- 자바스크립트가 c나 java와 같은 c-family와 구별되는 특징
- Prototype-based Object Oriented Language
- Scope 와 this
- dynamic typed 언어 혹은 loosely typed언어
- 이런 특성은 클래스 기반 객체지향언어(Java, C++, C# 등)에 익숙한 개발자를 혼란스럽게 하고
- 코드가 복잡해지거나 디버그와 테스트 공수가 증가하는 문제가 있어 규모가 큰 프로젝트에서 주의하여야 했다.
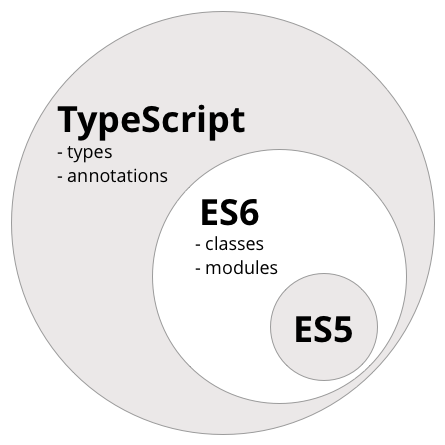
- JavaScript 대체 언어의 하나로써 JavaScript(ES5)의 Superset(상위확장)이다. C#의 창시자인 덴마크 출신 소프트웨어 엔지니어 Anders Hejlsberg(아네르스 하일스베르)가 개발을 주도한 TypeScript는 Microsoft에서 2012년 발표한 오픈소스로, 정적 타이핑을 지원하며 ES6(ECMAScript 2015)의 클래스, 모듈 등과 ES7의 Decorator 등을 지원한다.
-
TypeScript는 ES5의 Superset이므로 기존의 JavaScript(ES5) 문법을 그대로 사용할 수 있다. 또한, ES6의 새로운 기능들을 사용하기 위해 Babel과 같은 별도 트랜스파일러(Transpiler)를 사용하지 않아도 ES6의 새로운 기능을 기존의 JavaScript 엔진(현재의 브라우저 또는 Node.js)에서 실행할 수 있다.
-
이후 ECMAScript의 업그레이드에 따른 새로운 기능을 지속적으로 추가할 예정이여서 매년 업그레이드될 ECMAScript의 표준을 따라갈 수 있는 좋은 수단이 될 것이다.
- 정적 타입(Statically typed)
- Javascript의 다음의 함수는 2개요소를 인수를 전달받아 합치는 함수이다
- 개발자의 의도는 2개의 number를 더한값을 리턴하는것이였으나 string값을 요소로 받아 최초의도와 다른 함수가 되었다.
- 따라서 함수가 개발자의 의도에 따라 기능을 수행하도록 각 요소의 타입을 명시하여
- 의도하지 않은 error를 줄이는것이 typescript 이다.
function sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
console.log(sum('2', '3')); // '23'// 정확한 parameter의 타입을 명시하여 개발자의 의도에 따라 기능이 수행되도록 돕는다.
const sum = (a: number, b: number): number => {
return a + b;
};
console.log(sum(1, 2));
//! error : Argument of type 'string' is not assignable to parameter of type 'number'.
console.log(sum('1', '2'));- 강력한 객체지향 프로그래밍 지원
- 인터페이스, 제네릭 등과 같은 강력한 객체지향 프로그래밍 지원은 크고 복잡한 프로젝트의 코드 기반을 쉽게 구성할 수 있도록 도우며, Java, C# 등의 클래스 기반 객체지향 언어에 익숙한 개발자가 자바스크립트 프로젝트를 수행하는 데 진입 장벽을 낮추는 효과도 있다.
-
TypeScript 컴파일러 설치
// 설치
> npm install -g typescript
// 확인
> tsc -v- TypeScript 컴파일러(tsc)는 TypeScript파일(.ts)을 JavaScript 파일로 Transpiling을 한다.
// person.ts 생성
export class Person {
protected name: string;
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
sayHello() {
return 'Hello, ' + this.name;
}
}// person을 Transpiling
> tsc person- person.js 자동생성 된다 이때 버젼은 ES3이다 기본버젼이 ES3이기때문
// es6 버젼으로 Transpiling
> tsc person -t es6// student.ts
import { Person } from './person';
class Student extends Person {
study(): string {
return `${this.name} is studying.`;
}
}
const student = new Student('Lee');
console.log(student.sayHello());
console.log(student.study());// person.ts , student.ts 2개 동시에 Transpiling
> tsc person student
// watch -w 옵션으로 변경되었을때 자동으로 Transpiling
> tsc student --watch- tsc 옵션 설정 파일을 생성해서 매번 옵션을 지정하는 것은 대신한다
// tsconfig.json 생성
> tsc --init
// tsconfig.json을 무시
> tsc person
// tsconfig.json을 적용
> tsc// init
> yarn init
// devDependencies
> yarn add -D typescript nodemon ts-node @types/node
// tsc 설정
> tsc --init// package.json
{
...
