RPC框架,使用netty作为网络连接,使用zookeeper作为注册服务器。本项目主要分为三个部分,其一动态代理,其二netty网络通信,其三zookeeper客户端的使用。参考项目 黄勇老师教程
本项目中的zookeeper环境是基于docker安装的,使用的脚本命令如下:
1.下载镜像
docker pull zookeeper
2.启动容器并添加映射
docker run --privileged=true -d --name zookeeper --publish 2181:2181 -d zookeeper:latest
3.添加防火墙端口
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=2181/tcp --permanentzookeeper启动后无需其他的操作便可以直接使用,可以使用idea的插件连接zookeeper进行测试,Docker安装Zookeeper并进行操作
主要的测试是在test包下,src/main下为主要的逻辑代码,进行测试时需要首先打开zookeeper服务器,然后配置zookeeper服务器地址,因为我的是虚拟机中,所以需要更改为自己的服务ip地址,目录为src/test/resources/rpc.properties
# rpc server
rpc.service_address=127.0.0.1:8000
# zookeeper server
rpc.registry_address=192.168.60.130:2181服务的测试主要是包含两步,第一开启服务器,test/server/RpcBootStarp.java 为启动服务器。第二开启测试,test/RpcTest.java
package com.dwj.rpc.test;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:client-spring.xml")
public class RPCTest {
@Autowired
RpcProxy rpcProxy;
/**
* 测试返回string参数的代理
*/
@Test
public void HelloServiceTest(){
HelloService helloService = rpcProxy.create(HelloService.class);
String result = helloService.sayHello("World");
System.out.println(result);
}
/**
* 测试对个返回参数的代理
*/
@Test
public void PersonServiceTest(){
PersonService personService = rpcProxy.create(PersonService.class);
List<Person> result2 = personService.GetTestPerson("小明",3);
for (Person p : result2){
System.out.println(p);
}
}
}主要的实现类就是一个RpcProxy这个类,通过这个类使用netty进行网络连接调用远端的方法,因为用到了zookeeper所以在发送数据之前需要调用服务的发现,即获取到服务器的ip和监听端口。主要的关系就是客户端实现动态代理,服务器端实现反射调用函数。
其中调用的对应关系如下,首先是客户端:主要有两个待实现的接口。
package com.dwj.rpc.test.client;
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello(String name);
}
public interface PersonService {
List<Person> GetTestPerson(String name, int num);
}然后是服务器端,对应两个具体的继承接口并且实现的类。
package com.dwj.rpc.test.server;
@RpcService(value = HelloService.class,version = "1.0")
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "Hello " + name;
}
}
@RpcService(PersonService.class)
public class PersonServiceImpl implements PersonService {
@Override
public List<Person> GetTestPerson(String name, int num) {
List<Person> persons = new ArrayList<>(num);
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) {
persons.add(new Person(Integer.toString(i), name));
}
return persons;
}
}然后服务器通过使用RpcService注解,将这两个类扫描到HashMap容器中作为服务等待客户端调用,如下所示。
{com.dwj.rpc.test.client.HelloService=com.dwj.rpc.test.server.HelloServiceImpl@51fadaff,
com.dwj.rpc.test.client.PersonService=com.dwj.rpc.test.server.PersonServiceImpl@401f7633}以上为server中hashMap中的保存的键值对,即反射调用的映射关系只需要发送客户端的包名,便能够获取到对应的实例化对象。
注解的定义为:其中可以加上版本号进行实现。
//带有RpcService表示为直接的注解。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Component
public @interface RpcService {
/**
* 服务接口类
*/
Class<?> value();
/**
* 服务版本号
*/
String version() default "";
}客户端的动态代理实现:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T create(final Class<?> interfaceClass, final String serviceVersion) {
// 创建动态代理对象
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
interfaceClass.getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[]{interfaceClass},
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 创建 RPC 请求对象并设置请求属性
RpcRequest request = new RpcRequest();
request.setRequestId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
//获取到的接口名称 com.dwj.rpc.test.client.HelloService
request.setInterfaceName(method.getDeclaringClass().getName());
request.setServiceVersion(serviceVersion);
request.setMethodName(method.getName());
request.setParameterTypes(method.getParameterTypes());
request.setParameters(args);
// 获取 RPC 服务地址
// 使用HashMap作为缓存
// 通过interface的全限定类名进行回去服务器的名称, 需要加上这个version字段。。 明天在搞吧。
if (serviceDiscovery != null) {
String interFaceName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
// 需要判断 serviceVersion 是否为空。
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(serviceVersion)) {
interFaceName += "-" + serviceVersion;
}
serviceAddress = serviceDiscovery.discover(interFaceName);
}
//如果不使用zookeeper则需要将这个不进行注解。
