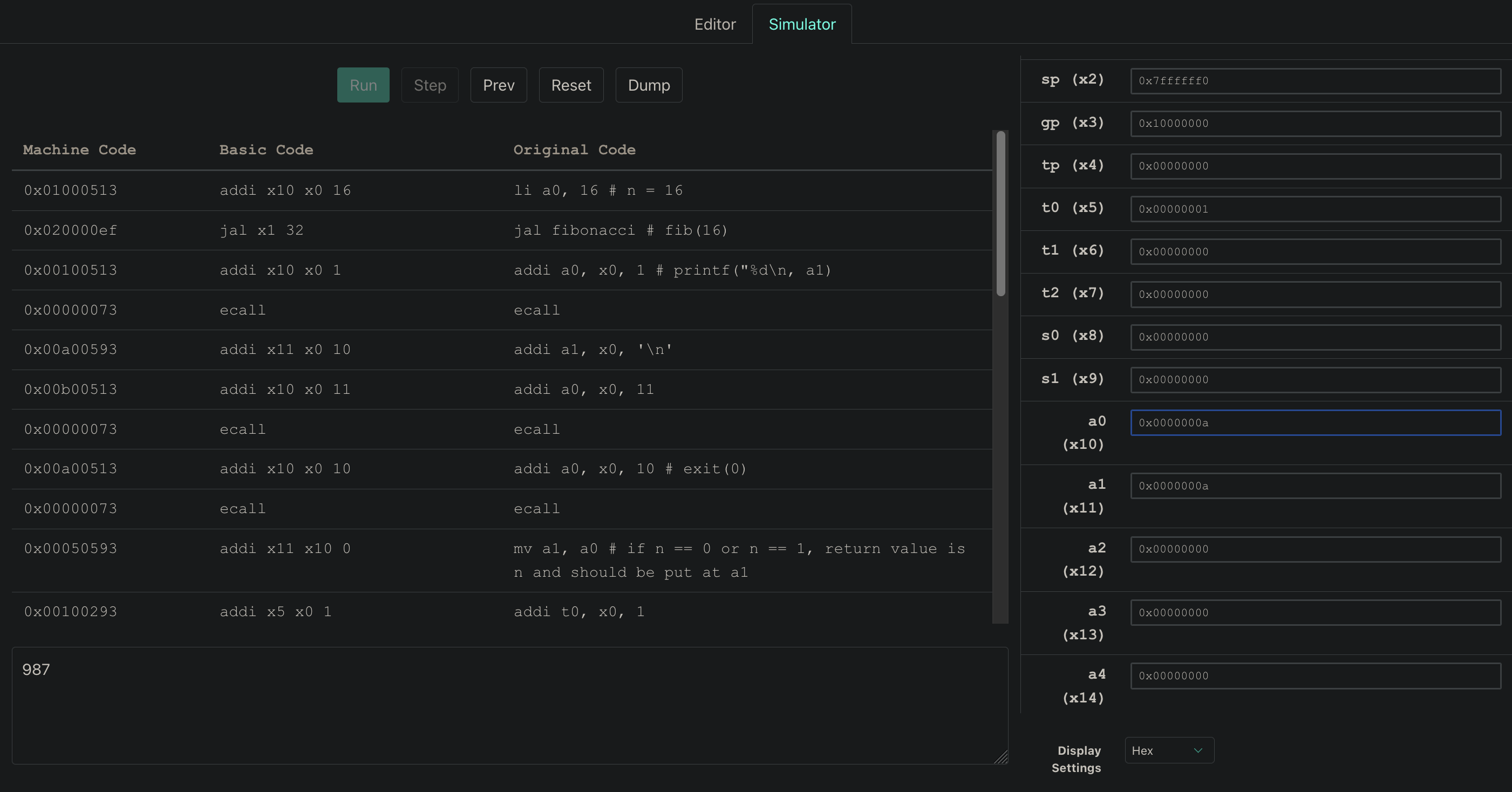
:::info
Note: the return value of fibonacci is still store in a1.
For better running experience, we print a1 with '\n' (which require us to override a1 with '\n') in main function, then exit.
