A.A. 2022/2023
Deep Learning and Generative Models Project assignment #11
Project objective:
- One shot learning with Cifar100 dataset
Dataset:
Network model:
- A CNN for image classification can be used for this task. Experiment with a custom one or finetuning a pretrained model (like resnet18)
Detailed information:
- train a classification model on a subset of classes (e.g. 90). Instead of classifying the different classes, train the model to determine if two images have the same class.
- Training such a model can be seen as a binary classification problem (0: different class, 1: same class)
- Then select the remaining classes and take only 1 element for each classes (support set) and the rest as queries. The objective is to classify correctly the queries comparing them with the support set.
Additional notes:
- Learn more about the task here: https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2021/05/an- introduction-to-few-shot-learning/
- Experiment with splitting the dataset in different ways (90-10, 80-20, 50-50 ecc)
Project specifications
The project was developed using a Siamese network with triplet loss, the reference network is a ResNet.
Different networks were tested, including custom ones, the best results were obtained with the ResNet56 related to this repository: https://github.com/akamaster/pytorch_resnet_cifar10*
Similarity learning
Similarity Learning is a supervised machine learning technique where the objective is to train the model to learn a similarity function that measures the similarity between two objects and produces a corresponding similarity score.
A high score indicates high similarity, while a low score indicates dissimilarity between the objects. This approach is commonly employed in one-shot classification scenarios, such as the use of siamese networks, which prove valuable in various contexts.
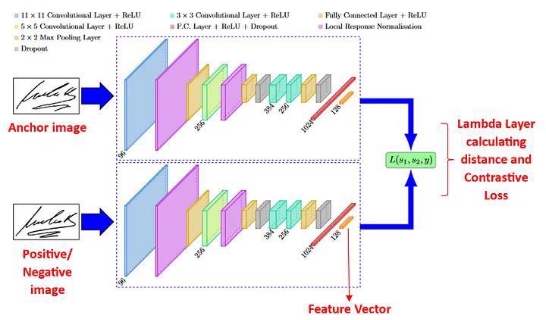
Siamese Network
The architecture of a Siamese network typically consists of two identical subnetworks (or twin networks) that share the same set of weights and parameters. These subnetworks are often referred to as Siamese Twins.
Each input sample is passed through its respective subnetwork, and the output representations are then compared to measure the similarity between the two inputs (1:Match, 0:Non-Match) to determine the Contrastive Loss..
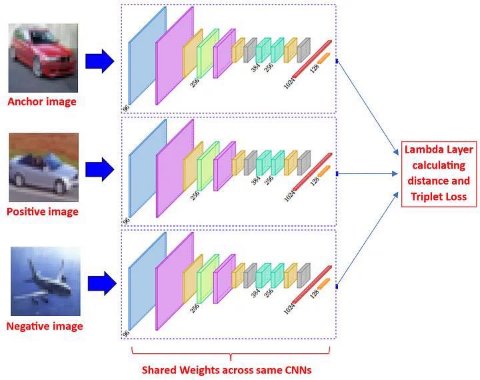
Siamese Network with Triplet Loss
The second type of Siamese neural networks is based on the calculation of the Euclidean/cosine distances between the embedding layers (feature vectors) of the CNNs triplets, i.e. between the anchor and the positive image, and between the anchor and the negative image. The Triplet Loss is then calculated completely in the Lambda layer, without direct comparisons with any reference truth.
Since research has shown that this Triplet Loss model is generally more robust than the Contrastive Loss model, the project was therefore developed using this approach.
The goal of Siamese Network
The goal of Siamese networks is to search for similar features among images of the same class. Therefore, after training, the distances between features of "similar" images will be decreased, and the distance between "different" images increased.
Euclidean Distance vs Cosine Distance
Although both distances were implemented in this project, the best results on CIFAR100 were produced using the cosine distance.
Experimental results:
Since the network learns the similarity and diversity of the domains, it can safely predict even domains not learned during the training phase. Of course, as we will show in the results, the quality of the few-shot domains depends on how many classes it learned during the training phase.
Hyperparameters
| Epochs | 150 |
|---|---|
| Learning Rate | 0.001 |
| Batch Size | 128 |
| Test Batch Size | 1000 |
| Binary Test Batch Size | 1000 |
Training on the entire CIFAR100 dataset
Below we will see the accuracy of CIFAR100 trained on all classes using this approach is around 82-83%.
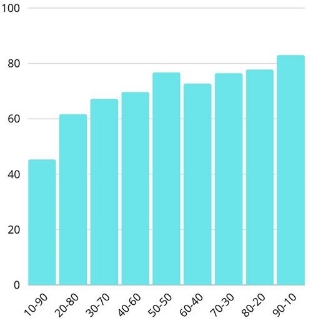
Several experiments will be reported training the network on a subset of CIFAR100 (90-10, 80-20, 70-30, 60-40, 50- 50, 40-60, 30-70, 20-80, 10-90)
Complete results:
- Test Accuracy (triplet): Given an anchor, positive and negative, this test is based on how many times the distance between anchor and positive is less than the distance between anchor and negative.
- Binary Test Accuracy: Given a pair of images, this test measures how many times it was correctly predicted whether the images belong to the same class or not.
- Mean Few Shot Accuracy: Given a pair of images from a subset excluded during the training phase, this test measures how many times it was correctly predicted whether the images belong to the same class or not.
| Training | Test Accuracy (triplet) | Binary Test Accuracy | Mean Few Shot Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10-90 | 86.90% | 78.82% | 45.3187% |
| 20-80 | 85.33% | 77.95% | 61.7224% |
| 30-70 | 85.11% | 79.13% | 67.2288% |
| 40-60 | 86.15% | 79.56% | 69.7237% |
| 50-50 | 86.79% | 78.26% | 76.7733% |
| 60-40 | 88.01% | 81.63% | 72.7345% |
| 70-30 | 88.58% | 81.24% | 76.5066% |
| 80-20 | 88.27% | 80.96% | 77.8149% |
| 90-10 | 88.34% | 80.95% | 83.0623% |
| 100-0 | 89.09% | 82.41% | - |
The results confirm the hypothesis that the Siamese network can generalize as the classes learned increase, an interesting case is the 90-10 training, the network was more accurate on unseen domains rather than those learned during the training.
As can be seen from the histogram, as the classes learned during the training phase increase, the model is able to classify even previously unseen domains better and better.
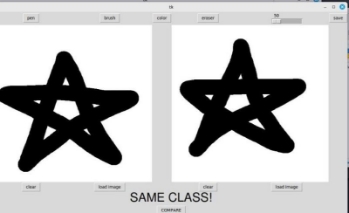
Extra (Interactive application based on MNIST):
The project's Siamese network was also trained on MNIST, the model subsequently took part in an interactive paint-like application, capable of recognizing whether hand-drawn images belong to the same domain or not.
Although the network was trained on MNIST (99% accuracy), the network can recognize similarities even in new hand-drawn domains.