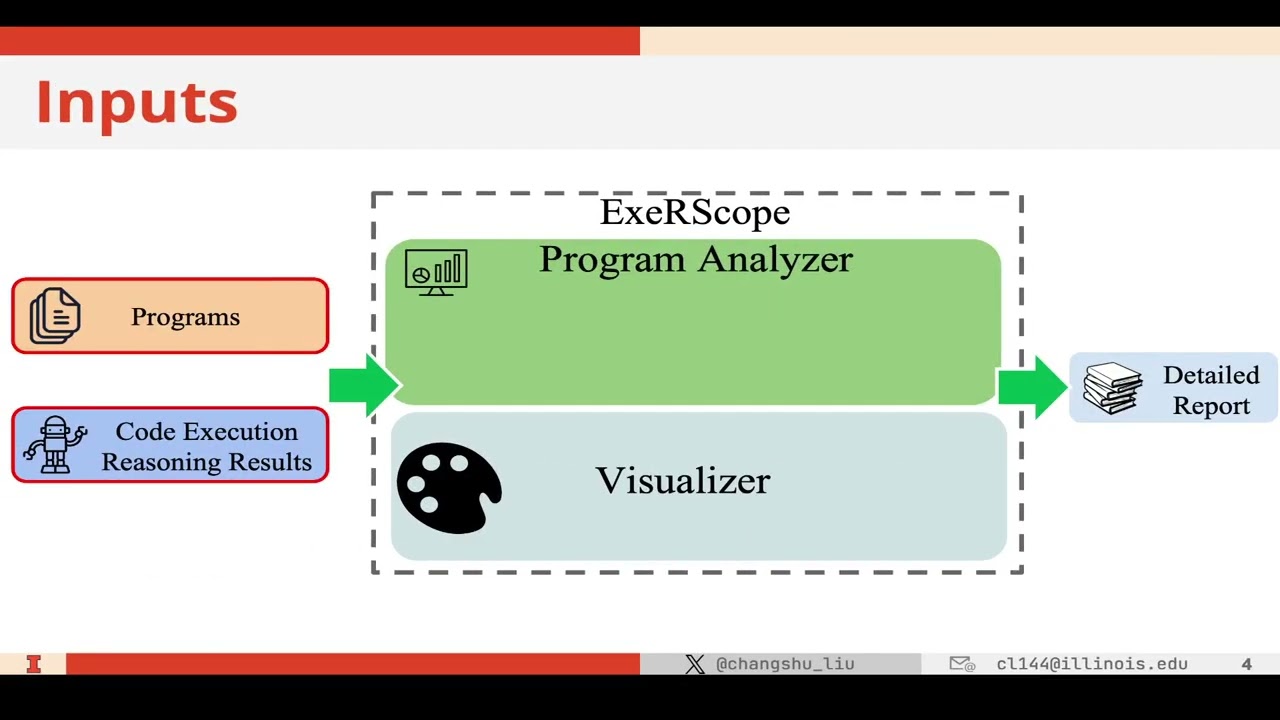
ExeRScope currently assesses the impact of different (1) program constructs, (2) program complexities, (3) programming properties such as loop length, and (4) variable types on code execution reasoning. Evaluation of ExeRScope on four programming benchmarks (Avatar, ClassEval, CRUXEval, and HumanEval) and six LLMs (GPT-4, Gemini-1.5-Pro, CodeLlama (Instruct-34b), DeepSeekCoder (Instruct-33b), SemCoder-S (6.7b), and Star-Coder2 (15b) shows its effectiveness and practicality.
We have provided a pre-built docker image to make using ExeRScope easier. Alternatively, you may clone the repository on your local machine, install the dependencies (as instructed below), and run available the commands.
Please use the following commands to pull the pre-built docker image and run the commands:
docker image pull ericliuuiuc/exerscope
If using the docker image, please go to the shell mode of the provided image to run the commands:
docker run -it ericliuuiuc/exerscope bash
To install all the dependencies on your local machine (if you decided not to use the docker image), run the following commands:
conda create -n exerscope python=3.8
conda activate exerscope
pip install -r requirements.txt
To run ExeRScope, please put the dataset under the dataset directory and the execution reasoning results from LLMs under Experiment_Results/ER (we have already provided the data to reproduce the results presented in the ExeRScope paper).
For each problem/program in the benchmark, please create an individual folder and store its code, input, and output in main.py, input.txt, and output.txt, respectively. Similarly, for the prediction of each problem, create an individual folder and store the parsed result in predict.txt.
Please follow the format under dataset/humaneval and Experiment_Results/ER/gpt-4-turbo/humaneval
First, move to the main directory to run the scripts (note that if you are using the docker image, you should first go to the bash mode as instructed above and then run the commands below):
cd analysis
bash analyze_constructs.sh
Running this command will generate the analysis related to the impact of programming constructs on the execution reasoning of LLMs (across benchmarks and per each LLM). The results figures/stats can be found under Experiment_Results/figures/constructs
bash analyze_complexity.sh
Running this command will generate the analysis related to the impact of programming complexity on the execution reasoning of LLMs (across benchmarks and per each LLM). The results figures/stats can be found under Experiment_Results/figures/progem_complexity
bash analyze_dynamic.sh
Running this command will generate the analysis related to the impact of dynamic properties on the execution reasoning of LLMs (across benchmarks and per each LLM). The results figures/stats can be found under Experiment_Results/figures/dynamic_property
bash analyze_types.sh
Running this command will generate the analysis related to the impact of output variable types on the execution reasoning of LLMs (across benchmarks and per each LLM). The results figures/stats can be found under Experiment_Results/figures/types