- Code snippet of
printf("%d\n", a1)addi a0, x0, 1 ecall addi a1, x0, '\n' addi a0, x0, 11 ecall - Code snippet of
exit(0)addi a0, x0, 10 ecall
:::
## fibonacci.S
## put input n in register x10 (a0)
## put output fibonacci(n) in register x11 (a1)
## use Venus to test correctness
.text
main:
## write assembly code here.
## call fibonacci function and get return value.
li a0, 16 # n = 16
jal fibonacci # fib(16)
addi a0, x0, 1 # printf("%d\n, a1)
ecall
addi a1, x0, '\n'
addi a0, x0, 11
ecall
addi a0, x0, 10 # exit(0)
ecall
fibonacci:
## fibonacci function
mv a1, a0 # if n == 0 or n == 1, return value is n and should be put at a1
addi t0, x0, 1
ble a1, t0, end # if n <= 1 then end
recur:
addi sp, sp, -12 # initiate stack, -12 is for alignment
sw ra, 0(sp) # push ra to stack
sw s0, 4(sp) # push s0 to stack (save s0 before use)
sw s1, 8(sp) # push s1 to stack (save s1 before use)
mv s0, a0 # s0 = n
addi a0, s0, -1 # reg a0: n - 1, as parameter of the next function call
jal fibonacci # call fib(n - 1)
mv s1, a1 # save result of fib(n - 1) to s1
addi a0, s0, -2 # reg a0: n - 2, as parameter of the next function call
jal fibonacci # call fib(n - 2)
add a1, s1, a1 # reg a1: fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2), as return value
lw ra, 0(sp) # load ra back
lw s0, 4(sp) # load s0 back
lw s1, 8(sp) # load s1 back
addi sp, sp, 12 # pop stack
end:
jr ra # jump to ra
:::success
Note: the result is not in a1, but at the output section:
Just change the register to store return value from a0 to a1, and everything will work fine :)
## fibonacci.S
.text # code section
.global fibonacci_asm # declar the sum_asm function as a global function
.type fibonacci_asm, @function # define sum_asm as a function
fibonacci_asm:
## fibonacci function
addi t0, x0, 1
ble a0, t0, end # if n <= 1 then end
recur:
addi sp, sp, -12 # initiate stack, -12 is for alignment
sw ra, 0(sp) # push ra to stack
sw s0, 4(sp) # push s0 to stack (save s0 before use)
sw s1, 8(sp) # push s1 to stack (save s1 before use)
mv s0, a0 # s0 = n
addi a0, s0, -1 # reg a0: n - 1, as parameter of the next function call
jal fibonacci_asm # call fib(n - 1)
mv s1, a0 # save result of fib(n - 1) to s1
addi a0, s0, -2 # reg a0: n - 2, as parameter of the next function call
jal fibonacci_asm # call fib(n - 2)
add a0, s1, a0 # reg a0: fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2), as return value
lw ra, 0(sp) # load ra back
lw s0, 4(sp) # load s0 back
lw s1, 8(sp) # load s1 back
addi sp, sp, 12 # pop stack
end:
jr ra # jump to ra
.size fibonacci_asm, .-fibonacci_asm
Just like what we've done in lab{2,4,5}, one can use shell script to run simulation:
./scripts/run rvc_pair hw2/fibonacci # compile
./scripts/run sim hw2/fibonacci # simulateand see the result like:
C code fibonacci_c=8
ASM code fibonacci_asm=8
Baremetal code runs to the end. (pressing `ctrl+a x` to quit)
QEMU: Terminated
In main.c we design two helper functions: print_meow and print_val for debugging. These functions are handy when it comes to cases that we want to peek values in the context of assemply code.
print_meow: can printMeowto make sure that assembly runs the order as we expected.jal print_meowprint_val: can peek value of registera0mv a0, REGISTER_TO_PEEK jal print_valprint_single_result: can peek the whole real-time sudoku table:::infomv a0, s jal print_single_results8is treated as common register (like global variables) among the whole process ofsudoku_2x2_asmfunction, storing the pointer of sudoku table. ::: At the same time, I refectorprint_sudoku_resultwhich reuseprint_single_resultto reduce reduncancy.
Before implementing the code in c or assembly, one should understand the algorithm to implement first. Fortunately, TA has provided us the psudocode. We translated it into C as:
static inline int solve(char *ls, int idx) {
if (idx == bound) {
return true;
}
if (ls[idx] > 0) {
return solve(ls, idx + 1);
} else {
for (char n = 1; n <= side_lim; ++n) {
ls[idx] = n; // mark
if (check(ls, idx) && solve(ls, idx + 1)) {
return true;
}
}
ls[idx] = 0;
return false;
}
}
:::success Note: to write a beautiful sudoku code that can also solve 3x3 or bigger cases (bounded by max bit-length of a single register), I defined three global constants at the front of c code:
const int box_width = 2;
const int side_lim = box_width * box_width;
const int bound = side_lim * side_lim;
Where box_width is the length of the single side of a number box; side_lim is the limit of single side of the 2d table (well, use 1d array as container); bound is the number of numbers in sudoku.
