The following notebook is an exercise for the Convolutional Neural Networks for Computer Vision course at Afeka College of Engineering.
It uses Flickr8K dataset for image captioning.
Submitted By:
- Tal Goldengoren
- Guy Kabiri
Table of Contents:
from dataloader import *
from model import *
from train import *
from utils import *
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pdassert torch.cuda.is_available()
np.random.seed(CFG.seed)
torch.manual_seed(CFG.seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed(CFG.seed)The dataset used in this exercise was Flickr8K.
It contains about 8,000 images, with 5 different captions each. Therefore, a total of about 40,000 captions.
As each image may be described in different ways by different people, having more than 1 caption for each image will assist in better training and evaluating the correctness of the predictions.
loader = get_loaders(batch_size=1, phase='test')['test']
captions_file = "data/flickr8k/captions.txt"
df = pd.read_csv(captions_file)df.info()<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 40455 entries, 0 to 40454
Data columns (total 2 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 image 40455 non-null object
1 caption 40455 non-null object
dtypes: object(2)
memory usage: 632.2+ KB
Some captions examples
df| image | caption | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | A child in a pink dress is climbing up a set o... |
| 1 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | A girl going into a wooden building . |
| 2 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | A little girl climbing into a wooden playhouse . |
| 3 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | A little girl climbing the stairs to her playh... |
| 4 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | A little girl in a pink dress going into a woo... |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 40450 | 997722733_0cb5439472.jpg | A man in a pink shirt climbs a rock face |
| 40451 | 997722733_0cb5439472.jpg | A man is rock climbing high in the air . |
| 40452 | 997722733_0cb5439472.jpg | A person in a red shirt climbing up a rock fac... |
| 40453 | 997722733_0cb5439472.jpg | A rock climber in a red shirt . |
| 40454 | 997722733_0cb5439472.jpg | A rock climber practices on a rock climbing wa... |
40455 rows × 2 columns
As can be seen above, each image has 5 captions, it means that during training all 5 captions should be taken into account when evaluating models performance.
num_images = len(df.image.unique())
train_img_size, valid_img_size, test_img_size = int(num_images*CFG.train_size), int(num_images*(1-CFG.train_size)/2), int(num_images*(1-CFG.train_size)/2)
train_cap_size, valid_cap_size, test_cap_size = train_img_size*5, valid_img_size*5, test_img_size*5
print('There are {} images in the dataset'.format(num_images))
print('Training set will contain {} images and {} captions'.format(train_img_size, train_cap_size))
print('Validation set will contain {} images and {} captions'.format(valid_img_size, valid_cap_size))
print('Test set will contain {} images and {} captions'.format(test_img_size, test_cap_size))There are 8091 images in the dataset
Training set will contain 6068 images and 30340 captions
Validation set will contain 1011 images and 5055 captions
Test set will contain 1011 images and 5055 captions
loader_iter = iter(loader)
_, caps, _ = next(loader_iter)
print(caps)tensor([[[ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]],
[[ 4, 4, 10, 10, 431]],
[[ 30, 431, 431, 21, 335]],
[[ 6, 6, 30, 6, 6]],
[[ 29, 17, 6, 17, 29]],
[[ 37, 324, 17, 29, 37]],
[[ 10, 37, 29, 8, 44]],
[[ 44, 423, 8, 10, 2]],
[[ 5, 44, 10, 423, 0]],
[[ 2, 5, 44, 44, 0]],
[[ 0, 2, 5, 5, 0]],
[[ 0, 0, 2, 2, 0]]])
for _ in range(2):
batch = next(loader_iter)
imgs, caps, _ = batch
print('Images shape: {}'.format(imgs.shape))
print('Captions shape: {}'.format(caps.shape))
print()Images shape: torch.Size([1, 3, 224, 224])
Captions shape: torch.Size([16, 1, 5])
Images shape: torch.Size([1, 3, 224, 224])
Captions shape: torch.Size([21, 1, 5])
The data will be provided to the model as follow:
Images: [B, C, H, W]
Captions: [MS, B, NC]
B=batch size
MS=max sentence length
NC=number of captions per image
As the images shape is quite understandable, the captions is a bit weird.
This shape is due to the different sentences length between the different samples.
When working with batches, the samples whitin each batch should be equals size, therefore, it is not possible to represent sentences with different lengths with a normal shape, and much easier to padding short sentences in that shape.
