-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Fun Fun Function
In this videos we will practise with a few different Higher Order Functions
All this functions are based on list-transformation. They turn your list into something else.
Functions are values
Basic function
console.log('Fun Fun Function')
var triple = function(x){
return x*3
}
var waffle = triple
console.log(waffle(30))Result in console === "90"
Exercise filtering data
First I made this array which is a variable with an array. It contains the kind of animal and a name that is given by each animal.
console.log('Fun Fun Function - Animals')
var animals = [
{name: 'Fluffykins', species: 'rabbit'},
{name: 'Caro', species: 'dog'},
{name: 'Hamilton', species: 'dog'},
{name: 'Harold', species: 'fish'},
{name: 'Ursula', species: 'cat'},
{name: 'Jimmy', species: 'fish'},
]The code we will use to filter the dogs out of the complete array would look like this:
var dogs = animals.filter(function(animal){
return animal.species === 'dog'
})The second codeline is easy to understand because the system will look for the species with the name 'dog'. === means equal value and equal type (source)
You can split the code in two seperete parts. That will look like this:
var isDog = function(animal){
return animal.species === 'dog'
}
var dogs = animals.filter(isDog)The var isDog is just a function that checks of an object is a dog. It had nothing to do with filtering yet. The var dog will handle the filtering of the object.
It's also possible to do the exact opposite. By this I mean filtering all the objects except the dogs. You can use the "reject" in stead of "filter".
var otherAnimals = animals.reject(isDog)So what are we seeing when we console.log the "dogs" variable? This is what will appear in the console:
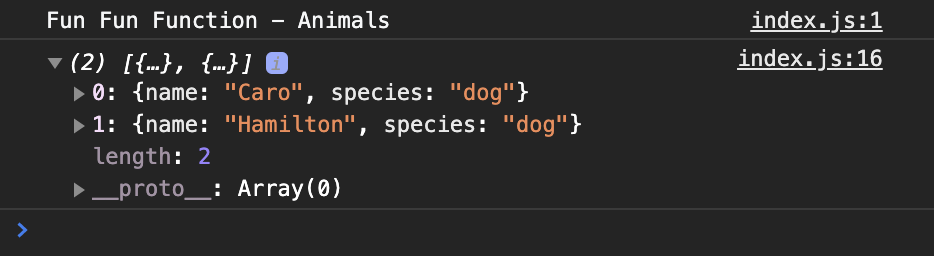
But now I just want to see the name of the dogs. How could we do this?
First I tried this method. But it won't work here because it will nog select the parts within the arrays of the name and species. But it will look voor the entire codeline. First I thought it will pick only the "name" of the array because I've set "0" in the codeline.
console.log(dogs.slice(0))To come up with a good codeline, I am writing exactly what I want the code to do:
From the variable "animals" I want to show the "name" of the "species" that are equal to "dog".
I asked Chelsea Doeleman to help me out. She came with the next code:
console.log(dogs.map(dog => dog.name))With this codeline, the browser will loop all dogs and will only show the names next. So this is what you'll see in the console:
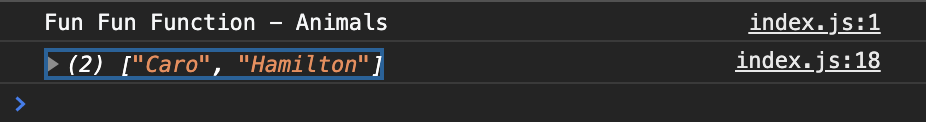
What are higher functions good for?
- Composition > small functions into other functions
Call-back functions
Filter will loop trough each item of the array You can use the function "find" to get a result of 1 array.
Also like a filter, it goed through an array. But unlike "filter" it doesn't throw the objects away, instead it transforms them. We will use the same animals array as in part 1. Because "map" is also a function on the array object, we can use it like this:
var names = animal.map()To get al the names visual in the console, the following code is required:
var names = animals.map(function(animal){
return animal.name
})U can expend the code a little bit by adding the next couple of things
var names = animals.map(function(animal){
return animal.name + ' is a ' + animal.species
})Then what you would see in the console is:
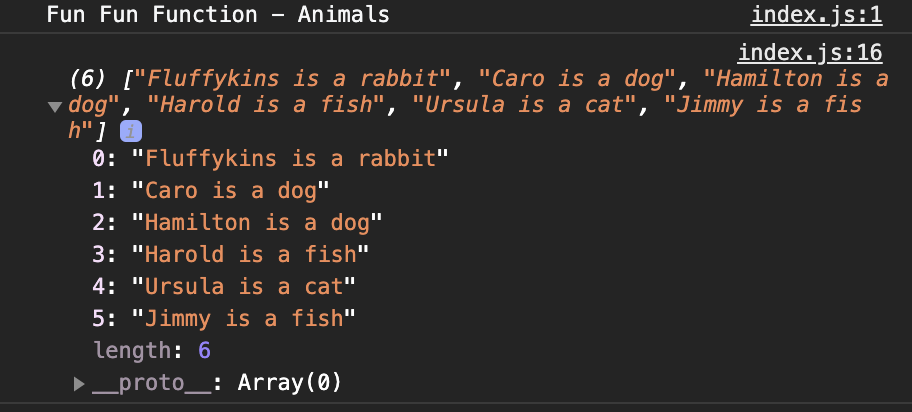
It can be easier by using arrow functions. It works like this:
var names = animals.map((animal) => animal.name)An method you can use for different kind of actions. In the example from the video we used "reduce" and "sum" to sum up all the amount values.
var orders = [
{ amount: 250 },
{ amount: 400 },
{ amount: 100 },
{ amount: 325 }
]
var totalAmount = orders.reduce((sum, order) => sum + order.amount, 0)
console.log(totalAmount);In the console we will see the total sum of 1075.
- Brainstorm
- Plan + schets