Since we're implementing 2x2 sudoku, the box_width is then become side_lim as well as bound will be automatically determined in compile time. Elegant!
:::
With solve, the sudoku2x2_c can be easily implemented as:
int sudoku_2x2_c(char *ls) { return solve(ls, 0); }
:::info
Notice that to make sudoku_2x2_c being able to deliver the information that whether the solving process solved successfully, we change the return value of sudoku_2x2_c into int (0 or 1).
:::
Then, we should finish the algorithm of check.
In order to check whether a number in some index is valid or not, we should check whether there exist number confliction in horizontal, vertical and nearby (in shome box) manners.
Before introducing the algorithm, I shall first introduce two simple helper constants: x and y, which is the mapping of 1d index onto 2d index.
const int x = idx % side_lim;
const int y = idx / side_lim;
And for recorder of number confliction, since there are just at most
int tb = 0; // bit table to check confliction
So the structure of check is:
static inline int check(char *ls, int idx) {
// constant definition
// horizontal check
// vertical check
// box check
// until here, not confliction...
return true;
}
Then, for the horizontal check, the algorithm is quite easy: scan along the same y axis by side_lim.
// in check
// horizontal scan by fixing y (in single dimension version)
int base = y * side_lim;
int tb = 0;
for (int i = base; i < base + side_lim; ++i) {
if (!check_and_mark(ls[i], &tb)) {
return false;
}
}
We can see that check_and_mark is the helper function that trully deals with number confliction detection. We'll introduce it later.
For the vertical check, the algorithm is still quite easy: scan along the same x axis by increment index with side_lim with side_lim times.
// in check
// vertical scan by fixing x
base = x;
tb = 0;
for (int i = base; i < bound; i += side_lim) {
if (!check_and_mark(ls[i], &tb)) {
return false;
}
}
This one is a bit tricky. Our algorithm is to map the x, y axis to baseX, baseY axis that is indexed according to box, not number.
For example, 2x2 sudoku has "four" number box, which lead to baseX and baseY have value
The implementation of axis mapping is suprisingly simple, using the integer division and multiply them back w.r.t. box_width:
int baseX = (x / box_width) * box_width;
int baseY = (y / box_width) * box_width;
We use nested loop to traverse the numbers in our target box. In each iteration, we re-map back the axis from 2d to 1d to access the sudoku table:
// box scan by indirect index mapping
tb = 0;
int baseX = (x / box_width) * box_width;
int baseY = (y / box_width) * box_width;
for (int i = 0; i < box_width; ++i) {
int offset = (i + baseY) * side_lim + baseX;
for (int j = 0; j < box_width; ++j) {
if (!check_and_mark(ls[offset + j], &tb)) {
return false;
}
}
}
:::success Note: we act as a human-body compiler optimizer to do loop-invariant code motion so that we can implement the according assembly code happier! :::
The meaning of this function is to reduce redundancy of writing the same code to check number confliction for horizontal, vertical and box manners in check function. I generalize the behavior of:
- Check if a number is not zero or...
- Whether a number conflicts with recorded numbers
- If yes, returns false.
- Otherwise, record current number and returns true.
Take the advantage of bitwise operations, our code can be so clean as:
static inline int check_and_mark(char shift, int *tb) {
int hot = 1 << shift;
if (shift && ((*tb) & hot))
return false;
*tb = (*tb) | hot;
return true;
}
:::info
Note: to modify a number of the other function, the simplest way in c is to use a pointer. However, we can do some tricks in assembly code...
:::
The methodology of implementation is... do what we've done in C code with some rearrangements.
Just like sudoku_2x2_c, we initialize the recursive code of solve, but with the initialization of common constants stored in s8-s11 registers, as the global variables of the whole algorithm.
:::info
This reduce the number of arguments to be passed to solve and check.
