Genome-wide detection of human variants that disrupt intronic branchpoints
-
The search for pathogenic candidate variants in massive parallel sequencing (MPS) or next-generation sequencing (NGS) data typically focuses on non-synonymous variants within coding sequences or variants in essential splice sites, while mostly ignoring non-coding intronic variants.
-
RNA splicing, as a necessary step for protein-coding gene expression in eukaryotic cells, operates its spliceosome mostly within introns to define the exon-intron boundaries and hence the coding sequences. Introns probably harbor a substantially larger number of pathogenic variants than has so far been appreciated.
-
Intronic branchpoint (BP) is recognized by spliceosome in the beginning of the splicing process, and constitutes a vulnerability of splicing by its potential variants. BP variants may potentially result in aberrant splicing consequences (exon skipping, intron retention), which could be deleterious to the gene product.
-
BPHunter is a genome-wide computational approach to systematically detect intronic variants that may disrupt BP recognition, efficiently and informatively. This standalone version can be easily implemented into NGS analysis by a one-line command. We also provided a BPHunter webserver with a user-friendly interface.
- Feb 2023: BPHunter official version-2 was released, with an additional program for processing VCF files in batch, and an additional output parameter 'BPHunter_HIGHRISK' (YES/NO) for labeling more promising candidate variants.
- Oct 2022: "Genome-wide detection of human variants that disrupt intronic branchpoints" that introduces BPHunter was published in PNAS.
- Aug 2022: BPHunter official version-1 was released.
- Jun 2021: BPHunter webserver & github were launched.
- Dec 2020: BPHunter prototype was completed.
Current version: version-2
The code is written in python3, and requires bedtools installed.
Due to the file size limit in GitHub, please download the BPHunter reference datasets and put them into your BPHunter folder.
To use the latest version-2, please download and replace the reference datasets.
Input: Variants in VCF format, with 5 mandatory and tab-delimited fields (CHROM, POS, ID, REF, ALT).
