Code and data recipes for the paper: Heterogeneous Target Speech Separation Efthymios Tzinis, Gordon Wichern, Aswin Subramanian, Paris Smaragdis, and Jonathan Le Roux
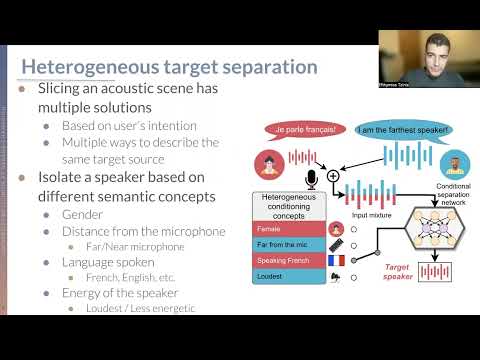
TLDR; The main contribution of this paper is to introduce a novel way of training conditional source separation networks using non-mutually exclusive semantic concepts. We try to make the conditioned models mimic humans' flexibility when selecting which source to attend to, by focusing on extracting sounds based on semantic concepts and criteria of different nature, i.e., heterogeneous, such as whether a speaker is near or far from the microphone, being soft or loud, or speaks in a certain language.
arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.03594
pdf: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2204.03594.pdf
Please cite as:
@inproceedings{tzinis22_interspeech,
author={Efthymios Tzinis and Gordon Wichern and Aswin Shanmugam Subramanian and Paris Smaragdis and Jonathan {Le Roux}},
title={{Heterogeneous Target Speech Separation}},
year=2022,
booktitle={Proc. Interspeech 2022},
pages={1796--1800},
doi={10.21437/Interspeech.2022-10717}
}Specifically, we make the following contributions:
- We introduce a novel heterogeneous target source separation task and publicly release the associated datasets.
- We propose a simple neural network architecture which can effectively separate target speech sources based on several non-mutually exclusive signal characteristic conditions, often outperforming PIT-based models with oracle assignment.
- We make several experimental discoveries: 1) heterogeneous conditioning can help cross-domain generalization, 2) robustness to non-discriminative concepts can be achieved with a small amount of such examples without impacting the overall conditional performance, and 3) adding extra easy conditions can lead to better learning on more difficult conditions.
- Heterogeneous Results
- Audio Demos
- Paths Configurations
- Datasets Preparation
- How to use the dataset loaders
Here is some small twitter thread explaining briefly our findings:
Feel free to enjoy some audio-samples here:
Change the dataset paths to the ones stored locally for all the root directories (the metadata paths are goin to be created after runnign the scripts presented below):
git clone https://github.com/etzinis/heterogeneous_separation.git
export PYTHONPATH={the path that you stored the github repo}:$PYTHONPATH
cd heterogeneous_separation
vim __config__.pyYou should change the following:
ROOT_DIRPATH = "the path that you stored the github repo"
WHAM_ROOT_PATH = "the path that you stored WHAM"
VOXFORGE_DATA_P = "the path that you stored VOXFORGE dataset split by language name"
LIBRISPEECH_DATA_P = "Point to the directory where all librispeech partitions lie in: e.g. train-clean-360, test-clean, etc."- WSJ0-2mix (WSJ0): gender and energy (louder/softer) conditions.
cd utils
➜ utils git:(main) ✗ python prepare_gender_loud_wsj0-2mix.py
/home/thymios/MERL/code/github_projects/heterogeneous_separation/heterogeneous_separation/dataset_loader/wham_speaker_gender_info.txt
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 3/3 [00:00<00:00, 12.11it/s]
Saving file to: /home/thymios/MERL/code/github_projects/heterogeneous_separation/heterogeneous_separation/dataset_loader/wsj02mix_metadata.txtSimilarly for the other two:
- Spatial LibriSpeech (SLIB): spatial location of the speakers (near/far field), gender, and energy conditions.
python prepare_librispeech.py- Spatial VoxForge (SVOX): language of the speaker (German/English/French/Spanish), spatial location of the speakers, energy conditions.
python prepare_voxforge.pyNow that everything is in place, one might use the combined multi-dataset loader in which one can specify the prior of selecting a dataset and also the samplign probability for fetching each conditional vector (e.g. given that we are goin to sample a mixture from spatial librispeech, then we can specify the probability of sampling the far/near-field speaker, the louder/whispering and the male/female). The datset uses online mixing You can test the generator as shown next:
cd heterogeneous_separation/dataset_loader
➜ dataset_loader git:(main) ✗ python multi_dataset_condition.py
/home/thymios/MERL/code/github_projects/heterogeneous_separation/heterogeneous_separation/dataset_loader/abstract_dataset.py:46: UserWarning: To copy construct from a tensor, it is recommended to use sourceTensor.clone().detach() or sourceTensor.clone().detach().requires_grad_(True), rather than torch.tensor(sourceTensor).
tensor_wav = torch.tensor(
==============================
Sampled datasets:
('WSJ02MIX', 'WSJ02MIX', 'SPATIAL_LIBRISPEECH', 'SPATIAL_LIBRISPEECH')
==============================
Query condition string:
('in_mix_cross_gender|m', 'whispering|whispering', 'near_field|near_field', 'far_field|far_field')
==============================
Query condition one-hot vectors:
tensor([[0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])
/home/thymios/MERL/code/github_projects/heterogeneous_separation/heterogeneous_separation/dataset_loader/abstract_dataset.py:46: UserWarning: To copy construct from a tensor, it is recommended to use sourceTensor.clone().detach() or sourceTensor.clone().detach().requires_grad_(True), rather than torch.tensor(sourceTensor).
tensor_wav = torch.tensor(
==============================
Sampled datasets:
('SPATIAL_LIBRISPEECH', 'SPATIAL_LIBRISPEECH', 'WSJ02MIX', 'WSJ02MIX')
==============================
Query condition string:
('far_field|far_field', 'near_field|near_field', 'whispering|whispering', 'in_mix_cross_gender|f')
==============================
Query condition one-hot vectors:
tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
Fetched batch in: 1.8959717750549316 secs