Train and evaluate the VQ-VAE model for our submission to the ZeroSpeech 2020 challenge. Voice conversion samples can be found here. Pretrained weights for the 2019 English and Indonesian datasets can be found here. Leader-board for the ZeroSpeech 2020 challenge can be found here.
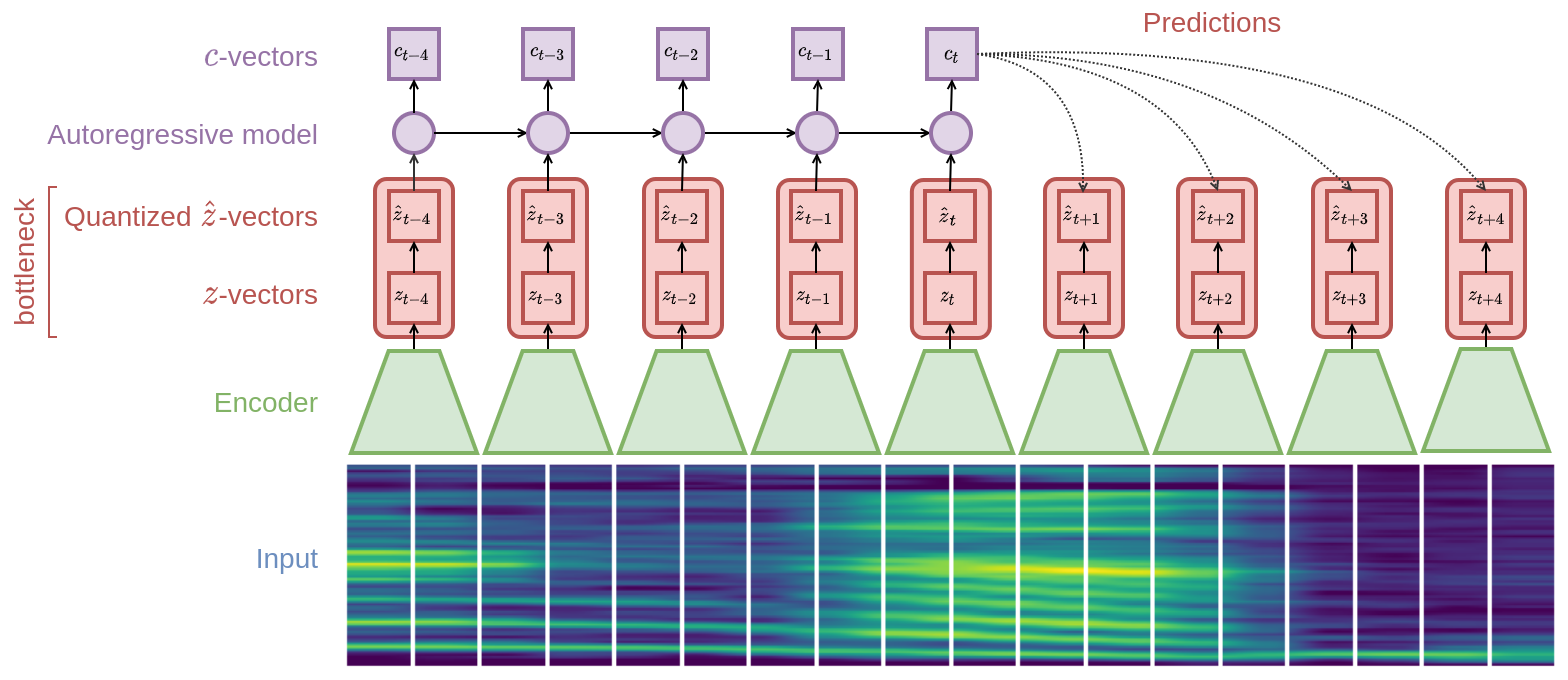
Fig 1: VQ-CPC model architecture.
-
Ensure you have Python 3 and PyTorch 1.4 or greater.
-
Install NVIDIA/apex for mixed precision training.
-
Install pip dependencies:
pip install requirements.txt -
For evaluation install bootphon/zerospeech2020.
-
Download and extract the ZeroSpeech2020 datasets.
-
Download the train/test splits here and extract in the root directory of the repo.
-
Preprocess audio and extract train/test log-Mel spectrograms:
python preprocess.py in_dir=/path/to/dataset dataset=[2019/english or 2019/surprise]Note:
in_dirmust be the path to the2019folder. Fordatasetchoose between2019/englishor2019/surprise. Other datasets will be added in the future.Example usage:
python preprocess.py in_dir=../datasets/2020/2019 dataset=2019/english
-
Train the VQ-CPC model (or download pretrained weights here):
python train_cpc.py checkpoint_dir=path/to/checkpoint_dir dataset=[2019/english or 2019/surprise]Example usage:
python train_cpc.py checkpoint_dir=checkpoints/cpc/2019english dataset=2019/english -
Train the vocoder:
python train_vocoder.py cpc_checkpoint=path/to/cpc/checkpoint checkpoint_dir=path/to/checkpoint_dir dataset=[2019/english or 2019/surprise]Example usage:
python train_vocoder.py cpc_checkpoint=checkpoints/cpc/english2019/model.ckpt-24000.pt checkpoint_dir=checkpoints/vocoder/english2019
python convert.py cpc_checkpoint=path/to/cpc/checkpoint vocoder_checkpoint=path/to/vocoder/checkpoint in_dir=path/to/wavs out_dir=path/to/out_dir synthesis_list=path/to/synthesis_list dataset=[2019/english or 2019/surprise]
Note: the synthesis list is a json file:
[
[
"english/test/S002_0379088085",
"V002",
"V002_0379088085"
]
]
containing a list of items with a) the path (relative to in_dir) of the source wav files;
b) the target speaker (see datasets/2019/english/speakers.json for a list of options);
and c) the target file name.
Example usage:
python convert.py cpc_checkpoint=checkpoints/cpc/english2019/model.ckpt-25000.pt vocoder_checkpoint=checkpoints/vocoder/english2019/model.ckpt-150000.pt in_dir=../datasets/2020/2019 out_dir=submission/2019/english/test synthesis_list=datasets/2019/english/synthesis.json in_dir=../../Datasets/2020/2019 dataset=2019/english
Voice conversion samples are available here.
-
Encode test data for evaluation:
python encode.py checkpoint=path/to/checkpoint out_dir=path/to/out_dir dataset=[2019/english or 2019/surprise]e.g. python encode.py checkpoint=checkpoints/2019english/model.ckpt-500000.pt out_dir=submission/2019/english/test dataset=2019/english -
Run ABX evaluation script (see bootphon/zerospeech2020).
The ABX score for the pretrained english model is:
{
"2019": {
"english": {
"scores": {
"abx": 13.444869807551896,
"bitrate": 421.3347459545065
},
"details_bitrate": {
"test": 421.3347459545065,
"auxiliary_embedding1": 817.3706731019037,
"auxiliary_embedding2": 817.6857350383482
},
"details_abx": {
"test": {
"cosine": 13.444869807551896,
"KL": 50.0,
"levenshtein": 27.836903478166363
},
"auxiliary_embedding1": {
"cosine": 12.47147337307366,
"KL": 50.0,
"levenshtein": 43.91132599798928
},
"auxiliary_embedding2": {
"cosine": 12.29162067184495,
"KL": 50.0,
"levenshtein": 44.29540315886812
}
}
}
}
}
This work is based on:
-
Aaron van den Oord, Yazhe Li, and Oriol Vinyals. "Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding." arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.03748 (2018).
-
Aaron van den Oord, and Oriol Vinyals. "Neural discrete representation learning." Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2017.