//serviceAddress = "127.0.0.1:8000";
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(serviceAddress)) {
throw new RuntimeException("server address is empty");
}
// 从 RPC 服务地址中解析主机名与端口号
String[] array = StringUtil.split(serviceAddress, ":");
String host = array[0];
int port = Integer.parseInt(array[1]);
// 创建 RPC 客户端对象并发送 RPC 请求
// 使用地址和端口进行数据连接,
RpcClient client = new RpcClient(host, port);
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
//但是这个获取到的response总是为空
RpcResponse response = client.send(request);
LOGGER.debug("time: {}ms", System.currentTimeMillis() - time);
if (response == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("response is null");
}
// 返回RPC响应结果
if (response.hasException()) {
throw response.getException();
} else {
return response.getResult();
}
}
}
);
}服务器端使用反射进行调用方法,主要就是进行解析request请求。
private Object handle(RpcRequest request) throws Exception {
// 获取服务对象
String serviceName = request.getInterfaceName();
String serviceVersion = request.getServiceVersion();
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(serviceVersion)) {
serviceName += "-" + serviceVersion;
}
//获取 hashMap中的保存的键值对
Object serviceBean = handlerMap.get(serviceName);
if (serviceBean == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("can not find service bean by key: %s", serviceName));
}
// 获取反射调用所需的参数
Class<?> serviceClass = serviceBean.getClass();
String methodName = request.getMethodName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = request.getParameterTypes();
Object[] parameters = request.getParameters();
// 执行反射调用
Method method = serviceClass.getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
method.setAccessible(true);
return method.invoke(serviceBean, parameters);
}上一个项目使用的是http协议进行的连接,现在打算使用netty作为网络连接。其实对于netty是不够了解的。
在此也涉及到序列化与反序列化。使用的是第三方工具类Protostuff。
<!-- Protostuff -->
<!--序列化工具-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dyuproject.protostuff</groupId>
<artifactId>protostuff-core</artifactId>
<version>1.0.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dyuproject.protostuff</groupId>
<artifactId>protostuff-runtime</artifactId>
<version>1.0.8</version>
</dependency>其中实现的方式为:
package com.dwj.rpc.common.util;
/**
* 序列化工具类(基于 Protostuff 实现)
*
*/
public class SerializationUtil {
private static Map<Class<?>, Schema<?>> cachedSchema = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static Objenesis objenesis = new ObjenesisStd(true);
private SerializationUtil() {
}
/**
* 序列化(对象 -> 字节数组)
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> byte[] serialize(T obj) {
Class<T> cls = (Class<T>) obj.getClass();
LinkedBuffer buffer = LinkedBuffer.allocate(LinkedBuffer.DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
try {
Schema<T> schema = getSchema(cls);
return ProtostuffIOUtil.toByteArray(obj, schema, buffer);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
buffer.clear();
}
}
/**
* 反序列化(字节数组 -> 对象)
*/
public static <T> T deserialize(byte[] data, Class<T> cls) {
try {
T message = objenesis.newInstance(cls);
Schema<T> schema = getSchema(cls);
ProtostuffIOUtil.mergeFrom(data, message, schema);
return message;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static <T> Schema<T> getSchema(Class<T> cls) {
Schema<T> schema = (Schema<T>) cachedSchema.get(cls);
if (schema == null) {
schema = RuntimeSchema.createFrom(cls);
cachedSchema.put(cls, schema);
}
return schema;
}
}具体的使用:
/**
* RPC 解码器
*/
public class RpcDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
private Class<?> genericClass;
public RpcDecoder(Class<?> genericClass) {
this.genericClass = genericClass;
}
@Override
public void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
if (in.readableBytes() < 4) {
return;
}
in.markReaderIndex();
int dataLength = in.readInt();
if (in.readableBytes() < dataLength) {
in.resetReaderIndex();
return;
}
byte[] data = new byte[dataLength];
in.readBytes(data);