"scripts": {
"dev": "nodemon --config nodemon.json index.ts",
"dev:debug": "nodemon --config nodemon.json --inspect-brk index.ts"
},
...
}
// nodemon.json
{
"restartable": "rs",
"ignore": [".git", "node_modules/", "dist/", "coverage/"],
"watch": ["./"],
"execMap": {
"ts": "node -r ts-node/register"
},
"env": {
"NODE_ENV": "development"
},
"ext": "js,json,ts"
}-
TypeScript를 사용하는 이유는 여러가지 있지만 가장 큰 장점은 다양한 도구의 지원을 받을 수 있다는 것이다. TypeScript는 정적 타입을 지원하므로 높은 수준의 IntelliSense나 리팩토링 등을 지원하며 이러란 도구의 지원은 대규모 프로젝트를 위한 필수적 요소이기도 하다.
-
프로젝트 내에는 필수적으로 다양한 라이브러리가 포함되는데 이 라이브러리들은 JavaScript로 작성되어있다. TypeScript는 ES5의 Superset(상위확장)이므로 JavaScript를 그대로 사용할 수 있다. 하지만 정적 타입이 없는 JavaScript를 그대로 사용하면 VSCode에서 제공하는 IntelliSense와 같은 다양한 도구의 지원을 받을 수 없다.
-
따라서 외부 JavaScript 라이브러리에 대해서도 타입체크를 수행하려면 해당 라이브러리의 타입이 정의되어 있는 정의 파일(Definition file)을 제공해야 한다.
> yarn add lodash
> yarn add -D @types/lodash// index.ts
import * as _ from 'lodash';
class Startup {
public static main(): number {
const group = _.groupBy(['one', 'two', 'three'], 'length');
console.log(group); // => { '3': ['one', 'two'], '5': ['three'] }
return 0;
}
}
Startup.main(); // { '3': [ 'one', 'two' ], '5': [ 'three' ] }- TypeScript는 ES5, ES6의 Superset(상위확장)이므로 자바스크립트의 타입을 그대로 사용할 수 있다. 자바스크립트의 타입 이외에도 TypeScript 고유의 타입이 추가로 제공
| Type | JS | TS | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | ◯ | ◯ | true와 false |
| null | ◯ | ◯ | 값이 없다는 것을 명시 |
| undefined | ◯ | ◯ | 값을 할당하지 않은 변수의 초기값 |
| number | ◯ | ◯ | 숫자(정수와 실수, Infinity, NaN) |
| string | ◯ | ◯ | 문자열 |
| symbol | ◯ | ◯ | 고유하고 수정 불가능한 데이터 타입. 주로 객체 프로퍼티들의 식별자로 사용 |
| object | ◯ | ◯ | 객체형(참조형) |
| array | ◯ | 배열 | |
| tuple | ◯ | 고정된 요소수 만큼의 타입을 미리 선언후 배열을 표현 | |
| enum | ◯ | 열거형. 숫자값 집합에 이름을 지정한 것이다. | |
| any | ◯ | 어떤 타입의 값이라도 할당 가능. | |
| void | ◯ | 일반적으로 함수에서 반환값이 없을 경우 사용한다. | |
| never | ◯ | 결코 발생하지 않는 값 |
-
- 클래스 정의(Class Definition)
//! error : 이경우 field 선언이 되어있지 않아
class Person {
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
}
class Person {
// class안에서 사용될 field 선언
name: string;
// name은 선언된 filed 이기 때문에 사용 가능
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
}-
- 접근 제한자(Access modifier)
- 다른 언어는 default가 protected이지만 typescript에서는 public
접근 가능성 public(default) protected private 클래스 내부 ◯ ◯ ◯ 자식 클래스 내부 ◯ ◯ ✕ 클래스 인스턴스 ◯ ✕ ✕
-
- 생성자 파라미터에 접근 제한자 선언
- 접근제한자가 사용된 파라미터는 암묵적으로 클래스 filed로 선언
class Person {
// class안에서 사용될 field 선언
// name: string;
// 접근제한자가 사용된 파라미터는 암묵적으로 클래스 filed로 선언된다
constructor(private name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
walk(): string {
return `person who name is ${this.name}`;
}
}- 접근 제한자를 선언하지 않은 생성자 파라미터는 생성자 내부에서만 유효한 지역변수가되어 외부 참조 불가능
class Person {
// name은 생성자 내부에서만 유효한 지역 변수이다.
