A Binary Search Tree is a tree based data structure. Each node in binary tree can have at most two children.
Binary Search tree is a Binary Tree which follows Bianry Search Tree Invariant(Property) i.e. For a Binary Tree
to be Binary Search Tree, the left node must be smaller then the root node and right node must be greater then
the root node.
Traversal is the process to visit all the nodes of a tree. Unlike linear data structure which is traversed in linear fashion Tree Data Structure can be traversed in different way and they are :- 1:- PreOrder Traversal 2:- InOrder Traversal 3:- PostOrder Traversal
- Traverse Left sub tree
- Visit the Root Node
- Traverse Right Sub Tree
- Traverse Left Sub Tree
- Traverse Right Subtree
- Visit the Root Node
Average Worst
INSERT O(Log(n)) O(n)
DELETE O(Log(n)) O(n)
SEARCH O(Log(n) O(n)
A complete binary tree is a tree in which at every level except possibly the last level is completely filled and all the nodes are as far left as possible.
A Priority Queue is an Abstract Data Type(ADT) that operates similar to a normal queue except that each element has certain priority. The priority of the element in the queue determines the order in which the elements are removed from the Priority Queue.
Abstract Data Type are those data type which can perform certain set of operations but doesn't care about how it is implemented. It does not specify how data is to be stored in the memory and what algorithms will be used for implementating the operations.
- Used in certail implementations of Djikstra's shortest Path algorithm.
- Anytime you need to dynamically fetch the next best or next worst element.
- Used in Huffman coding( which is ofter used for lossless data compression).
- Best First Search (BFS) algorithms such as A* use PQs to continously grab the next most promising node.
- Use by minimum spanning tree (MST) algorithms.
Often the standar library of most programming languages only provide a min PQ which sorts by smallest elements first, but sometimes we need a MAX PQ.
Since elements in a priority queue are comparable they implement some sort of Comparable interface which we can simpy negate to acheive a Max heap.
Priority Queue are ususally implemented with heaps since heaps gives Priority Queue the best possible time complexity.
The Priority Queue(PQ) is an Abstract Data Type(ADT),hence heaps are not the only way to impelement PQs. As an example, we could use an usorted list, but this would not give us the best possible time complexity.
There are many types of heaps we could use to implement a priority queue including:
- Binary Heap
- Fibonacci Heap
- Binomial Heap
- Pairing Heap
BINARY HEAP CONSTRUCTION :- O(n) POLLING :- O(log(n)) PEEKING :- O(1) ADDING :- O(log(n)) NAIVE REMOVING :- O(n) NAIVE CONTAINS :- O(n) ADVANCED REMOVING WITH HELP OF HASH TABLE :- O(log(n)) ADVANCED CONTAINS WITH HELP OF HASH TABLE :- O(1)
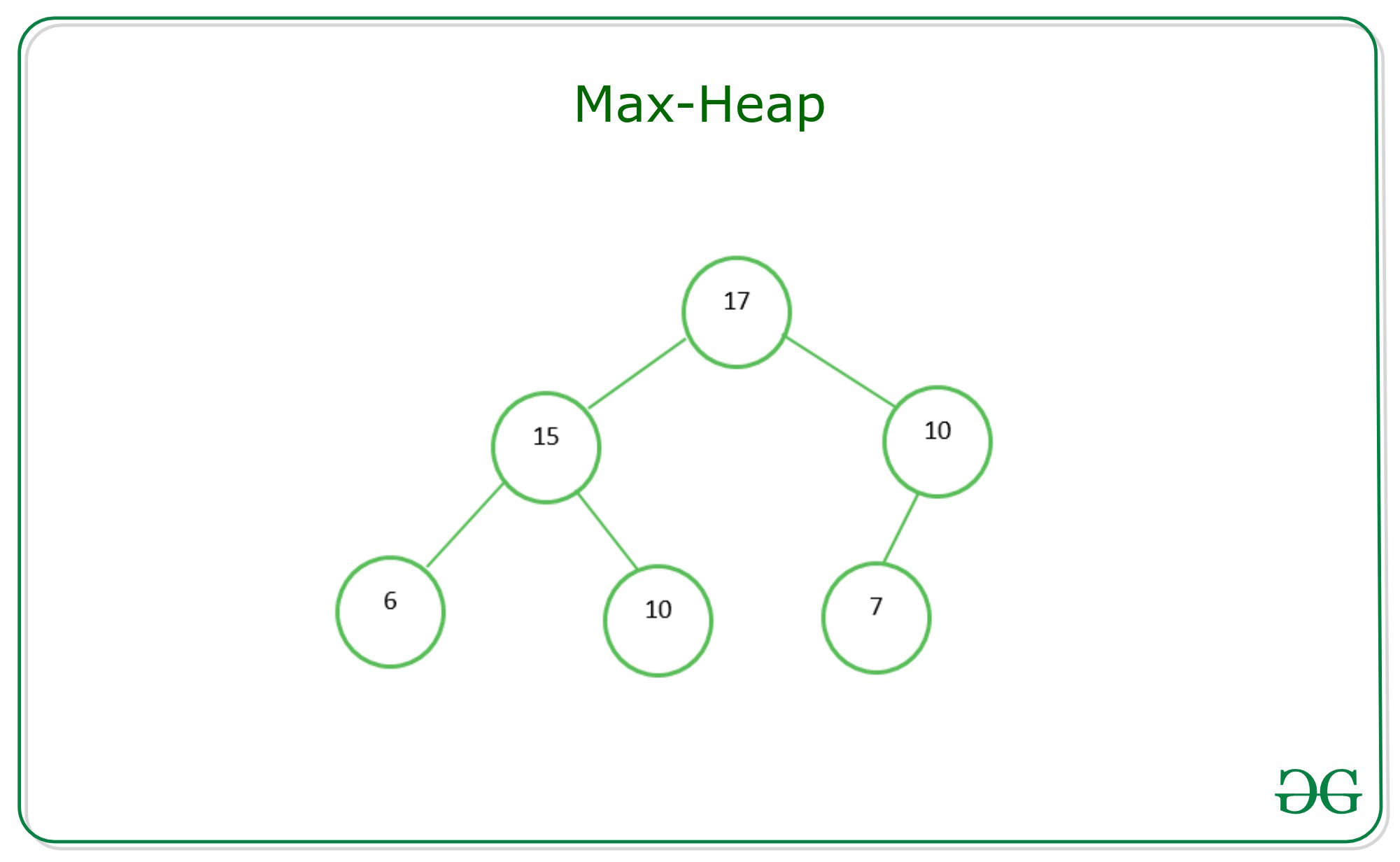
A Binary Heap or Heap is a Tree based Data Structure where the tree is a complete Binary Tree which follows Heap Invariant (Heap Property) i.e.
