v0.0
There are several macros for you:
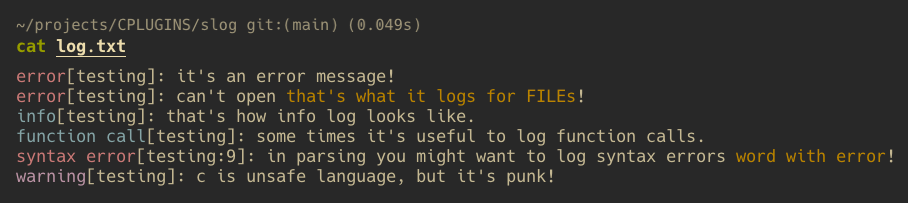
SLOG_ERROR(source, error);
SLOG_FAILED_FILE(source, file_name);To disable those define NERROR befor calling #include "slog/slog.h".
SLOG_INFO(source, info);
SLOG_FN_CALL(source, fn_name);
SLOG_SYNTAX_ERROR(source, line, message, word);
SLOG_WARNING(source, warning);To disable those define either NERROR or NLOG. In the last option you will still have error messages.
You have predefined colors:
[SLOG_BLACK, SLOG_RED, SLOG_GREEN, SLOG_YELLOW, SLOG_BLUE, SLOG_MAGENTA, SLOG_CYAN, SLOG_WHITE]
[SLOG_BR_BLACK, SLOG_BR_RED, SLOG_BR_GREEN, SLOG_BR_YELLOW, SLOG_BR_BLUE, SLOG_BR_MAGENTA, SLOG_BR_CYAN, SLOG_BR_WHITE]
And your colors for logging by defining: [MY_SLOG_MESSAGE_COLOR, MY_SLOG_ERROR_COLOR, MY_SLOG_WARNING_COLOR, MY_SLOG_INFO_COLOR]. The default values are: [SLOG_YELLOW, SLOG_RED, SLOG_RED, SLOG_MAGENTA, SLOG_BLUE] respectively
Currently you can set your logging file by adding few lines of code
FILE* $(YOUR_FILE);
#define SLOG_OUT $(YOUR_FILE)
#include "slog/slog.h"
...
int main () {
SLOG_OUT = fopen (...);Use keyword extern to log from other c files. By default logging is done directly
to stdout
Edit and run test.c on your machine to see how it looks like