The first sentence present along the first column of the matrix, the second sentence in the second column, and so on.
The images in the dataset are variety in shapes.
The backbone model which will be used in this architecture, will be a pre-trained model (ImageNet), therefore all the images will be resized into 224X244 shape.
Also, because the model is pre-trained, the images will be normalized into ImageNet mean and std values.
As nueral networks understand only numbers, and not words, all of the captions need to be transformed into numbers.
It means that each unique word in the dataset should get a unique number to reprenet it.
For this task, a pre-build vocabulary will be used, this vocabulary contains a large amount of words, each will be mapped into a unique number.
As dataset may contains words that appear only once in captions, the model will have hard time learning such words.
Therefore, only frequent words will be taking into account, while leaving the un-common words out, this can be addjust by a threshold, which means it is another hyper-parameter that can be tuned.
Moreover, the tokkenized vocabulary will hold a several unique words that have a special meaning:
<SOS>- Start of sentence<EOS>- End of sentence<PAD>- Paddind to generate equal size captions during training<UKN>- Any word under the frequent threshold
def get_sentences(dataloader, captions):
captions = captions.squeeze(1)
captions = torch.permute(captions, (1, 0))
num_sentences, num_word = captions.shape
sentences = []
for i in range(num_sentences):
words = [ dataloader.dataset.vocab.itos[int(word)] for word in captions[i] ] # convert tokenizes to words
eos_index = words.index('<EOS>') # find index of <EOS>
words = words[1 : eos_index] # remove <SOS> and <EOS>
sen = ' '.join(words)
sentences.append(sen)
return sentencesdef show_example(dataloader, rows=4, cols=2):
num_examples = cols*rows
global_offset = 14
font_size = 12
transform = get_transformer('print')