The tree must be maximally balanced and every node must be smaller then parent node for MAX Heap and greater then parnet node for MIN Heap.
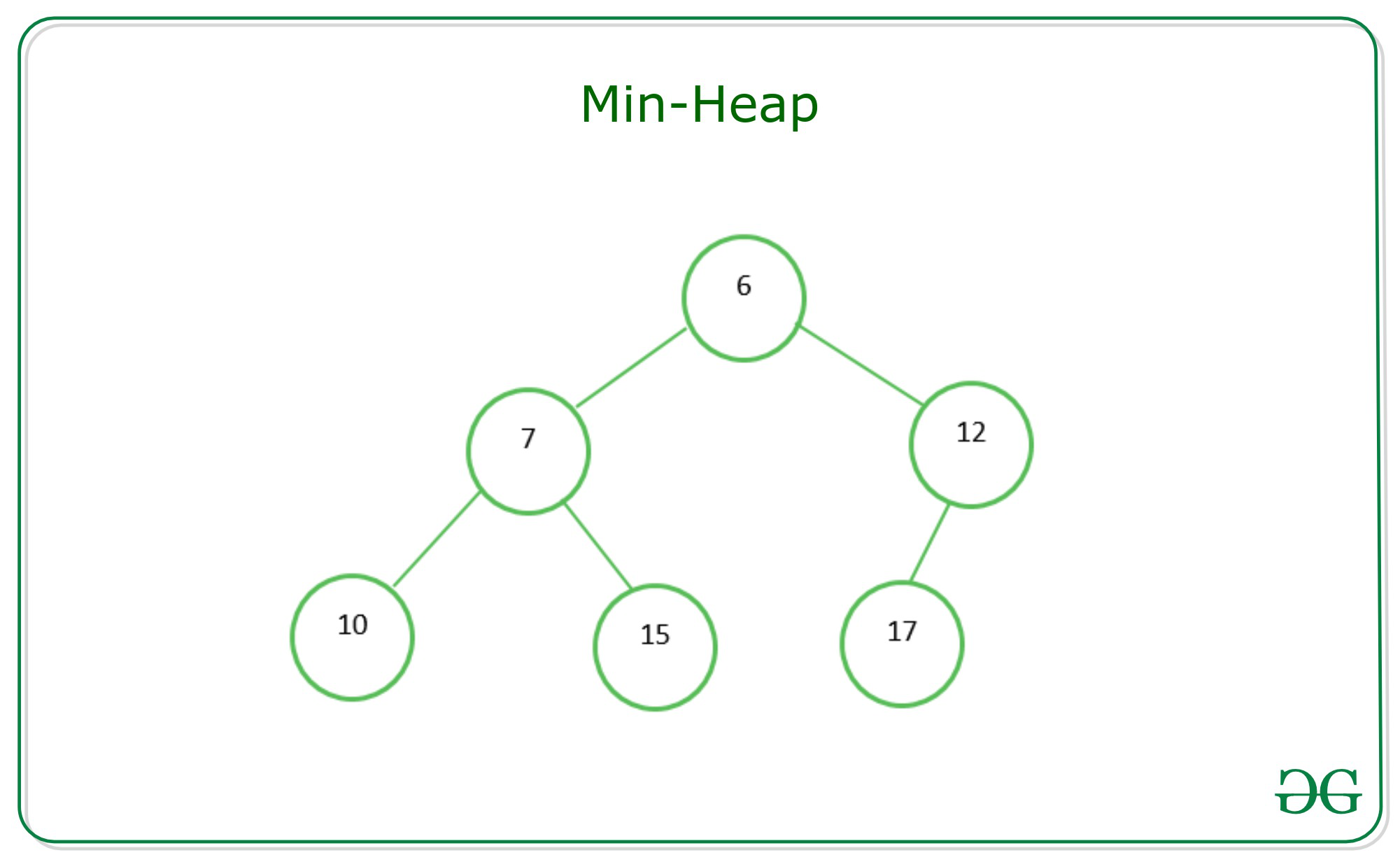
There are two types of Heap :-
Min Heap
In Min Heap the element based at the parent node must be smaller then the child node.
Heap insertion is always performed at the end of the Heap. Heapify is performed to main Heap Property after every insertion.
Removal operation of the Heap is performed on the root node of the Heap. The root element is replaced with the last element of the Heap and last element is removed from the HeapW. Heapify is performed inorder to satisfy the properties of Heap(HEAP Invariant).
Thus In Mean Heap, always minimum value are extracted while performing removal opearation.
And in case of Max Heap always maximum values are extracted while performing removal operation.
Heapify is the process of converting a binary tree into a Heap data structure.