Library to calculate potential, exponential, logarithmic, lineal and logistic regression in Arduino.
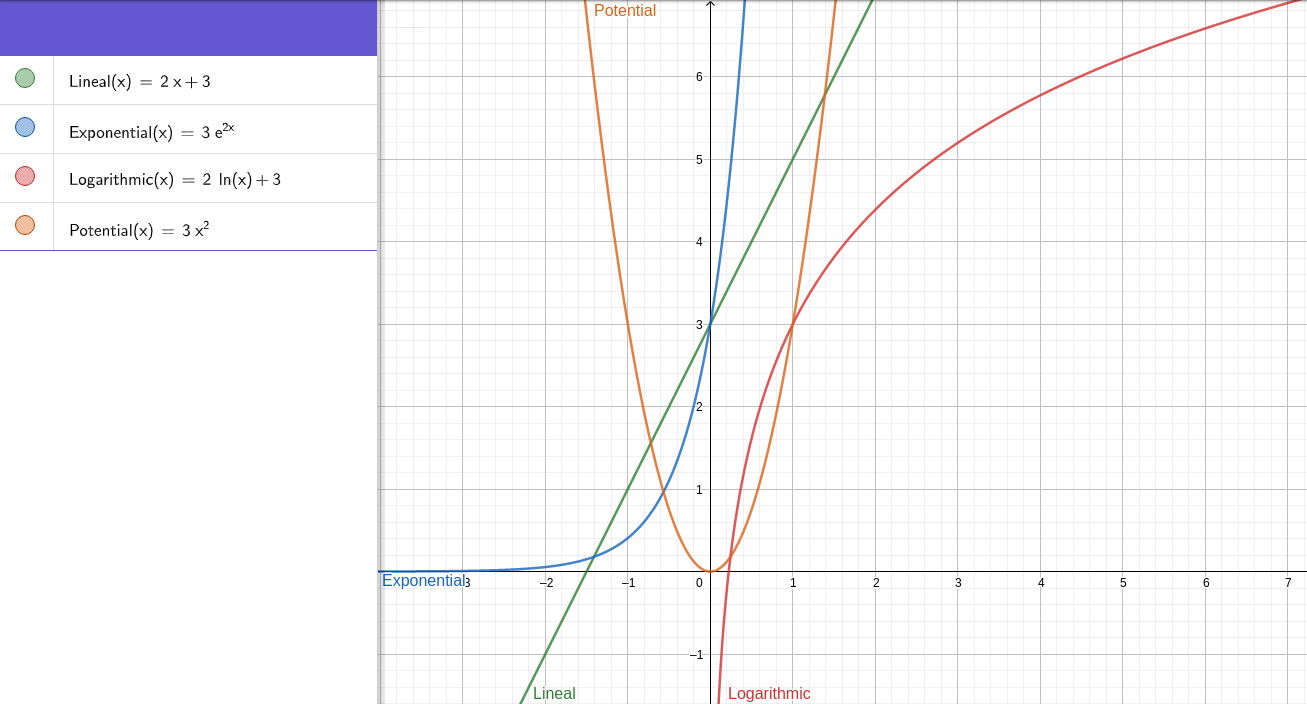
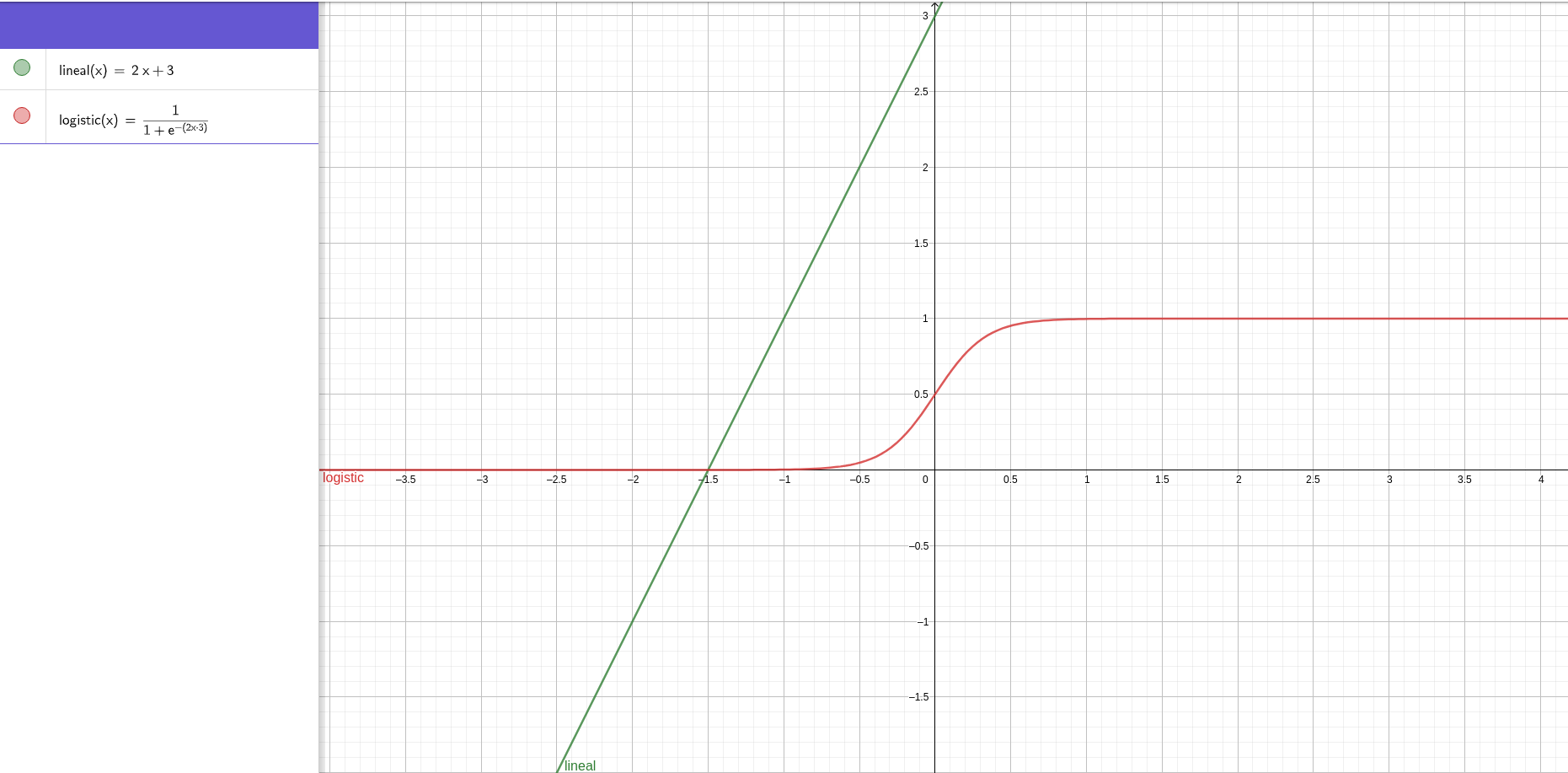
Lineal: Y = a*X + b
Exponential: Y = b * e^(a*X)
Logarithmic: Y = a*ln(X) + b
Potential: Y = b * x^a
Logistic: Y = 1 / (1 + e^-(a*x+b))
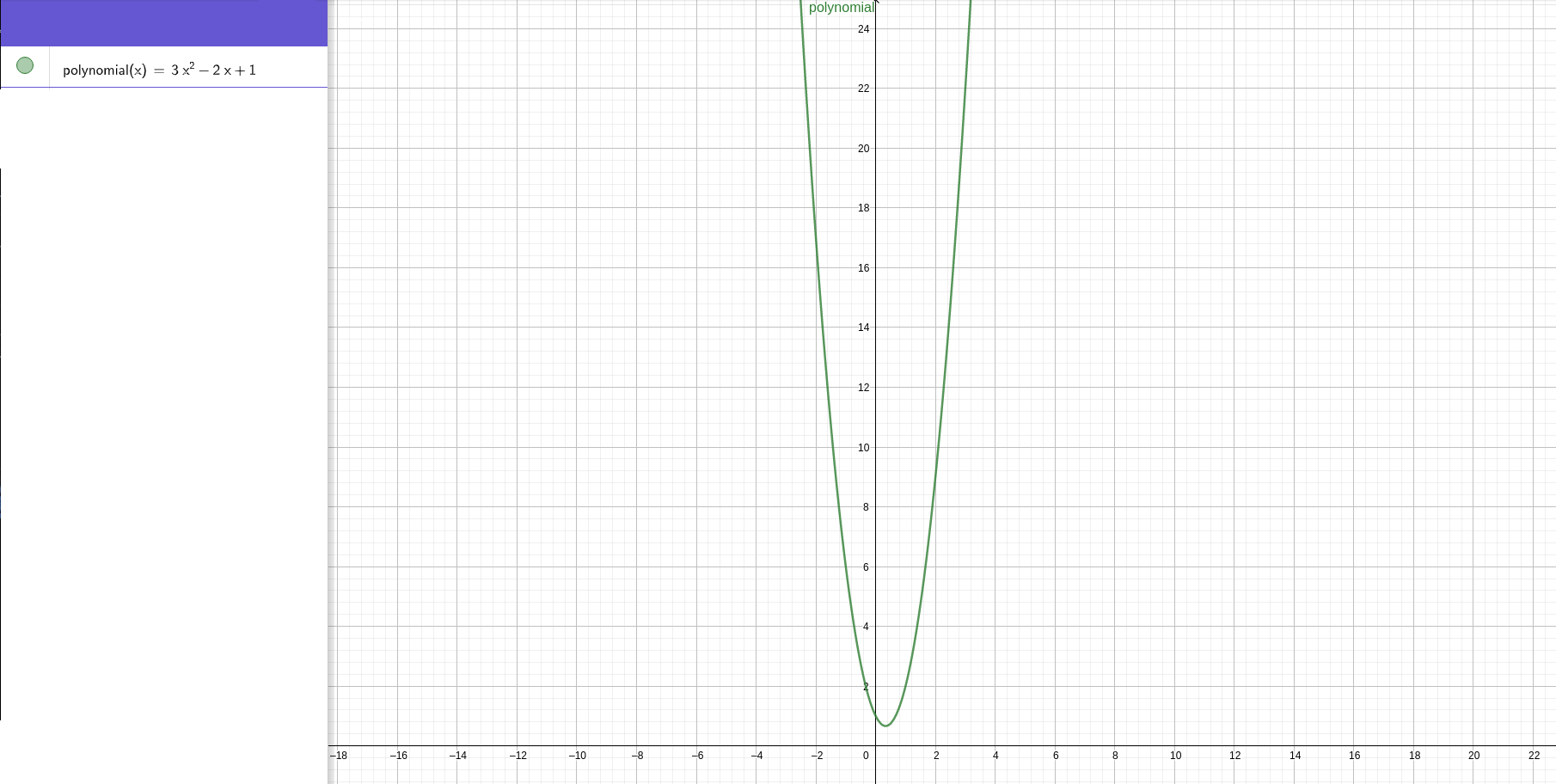
Polynomial: Y = a1x^2 + a2x + b
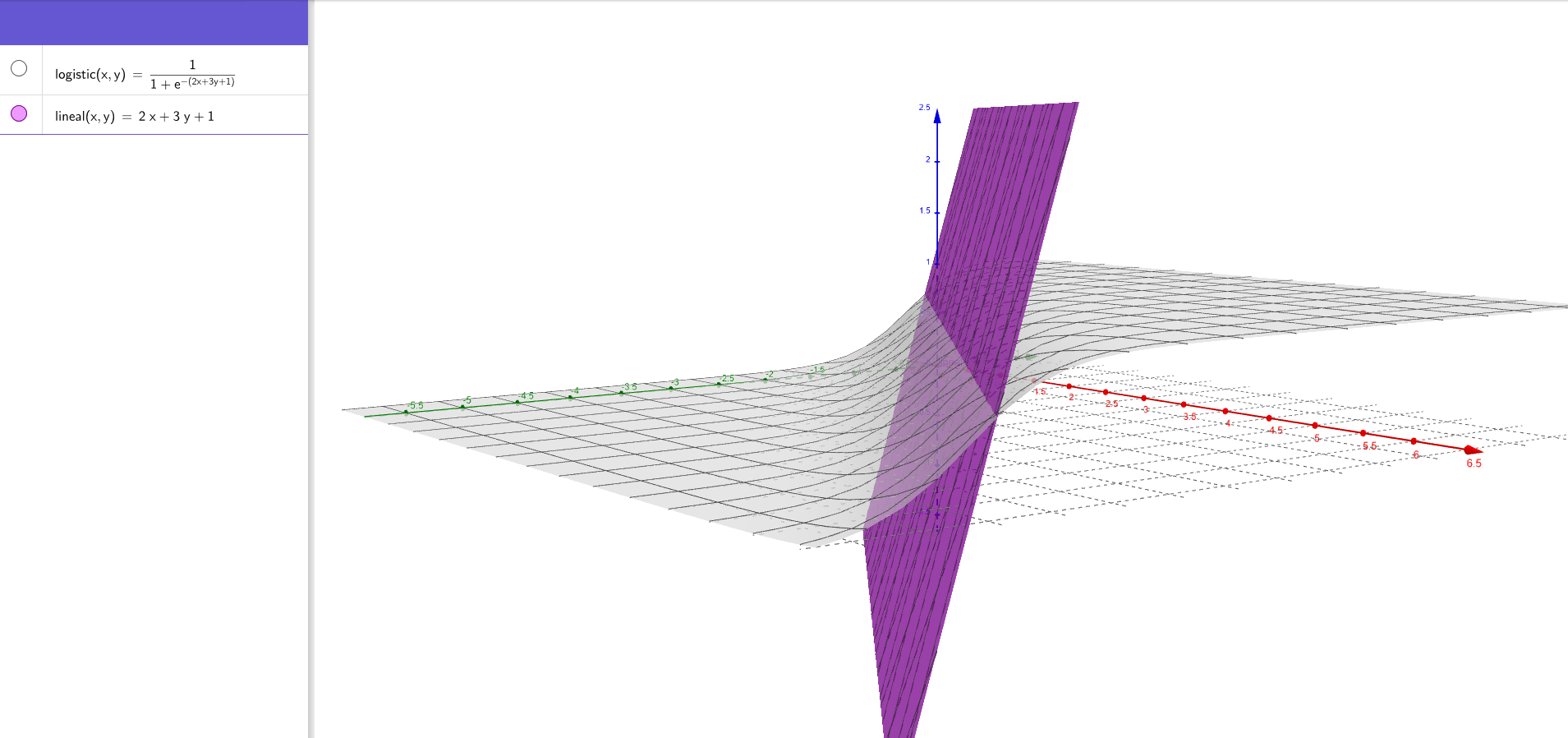
Linear2d: Y = a1x1 + a2x2 + b
Logistic2d:Y = 1 / (1 + e^-(1x1 + a2x2 + b))
Graphs with a = 2 and b = 3:
Logistic regression:
Polynomial regression:
Linear and Logistic 2 variables
#include <LinearRegression.h>
LinearRegression lr = LinearRegression();#include <ExponentialRegression.h>