fig, axs = plt.subplots(rows, cols, sharey=True, figsize=(10*cols, 10*rows))
for idx, (_, captions, img_id) in enumerate(dataloader):
if idx == num_examples:
break
img = transform(Image.open('data/flickr8k/images/' + img_id[0]).convert('RGB'))
# img = img.squeeze(0)
img = np.transpose(img, (1, 2, 0))
sentences = get_sentences(dataloader, captions)
ridx, cidx = idx//cols, idx%cols
axs[ridx, cidx].imshow(norm(img))
offset = global_offset
for sen in sentences:
axs[ridx, cidx].text(2, offset, sen, fontsize=font_size, color='white', bbox=dict(facecolor='black', alpha=0.5))
offset += global_offset
axs[ridx, cidx].axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
show_example(loader)The training process involved several configuration and trials:
Two backbone modleds were tested for the encoder, Resnet-152 and InceptionV3.
Various amount of LSTM layers were tested from 2, up to 5.
Several learning rates, as well as, different number of epochs and batch sizes.
For final configuration the following was used:
- Backbone: InceptionV3
- Embedded Size: 512
- Hidden Size: 512
- LSTM Layers: 3
- Batch Size: 32
- learning_rate: 1e-4
- num_epochs: 150
- drop_rate: 0.5
- Criterion: CrossEntropyLoss
- Optimizer: Adam
- Scheduler: ReduceLROnPlateau w/ factor=0.8, patience=2
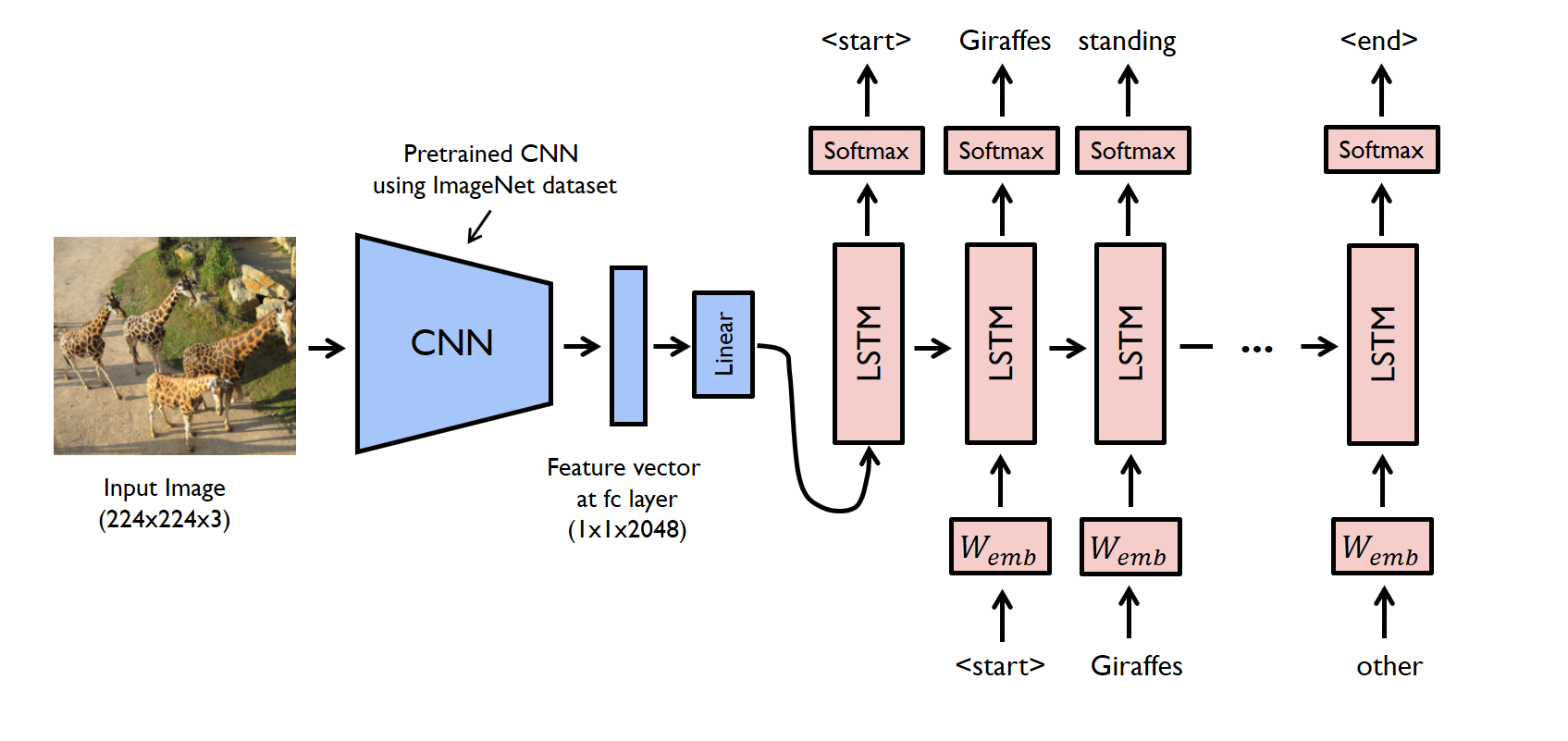
The backbone was a pre-trained model, and it was not trained during the training phase.
During training, first, an image goes through the CNN model in order to extract its features.
After extracting features, a linear layer will be used to map the features into the vocabulary embedding size, with a dropout layer on top of it for bettrer training.
Later on, this linear layer inserted into the decoder, which will pass the output of the embedding layer into certain amount of LSTM layers, in order to generate sequence of words.
For final prediction, a linear layer with the size of the vucabulary will be used to map the prediction to the correct words.