Note: we should use saved registers so that they'll be fine even if we call the other function (e.g. functions to print value for debugging). :::
sudoku_2x2_asm:
# solve(idx = 0)
# prologue: push stack
addi sp, sp, -20
sw ra, 0(sp)
sw s8, 4(sp) # will be use as global constant
sw s9, 8(sp) # will be use as global constant
sw s10, 12(sp) # will be use as global constant
sw s11, 16(sp) # will be use as global constant
# setup global variables for the whole
# recursive call to temperal registers
mv s8, a0 # s8 = ls (char array)
li s9, 2 # s9 (box_width) = 2
mul s10, s9, s9 # s10 (side_lim) = 4 = box_width ^ 2
mul s11, s10, s10 # s11 (bound) = 16 = side_lim ^ 2
# funciton call
li a0, 0 # start to "solve" from index 0
jal solve
# epilogue: pop stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
lw s8, 4(sp)
lw s9, 8(sp)
lw s10, 12(sp)
lw s11, 16(sp)
addi sp, sp, 20
ret
:::info I think the naming style and comments in this function is enough to explain what we've done :) :::
solve: # solve(a0 = idx)
beq a0, s11, solve_ret_true # if (idx == bound) return true
# prologue for all function calls: push stack
addi sp, sp, -20
sw ra, 0(sp)
sw s0, 4(sp) # we need s0 as current idx (a0)
sw s1, 8(sp) # we need s1 as n in loop
sw s2, 12(sp) # we need s2 as address of ls[idx]
sw s3, 16(sp) # we need s3 as value of ls[idx]
mv s0, a0 # s0 = idx
add s2, s8, s0 # s2 = address of ls[idx]
lb s3, 0(s2) # s3 = ls[idx]
bne s3, x0, call_solve_nxt_and_ret # if ls[idx] > (!=) 0, then call_solve_nxt_and_ret
# for loop
li s1, 1 # for n = 1
loop:
sb s1, 0(s2) # ls[idx] = n
mv a0, s0 # a0 = idx
jal check # check(idx)
beq a0, x0, to_nxt_loop # if check returns invalid, then prepare next loop
# solve(idx = idx + 1)
addi a0, s0, 1 # a0 = idx + 1
jal solve
bne a0, x0, solve_epilogue_ret_true # if recursive solve returns valid, then returns true
to_nxt_loop:
addi s1, s1, 1 # n += 1
bgt s1, s10, end_loop # if n > side_lim (4), end loop
j loop
end_loop:
sb x0, 0(s2) # ls[idx] = 0
j solve_epilogue_ret_false # return false
call_solve_nxt_and_ret:
# solve(idx = idx + 1)
# funciton call
addi a0, s0, 1 # a0 = idx + 1
jal solve
# epilogue: before return, pop stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
lw s0, 4(sp)
lw s1, 8(sp)
lw s2, 12(sp)
lw s3, 16(sp)
addi sp, sp, 20
# return a0 = solve(idx = idx + 1)
ret
solve_epilogue_ret_true:
# epilogue: before return, pop stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
lw s0, 4(sp)
lw s1, 8(sp)
lw s2, 12(sp)
lw s3, 16(sp)
addi sp, sp, 20
solve_ret_true:
li a0, 1 # a0 = true
ret
solve_epilogue_ret_false:
li a0, 0 # a0 = false
# epilogue: before return, pop stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
lw s0, 4(sp)
lw s1, 8(sp)
lw s2, 12(sp)
lw s3, 16(sp)
addi sp, sp, 20
ret
This function is a bit long. We can see the structure of assembly is:
check: # check(a0 = idx)
# prologue for all function calls
addi sp, sp, -28
sw ra, 0(sp)
sw s0, 4(sp) # will be used as tb, used as a shared register between check and check_and_mark
sw s1, 8(sp) # will be used as x and baseX
sw s2, 12(sp) # will be used as y and baseY
sw s3, 16(sp) # will be used as iterator (or i in nested loop)
sw s4, 20(sp) # will be used as iterator limit (or j in nested loop)
sw s5, 24(sp) # will be used as offset in nested loop
rem s1, a0, s10 # int x = idx % side_lim
div s2, a0, s10 # int y = idx / side_lim
# horizontal scan by fixing y (in single dimension version)
# ...
# vertical scan by fixing x
# ...
# box scan by indirect index mapping
# ...
li a0, 1 # return value: true
# epilogue: before return, pop stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
lw s0, 4(sp)
lw s1, 8(sp)
lw s2, 12(sp)
lw s3, 16(sp)
lw s4, 20(sp)
lw s5, 24(sp)
addi sp, sp, 28
ret
check_ret_false:
li a0, 0 # return value: false
# epilogue: before return, pop stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
lw s0, 4(sp)
lw s1, 8(sp)
lw s2, 12(sp)
lw s3, 16(sp)
lw s4, 20(sp)
lw s5, 24(sp)
addi sp, sp, 28
ret
You can see that there are two tricks here:
- Use
s0astbfor number confliction detection in normal-value manners, rather than using a pointer. This reduce the number of arguments to be passed tocheck_and_mark - Use the smallest numbers of local registers
s1-s5for looping three different cases.
