Given a 0-indexed n x n integer matrix grid, return the number of pairs (ri, cj) such that row ri and column cj are equal.
A row and column pair is considered equal if they contain the same elements in the same order (i.e., an equal array).
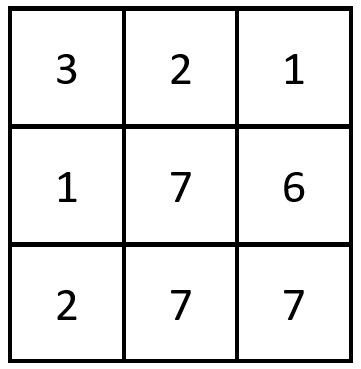
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[3,2,1],[1,7,6],[2,7,7]] Output: 1 Explanation: There is 1 equal row and column pair: - (Row 2, Column 1): [2,7,7]
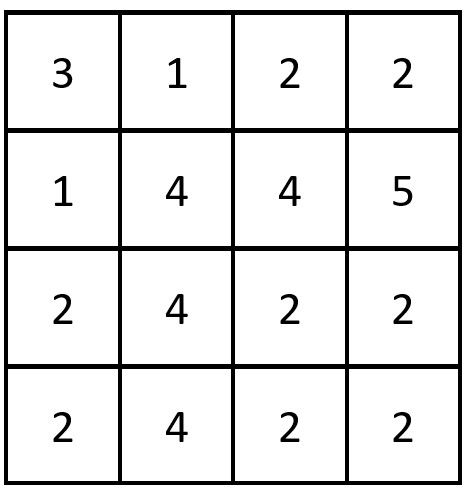
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[3,1,2,2],[1,4,4,5],[2,4,2,2],[2,4,2,2]] Output: 3 Explanation: There are 3 equal row and column pairs: - (Row 0, Column 0): [3,1,2,2] - (Row 2, Column 2): [2,4,2,2] - (Row 3, Column 2): [2,4,2,2]
Constraints:
n == grid.length == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 2001 <= grid[i][j] <= 105
class Solution:
def equalPairs(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(grid)
g = []
for j in range(n):
t = []
for i in range(n):
t.append(grid[i][j])
g.append(t)
return sum(row == col for row in grid for col in g)class Solution {
public int equalPairs(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int[][] g = new int[n][n];
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
g[i][j] = grid[j][i];
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int[] row : grid) {
for (int[] col : g) {
boolean ok = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (row[i] != col[i]) {
ok = false;
break;
}
}
if (ok) {
++ans;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int equalPairs(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size();
vector<vector<int>> g(n, vector<int>(n));
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
g[i][j] = grid[j][i];
int ans = 0;
for (auto row : grid)
for (auto col : g)
ans += row == col;
return ans;
}
};func equalPairs(grid [][]int) int {
n := len(grid)
g := make([][]int, n)
for i := range g {
g[i] = make([]int, n)
}
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
g[i][j] = grid[j][i]
}
}
ans := 0
for _, row := range grid {
for _, col := range g {
ok := true
for i, v := range row {
if v != col[i] {
ok = false
break
}
}
if ok {
ans++
}
}
}
return ans
}