# test_path = 'runs/26-11-21_10:36/test'
# test_path = 'runs/26-11-21_16:03/test'
test_path = 'runs/26-11-21_20:20/test'
test_df = pd.read_csv(test_path + '/test.csv')test_df| Unnamed: 0 | image | prediction | loss | 1-gram | 2-gram | 3-gram | 4-gram | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 3150659152_2ace03690b.jpg | <SOS> a man is standing on a rock overlooking ... | 3.138403 | 0.636364 | 0.356753 | 0.112244 | 0.064841 |
| 1 | 1 | 2222498879_9e82a100ab.jpg | <SOS> a dog is jumping over a hurdle . <EOS> | 1.556955 | 0.625000 | 0.422577 | 0.143842 | 0.087836 |
| 2 | 2 | 3126752627_dc2d6674da.jpg | <SOS> a football player in a red uniform is ru... | 1.948640 | 0.427367 | 0.181596 | 0.065234 | 0.040041 |
| 3 | 3 | 3257207516_9d2bc0ea04.jpg | <SOS> a man in a black shirt and a woman in a ... | 3.116272 | 0.357143 | 0.230022 | 0.182766 | 0.125008 |
| 4 | 4 | 2289096282_4ef120f189.jpg | <SOS> a man and a woman are sitting on a bench... | 3.108447 | 0.411765 | 0.160422 | 0.055566 | 0.033272 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 1007 | 1007 | 1303727066_23d0f6ed43.jpg | <SOS> a man in a black shirt and a woman in a ... | 3.242519 | 0.230769 | 0.096077 | 0.033755 | 0.020222 |
| 1008 | 1008 | 534886684_a6c9f40fa1.jpg | <SOS> a man in a black shirt and jeans is stan... | 2.602398 | 0.529412 | 0.363803 | 0.095914 | 0.050105 |
| 1009 | 1009 | 2431723485_bc6b8e6418.jpg | <SOS> a man in a red shirt and a black dog are... | 2.363976 | 0.394458 | 0.203299 | 0.061354 | 0.034292 |
| 1010 | 1010 | 3373481779_511937e09d.jpg | <SOS> a man in a red shirt and white shorts is... | 2.990329 | 0.500000 | 0.196116 | 0.068436 | 0.041316 |
| 1011 | 1011 | 3265964840_5374ed9c53.jpg | <SOS> a man in a red jacket is riding a bike o... | 1.752711 | 0.600000 | 0.462910 | 0.320647 | 0.228942 |
1012 rows × 8 columns
def get_clean_sentence(sentence):
stopwords = ['<SOS>', '<EOS>', '.']
words_list = sentence.split()
resultwords = [word for word in words_list if word.upper() not in stopwords]
return ' '.join(resultwords)
def get_two_line_sentence(sentence, max_words=18):
new_sen = sentence.split()
return ' '.join(new_sen[ : max_words]) + '\n' + ' '.join(new_sen[ max_words : ])
def get_plot_sentence(sentence, max_words=18):
clean_sentence = get_clean_sentence(sentence)
if len(clean_sentence.split()) > max_words:
return get_two_line_sentence(clean_sentence, max_words), True
return clean_sentence, False
def show_example(dataloader, df, rows=4, cols=2):
num_examples = cols*rows
global_offset = 14
font_size = 12
max_words = 18
transform = get_transformer('print')
examples_df = df[ : num_examples]
fig, axs = plt.subplots(rows, cols, sharey=True, figsize=(10*cols, 10*rows))
for i in range(num_examples):
img_id = examples_df.iloc[i]['image']
img = transform(Image.open('data/flickr8k/images/' + img_id).convert('RGB'))
img_index = np.where(np.array(dataloader.dataset.images) == img_id)[0][0]
captions = dataloader.dataset.__getitem__(img_index)[1]
img = np.transpose(img, (1, 2, 0))
sentences = get_sentences(dataloader, captions)
ridx, cidx = i//cols, i%cols
axs[ridx, cidx].imshow(norm(img))
offset = global_offset
for sen in sentences:
sen, two_lines = get_plot_sentence(sen, max_words)
if two_lines:
offset += global_offset//1.5
axs[ridx, cidx].text(2, offset, sen, fontsize=font_size, color='white', bbox=dict(facecolor='black', alpha=0.5))
offset += global_offset
df_img = test_df[test_df['image']==img_id]
pred = df_img['prediction'].item()
pred, two_lines = get_plot_sentence(pred, max_words)
if two_lines:
offset += global_offset//1.5
axs[ridx, cidx].text(2, offset, pred, fontsize=font_size, color='black', bbox=dict(facecolor='white', alpha=0.5))
filter_col = [col for col in df_img if col.endswith('-gram')]
offset = img.size(1) - ((len(filter_col) + 1) * global_offset)
loss = df_img['loss'].item()
title = 'loss: {:.5f}'.format(loss)
axs[ridx, cidx].text(2, offset, title, fontsize=font_size, color='black', bbox=dict(facecolor='white', alpha=0.5))
offset += global_offset
for col in filter_col:
score = df_img[col].item()
title = '{}: {:.5f}'.format(col, score)
axs[ridx, cidx].text(2, offset, title, fontsize=font_size, color='black', bbox=dict(facecolor='white', alpha=0.5))
offset += global_offset
axs[ridx, cidx].axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()test_df = test_df.sort_values(by=['1-gram', 'loss'], ascending=False)
show_example(loader, test_df.drop_duplicates(subset=['prediction']))test_df = test_df.sort_values(by=['1-gram', 'loss'], ascending=True)
show_example(loader, test_df.drop_duplicates(subset=['prediction']))