constructor(public firstName: string, name: string) {
console.log(name);
}
}
const foo = new Person('first', 'name'); // name
console.log(foo); // Person { firstName: 'first' }-
- readonly 키워드
- readonly가 선언된 filed는 선언 시, 생성자 내부에서만 값을할당할수 있다.
class Foo {
private readonly MAX_LEN: number = 5;
private readonly MSG: string;
constructor() {
this.MSG = 'hello';
// 생성자 내부여서 값 할당 가능.
this.MAX_LEN = 10;
}
log() {
// readonly가 선언된 프로퍼티는 재할당이 금지된다.
// this.MAX_LEN = 10; //! error: Cannot assign to 'MAX_LEN' because it is a constant or a read-only property.
console.log(`MAX_LEN: ${this.MAX_LEN}`); // MAX_LEN: 5
console.log(`MSG: ${this.MSG}`); // MSG: hello
}
}
new Foo().log();-
- static 키워드
- static(정적) 선언은 class의 인스턴스생성 없이 호출할수 있다.
class FooStatic {
//* static filed
static counter = 0;
constructor(public prop: any) {
this.prop = prop;
//* 생성될때마다 늘어남
FooStatic.counter++;
}
static staticMethod() {
//* 정적 method는 this를 사용할 수 없다.
//* 정적 method 내부에서 this는 클래스의 인스턴스가 아닌 클래스 자신을 가리킨다.
console.log(this); // [Function: FooStatic] { staticMethod: [Function], counter: 0 }
return 'staticMethod';
}
prototypeMethod() {
return this.prop;
}
}
//* static은 클래스 이름으로 호출한다.
console.log(FooStatic.staticMethod());
console.log(FooStatic.counter);
const fooStatic = new FooStatic(123);
//* 정적 method는 인스턴스로 호출할 수 없다.
// console.log(fooStatic.staticMethod()); //! error : Uncaught TypeError: foo.staticMethod is not a function
console.log(FooStatic.counter); // 1-
- 추상 클래스
- 하나 이상의 추상 method를 포함하는 클래스
- 추상 method : abstract 키워드를 사용하여 내용이없이 이름과 타입만 선언된 method.
- 직접 인스턴스를 생성할수 없고, 상속만을 위해 사용된다.
- 추상 클래스를 상속한 클래스는 추상 method를 반드시 구현하여야한다.
abstract class Animal {
//* 추상 method
abstract makeSound(): void;
//* 일반 method
move(): void {
console.log('roaming the earth...');
}
}
//* 직접 인스턴스를 생성할수 없다
// new Animal(); //! error : Cannot create an instance of an abstract class.
class Dog extends Animal {
//* 추상 클래스를 상속한 클래스는 추상 method를 반드시 구현해야 한다
makeSound(): void {
console.log('awoooooo...');
}
}
const myDog = new Dog();
myDog.makeSound();
myDog.move();- field : class 멤버 변수
- properties : field에 유연한 메커니즘을 제공하는 멤버 method (getter/setter와 같이)
-
- Introduction
- 인터페이스는 일반적으로 타입체크를 위해 사용되며 변수, 함수, 클래스에 사용할수있다.
- properties와 추상 method로 새로운 타입을 정의하는것
- 인터페이스에 선언된 properties 또는 method의 구현을 강제하여 일관성을 유지
- 직접 인스턴스를 생성할 수 없고 모든 method는 추상 method, 단 abstract 키워드를 사용안함
-
- 변수와 인터페이스
- 인터페이스는 변수의 타입으로 사용할수있다.
- 인터페이스를 사용하여 함수의 파라미터의 타입을 선언할수 있다.
//? interface definition
interface Todo {
id: number;
content: string;
completed: boolean;
}
//* 변수 todo의 타입으로 Todo interface를 선언하였다.
let todo: Todo;
//* 변수 todo는 Todo interface를 준수하여야 한다.
todo = { id: 1, content: 'typescript', completed: false };
let todos: Todo[] = [];
//* parameter todo의 타입으로 Todo interface를 선언
function addTodo(todo: Todo) {
todos = [...todos, todo];
}
const removeTodo = (): void => {
if (todos.length) {
todos.pop();
}
};
//* parameter todo는 Todo interface를 준수하여야 한다.
const newTodo: Todo = { id: 1, content: 'typescript', completed: false };
addTodo(newTodo);
console.log(todos); // [ { id: 1, content: 'typescript', completed: false } ]
removeTodo();
console.log(todos); // []-
- 함수와 인터페이스
- 타입이 선언된 파라미터 리스트와 리턴 타입을 정의하여 인터페이스로 함수의 타입을 정의할수있다.
