A simple logger which supports for logging stdout and stderr streams to console, file, and Loggly for Python.
-
Simple, easy-to-use, and also compatible with
loggingpackage -
Supports for logging to console, file, and Loggly service in real-time
-
Redirects stdout or stderr stream to the logger as log messages
-
Supports for coloring and formatting to terminal logging (based on
coloredlogspackage) -
Works with Python 2 and 3
- Supports for forwarding logs to Telegram
- Supports for forwarding logs to Slack
- Supports for tracing input and output data of function
- Add unit tests
logone can be installed using pip:
$ [sudo] pip install logone
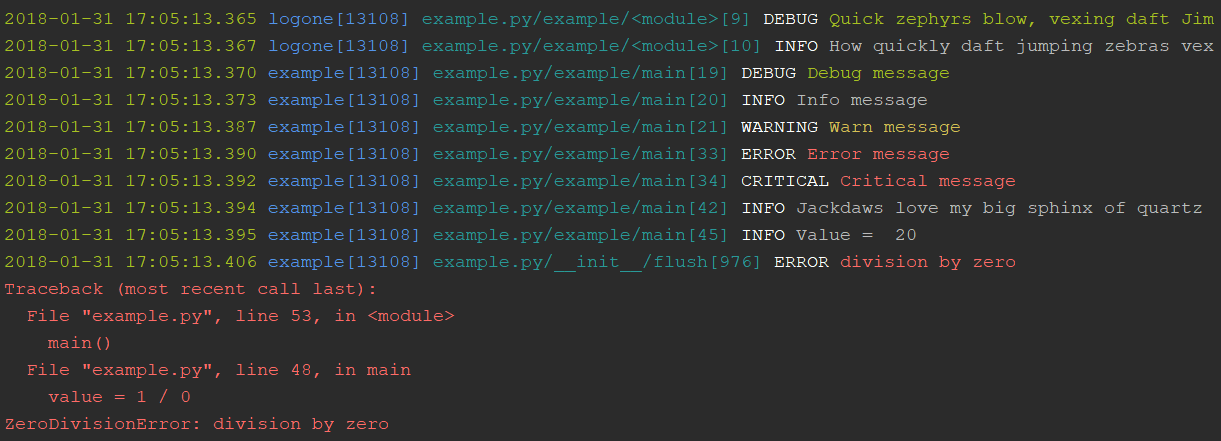
Here is an example of how easy it is to get started:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import logone
# Indicate `DEBUG` level (or higher) for the root logger
logone.set_level(level=logone.DEBUG)
# Now, we can log anything to the root logger
logone.debug('Quick zephyrs blow, vexing daft Jim')
logone.info('How quickly daft jumping zebras vex')
def main():
# Create a new logger if you do not want to use the root logger
logger = logone.get_logger('example')
logger.set_level(logone.DEBUG)
# Log something to the logger
logger.debug('Debug message')
logger.info('Info message')
logger.warning('Warn message')
# Set up the logger for logging `DEBUG` messages or higher to `example.log` file
# Learn more at: https://docs.python.org/3/library/logging.handlers.html#logging.handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler
logger.use_file(enabled=True, file_name='logs/example.log', level=logone.DEBUG,
when='d', interval=1, backup_count=10)
# Set up the logger for logging `DEBUG` messages or higher to Loggly service in real-time
logger.use_loggly(enabled=True, level=logone.DEBUG,
loggly_token='YOUR-CUSTOMER-TOKEN', loggly_tag='Python,Example')
# Log something to the logger, file, and Loggly service
logger.error('Error message')
logger.critical('Critical message')
# Redirect stdout stream to the logger as `INFO` messages (for `print` function,...)
logger.redirect_stdout(enabled=True, log_level=logone.INFO)
# Redirect stderr stream to the logger as `ERROR` messages (for unexpected error,...)
logger.redirect_stderr(enabled=True, log_level=logone.ERROR)
# These will be written to stdout stream and then redirected to the logger
print('Jackdaws love my big sphinx of quartz')
value = 20
print('Value = ', value)
# ZeroDivisionError exception will be written to stderr stream and then redirected to the logger
value = 1 / 0
print(value)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()And here is terminal output:
MIT