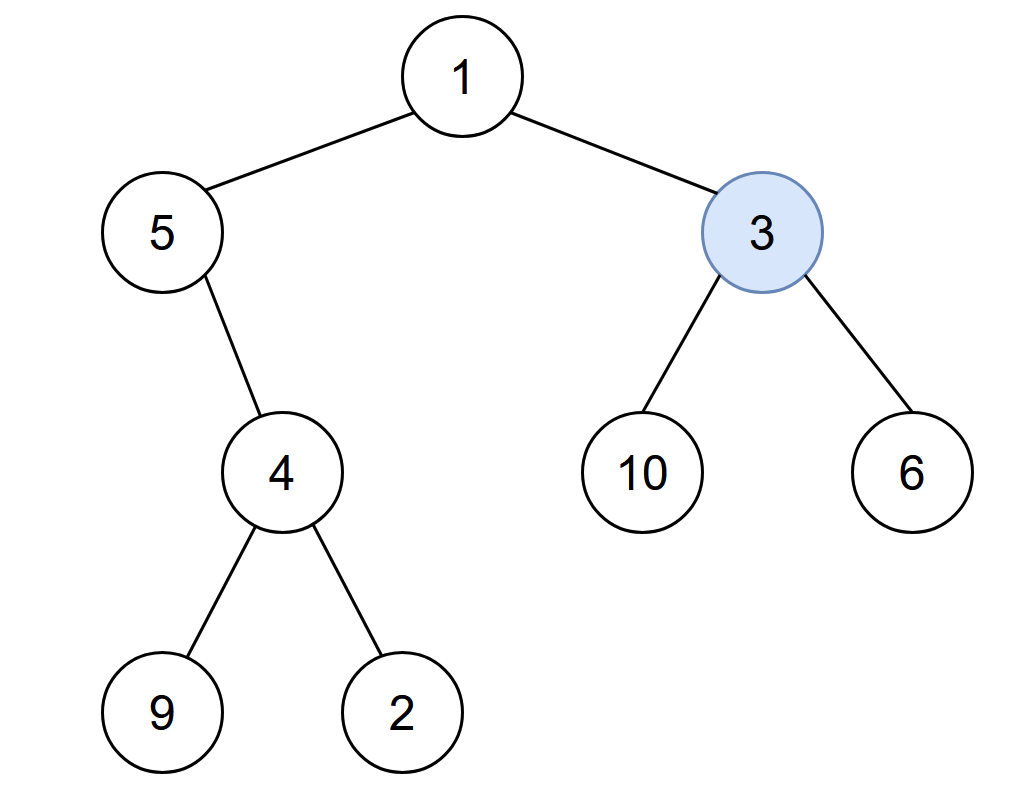
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,二叉树中节点的值 互不相同 。另给你一个整数 start 。在第 0 分钟,感染 将会从值为 start 的节点开始爆发。
每分钟,如果节点满足以下全部条件,就会被感染:
- 节点此前还没有感染。
- 节点与一个已感染节点相邻。
返回感染整棵树需要的分钟数。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,5,3,null,4,10,6,9,2], start = 3 输出:4 解释:节点按以下过程被感染: - 第 0 分钟:节点 3 - 第 1 分钟:节点 1、10、6 - 第 2 分钟:节点5 - 第 3 分钟:节点 4 - 第 4 分钟:节点 9 和 2 感染整棵树需要 4 分钟,所以返回 4 。
示例 2:
输入:root = [1], start = 1 输出:0 解释:第 0 分钟,树中唯一一个节点处于感染状态,返回 0 。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 105]内 1 <= Node.val <= 105- 每个节点的值 互不相同
- 树中必定存在值为
start的节点
方法一:DFS + BFS
先通过
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def amountOfTime(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], start: int) -> int:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return
if root.left:
g[root.val].append(root.left.val)
g[root.left.val].append(root.val)
if root.right:
g[root.val].append(root.right.val)
g[root.right.val].append(root.val)
dfs(root.left)
dfs(root.right)
g = defaultdict(list)
dfs(root)
vis = set()
q = deque([start])
ans = -1
while q:
ans += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
i = q.popleft()
vis.add(i)
for j in g[i]:
if j not in vis:
q.append(j)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private Map<Integer, List<Integer>> g = new HashMap<>();
public int amountOfTime(TreeNode root, int start) {
dfs(root);
Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
Set<Integer> vis = new HashSet<>();
q.offer(start);
int ans = -1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
++ans;
for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) {
int i = q.pollFirst();
vis.add(i);
if (g.containsKey(i)) {
for (int j : g.get(i)) {
if (!vis.contains(j)) {
q.offer(j);
}
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.left != null) {
g.computeIfAbsent(root.val, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(root.left.val);
g.computeIfAbsent(root.left.val, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(root.val);
}
if (root.right != null) {
g.computeIfAbsent(root.val, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(root.right.val);
g.computeIfAbsent(root.right.val, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(root.val);
}
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> g;
int amountOfTime(TreeNode* root, int start) {
dfs(root);
queue<int> q {{start}};
unordered_set<int> vis;
int ans = -1;
while (q.size()) {
++ans;
for (int n = q.size(); n; --n) {
int i = q.front();
q.pop();
vis.insert(i);
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (!vis.count(j)) {
q.push(j);
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
if (root->left) {
g[root->val].push_back(root->left->val);
g[root->left->val].push_back(root->val);
}
if (root->right) {
g[root->val].push_back(root->right->val);
g[root->right->val].push_back(root->val);
}
dfs(root->left);
dfs(root->right);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func amountOfTime(root *TreeNode, start int) int {
g := map[int][]int{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
if root.Left != nil {
g[root.Val] = append(g[root.Val], root.Left.Val)
g[root.Left.Val] = append(g[root.Left.Val], root.Val)
}
if root.Right != nil {
g[root.Val] = append(g[root.Val], root.Right.Val)
g[root.Right.Val] = append(g[root.Right.Val], root.Val)
}
dfs(root.Left)
dfs(root.Right)
}
dfs(root)
q := []int{start}
ans := -1
vis := map[int]bool{}
for len(q) > 0 {
ans++
for n := len(q); n > 0; n-- {
i := q[0]
q = q[1:]
vis[i] = true
for _, j := range g[i] {
if !vis[j] {
q = append(q, j)
}
}
}
}
return ans
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function amountOfTime(root: TreeNode | null, start: number): number {
const map = new Map<number, number[]>();
const create = ({ val, left, right }: TreeNode) => {
if (left != null) {
map.set(val, [...(map.get(val) ?? []), left.val]);
map.set(left.val, [...(map.get(left.val) ?? []), val]);
create(left);
}
if (right != null) {
map.set(val, [...(map.get(val) ?? []), right.val]);
map.set(right.val, [...(map.get(right.val) ?? []), val]);
create(right);
}
};
create(root);
const dfs = (st: number, fa: number) => {
let res = 0;
for (const v of map.get(st) ?? []) {
if (v !== fa) {
res = Math.max(res, dfs(v, st) + 1);
}
}
return res;
};
return dfs(start, -1);
}