Aiming at the problem that the differences in heterogeneous remote sensing images in imaging modes, time phases, and resolutions make matching difficult, a new deep learning feature matching method is proposed. The results show that the algorithm in this paper has strong adaptability and robustness, and is superior to other algorithms in terms of the number and distribution of matching points, efficiency, and adaptability. This repository contains the implementation of the following paper:
"A Heterogeneous Remote-Sensing Image Matching Method Based on Deep Learning Feature" (in Chinese)
一种基于深度学习特征的异源遥感影像匹配算法
The main idea and code of feature extracting in this repository are based on D2-Net.
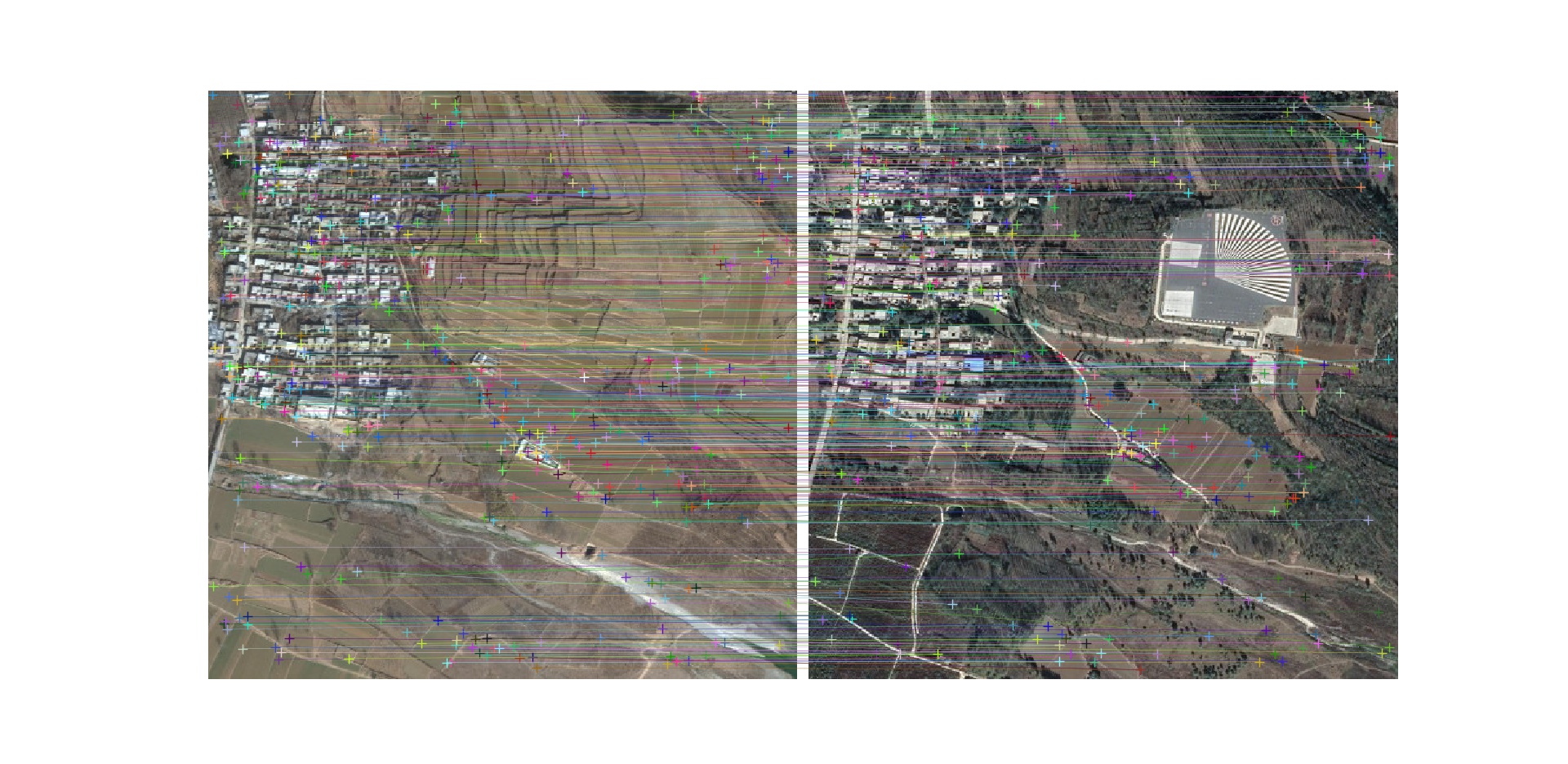 Matching result between google earth images (in 2009 & 2018)
Matching result between google earth images (in 2009 & 2018)
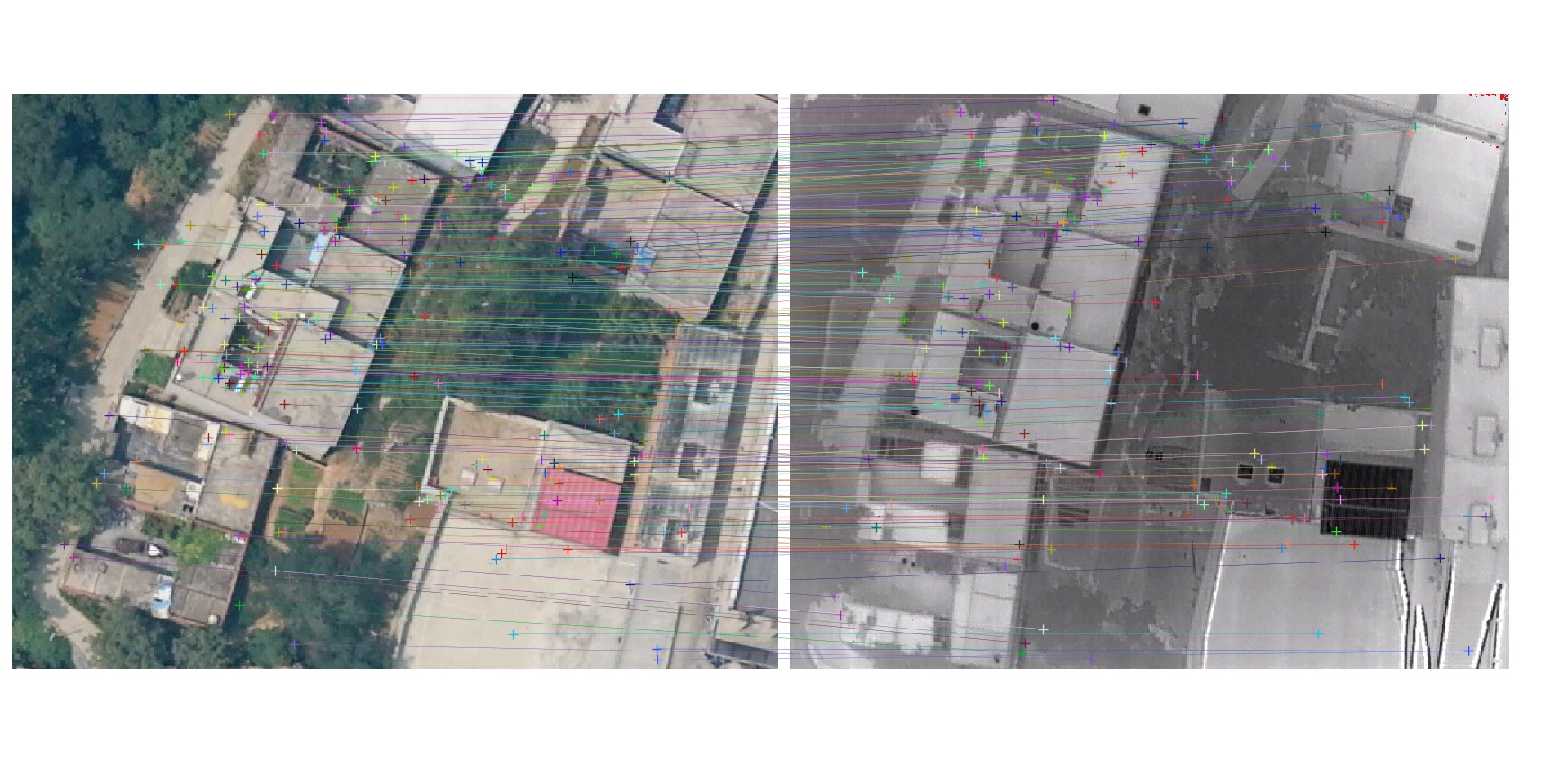 Matching result between uav optical image and thermal infrared image
Matching result between uav optical image and thermal infrared image
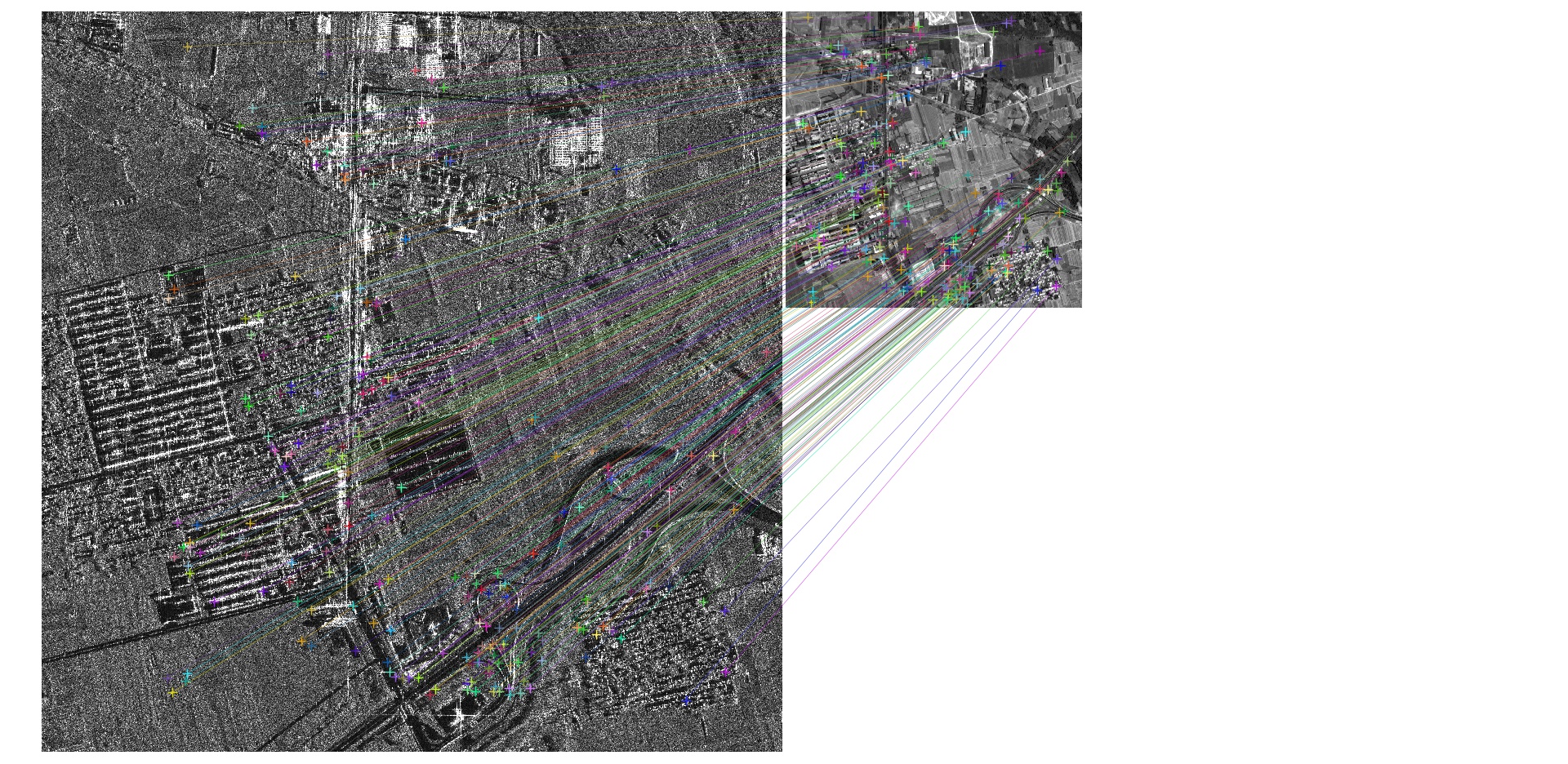 Matching result between SAR image (GF-3) & optical satellite(ZY-3) image
