给你一个二维整数数组 descriptions ,其中 descriptions[i] = [parenti, childi, isLefti] 表示 parenti 是 childi 在 二叉树 中的 父节点,二叉树中各节点的值 互不相同 。此外:
- 如果
isLefti == 1,那么childi就是parenti的左子节点。 - 如果
isLefti == 0,那么childi就是parenti的右子节点。
请你根据 descriptions 的描述来构造二叉树并返回其 根节点 。
测试用例会保证可以构造出 有效 的二叉树。
示例 1:
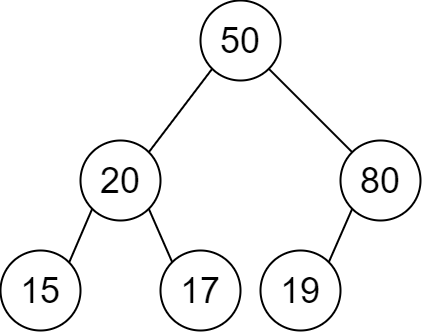
输入:descriptions = [[20,15,1],[20,17,0],[50,20,1],[50,80,0],[80,19,1]] 输出:[50,20,80,15,17,19] 解释:根节点是值为 50 的节点,因为它没有父节点。 结果二叉树如上图所示。
示例 2:
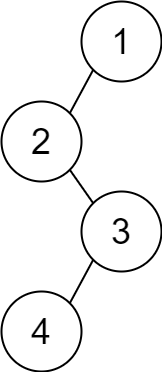
输入:descriptions = [[1,2,1],[2,3,0],[3,4,1]] 输出:[1,2,null,null,3,4] 解释:根节点是值为 1 的节点,因为它没有父节点。 结果二叉树如上图所示。
提示:
1 <= descriptions.length <= 104descriptions[i].length == 31 <= parenti, childi <= 1050 <= isLefti <= 1descriptions所描述的二叉树是一棵有效二叉树
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def createBinaryTree(self, descriptions: List[List[int]]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
g = defaultdict(TreeNode)
vis = set()
for p, c, left in descriptions:
if p not in g:
g[p] = TreeNode(p)
if c not in g:
g[c] = TreeNode(c)
if left:
g[p].left = g[c]
else:
g[p].right = g[c]
vis.add(c)
for v, node in g.items():
if v not in vis:
return node/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode createBinaryTree(int[][] descriptions) {
Map<Integer, TreeNode> m = new HashMap<>();
Set<Integer> vis = new HashSet<>();
for (int[] d : descriptions) {
int p = d[0], c = d[1], isLeft = d[2];
if (!m.containsKey(p)) {
m.put(p, new TreeNode(p));
}
if (!m.containsKey(c)) {
m.put(c, new TreeNode(c));
}
if (isLeft == 1) {
m.get(p).left = m.get(c);
} else {
m.get(p).right = m.get(c);
}
vis.add(c);
}
for (Map.Entry<Integer, TreeNode> entry : m.entrySet()) {
if (!vis.contains(entry.getKey())) {
return entry.getValue();
}
}
return null;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function createBinaryTree(descriptions: number[][]): TreeNode | null {
const map = new Map<number, [number, number]>();
const isRoot = new Map<number, boolean>();
for (const [parent, child, isLeft] of descriptions) {
let [left, right] = map.get(parent) ?? [0, 0];
if (isLeft) {
left = child;
} else {
right = child;
}
if (!isRoot.has(parent)) {
isRoot.set(parent, true);
}
isRoot.set(child, false);
map.set(parent, [left, right]);
}
const dfs = (val: number) => {
if (val === 0) {
return null;
}
const [left, right] = map.get(val) ?? [0, 0];
return new TreeNode(val, dfs(left), dfs(right));
};
for (const [key, val] of isRoot.entries()) {
if (val) {
return dfs(key);
}
}
return null;
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::collections::HashMap;
impl Solution {
fn dfs(val: i32, map: &HashMap<i32, [i32; 2]>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
if val == 0 {
return None;
}
let mut left = None;
let mut right = None;
if let Some(&[l_val, r_val]) = map.get(&val) {
left = Self::dfs(l_val, map);
right = Self::dfs(r_val, map);
}
Some(Rc::new(RefCell::new(TreeNode { val, left, right })))
}
pub fn create_binary_tree(descriptions: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
let mut map = HashMap::new();
let mut is_root = HashMap::new();
for description in descriptions.iter() {
let (parent, child, is_left) = (description[0], description[1], description[2] == 1);
let [mut left, mut right] = map.get(&parent).unwrap_or(&[0, 0]);
if is_left {
left = child;
} else {
right = child;
}
if !is_root.contains_key(&parent) {
is_root.insert(parent, true);
}
is_root.insert(child, false);
map.insert(parent, [left, right]);
}
for key in is_root.keys() {
if *is_root.get(key).unwrap() {
return Self::dfs(*key, &map);
}
}
None
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* createBinaryTree(vector<vector<int>>& descriptions) {
unordered_map<int, TreeNode*> m;
unordered_set<int> vis;
for (auto& d : descriptions) {
int p = d[0], c = d[1], left = d[2];
if (!m.count(p)) m[p] = new TreeNode(p);
if (!m.count(c)) m[c] = new TreeNode(c);
if (left)
m[p]->left = m[c];
else
m[p]->right = m[c];
vis.insert(c);
}
for (auto& [v, node] : m) {
if (!vis.count(v)) return node;
}
return nullptr;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func createBinaryTree(descriptions [][]int) *TreeNode {
m := make(map[int]*TreeNode)
vis := make(map[int]bool)
for _, d := range descriptions {
p, c, left := d[0], d[1], d[2]
if m[p] == nil {
m[p] = &TreeNode{Val: p}
}
if m[c] == nil {
m[c] = &TreeNode{Val: c}
}
if left == 1 {
m[p].Left = m[c]
} else {
m[p].Right = m[c]
}
vis[c] = true
}
for v, node := range m {
if !vis[v] {
return node
}
}
return nil
}