out.add(SerializationUtil.deserialize(data, genericClass));
}
}package com.dwj.rpc.common.codec;
/**
* RPC 编码器
*/
public class RpcEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder {
private Class<?> genericClass;
public RpcEncoder(Class<?> genericClass) {
this.genericClass = genericClass;
}
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object in, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
if (genericClass.isInstance(in)) {
byte[] data = SerializationUtil.serialize(in);
out.writeInt(data.length);
out.writeBytes(data);
}
}
}使用封装体的方式使得关系更加的方便
package com.dwj.rpc.common.bean;
/**
* 封装 RPC 请求
*/
public class RpcRequest {
private String requestId; //请求id
private String interfaceName; //请求接口名称
private String serviceVersion; //请求版本
private String methodName; //请求方法名
private Class<?>[] parameterTypes; //请求参数类型
private Object[] parameters; //请求参数。
//get set
}package com.dwj.rpc.common.bean;
/**
* 封装 RPC 响应
*/
public class RpcResponse {
private String requestId;
private Exception exception;
private Object result;
//get set
}客户端进行与服务器交互
package com.dwj.rpc.client;
public class RpcClient extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponse> {
// send 以后就是使用这个东西进行获取。
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, RpcResponse rpcResponse) throws Exception {
this.response = rpcResponse;
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
LOGGER.error("api caught exception", cause);
ctx.close();
}
/**
* 发送数据到服务器。
* @param request 发送请求
* @return 返回响应数据
* @throws Exception
*/
public RpcResponse send(RpcRequest request) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 创建并初始化 Netty 客户端 Bootstrap 对象
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new RpcEncoder(RpcRequest.class)); // 编码 RPC 请求
pipeline.addLast(new RpcDecoder(RpcResponse.class)); // 解码 RPC 响应
pipeline.addLast(RpcClient.this); // 处理 RPC 响应
}
});
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);
// 连接 RPC 服务器
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
// 写入 RPC 请求数据并关闭连接
Channel channel = future.channel();
channel.writeAndFlush(request).sync();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
// 返回 RPC 响应对象
return response;
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}服务器端:
package com.dwj.rpc.server;
public class RpcServer implements ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean {
//在进行设置好参数以后,进行开启服务器
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 创建并初始化 Netty 服务端 Bootstrap 对象
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup);
bootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new RpcDecoder(RpcRequest.class)); // 解码 RPC 请求
pipeline.addLast(new RpcEncoder(RpcResponse.class)); // 编码 RPC 响应
pipeline.addLast(new RpcServerHandler(handlerMap)); // 处理 RPC 请求
}
});
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024);
bootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
// 获取 RPC 服务器的 IP 地址与端口号
String[] addressArray = StringUtil.split(serviceAddress, ":");
String ip = addressArray[0];
int port = Integer.parseInt(addressArray[1]);
// 启动 RPC 服务器
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(ip, port).sync();
// 注册服务到zookeeper服务器
if (serviceRegistry != null) {
// 获取本地扫描到的所有 注解的接口,放入数组。
List<String> interfaceNames = new ArrayList<>(handlerMap.keySet());
serviceRegistry.register(serviceAddress, interfaceNames);
LOGGER.debug("register service: {} => {}", interfaceNames.toString(), serviceAddress);
}
LOGGER.debug("server started on port {}", port);
System.out.println("server started on port" + port);
// 关闭 RPC 服务器
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}服务器获取客户端的数据。
package com.dwj.rpc.server;
public class RpcServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcRequest> {
@Override
public void channelRead0(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcRequest request) throws Exception {
// 创建并初始化 RPC 响应对象
RpcResponse response = new RpcResponse();
response.setRequestId(request.getRequestId());
