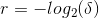Mixed-counters quotient filter(MQF) is a new variant of the Counting quotient filter(CQF) with novel counting and labeling systems. The new counting system adapts to a wider range of data distributions for increased space efficiency and is faster than the CQF for insertions and queries in most of the tested scenarios. A buffered version of the MQF can offload storage to disk, trading speed of insertions and queries for a significant memory reduction. The labeling system provides a flexible framework for assigning labels to member items while maintaining good data locality and a concise memory representation. These labels serve as a minimal perfect hash function but are ~10 fold faster than BBhash, with no need to re-analyze the original data for further insertions or deletions.
Shokrof, M., Brown, C.T. & Mansour, T.A. MQF and buffered MQF: quotient filters for efficient storage of k-mers with their counts and metadata. BMC Bioinformatics 22, 71 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-021-03996-x
MQF requires g++ >7 and cmake >3.2.
To download and compile the library:
git clone git@github.com:dib-lab/MQF.git
mkdir MQF/build
cd MQF/build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
makeTo run the library tests:
ctest --verboseto install the library on the system:
make installMQF shared library will be written at MQF/lib. To add MQF to your project
g++ -o main main.cpp -IMQF/include/ MQF/lib/libMQF.aMQF Initialization requires the estimation of some parameters: number of slots, Key bits, fixed counter size, and labels size.
Fixed-size counter size is estimated from the shape of data distribution. If most of the items are singletons. The fixed-size counter should be limited to 1 bit. However, If a big portion of items is repeated more than one time, a bigger fixed-size counter will hold more counts and thus save slots.
The number of slots is estimated from the number of items expected to be inserted into the filter. Slots are used for inserting the remaining part of the hash of the items and the count. After calculating the required number of slots, multiply the result by 1.05 because MQF can't be filled by more than 95% of its capacity. Then, round the result to the nearest bigger power of two.
Key bits equal to log2(number of slots) + the remaining part bits. the remaining part bits is estimated from the desired accuracy using the formula below.
Label size is straightforward to be estimated. it can be set to zero if labels are not necessary.
- qf_init Initialize mqf .
void qf_init(QF *qf, uint64_t nslots, uint64_t key_bits, uint64_t label_bits,uint64_t fixed_counter_size, bool mem, const char *path, uint32_t seed);- Qf* qf : pointer to the Filter.
- uint64_t nslots : Number of slots in the filter. Should be of power of two. Maximum number of items to be inserted depends on this number.
- uint64_t key_bits: Number of bits in the hash values.
- uint64_t label_bits: Number of bits in label value.
- uint64_t fixed_counter_size: Fixed counter size. must be > 0.
- bool mem: Flag to create the filter on memory. IF false, mmap is used.
- const char * path: In case of mmap. Path of the file used to pack the filter.
- uint32_t seed: useless value. To be removed
- qf_destroy
- estimate
- Insert : Increment the counter for this item by count.
bool qf_insert(QF *qf, uint64_t key,
uint64_t count,bool lock, bool spin);- Qf* qf : pointer to the Filter
- uint64_t key : hash of the item to be inserted.
- uint64_t count: Count to be added
- bool lock: For Multithreading, Lock the * slot used by the current thread so that other threads can't change the value
- bool spin: For Multithreading, If there is a lock on the target slot. wait until the lock is freed and insert the count.
- returns True if the insertion succeeded.
- Count: Return the number of times key has been inserted, with any value, into qf.
uint64_t qf_count_key(const QF *qf, uint64_t key);- Qf* qf : pointer to the Filter
- uint64_t key : hash of the item to be counted.
- returns the number of times the item is inserted.
- Remove: Decrement the counter for this item by count.
bool qf_remove(QF *qf, uint64_t hash, uint64_t count, bool lock, bool spin);- Qf* qf : pointer to the Filter
- uint64_t key : hash of the item to be removed
- uint64_t count: Count to be removed
- bool lock: For Multithreading, Lock the slot used by the current thread so that other threads can't change the value
- bool spin: For Multithreading, If there is a lock on the target slot. wait until the lock is freed and insert the count.
- Add/Remove label to elements
uint64_t qf_add_label(const QF *qf, uint64_t key, uint64_t label, bool lock, bool spin);
uint64_t qf_get_label(const QF *qf, uint64_t key);
uint64_t qf_remove_label(const QF *qf, uint64_t key, bool lock, bool spin);- Qf* qf : pointer to the Filter
- uint64_t key : hash of the item.
- uint64_t label: label for the item.
- bool lock: For Multithreading, Lock the slot used by the current thread so that other threads can't change the value
- bool spin: For Multithreading, If there is a lock on the target slot. wait until the lock is freed and insert the count.
- Resize: resize the filter into a bigger or smaller one
QF* qf_resize(QF* qf, int newQ, const char * originalFilename=NULL, const char * newFilename=NULL);- Qf* qf : pointer to the Filter
- uint64_t newQ: new number of slots(Q). the slot size will be recalculated to keep the range constant.
- string originalFilename(optional): dump the current filter to the disk to free space for the new filter. Filename is provided as the content of the string.
- string newFilename(optional): the new filter is created on disk. Filename is provided as the content of the string.
- returns a pointer to the new filter
- Merge: merge more than one filter into a final one.
void qf_merge(QF *qfa, QF *qfb, QF *qfc);
void qf_multi_merge(QF *qf_arr[], int nqf, QF *qfr);- Invertible Merge: Invertible merge offers addiotinal functionality to normal merge. Original source filter can be queried for each key. Invertiable merge function adds label for each key and creates index structure. The index is map of an integer and vector of integers where the integer is the value of the labels and vector on integers is the ids of the source filters.
void qf_invertable_merge(QF *qf_arr[], int nqf, QF *qfr,std::map<uint64_t, std::vector<int> > *inverted_index_ptr);- Qf* qf_arr : input array of filters
- int nqf: number of filters
- QF* qfr: pointer to the output filter.
- map (uint64_t,vector(int) ) inverted_index_ptr: Pointer to the output index.
- Compare: check if two filters have the same items, counts and labels.
bool qf_equals(QF *qfa, QF *qfb);- Intersect calculate the intersection between two filters.
void qf_intersect(QF *qfa, QF *qfb, QF *qfc);- Subtract subtract the second filter from the first.
void qf_subtract(QF *qfa, QF *qfb, QF *qfc);- Space: returns the space percent occupied by the inserted items.
int qf_space(QF *qf);- Capacity
- Copy
- Serialize/ Deserialize
- MMap read
The MQF project is published on BMC Bioinformatics; please, cite that paper if you use the MQF in your project.
@article{Shokrof2021,
doi = {10.1186/s12859-021-03996-x},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-021-03996-x},
year = {2021},
month = feb,
publisher = {Springer Science and Business Media {LLC}},
volume = {22},
number = {1},
author = {Moustafa Shokrof and C. Titus Brown and Tamer A. Mansour},
title = {{MQF} and buffered {MQF}: quotient filters for efficient storage of k-mers with their counts and metadata},
journal = {{BMC} Bioinformatics}
}