For horizontal case, the implementation is:
# horizontal scan by fixing y (in single dimension version)
mul s3, s2, s10 # int base = y * side_lim
add s4, s3, s10 # let s4 as iteration limit = base + side_lim
li s0, 0 # tb = 0 (initialize mark table)
check_h_loop: # loop for horizontal scanning
add a0, s8, s3 # a0 = position of ls[i]
lb a0, 0(a0) # a0 = ls[i]
jal check_and_mark # check_and_mark(shift = ls[i])
beq a0, x0, check_ret_false # if check_and_mark returns false, then check_ret_false
addi s3, s3, 1 # i++
blt s3, s4, check_h_loop # if i < base + side_lim then check_h_loop
and vertical case:
# vertical scan by fixing x
mv s3, s1 # int base = x
mv s4, s11 # let s4 as iteration limit = bound
li s0, 0 # tb = 0 (initialize mark table)
check_v_loop: # loop for vertical scanning
add a0, s8, s3 # a0 = position of ls[i]
lb a0, 0(a0) # a0 = ls[i]
jal check_and_mark # check_and_mark(shift = ls[i])
beq a0, x0, check_ret_false # if check_and_mark returns false, then check_ret_false
add s3, s3, s10 # i += side_lim
blt s3, s4, check_v_loop # if i < bound then check_v_loop
and box case:
# box scan by indirect index mapping
div s1, s1, s9 # s1 = x / box_width
mul s1, s1, s9 # int baseX = (x / box_width) * box_width
div s2, s2, s9 # s2 = y / box_width
mul s2, s2, s9 # int baseY = (y / box_width) * box_width
li s0, 0 # tb = 0 (initialize mark table)
# for (int i = 0; i < box_width; ++i)
li s3, 0 # i = 0
check_b_first_loop: # first loop for box scanning
add s5, s3, s2 # s5 = i + baseY
mul s5, s5, s10 # s5 = (i + baseY) * side_lim
add s5, s5, s1 # offset = (i + baseY) * side_lim + baseX
# for (int j = 0; j < box_width; ++j)
li s4, 0 # j = 0
check_b_second_loop: # second loop for box scanning
mv a0, s8
add a0, s8, s5 # a0 = ls + offset
add a0, a0, s4 # a0 = position of ls[offset + j]
lb a0, 0(a0) # a0 = ls[i]
jal check_and_mark # check_and_mark(shift = ls[i])
beq a0, x0, check_ret_false # if check_and_mark returns false, then check_ret_false
addi s4, s4, 1 # j++
blt s4, s9, check_b_second_loop # if j < box_width then check_b_second_loop
# end of j for loop
addi s3, s3, 1 # i++
blt s3, s9, check_b_first_loop # if i < box_width then check_b_first_loop
# end of i for loop
:::info I think the naming style and comments in this function is enough to explain what we've done :) :::
check_and_mark: # check_and_mark(shift)
# prologue for all function calls
addi sp, sp, -12
sw ra, 0(sp)
sw s1, 4(sp)
sw s2, 8(sp)
li s1, 1
sll s1, s1, a0 # int hot = 1 << shift
beq a0, x0, check_and_mark_ret_true # if shift == 0, return true
and t0, s0, s1 # t0 = tb & hot
beq t0, x0, check_and_mark_ret_true # (tb & hot) == 0, no overlap --> return true
li a0, 0 # return valuie: false
# epilogue: before return, pop stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
lw s1, 4(sp)
lw s2, 8(sp)
addi sp, sp, 12
ret
check_and_mark_ret_true:
or s0, s0, s1 # tb = tb | hot, i.e. mark table
li a0, 1 # return valuie: true
# epilogue: before return, pop stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
lw s1, 4(sp)
lw s2, 8(sp)
addi sp, sp, 12
ret
One can compile the program with:
./scripts/run hw3cand run with command:
./scripts/run sim hw3/hw3cto get the result of:
Is sudoku solvable using C function? value: [1]
Is sudoku solvable using risc-v assembly? value: [1]
Output c & assembly function result
c result :
4 1 2 3
3 2 1 4
2 3 4 1
1 4 3 2
assembly result :
4 1 2 3
3 2 1 4
2 3 4 1
1 4 3 2
your c & assembly got same result!
Baremetal code runs to the end. (pressing `ctrl+a x` to quit)
QEMU: Terminated
:::info I may finish this in... someday...
