Python library for the Red Robotics 'HeadBoard' and 'SideBoard' Raspberry Pi add on robotics boards.
Simple python commands for controlling motors, servos and Neopixels (WS2812B).
Works with Python 2 or 3.
Drive a robot with a variety of controllers with example code for Rock Candy and PiHut PS3 Gamepads, Wiimote and generic bluetooth gamepads.
Get a robot up and running in minutes!
This guide assumes a working knowledge of the Raspberry Pi, how to set one up headlessly, and how to connect remotely via SSH. Here's a great guide on how to do it from Adafruit.
Beginner tutorials and videos coming soon.
Download the pre-configured SD card Image onto your PC from here.
User: pi
Hostname: redrobotics
Password: redboard
Write the image to a SD Card using Etcher, free download here.
When it's finished eject the SD card but insert it straight back into your PC.
Start by downloading the 'wpa_supplicant.conf' file.
Right click on the following link then click on 'Open Link In New Tab'
wpa_supplicant.conf.
Click on the Down arrow in the top right of the screen to download the file, then click OK to save.
In Windows 10 look in your Downloads folder. Right click on the file then choose 'open with' then 'More apps' and select Wordpad. Don't use Notepad as it changes the text format.
Delete the text "Your WIFI Network" (keeping the quotes) and enter the name of your own WIFI network.
Then delete the text "Your WIFI Password" and enter your own WIFI password.
Save the file, Then using your file manager drag this file on to the Drive labelled 'boot'
Eject the SD card and insert it into your Raspberry Pi.
Now turn on your PI. You are ready to make a robot!
If you have successfully connected to a wireless network, once your Pi has booted up it will flash the last three digits of it's IP address on the on-board Neopixel.
If it flashes white, It's not connected to the internet.
You can of course use raspberrypi.local (or redrobotics.local if you are using the pre-configured SD image), but this is not so great in a classroom full of Pi's with the same hostname! More info here.
The Neopixel will show the last part of your IP address by flashing different colours, red for the first digit, green for the second and blue for the last.
Here are some examples:
If your IP address is 192.168.0.123, the Neopixel will flash red once, green twice and blue three times.
If your IP address is 172.16.1.108, the Neopixel will flash red once, it won't flash green then it will flash blue eight times.
If your IP address is 192.168.31.15, the Neopixel won't flash red, then it will flash green once then blue five times.
If you miss it, you can momentarily press the on-board push button to flash the IP address again (wait a few seconds after pressing the button. Also - don't hold the button down as this will reset the Pi - more on this later!).
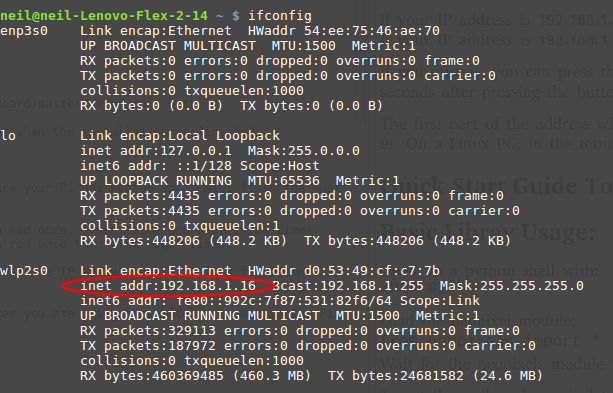
The first part of the address will be the same as the computer you are using to remotely connect to the Pi. On a Linux PC, in the terminal type:
ifconfig
Then hit the 'Enter' key.
The highlighted text shows the IP address, take the first three sets of digits then add the number as shown on the Neopixel. If the Neopixel flashed red once, green once and blue twice, your PI's IP address would be: 192.168.1.112
Screenshots for Windows coming soon!
You can easily modify an existing toy or use a DIY robot kit. We have created a number of different robots and the files will be available to download soon, so you can 3D print or laser cut your own.
Here's an image to show you how to wire up your bot:
The Headboard can drive two motors independently, at 1Amp each continuously.
If your Pi resets unexpectedly, you are probably trying to drive motors that are too large (more on this later).
Once your battery pack and motors are wired up, it's easy to start controlling your bot.
Power up your Pi by switching the power switch to the on position. When it's powered up, SSH into it from your PC. Adafruit's guide here.
Once you are connected, run the keyboard_control.py program by entering:
sudo python3 keyboard_control.py
Then hit the 'Enter' key.
TIP! - You need to use 'sudo' for the Neopixels to work.