//* 함수 인터페이스의 정의
interface SquareFunc {
(num: number): number;
}
//* 함수 인터페이스를 구현하는 함수는 인터페이스를 준수하여야한다.
const squareFunc: SquareFunc = function (num: number) {
return num * num;
};
const cubicFunc: SquareFunc = (num: number) => {
return num * num * num;
};
console.log(squareFunc(2)); // 4
console.log(cubicFunc(2)); // 8-
- 클래스와 인터페이스
- 인터페이스에 implements 받은 클래스는 지정된 인터페이스를 구현해야한다
- 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스의 일관성을 유지할수 있는 장점을 갖는다.
- 인터페이스는 직접 인스턴스를 생성할 수 없다.
- 즉, 인터페이스는 도면 / 클래스는 공장
- 인터페이스는 properties와 method를 포함한다. 단 method는 추상 method이다.
//* interface의 정의
interface IUser {
name: string;
age: number;
sayIam(): void;
}
//* interface를 구현하는 클래스는 properties와 추상 method를 구현해야한다.
class User implements IUser {
//* interface에서 정의한 properties 구현
constructor(public name: string, public age: number) {}
//* interface에서 정의한 추상 method 구현
sayIam() {
console.log(`i am ${this.name}, ${this.age}`);
}
}
interface ITodo {
id: number;
content: string;
complemented: boolean;
user: User;
}
//* Todo 클래스는 ITodo 인터페이스를 구현해야한다.
class Todo implements ITodo {
constructor(
public id: number,
public content: string,
public complemented: boolean,
public user: User
) {}
}
const greeter = (user: IUser): void => {
user.sayIam();
};
const user = new User('ju', 28);
greeter(user);
const todo = new Todo(1, 'Typescript', false, user);
console.log(todo);-
- Duck typing
- 인터페이스를 구현하였다고 타입체크를 통과하는 유일한방법은 아니다
- 타입체크에서 중요한것은 값을 실제로 가지고 있는것이다.
interface IDuck {
quack(): void;
}
class MallardDuck implements IDuck {
quack() {
console.log('Quack!');
}
}
class RedheadDuck {
quack() {
console.log('q~uack!');
}
}
function makeNoise(duck: IDuck): void {
duck.quack();
}
//* IDuck에 영향을 받지 않고 구현된 RedheadDuck class도
//* makeNoise parameter의 타입 체크를 실제 값으로만 체크하기 떄문에 통과한다
makeNoise(new MallardDuck()); // Quack!
makeNoise(new RedheadDuck()); // q~uack!- TypeScript는 해당 인터페이스에서 정의한 프로퍼티나 메소드를 가지고 있다면 그 인터페이스를 구현한 것으로 인정한다.
interface IPerson {
name: string;
}
function sayHello(person: IPerson): void {
console.log(`hello ${person.name}`);
}
//* parameter에 정의된 타입과 정확히 일치하지않지만 적용가능
const me = { name: 'Lee', age: 18 };
sayHello(me);- interface는 개발단계에서 도움을 주기 위해 제공되는 기능으로 자바스크립트 표준이 아니다.
- 따라서 위 예제를 트랜스 파일링하면 다음과 같다
function sayHello(person) {
console.log('hello ' + person.name);
}
var me = { name: 'Lee', age: 18 };
sayHello(me);-
- 선택적 프로퍼티(Optional Property)
- 인터페이스의 properties가 선택적으로 필요한 경우 ? 키워드 사용
interface UserInfo {
username: string;
password: string;
age?: number;
address?: string;
}
const userInfo: UserInfo = {
username: 'ju',
password: 'aadd',
age: 4,
};
console.log(userInfo);-
- 인터페이스 상속
- extends 키워드로 상속가능, 복수 가능
interface Person {
name: string;
age?: number;
}
interface Robot {
ai: boolean;
}
interface Humanoid extends Person, Robot {
upgrade: number;
}
const humanoid: Humanoid = {
name: 'ju',
age: 12,
ai: true,
upgrade: 3,
};
console.log(humanoid);- Type Alias는 새로운 타입을 정의한다
type Gender = 'male' | 'female';
interface Person {
gender: Gender;
name: string;
age?: number;
}
//* 빈 객체를 Person 타입으로 지정
const person = {} as Person;
// person.gender = 'gi'; //! error : Type '"gi"' is not assignable to type 'Gender'.
person.gender = 'male';
person.name = 'Lee';
person.age = 20;
// person.address = 'seoul'; //! error : Property 'address' does not exist on type 'Person'.
