image_pattern - package for creating image templates and generation of images from these templates using changing content.
It is often necessary to generate the same type of images with changing content. For example, images to be shared to social networks or to create a user avatar with the name (if no picture for the avatar is specified).
I wanted to have a declarative way to describe image templates, and simple generation of images from them. I hope I made it.
pip3 install image-patternFirst we need to create the pattern. We'll create an image pattern of the avatar.
The image pattern is defined with thePattern as follows:
from image_pattern import Pattern
class Avatar(Pattern):
passEach image pattern consists of two components:
- canvas - the image canvas settings, such as size;
- layers - layers that contain image content;
from image_pattern import (
Pattern,
Canvas,
)
class Avatar(Pattern):
canvas = Canvas(size=(200, 200))In this case we created an empty pattern for 200x200 image.
Now, we can generate an image from it with the code:
avatar_pattern = Avatar()
image = avatar_pattern.render()
image.save('avatar.jpg', 'JPEG')And we get the next image:
Now we need to set content. We'll start by adding the first layer:
from __future__ import annotations
from typing import List
from image_pattern import (
Pattern,
Canvas,
Layer,
Rectangle,
Point,
)
class Avatar(Pattern):
canvas = Canvas(
size=(200, 200),
)
layers: List[Layer] = [
Layer(
Rectangle(
size=(100, 200),
point=Point(x=0, y=0),
background_color=(51, 204, 255),
),
Rectangle(
size=(100, 200),
point=Point(x=100, y=0),
background_color=(255, 51, 153),
),
),
]
avatar_pattern = Avatar()
image = avatar_pattern.render()
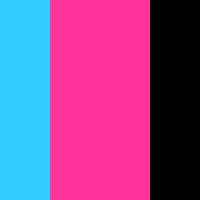
image.save('avatar.jpg', 'JPEG')Let's run the script and get the image:
What's going on here:
- We added a list of layers that contains one layer.
- This layer contains two rectangles;
- The
sizeproperty specifies the size of the rectangle in pixels; - The
pointproperty specifies a point on the canvas indicating the upper left corner of the element; - The
background_colorproperty specifies the color of the rectangle in the RGB system.
More information about the elements and their properties can be found in API.
After reviewing this example, a reasonable question may arise: Why do we need layers? So that no overlapping of elements occurs within one layer. For example, if we move the right rectangle by 50 pixels to the left inside one layer to make it run over the left rectangle:
...
Layer(
Rectangle(
size=(100, 200),
point=Point(x=0, y=0),
background_color=(51, 204, 255),
),
Rectangle(
size=(100, 200),
point=Point(x=50, y=0),
background_color=(255, 51, 153),
),
),
...we'll generate the next image:
As we can see, the right rectangle is missing from the image. If we increase the height of the image, we can see where it disappeared:
...
class Avatar(Pattern):
canvas = Canvas(
size=(200, 400),
)
...As we can see, the right rectangle has shifted to down so as not to intersect with the left rectangle in the same layer. The rule of shifting elements is very simple - elements are always shifted down. This is especially useful for working with texts. When the length of text is unknown.
But if we return the height of 200 pixels and place the rectangles in different layers:
...
layers: List[Layer] = [
Layer(
Rectangle(
size=(100, 200),
point=Point(x=0, y=0),
background_color=(51, 204, 255),
),
),
Layer(
Rectangle(
size=(100, 200),
point=Point(x=50, y=0),
background_color=(255, 51, 153),
),
),
]
...then we can generate the next image:
As we can see, the rectangles are superimposed on each other. That's because the layers serve to specifically to put elements on top of each other.
Okay, now we need to write a text in our image For this we will need a text element and a new layer:
...
Layer(
Text(
text='Image Pattern',
font=FONT_PATH,
font_color=(255, 255, 255),
font_size=42,
point=Point(x=0, y=0),
margin=Position(
top=20,
left=20,
right=20,
),
)
),
...You can read more about the element in the API section. By running the script, we get the image:
Template takes into account the transfer of text by words, if there is not enough space for the text. We can also specify fonts, alignment and indents.
Let's put the first letters of words in the center of the image:
...
from image_pattern import (
...
HorizontalAlignment,
VerticalAlignment,
)
...
Layer(
Text(
text='IP',
font=FONT_PATH,
font_color=(255, 255, 255),
font_size=102,
point=Point(x=100, y=100),
margin=Position(
left=20,
right=20,
),
horizontal_alignment=HorizontalAlignment.CENTER,
vertical_alignment=VerticalAlignment.CENTER,
),
),
...We got the image:
Hmm... We have the feeling that the text is not in center of the image.
However, that's not entirely true. This is because the image template is used to align the width of the entire line.
And since the width of the letter I is less than the width of the letter P, the text looks as if shifted.
To get rid of this effect, we will try to place each letter in the center of its rectangle as follows.
...
Text(
text='I',
font=FONT_PATH,
font_color=(255, 255, 255),
font_size=102,
point=Point(x=50, y=100),
margin=Position(
left=20,
right=20,
),
horizontal_alignment=HorizontalAlignment.CENTER,
vertical_alignment=VerticalAlignment.CENTER,
),
Text(
text='P',
font=FONT_PATH,
font_color=(255, 255, 255),
font_size=102,
point=Point(x=150, y=100),
margin=Position(
left=20,
right=20,
),
horizontal_alignment=HorizontalAlignment.CENTER,
vertical_alignment=VerticalAlignment.CENTER,
),
...Having executed the script, we will get the following image:
Success!
But what do we do if we need to change the text in the image often? For this purpose, the template provides a context:
...
from image_pattern import (
...
Context,
)
...
class AvatarContext(Context):
first_char: str
second_char: str
...