try {
Object result = handle(request); //处理请求体,反射执行。
response.setResult(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("handle result failure", e);
response.setException(e);
}
// 写入 RPC 响应对象并自动关闭连接
ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
LOGGER.error("server caught exception", cause);
ctx.close();
}
}使用zookeeper客户端进行服务的创建节点的时候,使用"/"表示一个目录,如
parent = "/servcice";
child = parent + "/interface"这样就表示创建了两个目录, 如果不加 “/” ,则直接表示根节点,会被覆盖,所以在创建的时候,需要做好拼接。
注册服务主要是在服务器启动的时候进行使用,查看服务器的spring配置文件可以看出,在初始化服务器的时候,需要将服务器发现对象注入进去,并且使用也是,直接调用注册函数即可,其中注册需要传递两个参数,服务器ip地址,系统扫描到的接口全限定类名。
rpcServer.java
// 注册服务到zookeeper服务器
if (serviceRegistry != null) {
// 获取本地扫描到的所有 注解的接口,放入数组。
List<String> interfaceNames = new ArrayList<>(handlerMap.keySet());
serviceRegistry.register(serviceAddress, interfaceNames);
LOGGER.debug("register service: {} => {}", interfaceNames.toString(), serviceAddress);
}
LOGGER.debug("server started on port {}", port);注册则是与之对应,主要就是在进行代理的时候进行发现服务器的ip地址,然后进行服务器的连接,需要将接口的全新定类名传递过去,从缓存中找到对应的服务器地址。
RpcProxy.java
// 获取 RPC 服务地址
if (serviceDiscovery != null) {
String interFaceName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
// 需要判断 serviceVersion 是否为空。
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(serviceVersion)) {
interFaceName += "-" + serviceVersion;
}
serviceAddress = serviceDiscovery.discover(interFaceName);
}
//如果不使用zookeeper则需要将这个不进行注解。
//serviceAddress = "127.0.0.1:8000";
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(serviceAddress)) {
throw new RuntimeException("server address is empty");
}
// 从 RPC 服务地址中解析主机名与端口号
String[] array = StringUtil.split(serviceAddress, ":");
String host = array[0];
int port = Integer.parseInt(array[1]);从缓存中找到对应的地址。
ZooKeeperServiceDiscovery.class
@Override
public String discover(String interfaceName) throws IOException {
// 直接从数据中进行获取。
return serviceMap.get(interfaceName);
}所有的与zookeeper服务器交互都是基于zookeeper客户端这个类进行,其中新建一个zookeeper客户端如下,需要注意的是,在进行创建zookeeper客户端时候需要使用CountDownLatch线程同步进行连接服务器。
private CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
private final ZooKeeper zooKeeper;
// 需要在构造器中进行初始化、
public ZooKeeperServiceRegistry(String zkAddress) throws IOException {
// 初始化的时候就进行连接到zookeeper服务器。
this.zooKeeper = new ZooKeeper(zkAddress, Constant.ZK_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT, this);
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}其中zookeeper的监听器为:需要此类继承Watcher接口。
// 创建zookeeper同步所需要的同步锁。
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent watchedEvent) {
if (watchedEvent.getState() == Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected){
latch.countDown();
}
}现阶段的注册都是只是单纯的把服务器的ip注册到zookeeper服务器中,并没有指定每一个service对应的服务器ip。具体的实现代码:
// 注册持久性registry节点 其中只需要serviceAddress 就行,而 service 无序注册。
// 还需要传递 interfaceName。
@Override
public void register(String serviceAddress, List<String> interfaceName) throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
// 创建 registry 节点(持久)
String registryPath = Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH;
LOGGER.debug("create registry node: {}", registryPath);
// 当没有注册的时候才会进行注册。
if (null == zooKeeper.exists(registryPath, false)) {
// new byte[0] 表示该节点只是一个父节点,没有值。
zooKeeper.create(registryPath, new byte[0], ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
}
// 注册服务节点。
for (String name:interfaceName) {
// 需要将所有的接口服务发布出去。
String InterfacePath = registryPath + "/" + name ;
// InterfacePath = registry/com.dwj.rpc.test.client.HelloService-1.0
if (null == zooKeeper.exists(InterfacePath,false)){ // 如果没有该节点就进行注册。
zooKeeper.create(InterfacePath, new byte[0], ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.PERSISTENT); //创建持久节点。
}
// 建立Provider节点,
String providerPath = InterfacePath + Constant.ZK_PROViDE_PATH;
// providerPath = registry/com.dwj.rpc.test.client.HelloService-1.0/provider
if (null == zooKeeper.exists(providerPath,false)){
zooKeeper.create(providerPath, new byte[0], ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.PERSISTENT); //创建持久节点。