Note: partially finished! :::
According to the formula in Pytorch website, the implementation should be something like:
void maxpool2d_c(const int8_t *input_X, int32_t input_X_dimW,
int32_t input_X_dimH, int32_t input_X_dimC, int8_t *output_Y,
int32_t kernel_W, int32_t kernel_H, int32_t stride_W,
int32_t stride_H) {
const int h_out = (input_X_dimH - kernel_H) / stride_H + 1;
const int w_out = (input_X_dimW - kernel_W) / stride_W + 1;
const int square_sz = input_X_dimH * input_X_dimW;
const int out_square_sz = h_out * w_out;
for (int c = 0; c < input_X_dimC; ++c) {
for (int h = 0; h < h_out; ++h) {
for (int w = 0; w < w_out; ++w) {
int mx = 0;
int h_offset = stride_H * h;
int w_offset = stride_W * w;
for (int kh = 0; kh < kernel_H; ++kh) {
for (int kw = 0; kw < kernel_W; ++kw) {
int h_idx = h_offset + kh;
int w_idx = w_offset + kw;
int8_t cur = input_X[h_idx * input_X_dimW + w_idx + square_sz * c];
print_debug_msg("%d,\t", cur);
/**
* @brief Bitwise hack to find max of two numbers
* ref:
* http://graphics.stanford.edu/~seander/bithacks.html#IntegerMinOrMax
*/
mx = mx ^ ((mx ^ cur) & -(mx < cur)); // max(mx, cur)
}
}
print_debug_msg(" --> %d\n", mx);
output_Y[h * w_out + w + out_square_sz * c] = mx;
}
}
}
}
You can see that there exists several lines for debugging: print_debug_msg. It's defined and implemented in util.h, just like what we've done in lab02.
#ifndef UTIL_H
#define UTIL_H
#ifdef DEBUG_MODE
/**
* @brief Print debug message if DEBUG_MODE is defined
* otherwise, this will be optimized off
*/
#define print_debug_msg(...) \
{ \
printf(__VA_ARGS__); \
fflush(stdout); \
}
#else
#define print_debug_msg(...) \
{}
#endif
#endif /* UTIL_H */
To verify the function of maxpool2d_c, we can use the Pytorch version of maxpool with random input.
The testing structure is in single_c_py_random_test in main.c, it:
- Generate random parameters and input
const int dim_limit = 50; const int stride_limit = 4; const int kernel_limit = 4; const int32_t input_X_dimH = rand() % dim_limit + 4; const int32_t input_X_dimW = rand() % dim_limit + 4; const int32_t input_X_dimC = rand() % 3 + 1; const int32_t stride_H = rand() % stride_limit + 1; const int32_t stride_W = rand() % stride_limit + 1; const int32_t kernel_H = rand() % kernel_limit + 1; const int32_t kernel_W = rand() % kernel_limit + 1; int8_t *input = (int8_t *)malloc(sizeof(int8_t) * input_X_dimH * input_X_dimW * input_X_dimC); // ... const int32_t square_sz = input_X_dimW * input_X_dimH; for (int c = 0; c < input_X_dimC; ++c) { for (int h = 0; h < input_X_dimH; ++h) { for (int w = 0; w < input_X_dimW; ++w) { int8_t rand_val = rand() % INT8_MAX; input[h * input_X_dimW + w + square_sz * c] = rand_val; // ... } // ... } // ... } // ... - Write the generated parameters and input into file
rand_input.txt// save array as file FILE *fp = fopen("Bonus/rand_input.txt", "w"); fprintf(fp, "%d %d %d\n", input_X_dimC, input_X_dimH, input_X_dimW); fprintf(fp, "%d %d\n", stride_H, stride_W); fprintf(fp, "%d %d\n", kernel_H, kernel_W); print_debug_msg("input: %d %d %d\n", input_X_dimC, input_X_dimH, input_X_dimW); print_debug_msg("stride: %d %d\n", stride_H, stride_W); print_debug_msg("kernel: %d %d\n", kernel_H, kernel_W); fprintf(fp, "[ "); for (int h = 0; h < input_X_dimH; ++h) { for (int w = 0; w < input_X_dimW; ++w) { int8_t rand_val = rand() % INT8_MAX; // ... fprintf(fp, "%d, ", rand_val); } } fprintf(fp, " ]"); fclose(fp); - Run
maxpool2d_cand write resultmaxpool2d_c(input, input_X_dimW, input_X_dimH, input_X_dimC, output, kernel_W, kernel_H, stride_W, stride_H); fp = fopen("Bonus/c_output.txt", "w"); // also save array as file const int32_t out_square_sz = h_out * w_out; for (int c = 0; c < input_X_dimC; ++c) { for (int h = 0; h < h_out; ++h) { for (int w = 0; w < w_out; ++w) { fprintf(fp, "%d\n", output[h * w_out + w + out_square_sz * c]); } } } fclose(fp); - Invoke python script to generate the golden and use
diffcommand to check the correctness of output#ifdef DEBUG_MODE system("python3 Bonus/maxpool.py -d"); #else system("python3 Bonus/maxpool.py"); #endif system("command -v colordiff > /dev/null || (sudo apt update && sudo apt install " "colordiff)"); /** * if no output, then everything works fine :) */ int res = system("colordiff Bonus/c_output.txt Bonus/py_output.txt");
We run the random tests
void maxpool_c_py_test() {
const int tests = 20;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tests; ++i) {
cnt += single_c_py_random_test();
}
if (!cnt) {
printf("Passed %d random tests\n", tests);
} else {
printf("%d WA within %d random tests\n", cnt, tests);
}
}
int main() {
maxpool_c_py_test();
// ...
