编码过程中,踩了一些小坑,做下记录:
- 1.全局变量
count与std:count矛盾,建议用其他变量名。 - 2.内存泄漏问题 注意空间要开够 指针不可越界
main函数内开辟的栈空间大小一般为8MB 若要开辟较大的数组 请去main函数之外 - 3.编译器错误 推荐大家使用教新的较稳定的编译器
- 4.文件操作 打开后记得关闭 否则会占用系统资源
- 5.申请完空间,要记得释放,养成习惯。释放函数不可张冠李戴(留心编译器的
Warning)。malloc/free,new/delete要配对使用。具体原因可参考 这篇文章
准备一个字符文件,要求:
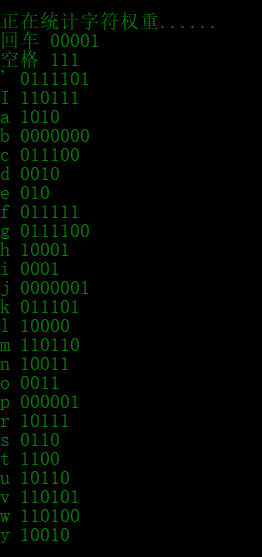
- 统计该文件中各种字符的频率
- 对各字符进行 Huffman编码,显示每个字符的编码
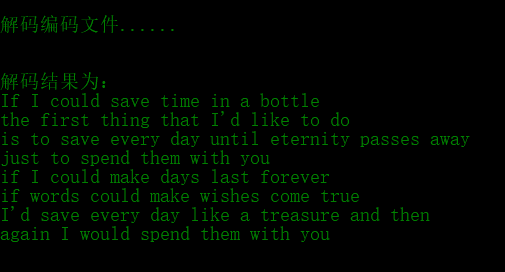
- 以及将该文件翻译成 Huffman编码文件
- 再将 Huffman编码文件翻译成源文件
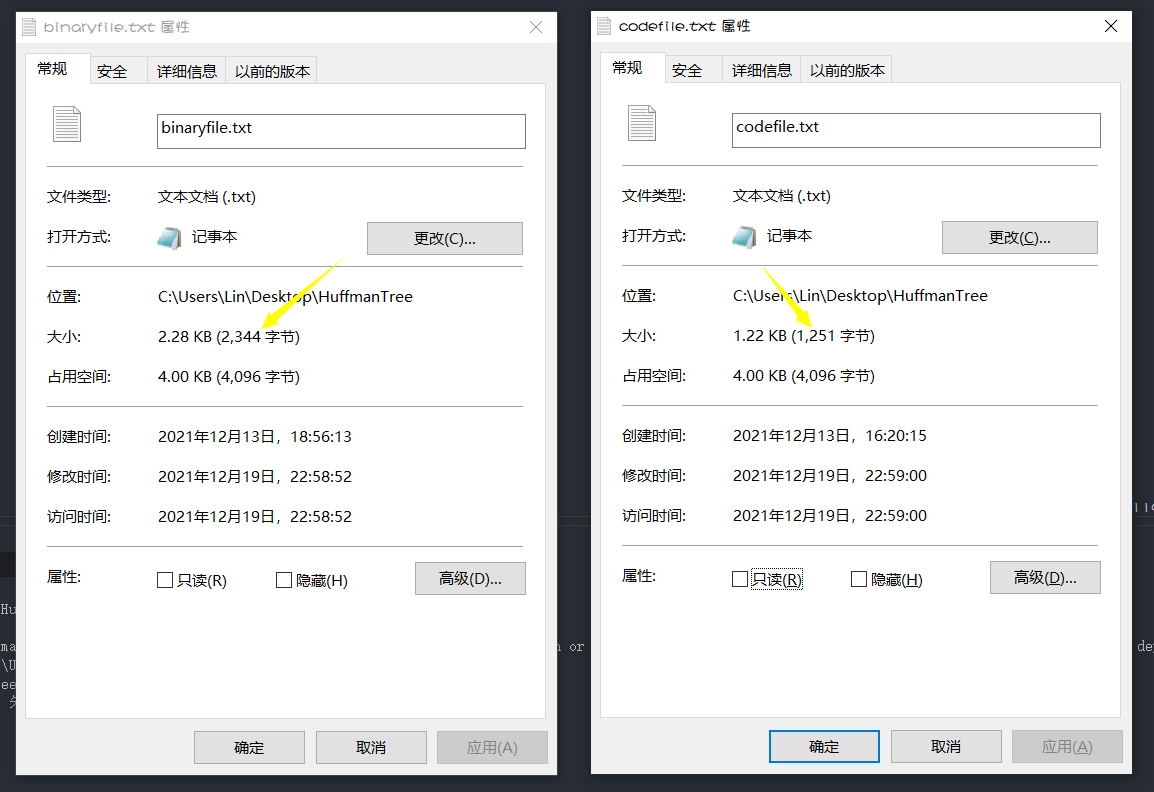
- 显示每个字符以一个字节进行二进制编码后的编码文件
实现步骤可分为:
- 统计被编码文件中个字符出现的频数,即统计权重
- 根据权重,构造哈夫曼树,进行哈夫曼编码
- 读取文件进行二进制编码
- 读取文件,将每个字符匹配哈夫曼编码,写入新文件,即完成编码
- 读取编码文件,根据哈夫曼编码进行解码,并写入新文件
- 对比二进制编码和哈夫曼编码后的文件字节大小,并计算压缩率
这里我准备了一首小诗,写入文件,并将其命名为poem.txt
If I could save time in a bottle
the first thing that I'd like to do
is to save every day until eternity passes away
just to spend them with you
if I could make days last forever
if words could make wishes come true
I'd save every day like a treasure and then
again I would spend them with you// 定义哈夫曼树节点
typedef struct {
int weight;
int parent;
int l_child;
int r_child;
char data;
} HTNode, * HuffmanTree;
typedef char** HuffmanCode;//统计该文件中各种字符的频率
void frequencyRecord(HuffmanTree& HT) {
HuffmanTree TEMP;
TEMP = new HTNode[130];
for (int i = 0; i < 130; ++i) {
TEMP[i].weight = 0;
}
ifstream originFile("poem.txt");
originFile.seekg(0);
if (!originFile) {
cout << "Can't find the file!" << endl;
} else {
char _data;
cin.unsetf(ios::skipws);
while (!originFile.eof()) {
if (originFile.get(_data)) {
TEMP[_data].data = _data;
TEMP[_data].weight++;
}
}
originFile.close();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 130; ++i) {
if (TEMP[i].weight != 0) {
N++;
}
}
HT = new HTNode[2 * N];
int k = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 130; ++i) {
if (TEMP[i].weight != 0) {
HT[k++] = TEMP[i];
}
}
}//对各字符进行 Huffman编码,显示每个字符的编码
void HuffmanCoding(HuffmanTree& HT, HuffmanCode& HC) {
int m = 2 * N - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
HT[i].parent = 0;
HT[i].l_child = 0;
HT[i].r_child = 0;
}
for (int i = N + 1; i <= m; ++i) {
HT[i].weight = 0;
HT[i].parent = 0;
HT[i].l_child = 0;
HT[i].r_child = 0;
HT[i].data = '#';
}
int child1, child2;
for (int i = N + 1; i <= m; i++) {
select(HT, i - 1, child1, child2);
HT[child1].parent = i;
HT[child2].parent = i;
HT[i].l_child = child1;
HT[i].r_child = child2;
HT[i].weight = HT[child1].weight + HT[child2].weight;
}
HC = new char* [N + 1];
char* cd = new char[N];
cd[N - 1] = '\0';
int start, c, f;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
start = N - 1;