}
// 此时在进行注册服务器地址,这时候如果有新的服务器提供者运行,那么也会直接的增加新的数据。
String addressPath = providerPath + "/" + serviceAddress;
// addressPath = registry/com.dwj.rpc.test.client.HelloService-1.0/provider/127.0.0.1:8000;
if (null == zooKeeper.exists(addressPath,false)){
zooKeeper.create(addressPath, new byte[0], ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL); //创建临时节点。
}
LOGGER.debug("create zookeeper node ({} => {})", addressPath, serviceAddress);
}
}需要说明的是,路径的规划为:
public interface Constant {
int ZK_SESSION_TIMEOUT = 5000;
int ZK_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT = 1000;
String ZK_REGISTRY_PATH = "/registry";
String ZK_PROViDE_PATH = "/provider";
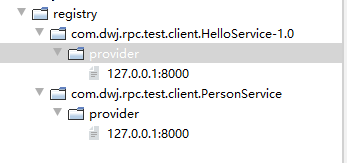
}其中注册的结果如下所示:
可以看出,其中registry、服务全限定性类名和provider为持久性节点,provider下会保存所有提供同类服务的服务器节点的ip,采用的是CreateMode.EPHEMERAL临时节点模式,提供了地址和端口。
服务发现与注册是相辅相成的,也是先要创建一个zookeeper客户端,然后进行连接并进行查询,在本项目中采用的是使用一个watcher进行检测服务器,
public class ZooKeeperServiceDiscovery implements ServiceDiscovery, Watcher {
// 记录缓存,同步HashMap进行存储数据。
private final Map<String, List<String>> serviceMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public ZooKeeperServiceDiscovery(String zkAddress) throws IOException {
// 创建 ZooKeeper 客户端
zooKeeper = new ZooKeeper(zkAddress, Constant.ZK_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT, this);
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//看着结点。
watchNode(zooKeeper);
}
// 根据接口的名称发现对应服务器的ip地址和端口。 每次获取都是从HashMap中获取,避免多次连接。
@Override
public String discover(String interfaceName) throws IOException {
// 这是一个List,然后重新从中间获取到对应列表进行负载均衡。
List<String> result = serviceMap.get(interfaceName);
// 使用负载均衡算法进行实现。 获取单例负载均衡对象。
ClusterStrategy clusterStrategy = ClusterStrategyImpl.getUniqueInstance(); //
return clusterStrategy.select(result);
}
// 每次开始的时候会直接的进行连接。获取到所有的数据。
// 实现监听ZK_REGISTRY_PATH的child节点,当节点进行变化的时候便会回调这个方法,然后进行重新更新HashMap。
private void watchNode(final ZooKeeper zk) {
serviceMap.clear(); //每次在进行检测子节点的变化的时候,需要先将Map 更新,然后在进行重新赋值。 所以要使用 ConcurrentHashMap
// 进行数据的同步
try {
// 将register下所有的节点进行遍历。 当触发event以后 这个便失效,所以需要反复的注册event监视器。
List<String> nodeList = zk.getChildren(Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH, event -> {
if (event.getType() == Event.EventType.NodeChildrenChanged) {
watchNode(zk); // 这时候会重新的调用方法,然后进行更新状态。
LOGGER.debug("Watcher:", "子节点的值发生了变化");
}
});
// 然后遍历registry节点下所有的节点。 并且使用HashMap缓存。
for (String node : nodeList) {
// 在获取节点的时候需要使用监听器。
List<String> serverList = zk.getChildren(Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH + "/" + node +
Constant.ZK_PROViDE_PATH, true, null);
// 存到HashMap中。
serviceMap.put(node,serverList);
}
LOGGER.debug("serviceMap data: {}", serviceMap);
LOGGER.debug("Service discovery triggered updating connected server node.");
} catch (KeeperException | InterruptedException e) {
LOGGER.error("", e);
}
}
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent watchedEvent) {
if (watchedEvent.getState() == Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected){
latch.countDown();
}
}
}服务发现采取的逻辑是,在刚开始的时候会从zookeeper中获取到所有的节点的列表,然后保存在ConcurrentHashMap中,并且一直监听这个节点的变化,当节点有变化的时候,便会更新ConcurrentHashMap,始终保存最新的服务缓存。
public class ClusterStrategyImpl implements ClusterStrategy {
// 使用volatile
private volatile static ClusterStrategyImpl uniqueInstance;
private ClusterStrategyImpl() {
}
public static ClusterStrategy getUniqueInstance() {
if (uniqueInstance == null) {
synchronized (ClusterStrategyImpl.class) {
if (uniqueInstance == null) {
uniqueInstance = new ClusterStrategyImpl();
}
}
}
return uniqueInstance;
}
@Override
public synchronized String select(List<String> providerIp) {
if (providerIp.size() == 1){
return providerIp.get(0);
}else {
int MAX_LEN = providerIp.size();
int index = RandomUtils.nextInt(0, MAX_LEN - 1); // 随机选择一个数据进行。
return providerIp.get(index);
}
}
}使用随机算法从服务器列表中选择一个服务器进行连接,达到负载均衡的目的,另外考虑并发问题,使用单例池加锁进行负载均衡。
以上便完成了整个的监听逻辑的设定。