This library numerically solves the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations in both two-dimensional and three-dimensional planar and curved channels using the finite-difference method. While the primary objective is to simulate Taylor-Couette flows, the solver can also be applied to planar flow simulations.
For details on the governing equations and numerical methods ensuring conservative and consistent schemes, refer to the documentation.
- Energy-consistent treatment of advective, pressure-gradient, and diffusive terms, ensuring proper conservation properties.
- MPI parallelization.
- Efficient FFT-based direct Poisson solver.
- Explicit and implicit treatments of diffusive terms in all spatial directions.
- Scalar transport simulation.
- C compiler
- MPI
- FFTW3
- Python3 (only required for initializing flow fields in
NPYformat)
-
Set up your workspace
mkdir -p /path/to/your/directory cd /path/to/your/directory
-
Clone the repository
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/NaokiHori/SimpleTCSolver cd SimpleTCSolver
-
Set initial conditions
Python3is used to generate the initial flow fields asNPYfiles.cd initial_condition make output bash main.sh cd ..
-
Build the solver
make output make all
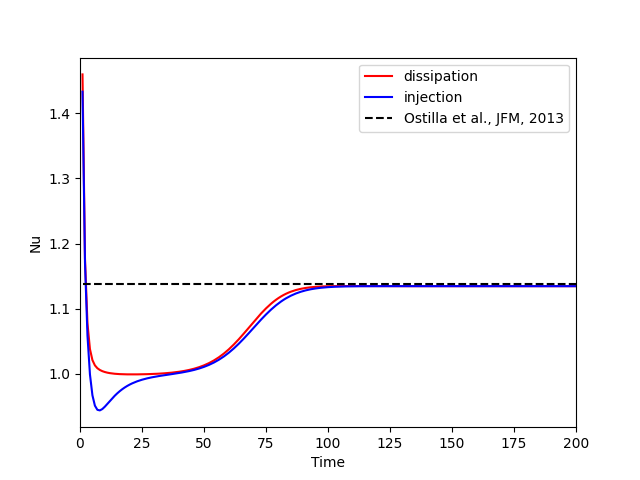
The black-dashed line represents reference results from Ostilla et al., J. Fluid Mech. (719), 2013.
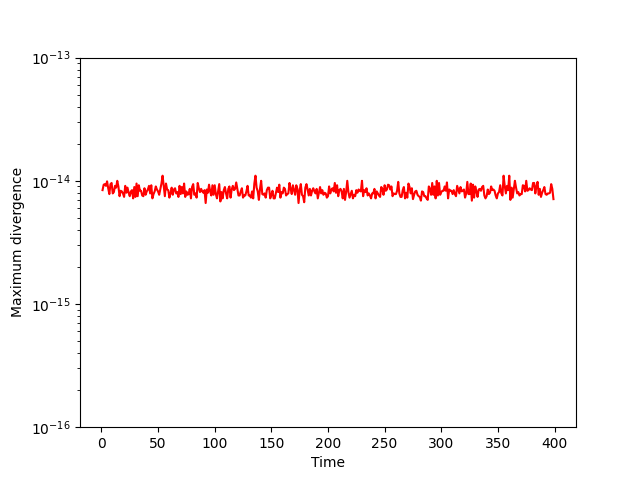
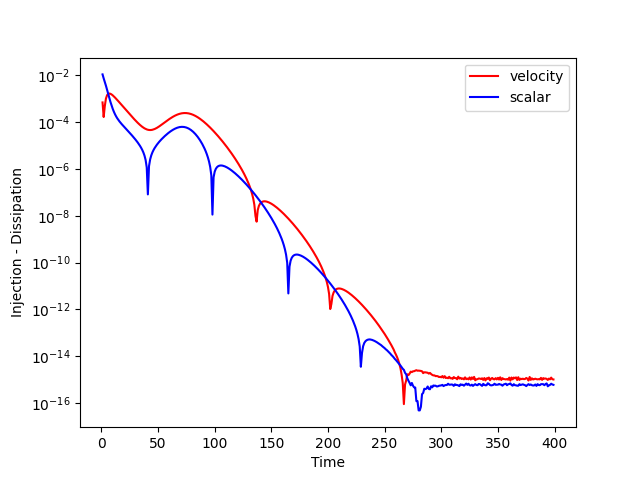
The numerical scheme is designed to ensure energy injection and dissipation remain perfectly balanced (up to rounding error) in steady states:
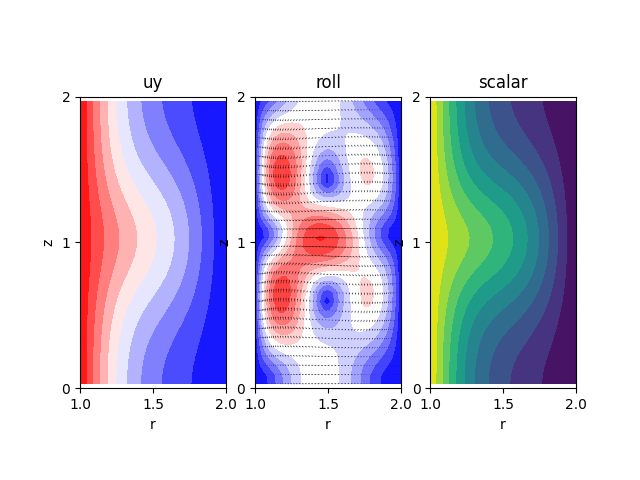
Since Taylor-Couette flows are inherently three-dimensional, the default solver is designed for 3D simulations. However, a 2D version that extracts radial-azimuthal motions is available in the 2d branch.
This solver can also be used for planar flow simulations (e.g., normal channel flows). To enable this mode, set the is_curved flag in the flow initializer to false. For more details, refer to the documentation.
I would like to thank Dr. Kazuyasu Sugiyama for insightful discussions at Flow for Future - PoF25 and the 37th CFD Symposium.