for (c = i, f = HT[i].parent; f != 0; c = f, f = HT[f].parent) {
if (HT[f].l_child == c) cd[--start] = '0';
else cd[--start] = '1';
}
HC[i] = new char[N - start];
strcpy(HC[i], &cd[start]);
}
delete[] cd;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (HT[i].data == '\n') {
cout << "回车" << " " << HC[i] << endl;
} else if (HT[i].data == ' ') {
cout << "空格" << " " << HC[i] << endl;
} else {
cout << HT[i].data << " " << HC[i] << endl;;
}
}
}//找出最小的两个叶子节点
void select(HuffmanTree HT, int num, int& child1, int& child2) {
child1 = child2 = 0;
int w1 = 0, w2 = 0;
//Start finding...
for (int i = 1; i <= num; ++i) {
if (HT[i].parent == 0) {
if (child1 == 0) {
child1 = i;
w1 = HT[i].weight;
continue;
}
if (child2 == 0) {
child2 = i;
w2 = HT[i].weight;
continue;
}
if (w1 > w2 && w1 > HT[i].weight) {
child1 = i;
w1 = HT[i].weight;
continue;
}
if (w2 > w1 && w2 > HT[i].weight) {
child2 = i;
w2 = HT[i].weight;
continue;
}
}
}
// 使得w1永远小于w2
int temp;
if (w1 > w2) {
temp = child1;
child1 = child2;
child2 = temp;
}
}//将该文件翻译成 Huffman编码文件
void zip(HuffmanTree& HT, HuffmanCode& HC, vector<string>& code) {
ofstream codeFile("codefile.txt");
ifstream originFile("poem.txt");
if (!codeFile) {
cout << "Can't find the file!" << endl;
} else {
char _data;
cin.unsetf(ios::skipws);
while (!originFile.eof()) {
if (originFile.get(_data)) {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
if (HT[i].data == _data) {
codeFile << HC[i];
code.push_back(HC[i]);
}
}
}
}
}
codeFile.close();
}//再将 Huffman编码文件翻译成源文件
void unzip(HuffmanTree& HT, HuffmanCode& HC, vector<string>& code) {
ofstream decodeFile("decodefile.txt");
if (!decodeFile) {
cout << "Can't find the file!" << endl;
} else {
vector<string>::iterator v = code.begin();
while (v != code.end()) {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
if (HC[i] == *v) {
decodeFile << HT[i].data;
}
}
v++;
}
}
decodeFile.close();
}//显示每个字符以一个字节进行二进制编码后的编码文件
void binaryCode() {
ofstream binaryFile("binaryfile.txt");
ifstream originFile("poem.txt");
originFile.seekg(0);
if (!originFile) {
cout << "Can't find the file!" << endl;
} else {
char _data;
cin.unsetf(ios::skipws);
while (!originFile.eof()) {
if (originFile.get(_data)) {
bitset<8> data(_data);
binaryFile << data;
}
}
originFile.close();
}
}发现这里实际大小与占用空间不一样?这篇文章可以解答你的疑惑
通过编写利用哈夫曼算法实现的文件编码解码小工具,可加深对哈夫曼算法的理解,以及编码的熟练度。
同时,体会到通过算法减少文本空间,降低计算机磁盘负荷的妙处,我们需要优秀的算法来提升计算机性能。在实际的压缩算法中虽然很少听到哈夫曼编码,但其实它并没有被淘汰,而是作为核心的算法,结合了其他的压缩算法,实现对文件(文本,PPT,图片,电影等)的压缩,给日常生活带来极大便利。
本人的小工具仅针对英文大小字母及' '\n' ' '字符针对性的进行了哈夫曼编码,若想实现中文及各种支持语言的编码,可在此代码基础上,进行优化,源码地址为https://github.com/Cheung0-bit/HuffmanTreeCoding,欢迎PR;