}
And for the python code, the framework can be:
# ...
ls = []
input_X_dimC, input_X_dimH, input_X_dimW = 0, 0, 0
strideH, strideW = 0, 0
kernelH, kernelW = 0, 0
# read parameters and random list
with open("Bonus/rand_input.txt", "r") as rand_file:
it = rand_file.readlines()
input_X_dimC, input_X_dimH, input_X_dimW = ls_to_int(it[0].strip().split())
strideH, strideW = ls_to_int(it[1].strip().split())
kernelH, kernelW = ls_to_int(it[2].strip().split())
ls = ls_to_int(eval(it[3]))
# ...
# run maxpool algorithm
ls = torch.tensor(ls).reshape((input_X_dimC, input_X_dimH, input_X_dimW))
# ...
maxpool = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(kernelH, kernelW), stride=(strideH, strideW))
ls: torch.Tensor = maxpool.forward((ls))
ls = torch.flatten(ls)
# ...
# write result to file
with open("Bonus/py_output.txt", "w") as f:
for n in ls.numpy():
f.write(f"{n}\n")
One can run code with:
./scripts/run bonus_cand see the all-passed information:
Passed 20 random tests
The implementation of maxpool2d is not that hard.
## maxpool2d.S
.text # code section
.global maxpool2d_asm # declar the sum_asm function as a global function
.type maxpool2d_asm, @function # define maxpool2d_asm as a function
maxpool2d_asm:
# maxpool2d_c(
#const int8_t *input_X = a0
# int32_t input_X_dimW = a1
# int32_t input_X_dimH = a2
# int32_t input_X_dimC = a3
# int8_t *output_Y = a4
# int32_t kernel_WH = a5 -> kernel_H
# int32_t stride_WH = a6 -> stride_H
# )
# prologue: push stack
addi sp, sp, -52
sw ra, 0(sp)
sw s0, 4(sp) # kernel_W
sw s1, 8(sp) # stride_W
sw s2, 12(sp) # h_out
sw s3, 16(sp) # w_out
sw s4, 20(sp) # square_sz
sw s5, 24(sp) # out_square_sz
sw s6, 28(sp) # c
sw s7, 32(sp) # c_offset
sw s8, 36(sp) # out_c_offset
sw s9, 40(sp) # h
sw s10, 44(sp) # w
sw s11, 48(sp) # mx
# t0: h_offset
# t1: w_offset
# t2: kh
# t3: kw
# t4: h_idx -> idx -> position of input_X[idx] -> cur
# t5: w_idx -> o_idx -> position of output_Y[o_idx], then assign value
srli s0, a5, 16 # s0 = kernel_W
li t0, 0x0ffff
and a5, a5, t0 # a5 = kernel_H (mask with 0x0000ffff)
srli s1, a6, 16 # s1 = stride_W
and a6, a6, t0 # a5 = stride_H (mask with 0x0000ffff)
sub s2, a2, a5
div s2, s2, a6
addi s2, s2, 1 # s2 = h_out
sub s3, a1, s0
div s3, s3, s1
addi s3, s3, 1 # s3 = w_out
mul s4, a1, a2 # s4 = square_sz
mul s5, s2, s3 # s4 = out_square_sz
# for (int c = 0; c < input_X_dimC; ++c) {
li s6, 0 # c = 0
loopC:
beq s6, a3, endLoopC # if c == input_X_dimC, end
mul s7, s4, s6 # s7 = c_offset
mul s8, s5, s6 # s8 = out_c_offset
# for (int h = 0; h < h_out; ++h) {
li s9, 0 # h = 0
loopH:
beq s9, s2, endLoopH # if h == h_out, end
# for (int w = 0; w < w_out; ++w) {
li s10, 0 # w = 0
loopW:
beq s10, s3, endLoopW # if w == w_out, end
li s11, 0 # mx = 0
mul t0, a6, s9 # t0 = h_offset
mul t1, s1, s10 # t1 = w_offset
li t2, 0 # kh = 0
loopKH:
beq t2, a5, endLoopKH # if kh == kernel_H, end
li t3, 0 # kw = 0
loopKW:
beq t3, s0, endLoopKW # if kw == kernel_W, end
add t4, t0, t2 # t4 = h_idx
add t5, t1, t3 # t5 = w_idx
mul t4, t4, a1 # h_idx * input_X_dimW
add t4, t4, t5 # h_idx * input_X_dimW + w_idx
add t4, t4, s7 # idx = h_idx * input_X_dimW + w_idx + c_offset
add t4, t4, a0 # position of input_X[idx]
lb t4, 0(t4) # t4 = cur = input_X[idx]