console.log(person);
//* 문자열 리터럴로 타입 지정
type Str = 'Lee';
//* 유니온 타입으로 타입 지정
type Union = string | null;
//* 문자열 유니온 타입으로 타입 지정
type Name = 'Lee' | 'Kim';
//* 숫자 리터럴 유니온 타입으로 타입 지정
type Num = 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5;
//* 객체 리터럴 유니온 타입으로 타입 지정
type Obj = { a: 1 } | { b: 2 };
//* 함수 유니온 타입으로 타입 지정
type Func = (() => string) | (() => void);
//* 인터페이스 유니온 타입으로 타입 지정
type Shape = Name | Num | Obj;
//* 튜플로 타입 지정
type Tuple = [string, boolean];
const t: Tuple = ['d', false];- 정적 언어의 특징인 정의 시점에 매개변수나 반환값의 타입을 선언.
- 함수 또는 클래스를 정의 하는 시점에 매개변수나 반환값의 선언하기 어려운 경우가 있다.
class Queue {
protected data: any[] = [];
push(item: any) {
this.data.push(item);
}
pop() {
return this.data.shift();
}
}
const queue = new Queue();
queue.push(0);
queue.push('1'); // 의도하지 않은 실수!
console.log(queue.pop().toFixed()); // 0
console.log(queue.pop().toFixed()); //! error : Runtime error
//* Number.prototype.toFixed 로 '1'에서 error 발생- 위와 같은 경우 number 타입 전용 NumberQueue 클래스 정의하여 error 해결 가능
//* 위 문제를 해결하기 위해 새로운 queue 정의
class NumberQueue extends Queue {
//* number 타입의 요소만을 push한다.
push(item: number) {
super.push(item);
}
pop(): number {
return super.pop();
}
}
const queue2 = new NumberQueue();
queue2.push(0);
// queue2.push('1'); //! error : Argument of type 'string' is not assignable to parameter of type 'number'.
queue2.push(+'1');- 다양한 타입을 지원 시 타입 별로 클래스를 상속받아 추가해야 하므로 이 또한 좋은 방법은 아니다.
- 이러한 경우 제네릭이 해결 방법이 될수 있다.
class Queue<T> {
protected data: Array<T> = [];
push(item: T) {
this.data.push(item);
}
pop(): T | undefined {
return this.data.shift();
}
}
//* number 전용 Queue
const numberQueue = new Queue<number>();
numberQueue.push(0);
// numberQueue.push('1'); //! error : Argument of type 'string' is not assignable to parameter of type 'number'.
numberQueue.push(+'1');
//? [optional chaining](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/release-notes/typescript-3-7.html#optional-chaining)
//* 값의 존재 여부 확인
console.log(numberQueue.pop()?.toFixed()); // 0
console.log(numberQueue.pop()?.toFixed()); // 1
console.log(numberQueue.pop()?.toFixed()); // undefined
//* string 전용 Queue
const stringQueue = new Queue<string>();
stringQueue.push('Hello');
stringQueue.push('World');
console.log(stringQueue.pop()?.toUpperCase()); // HELLO
console.log(stringQueue.pop()?.toUpperCase()); // WORLD
console.log(stringQueue.pop()?.toUpperCase()); // undefined
//* 커스텀 객체 전용 Queue
const myQueue = new Queue<{ name: string; age: number }>();
myQueue.push({ name: 'Lee', age: 10 });
myQueue.push({ name: 'Kim', age: 20 });
console.log(myQueue.pop()); // { name: 'Lee', age: 10 }
console.log(myQueue.pop()); // { name: 'Kim', age: 20 }
console.log(myQueue.pop()); // undefined-
제네릭은 생성 시점에 타입을 명시하여 다양한 타입을 사용할 수 있도록 하는 기법
-
한번의 선언으로 다양한 타입에 재사용이 가능하다는 장점
-
T는 제네릭을 선언할 때 관용적으로 사용되는 식별자로 타입 파라미터(Type parameter)라 한다.
- 함수에서 사용하면 다양한 매개변수와 리턴값을 사용할수 있다.
function reverse<T>(items: T[]): T[] {
return items.reverse();
}
const arg = [1, '2', 3, 4, 5];
//* parameter(인수)에 의해 타입 매개변수가 결정된다
const reversed = reverse(arg);
console.log(reversed); // [ 5, 4, 3, '2', 1 ]
const list = [{ name: 'Lee' }, { name: 'Kim' }];
const reverseList = reverse(list);
console.log(reverseList); // [ { name: 'Kim' }, { name: 'Lee' } ]