-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 37
Neutralization rules
Greg Landrum edited this page Dec 4, 2019
·
10 revisions
The general idea behind the neutralization rules is to either add or remove Hs to make the formal charges on atoms neutral. Some additional notes on this:
- Individual atoms will never be neutralized if the result would leave a net charge on the molecule.
- Hs will not be added/removed to create a new charged atom in order to attain overall neutrality.
| Original | Neutralized | Notes |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
Add/remove Hs to bring charge to zero |
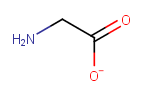 |
 |
Add H to bring charge to zero |
 |
 |
Remove H to bring charge to zero |
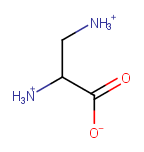 |
 |
Add/remove Hs to bring charge to zero |
 |
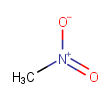 |
Zwitterionic form |
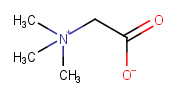 |
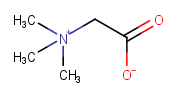 |
Adding H to neutralize carboxylic acid would leave the molecule with a charge |
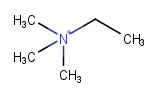 |
 |
nothing to do here |
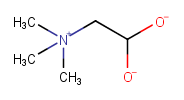 |
 |
Two symmetric choices for where to add the H to make the molecule neutral |
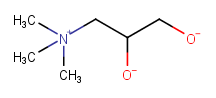 |
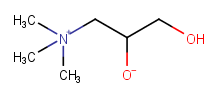 |
"Arbitrary choice", but will be done canonically (so that the same arbitrary answer is always generated) |
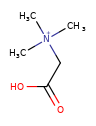 |
 |
New atomic charges will not be created, even if that leads to a net neutral molecule. |
| Original | Neutralized | Parent | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
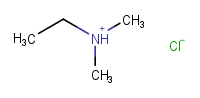 |
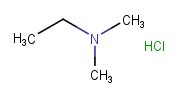 |
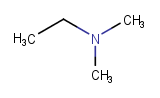 |
|
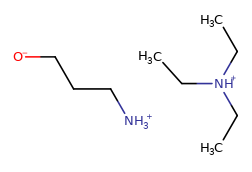 |
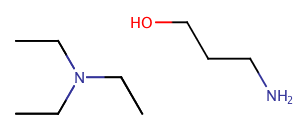 |
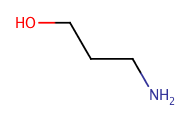 |
Assumes CCN(CC)CC is a salt and NCCCO is not a salt. |
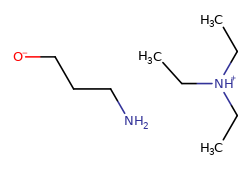 |
 |
 |
Assumes CCN(CC)CC is a salt and NCCCO is not a salt. |
 |
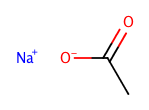 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
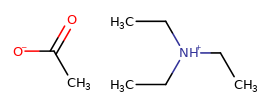 |
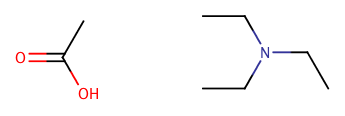 |
 |
|
 |
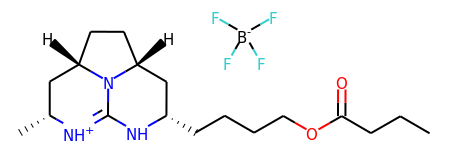 |
 |