This repo is outdated and will no longer be maintained.
Piecewise pooling layer in Keras.
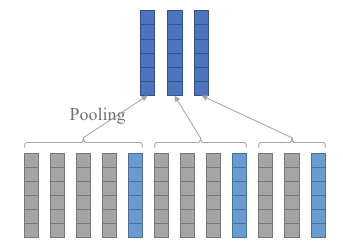
pip install git+https://github.com/cyberzhg/keras-piecewise-pooling.gitThe layer is used for pooling sequential data with given slicing positions:
import keras
import numpy as np
from keras_piecewise_pooling import PiecewisePooling1D
data = [[[1, 3, 2, 5], [7, 9, 2, 3], [0, 1, 7, 2], [4, 7, 2, 5]]]
positions = [[1, 3, 4]]
piece_num = len(positions[0])
data_input = keras.layers.Input(shape=(None, None))
position_input = keras.layers.Input(shape=(piece_num,), dtype='int32')
pool_layer = PiecewisePooling1D(pool_type=PiecewisePooling1D.POOL_TYPE_AVERAGE)([data_input, position_input])
model = keras.models.Model(inputs=[data_input, position_input], outputs=pool_layer)
model.compile(optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(), loss=keras.losses.mean_squared_error)
model.summary()
print(model.predict([np.asarray(data), np.asarray(positions)]).tolist())
# The result will be close to:
# [[
# [1.0, 3.0, 2.0, 5.0],
# [3.5, 5.0, 4.5, 2.5],
# [4.0, 7.0, 2.0, 5.0],
# ]]PiecewisePooling1D has two input layers, the first is the layer to be processed, the second is the layer representing positions. The last column of the positions must be the lengths of the sequences.
You can write your own pooling functions:
PiecewisePooling1D(pool_type=lambda x: K.min(x, axis=1))Remember to set custom_objects:
keras.models.load_model(model_path, custom_objects=PiecewisePooling1D.get_custom_objects())You'll get -inf values if you have empty intervals in the default max pooling setting. Activation layers like ReLU will help preventing nan losses.