Given an integer array nums where the elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balanced binary search tree.
A height-balanced binary tree is a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differs by more than one.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9] Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5] Explanation: [0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] is also accepted: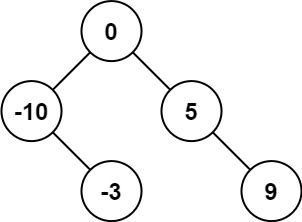
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,3] Output: [3,1] Explanation: [1,null,3] and [3,1] are both height-balanced BSTs.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-104 <= nums[i] <= 104numsis sorted in a strictly increasing order.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
def buildBST(nums, start, end):
if start > end:
return None
mid = (start + end) >> 1
return TreeNode(nums[mid], buildBST(nums, start, mid - 1), buildBST(nums, mid + 1, end))
return buildBST(nums, 0, len(nums) - 1)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return buildBST(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode buildBST(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return null;
}
int mid = (start + end) >> 1;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = buildBST(nums, start, mid - 1);
root.right = buildBST(nums, mid + 1, end);
return root;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *sortedArrayToBST(vector<int> &nums) {
return buildBST(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
}
private:
TreeNode *buildBST(vector<int> &nums, int start, int end) {
if (start > end)
return nullptr;
int mid = start + end >> 1;
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root->left = buildBST(nums, start, mid - 1);
root->right = buildBST(nums, mid + 1, end);
return root;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var sortedArrayToBST = function (nums) {
const buildBST = (nums, start, end) => {
if (start > end) {
return null;
}
const mid = (start + end) >> 1;
const root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = buildBST(nums, start, mid - 1);
root.right = buildBST(nums, mid + 1, end);
return root;
};
return buildBST(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func sortedArrayToBST(nums []int) *TreeNode {
return buildBST(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
}
func buildBST(nums []int, start, end int) *TreeNode {
if start > end {
return nil
}
mid := (start + end) >> 1
return &TreeNode{
Val: nums[mid],
Left: buildBST(nums, start, mid-1),
Right: buildBST(nums, mid+1, end),
}
}


