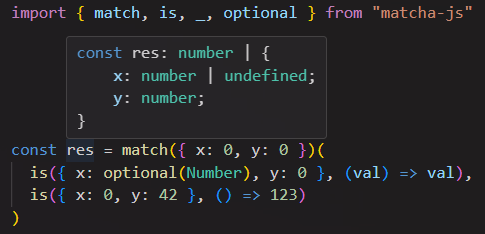
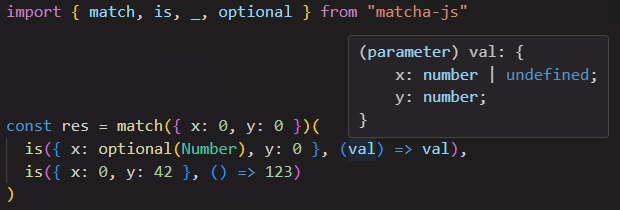
Usage:
import { match, _ } from "matcha-js"
const x = 1
match(x)(
[1, () => console.log("one")],
[2, () => console.log("two")],
[3, () => console.log("three")]
)
// "one"
const y = match(42)(
[1, () => "one"],
[2, () => "two"],
[3, () => "three"],
[_, () => "something else"]
)
console.log(y) // "something else"If we want to take advantage of matcha's type inference, we can use the is function to type-narrow the variable the the match handler:
import { match, type } from "matcha-js"
const someVariable: unknown = { x: 0, y: 0 }
match(x)(
is({ x: type(Number), y: type(Number) }, (pt) => console.log(pt.x, pt.y)),
[_, () => console.log("not a point")]
)
// 0 0Objects:
import { match, type } from "matcha-js"
const point = { x: 1, y: 2 }
match(point)(
[{ x: 1, y: 42 }, () => console.log("point is 1, 42")],
[{ x: 1, y: type(Number) }, () => console.log("point is 1, (a number)")],
[{ x: type(Number), y: 2 }, () => console.log("point is (a number), 2")]
)
// "point is 1, (a number)"
match({ x: 1, y: { z: 2, a: "test" } })([
{ x: 1, y: { z: type(Number), ..._ } },
() => console.log("point is {x: 1, y: { z: (a number), ..._ }}"),
])
// "point is {x: 1, y: { z: (a number), ..._ }}"Arrays:
import { match, type } from "matcha-js"
const value = [1, 2, 3]
match(value)(
[[1, 2, 3], () => console.log("value is [1, 2, 3]")],
[[1, 2, type(Number)], () => console.log("value is [1, 2, (a number)]")],
[[], () => console.log("value is an empty array")]
)
// "value is [1, 2, 3]"
match([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, "Test"])(
[[...type(Number), type(String)], () => console.log("value is [...(a number), (a string)]")],
[_, () => console.log("no match")]
)
// "value is [...(a number), (a string)]"
match([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, "Test", {}, []])(
[
[...type(Number), type(String), ..._],
() => console.log("value is [...(a number), (a string), ..._]"),
],
[_, () => console.log("no match")]
)
// "value is [...(a number), (a string), ..._]"Classes:
import { match } from "matcha-js"
const value = "Hello World"
match(value)(
[String, () => console.log("value is a string")],
[Number, () => console.log("value is a number")]
)
// "value is a string"Regex:
import { match } from "matcha-js"
const value = "Supercalifragilisticexpialidocious"
match(value)(
[/^[a-zA-Z]+$/, () => console.log("value is a string of letters")],
[/^[0-9]+$/, () => console.log("value is a string of numbers")]
)
// "value is a string of letters"Complex matching:
import { match, type, _ } from "matcha-js"
const value = { x: 1, y: { z: 2 } }
match(value)([
{ x: _, y: { z: type(Number) } },
() => console.log("value is {x: _, y: { z: (a number) }}"),
])
// "value is {x: _, y: { z: (a number) }}"Nullables:
import { match, nullable, type } from "matcha-js"
match(null)(
[nullable(String), () => console.log("value is a string or null")],
[nullable(Number), () => console.log("value is a number or null")]
)
// "value is a string or null"
match({ a: 123, b: null })([
{ a: type(Number), b: nullable(String) },
() => console.log("value is {a: (a number), b: (a string or null)}"),
])
// "value is {a: (a number), b: (a string or null)}"Optionals:
import { match, optional, type } from "matcha-js"
match(undefined)(
[optional(String), () => console.log("value is a string or undefined")],
[optional(Number), () => console.log("value is a number or undefined")]
)
// "value is a string or undefined"
match({ a: 123 })([
{ a: type(Number), b: optional(String) },
() => console.log("value is {a: (a number), b: (a string or undefined)}"),
])
// "value is {a: (a number), b: (a string or undefined)}"