Wait for a few seconds for everything to load.
You should now be able to drive your bot around using the following keys:
W = Forwards
S = Backwards
A = Left
D = Right
T = Turbo - toggles fast and slow
R = Reverse steering - If your bot goes left when it should go right!
If you need to stop quickly, hit the Spacebar.
If your robot goes in the wrong direction, you may need to swap over the wires that go to the motor(s). Press the W key to go forwards and check which way the motors turn, if one (or both) go backwards, swap it's wires over.
If you have a RockCandy or PiHut PS3 controller, you can run the tanksteer.py or carsteer.py programs. They work with either controller.
With the tanksteer program, the left analogue stick controls the left motor and the right stick controls the right motor. Push both sticks up for forward, both down for backwards and one up, one down to turn.
For carsteer the left stick controls the speed and direction of both motors - push up to go forwards and down for backwards. The right stick is for steering - push the stick left or right to steer.
Short press- less than a second: the on-board red LED will flash off, The on-board Neopixel will flash the IP address of you Pi (see "What's my IP address?" above).
Medium press - between 1 and 4 seconds: On-board red LED flashes on and off - Pi resets.
Long press - greater than 4 seconds: On-board red LED turns off - Pi shuts down.
Wait 20 seconds before sliding the power switch to make sure the Pi has had enough time to shutdown.
The reset switch can be reprogrammed for your own use - more on this later.
Follow all commands with the 'Enter' key.
Open up a python shell with:
sudo python3
Load the redboard module:
import redboard
Wait for a few seconds, the neopixels module takes a few seconds to load.
Let's start with the on-board Neopixel, as you don't need to plug anything else into the board.
To set the on-board neopixel to full red type:
redboard.red()
You can also set the brightness by adding a number between 0-255,
Red half bright:
redboard.red(127)
This also works with blue and green and white:
redboard.blue()
redboard.green()
redboard.white()
If you want different colours, use:
setColour(0,128,0,128)
This will give you purple. The first value is the position of the neopixel (0 for the one on the Headboard).
The next three numbers are the red, green and blue values.
Orange:
redboard.setColour(0,255,165,000)
Yellow:
redboard.setColour(0,255,255,0)
You can fade red up and down with:
redboard.heartBeat()
Ctrl + c to stop
Attach more Neopixels to the 3pin header, pay attention to the pin markings on the board (picture coming soon).
With eight led's attached - try:
redboard.knightRider()
Ctrl + c to stop
To run the Adafruit example:
redboard.demo()
Check the neopixels.py program for code examples.
There will be a tutorial soon to show how to sequence Neopixels at the same time as driving your bot.
To turn all neopixels off:
redboard.clear()
Motor1 full speed forwards:
redboard.M1(100)
Motor1 half speed forwards:
redboard.M1(50)
Motor1 full speed backwards:
redboard.M1(-100)
Motor1 stop:
redboard.M1(0)
Motor2 full speed forwards:
redboard.M2(100)
Motor2 stop:
redboard.M2(0)
If you prefer, you can use 8 bit values (0-255) to set the speed. This is useful if you are using analogue joysticks to control your robot. You can send the value read from the joystick straight to the motor.
See the tanksteer.py and carsteer.py programs for examples.
Motor1 full speed:
redboard.M1_8bit(255)
Motor2 half speed:
redboard.M2_8bit(127)
Motor2 half speed Backwards:
redboard.M2_8bit(-127)
You can connect two servos - servo0 and servo1
Set the angle of the servo directly - to set the servo to the centre position:
redboard.servo0(0)
Or for servo1:
redboard.servo1(0)
90 degrees:
redboard.servo0(90)
-45 degrees
redboard.servo0(-45)
If you prefer, you can set the servo position by the pulse width. Minimum value is 500, max is 2500.
Centre:
redboard.servo0_P(1500)
+90 degrees:
redboard.servo0_P(500)
-45 degrees:
redboard.servo0_P(2000)
-90 degrees:
redboard.servo0_P(2500)
Cut the power to the servo with:
redboard.servo0_off()
If you like, you can install everything from scratch. It takes a very long time...
It's best to start with a fresh install of Raspian Lite. Download it from the Raspberry Pi website.
Set up your Pi and connect it to your Wifi network.
Once your Pi is up and running, make sure everything is up to date by copying and pasting the following in the terminal, then hit the 'ENTER' key:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -y
When that's finished, enter:
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/RedRobotics/RedBoard/master/setup.sh | bash
This will install all the files you need, your Pi will reboot when the installation is finished.