Matching result between SAR image (GF-3) & optical satellite(ZY-3) image
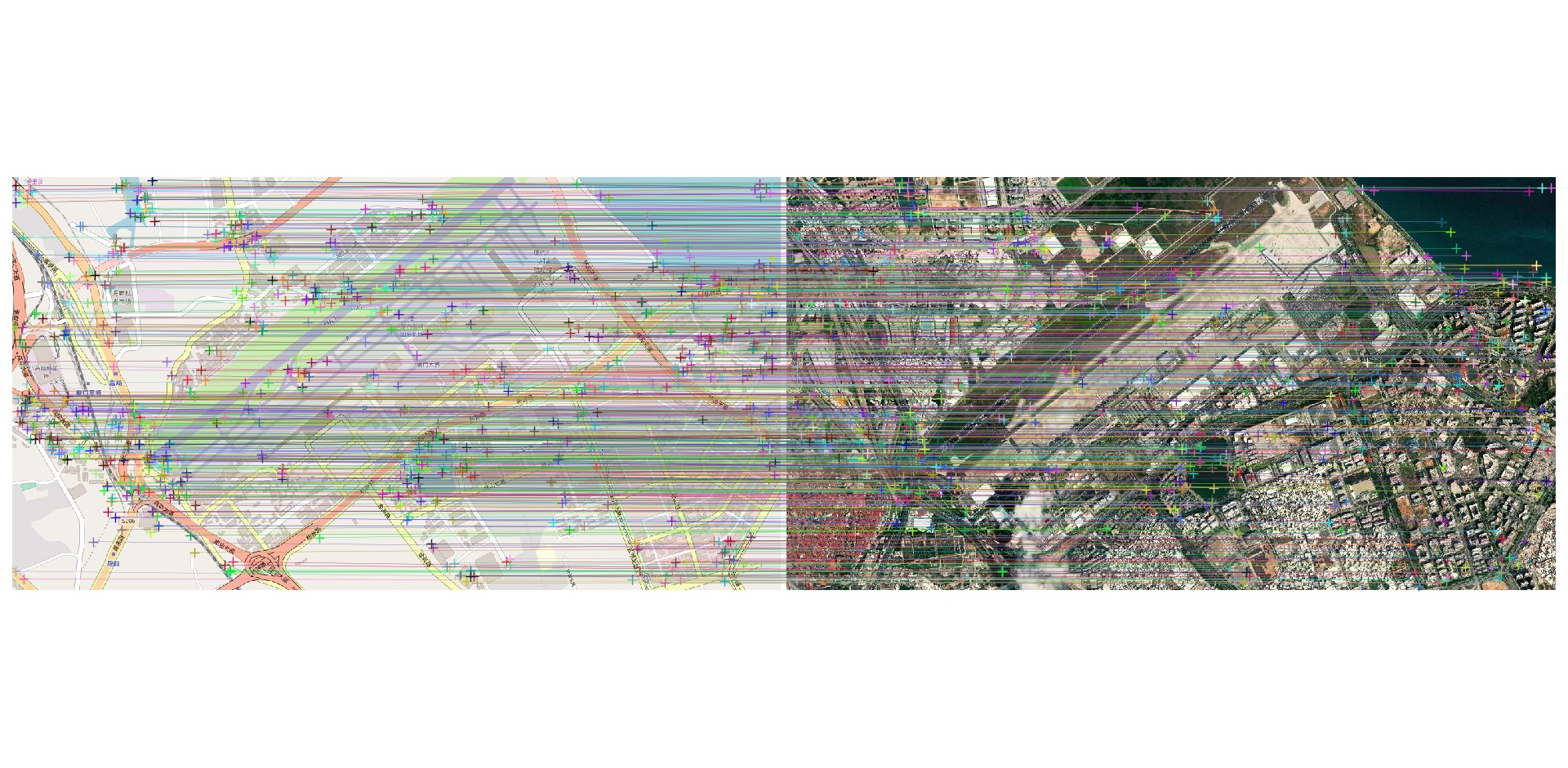 Matching result between satellite image & map
Matching result between satellite image & map
Python 3.7+ is recommended for running our code. Conda can be used to install the required packages:
- PyTorch 1.4.0+
- OpenCV
- SciPy
- Matplotlib
- skimage
We collected a set of test data named "df-sm-data", including images from space-borne SAR and visible light sensors, drone thermal infrared sensors, and Google Earth images. You may find them in the directory "df-sm-data" in this repository.
The off-the-shelf VGG16 weights and their tuned counterpart can be downloaded by running:
mkdir models
wget https://dsmn.ml/files/d2-net/d2_tf.pth -O models/d2_tf.pthcnnmatching.py contains the majority of the code. Run cnnmatching.py for testing:
python3 cnnmatching.pyYou may change the images path in the code just like:
imgfile1 = 'df-ms-data/1/df-googleearth-500-20091227.jpg'
imgfile2 = 'df-ms-data/1/df-googleearth-500-20181029.jpg'