- The 48 published pathogenic BP variants are provided as the example input. (Example_var_BP.vcf)
Output: BPHunter-detected variants will be output with the following annotations.
- SAMPLE (only for BPHunter_VCF_batch.py)
- CHROM, POS, ID, REF, ALT (exactly the same as input)
- STRAND: +/-
- VAR_TYPE: snv, x-nt del, x-nt ins
- GENE: gene symbol
- TRANSCRIPT_IVS: ENST123456789_IVS10
- CANONICAL: canonical transcript_IVS, or '.'
- BP_NAME: m/e/cBP_chrom_pos_strand_nucleotide
- BP_ACC_DIST: distance from BP to the acceptor site
- BP_RANK: rank of BP in this intron
- BP_TOTAL: total number of BP in this intron
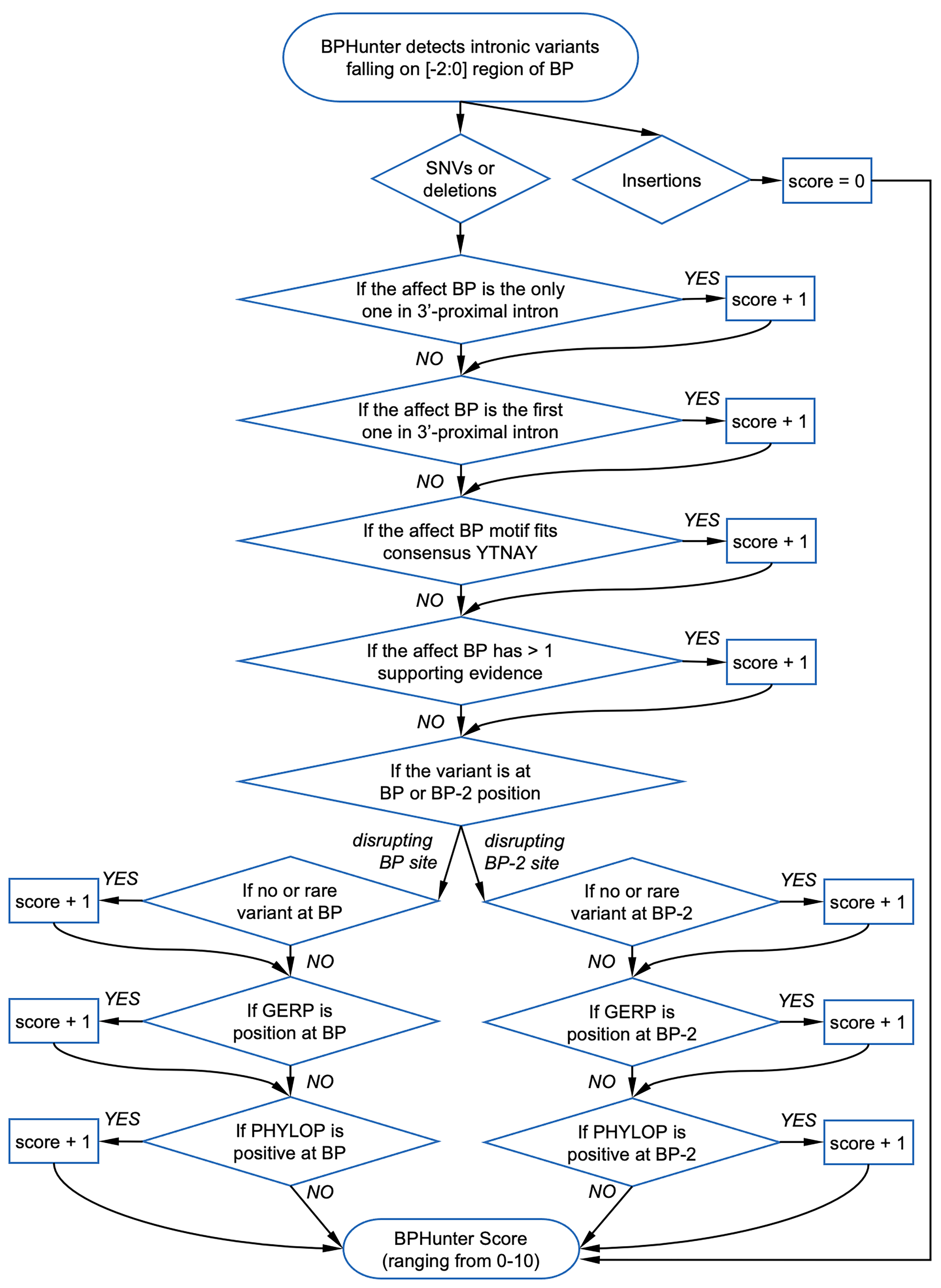
- BP_HIT: BP position (-2, -1, 0) hit by the variant
- BP_SOURCE: number of sources supporting this BP position
- CONSENSUS: level of consensus (1:YTNAY, 2:YTNA, 3:TNA, 4:YNA, 0:none)
- BP/BP2_GERP: conservation score GERP for BP and BP-2 positions
- BP/BP2_PHYL: conservation score PHYLOP for BP and BP-2 positions
- BPHunter_HIGHRISK: YES/NO if a BP variant considered as high-risk
- BPHunter_SCORE: score of a BP variant (suggested cutoff>=3, max=10)
python BPHunter_VCF.py -i variants.vcf
python BPHunter_VCF.py -i variants.vcf -g GRCh37 -t all
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| -i | file | variants in VCF format, with 5 fields (CHROM, POS, ID, REF, ALT) | N.A. |
| -g | str | human reference genome assembly (GRCh37 / GRCh38) | GRCh37 |
| -t | str | all / canonical transcripts? | all |
python BPHunter_VCF_batch.py -d /dir -s samplelist.txt -o output.csv
python BPHunter_VCF_batch.py -d /dir -s samplelist.txt -o output.csv -g GRCh37 -t all
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| -d | str | directory of VCF files | N.A. |
| -s | file | sample list (without .vcf extension) to be screened in the above directory | N.A. |
| -o | str | output CSV filename | N.A. |
| -g | str | human reference genome assembly (GRCh37 / GRCh38) | GRCh37 |
| -t | str | all / canonical transcripts? | all |
- Zhang P. et al. Genome-wide detection of human variants that disrupt intronic branchpoints. PNAS. 119(44):e2211194119. 2022.
Developer: Peng Zhang, Ph.D.
Email: pzhang@rockefeller.edu
Laboratory: St. Giles Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases
Institution: The Rockefeller University, New York, NY, USA