ExponentialRegression er = ExponentialRegression;#include <LogarithmicRegression.h>
LogarithmicRegression lr = LogarithmicRegression();#include <PotentialRegression.h>
PotentialRegression pr = PotentialRegression();#include <LogisticRegression.h>
LogisticRegression pr = LogisticRegression();#include < PolynomialRegression.h>
PolynomialRegression pr = PolynomialRegression();#include <LinearRegression2d.h>
LinearRegression lr = LinearRegression2d();#include <LogisticRegression2d.h>
LogisticRegression pr = LogisticRegression2d();void learn(double x, double y); Learns one example.
- x: value of X
- y: value of Y
double calculate(double x1); Estimates value of Y for X
- x: value of x
double correlation(); Return correlation value
void reset(); Reset values. Start learning since zero.
void parameters(double values[]);Return parameters of the regression y = mx + b
- values[0] = m;
- values[1] = b;
In polynomial values are y = b1x^2 + b2x + a :
- values[0] = b1;
- values[1] = b2;
- values[2] = a;
double error(double x, double y); Return estimation error. If you need more options to calculate error you can use error module from SimpleStatisticsArduino
void samples();Return number of examples learned
void learn(double x1, double x2, double y); Learns one example.
- x1: value of X1
- x2: value of X2
- y: value of Y
double calculate(double x1, double x2); Estimates value of Y
- x1: value of x1
- x2: value of x2
double correlation(); Return correlation value
double correlationX1Y(); Return correlation value between X1 and Y
double correlationX1Y(); Return correlation value between X1 and Y
double correlationX2Y(); Return correlation value between X2 and Y
double correlationX1X2(); Return correlation value between X1 and X2
void reset(); Reset values. Start learning since zero.
void parameters(double values[]);Return parameters of the regression y = b1x1 + b2x2 + a
- values[0] = b1;
- values[1] = b2;
- values[2] = a;
double error(double x1, double x2, double y); Return estimation error. If you need more options to calculate error you can use error module from SimpleStatisticsArduino
void samples();Return number of examples learned