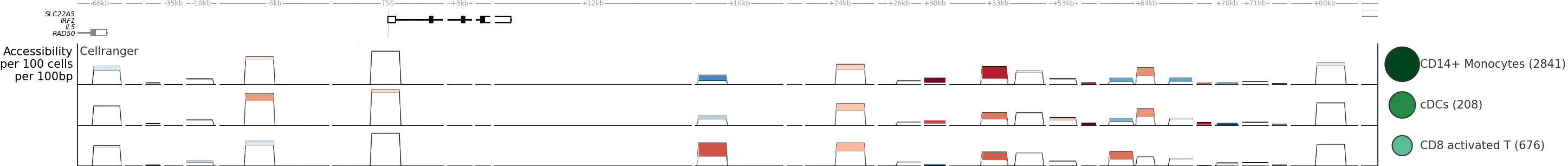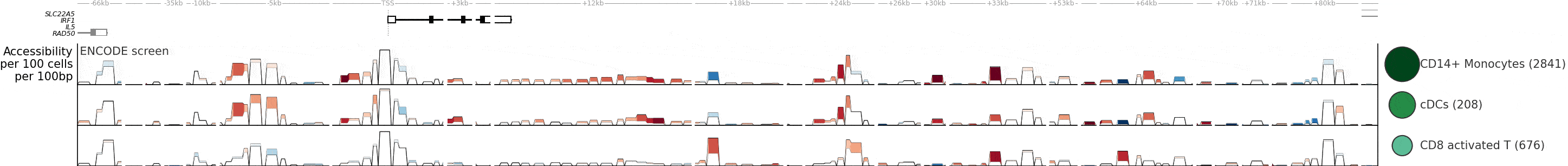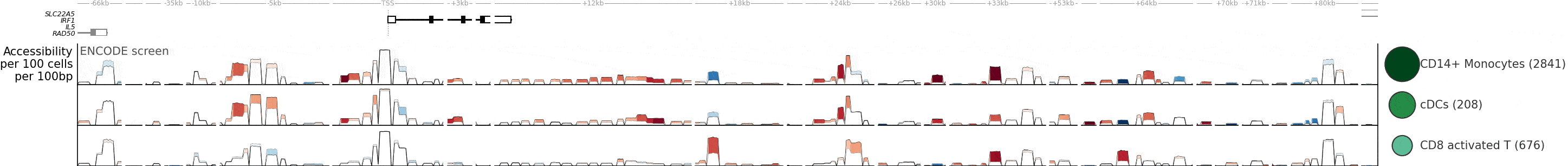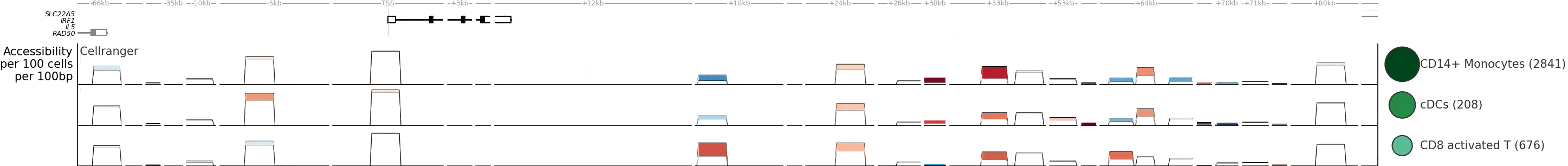
ChromatinHD analyzes single-cell ATAC+RNA data using the raw fragments as input, by automatically adapting the scale at which relevant chromatin changes on a per-position, per-cell, and per-gene basis. This enables identification of functional chromatin changes regardless of whether they occur in a narrow or broad region.
As we show in our paper:
- Compared to the typical approach (peak calling + statistical analysis), ChromatinHD models are better able to capture functional chromatin changes. This is because there are extensive functional accessibility changes both outside and within peaks (Figure 3).
- ChromatinHD models can capture long-range interactions by considering fragments co-occuring within the same cell (Figure 4).
- ChromatinHD models can also capture changes in fragment size that are related to gene expression changes, likely driven by dense direct and indirect binding of transcription factors (Figure 5).