This repository contains the dataset and code of LoFTI.
LoFTI is an evaluation benchmark spanning multiple geographical locales that can be used to test the localization and factual transfer abilities of LLMs.
It can be used as a benchmark to evaluate the capabilities of LLMs in the Indian context.
- Generating a localized response given a common question that can be asked across locations
- Factuality transfer from one locale to another.
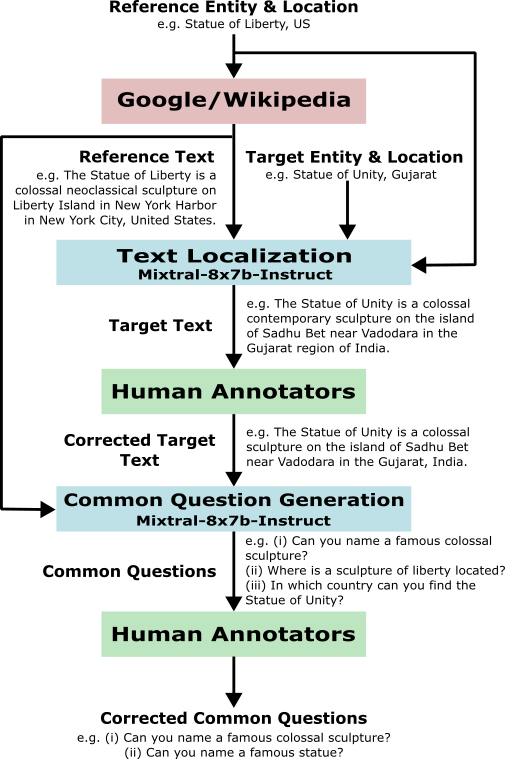
Illustration of LLM’s localized factual text transfer capabilities.
LoFTI dataset is available in the dataset folder.
- Region: The region of the reference location.
- Category: The category of the entity in the factual text.
- Reference Location: A non-Indian location.
- Reference Entity: An entity from the reference location.
- Reference Text: Factual text about the reference entity.
- Target Location: A location in India.
- True Target Entity: An example of a correct localization of the reference entity in the target location.
- True Target Text: A localized factual text of the true target entity.
- Hyperlocal Score: The degree of hyperlocality within the Indian context. The dataset includes three hyperlocality scores: 1, 2, and 3. These scores correspond to the target locations ‘India,’ ‘any state in India,’ and ‘any city in India,’ respectively.
- High Cardinality: Cardinality denotes the potential count of replaceable entities for the reference entity within the target location. A high cardinality suggests there are many such replaceable entities. This feature is denoted by ’yes’ or ’no’ values.
- Common Questions: Questions extracted from the reference and the target texts.
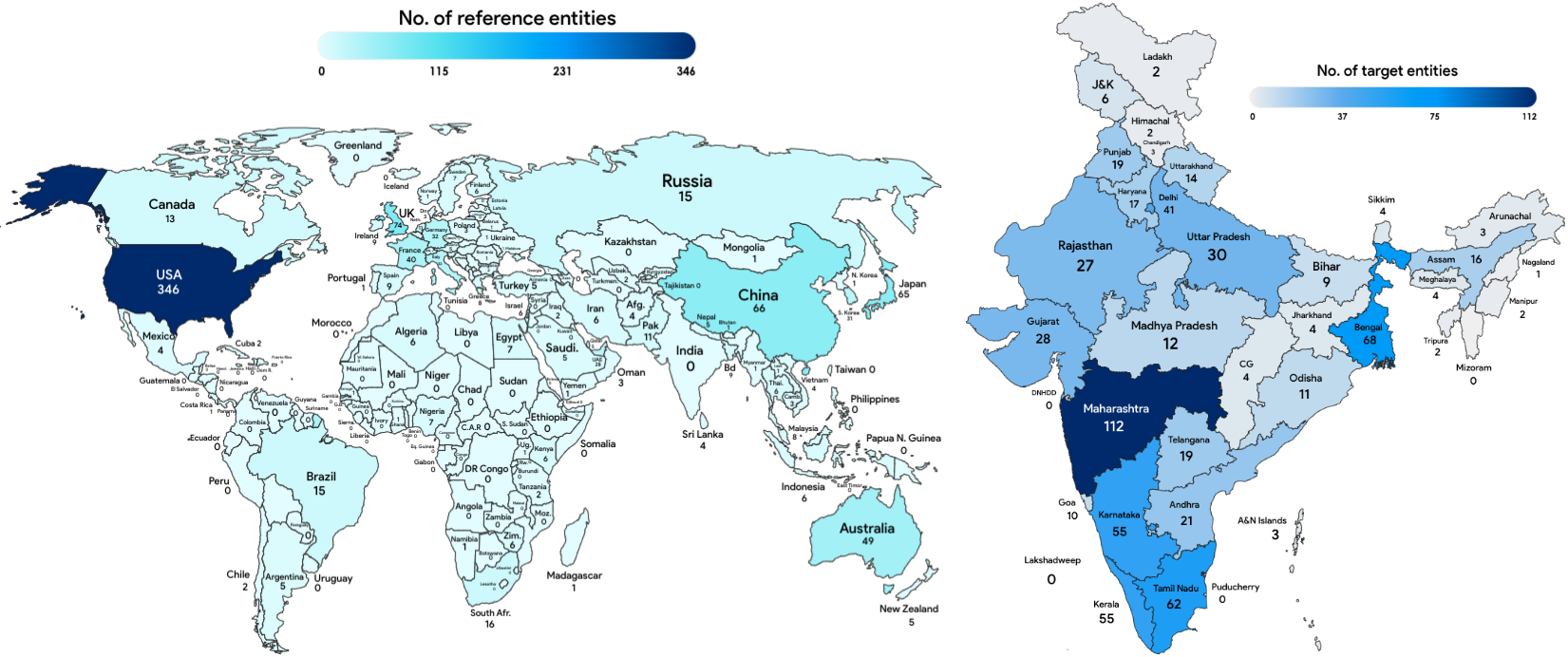
The global distribution of the reference entities and the spread of target entities in India.
- Entity pairs: Humman annotators
- Reference text: Google API Client/Wikipedia
- Target text: TheBloke/Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1-GGUF(Q4_K_M)
- Common questions: TheBloke/Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1-GGUF(Q4_K_M)
To ensure the correctness of the LOFTI dataset, all the generations were carefully checked by human annotators. These annotators represent diverse demographics and have knowledge about samples from different geographic and hyperlocal regions.
git clone https://github.com/csalt-research/LoFTI.git
cd LoFTI
Build the Docker image:
docker build -t lofti-image .
Run the Docker container with GPU support:
docker run -it --gpus all --name lofti-container lofti-image
Model setup:
- For GGUF files:
- The code supports any model in GGUF format. Download the GGUF files at
llama.cpp/models/. - You can download the gguf files using huggingface-cli. For example:
huggingface-cli download TheBloke/Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1-GGUF mixtral-8x7b-instruct-v0.1.Q4_K_M.gguf --local-dir . --local-dir-use-symlinks False - GGUF files for some models:
- Mixtral_8x7B: Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1_Q4_K_M
- Llama3: Llama-3-8B-Instruct.Q4_K_M
- The code supports any model in GGUF format. Download the GGUF files at
- For openai models:
- Models used: gpt-3.5-turbo, gpt-4-turbo
- Upload your OpenAI API key at
utils/api.pyasOPENAI_KEY="xxxxxx" - Refer: OpenAI Models, OpenAI API
To do localized text transfer from a reference sentence to a target location on LoFTI dataset:
python3 localized_text_transfer.py \
--model model \
--prompt_format prompt_format \
--output_path output_path
model: LLM model path (gguf format) or openai model names (like gpt-4-turbo).
prompt_format: Prompt format for the model. Supported formats: 'llama', 'mixtral, 'gpt'.
output_path: Output file path to a JSON file to store the generations.
Example:
python3 localized_text_transfer.py \
--model gpt-3.5-turbo \
--prompt_format gpt \
--output_path outputs/TT_gpt3.5_generation.json
To do localized question answering for a given factual question and a target location on LoFTI dataset:
python3 localized_QA.py \
--model model \
--prompt_format prompt_format \
--output_path output_path
model: LLM model path (gguf format) or openai model names (like gpt-4-turbo).
prompt_format: Prompt format for the model. Supported formats: 'llama', 'mixtral, 'gpt'.
output_path: Output file path to a JSON file to store the generations.
Example:
python3 localized_text_transfer.py \
--model gpt-3.5-turbo \
--prompt_format gpt \
--output_path outputs/QA_gpt3.5_generation.json
To evaluate the generations obtained for LoFTI using an LLMdo localized question answering for a given factual question and a target location on the LoFTI dataset:
python3 llm_evaluator.py \
--model model \
--eval_type eval_type \
--eval_json_file eval_json_file \
--eval_metric ['eval_metric1', 'eval_metric2'] \
--output_path output_path
model: Openai model names (like gpt-4-turbo).
eval_type: Provide QA for localized question answering, TT for localized text transfer.
eval_json_file: File to evaluate (JSON).
eval_metric: List of metrics to evaluate. Metrics supported EC, CQ, and FC.
output_path: Output file path to a JSON file to store the evaluations.