Text(
text=AvatarContext.var('first_char'),
...
),
Text(
text=AvatarContext.var('second_char'),
...
),
...
context = AvatarContext(
first_char='I',
second_char='P',
)
avatar_pattern = Avatar(context=context)
...Now we can change the content of the generated image without changing the template itself.
See the full code of the example in ./examples/avatar.py.
All classes are inherited from pydantic.BaseModel to validate passed arguments, which imposes certain specifics when working with api.
Basic template class. The template must be inherited from it. To create a template, you need to override the following attributes:
- canvas - attribute of the
Canvastype. Sets the properties of the canvas. - layers - attribute of the
List[Layer]type. Sets a list of layers.
- context - an argument of the
Contexttype that will be passed to the elements to form their properties.
- render - returns the generated image object of the
PIL.Imagetype; - render_to_blob(**save_kwargs) - returns the generated image object of the
io.BytesIOtype. Accepts the parameters passed to the methodPIL.Image.save(). such asqualityand etc. See more. You cannot pass the image format, as it is saved inJPEG. Made simply for easy use of the generation results.
The object describing the properties of the canvas.
- size - is the size of the canvas. It can be set as
Tuple[int, int]as well as context variable.
An object that describes a layer containing image content. The layers are overlapping, starting from the first layer in the list - the bottom layer, and ending with the last layer in the list - the top layer.
- *elements - a list of items
RecatngleorTextto add to the image.
An object that describes the context of an image. The context is described by the object attributes.
The context is an heir to pydantic.BaseModel, so it requires a description of the types to perform the validation.
- var(attribute_name: str) - indicates which context variable to use for this attribute.
An object that adds rectangles to an image.
- point -
Pointobject, which points to the upper left corner of the element in the image; - horizontal_alignment - one of the values of the enumeration
HorizontalAlignment, to specify the horizontal alignment. Can be set from a context variable. By default -HorizontalAlignment.LEFT; - vertical_alignment - one of the values of the enumeration
VerticalAlignment, to specify the vertical alignment. Can be set from a context variable. By default -VerticalAlignment.TOP; - size - element size. It can be set as
Tuple[int, int]as well as context variable; - brightness - element brightness. Optional argument. It ca be set as
floatfrom 0 to 1 or context variable; - background_image - sets the background image for the element. Optional argument. Must set the path to the image. Can be set from a context variable. The background image is scaled to the same extent as set in css -
background-size: cover;. - background_color - sets the color of background of the element. Optional argument if set
background_image. Used when generating an element only when the propertybackground_imageis not set. It can be set as RGBTuple[int, int, int]or RGBATuple[int, int, int]. Can be set from a context variable. - alpha - alpha assignment. Optional argument. It can be set as
intfrom 0 to 255. Can be set from a context variable.
An object that adds text to the image.
- point -
Pointobject, which points to the upper left corner of the element in the image; - horizontal_alignment - one of the values of the enumeration
HorizontalAlignment, to specify the horizontal alignment. Can be set from a context variable. By default -HorizontalAlignment.LEFT; - vertical_alignment - one of the values of the enumeration
VerticalAlignment, to specify the vertical alignment. Can be set from a context variable. By default -VerticalAlignment.TOP; - font - specifies the font to be used for text. Presented as a path to OpenType or TrueType font. Can be set from a context variable.
- font_size - sets the font size. It can be represented by a
intor context variable. By default -12; - font_color - sets the font color as RGB
Tuple[int, int, int]. Can be set from context variable. By default -(0, 0, 0); - text - specifies, directly, the text to be added to the image. It can be set as
stror context variable; - line_height - sets the height of the line. Optional argument. It can be set as
intor context variable; - margin - sets the indents for the text relative to the canvas. Optional argument. It can be set as
Positionor context variable;
Describes the point on the canvas.
- x - x coordinate as
int; - y - y coordinate as
int.
Describes the position of the element relative to the sides of the canvas. For example, indents for text.
- top -
intindented from the top edge of the canvas; - right -
intindented from the right edge of the canvas; - bottom -
intindented from the bottom edge of the canvas; - left -
intindented from the left edge of the canvas.
Provides horizontal alignment options.
- HorizontalAlignment.LEFT - left edge alignment;
- HorizontalAlignment.CENTER - center alignment;
- HorizontalAlignment.RIGHT - right edge alignment.
Provides vertical alignment options.
- VerticalAlignment.TOP - top edge alignment;
- VerticalAlignment.CENTER - center alignment;
- VerticalAlignment.BOTTOM - bottom edge alignment.
For integration with django, the package provides the image_pattern.cotrib.ImagePatternField field inherited from django.db.models.ImageField.
The field has a preset element blank = True relative to ImageField and a number of new arguments:
- pattern - image pattern;
- context -
callbackobject method that returns the context for generating the image. Optional argument. if the method is not specified, the object methodget_image_pattern_contextwill be used; - should_be_created -
callbackobject method, indicating the need to generate an image. Optional argument. the method is not specified, the object methodimage_pattern_should_be_createdwill be used.
The image is generated if the field is empty and should_be_created returns True.
For more information ImagePatternFieldsee the example project in ./django_example.
- Make it possible to change the image format.
- Do something with the autocomplete to create objects (Since all objects are inherited from pydantic.BaseModel, they do not contain meta information for the autocomplete. Perhaps should manually write all the constructors.).
- Think about using context. Using Context.var() with a string name does not seem to be the best way.
- Make it possible to shift within the layer not only to down, but also to the right.
- Setting the center of the background image.
- Test refactoring and bringing coverage to 100%.
- Setup linter.
- Check with mypy.
- Setup github actions.