student pastes their code into the site, clicks submit, and almost immediately receives back their results.
-
All-or-nothing correctness. If the student's code fails any test, it is wrong. Essentially (thinking in a quiz context) it earns zero marks. Code has to pass all tests to be deemed mark-worthy.
-
Simplicity. The question statement should be simple. The solution should also be reasonably simple. The display of results is simple and the student knows immediately what test cases failed. There are no complex regular-expression failures for the students to puzzle over nor uncertainties over what the test data was.
-
Rewarding green ticks. As noted above, the colour and display of a correct results table is highly satisfying and a strong motivation to succeed.
The first two of these requirements are particularly critical. While they can be accommodated within Moodle by using an adaptive quiz behaviour in conjunction with an all-or-nothing marking scheme, they are not how many people view a Moodle quiz. Quizzes are commonly marked only after submission of all questions, and there is usually a perception that part marks will be awarded for "partially correct" answers. However, awarding marks to a piece of code according to how many test cases it passes can give almost meaningless results. For example, a function that always just returns 0, or the empty list or equivalent, will usually pass several of the tests, but surely it shouldn't be given any marks? Seriously flawed code, for example a string tokenizing function that works only with alphabetic data, may get well over half marks if the question-setter was not expecting such flaws.
Accordingly, CodeRunner questions always use Moodle's adaptive behaviour, regardless of the behaviour set for the quiz in which the questions are being run. Students can check their code for correctness as soon as it has been entered and, if their answer is wrong, can resubmit, usually for a small penalty. The mark obtained in a programming-style quiz is thus determined primarily by how many of the problems the student can solve in the given time, and secondarily by how many submissions the student needs to make on each question.