Example:
python3 llm_evaluator.py \
--model gpt-4-turbo \
--eval_type TT \
--eval_json_file outputs/TT_gpt3.5_generation.json \
--eval_metric ['EC', 'CQ', 'FC'] \
--output_path outputs/TT_gpt3.5_gen_eval_gpt4_EC_CQ_FC.json
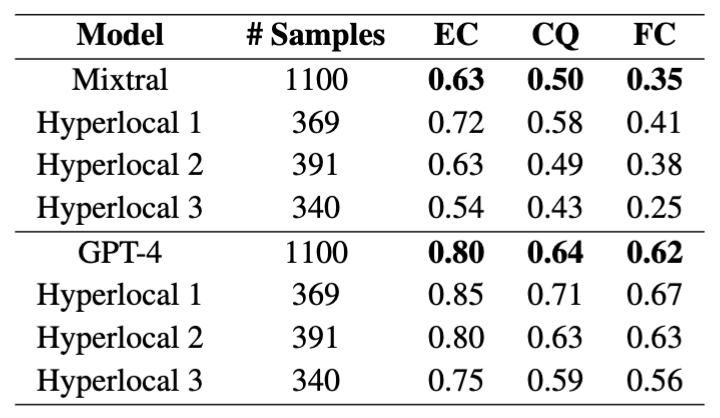
- GPT-4 evaluation of Mixtral8x7B and GPT-4 for localized text generation on LoFTI:
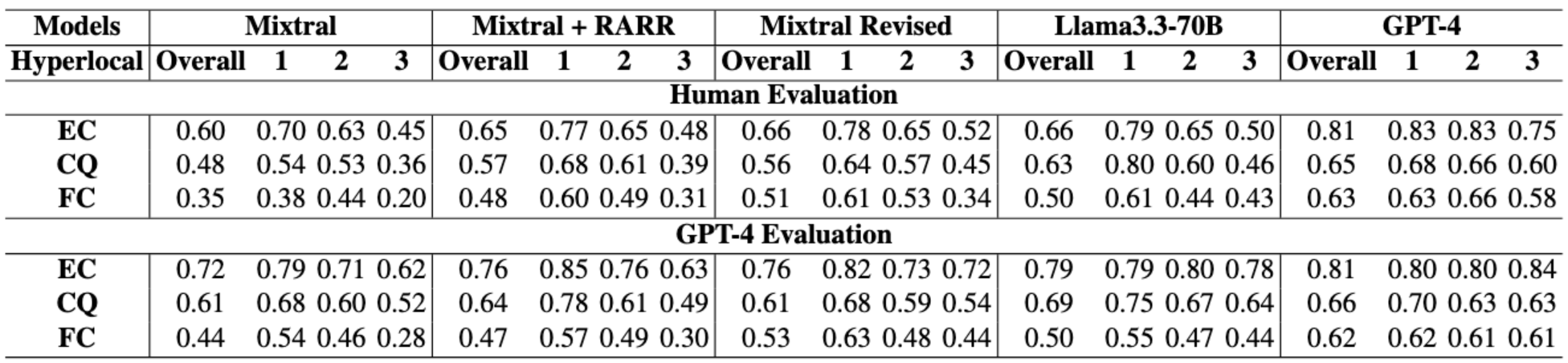
- GPT-4 evaluation of Mixtral8x7B, Mixtral + RARR, Mixtral Revised, Llama3-8B, and GPT-4 for localized text transfer (TT) on LoFTI subset:
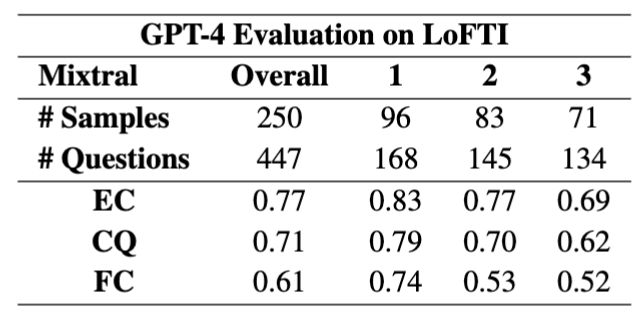
- GPT-4 evaluation of Mixtral8x7B for localized question answering (QA) on LoFTI:
- The dataset is designed for localization from different locations in the world to India only. In order to perform localization to regions other than in India, we will need additional annotations. This is also reserved for a future release.
- LoFTI is entirely in English and does not contain any multilingual localizations. It is possible to use simple translation models to translate the data but it is not robust. This is a significant extension that we also intend to explore as future work.
- There can be several correct target entities localized to a target location which we refer to as high cardinality. High cardinality can make it hard to make the resulting evaluations precise, especially since some entities can be added in the future with respect to localization.