# get max using branching
bge s11, t4, noMaxChange # if mx > cur -> no change
mv s11, t4 # otherwise, mx = cur
noMaxChange:
addi t3, t3, 1 # kw++
j loopKW
endLoopKW:
addi t2, t2, 1 # kh++
j loopKH
endLoopKH:
# store local max
mul t5, s9, s3 # h * w_out
add t5, t5, s10 # h * w_out + w
add t5, t5, s8 # o_idx = h * w_out + w + out_c_offset
add t5, t5, a4 # position of outputY[o_idx]
sb s11, 0(t5) # outputY[o_idx] = mx
addi s10, s10, 1 # w++
j loopW
endLoopW:
addi s9, s9, 1 # h++
j loopH
endLoopH:
addi s6, s6, 1 # c++
j loopC
endLoopC:
# epilogue: pop stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
lw s0, 4(sp)
lw s1, 8(sp)
lw s2, 12(sp)
lw s3, 16(sp)
lw s4, 20(sp)
lw s5, 24(sp)
lw s6, 28(sp)
lw s7, 32(sp)
lw s8, 36(sp)
lw s9, 40(sp)
lw s10, 44(sp)
lw s11, 48(sp)
addi sp, sp, 52
ret
.size maxpool2d_asm, .-maxpool2d_asm
There exists some tricks that simplify and optimize the implementation.
- We combine
kernel_Handkernel_W,stride_Handstride_Was single argument. Since risv-c can only have at most 8 arguments and there are 9 arguments inmaxpool_c, with this trickm we can shrink the number of arguments to 7, which can be passed without engaging stack operations. - Just like Hw6-3, we the human compiler can use loop invariant code motion to reduce redundant operations. We apply this to all the possible instance.
- All local paraneters are manipulate using registers only. This speed up the whole process without accessing memory redundantly.
:::info Note: While in C we use bitwise tricks to implement branchless max operation, we use normal branch in assembly, since this the number of operations in branchless version is a bit... long. :::
One can run script to compile and run the code with:
./scripts/run bonus_asm
./scripts/run sim Bonus/bonus_asmand see the passed message:
Passed 100 random tests
Baremetal code runs to the end. (pressing `ctrl+a x` to quit)
QEMU: TerminatedThe implementation of a little bit different from c-python version, since the we can't use srand(time(NULL)) and malloc. However, we can still apply random test by initializing arrays with the space in some range limitation. Within that limitation, we conduct all the random tests.
Code below shows how we run the programs and verify the result.
// in single_c_asm_random_test
int8_t c_output[max_input_X_dimH * max_input_X_dimW * max_input_X_dimC];
int8_t asm_output[max_input_X_dimH * max_input_X_dimW * max_input_X_dimC];
maxpool2d_c(input, input_X_dimW, input_X_dimH, input_X_dimC, c_output,
kernel_W, kernel_H, stride_W, stride_H);
maxpool2d_asm(input, input_X_dimW, input_X_dimH, input_X_dimC, asm_output,
(kernel_W << (sizeof(int32_t) * 4)) | kernel_H,
(stride_W << (sizeof(int32_t) * 4)) | stride_H);
int wa_cnt = 0;
char str[25];
const int32_t out_square_sz = h_out * w_out;
for (int c = 0; c < input_X_dimC; ++c) {
for (int h = 0; h < h_out; ++h) {
for (int w = 0; w < w_out; ++w) {
int idx = h * w_out + w + out_square_sz * c;
if (c_output[idx] != asm_output[idx]) {
puts("c: [");
itoa(c_output[idx], str, 10);
puts(str);
puts("] != asm: [");
itoa(asm_output[idx], str, 10);
puts(str);
puts("]\n");
wa_cnt += 1;
}
}
}
}
return wa_cnt;
This is mentioned in the implementation of assembly code :)