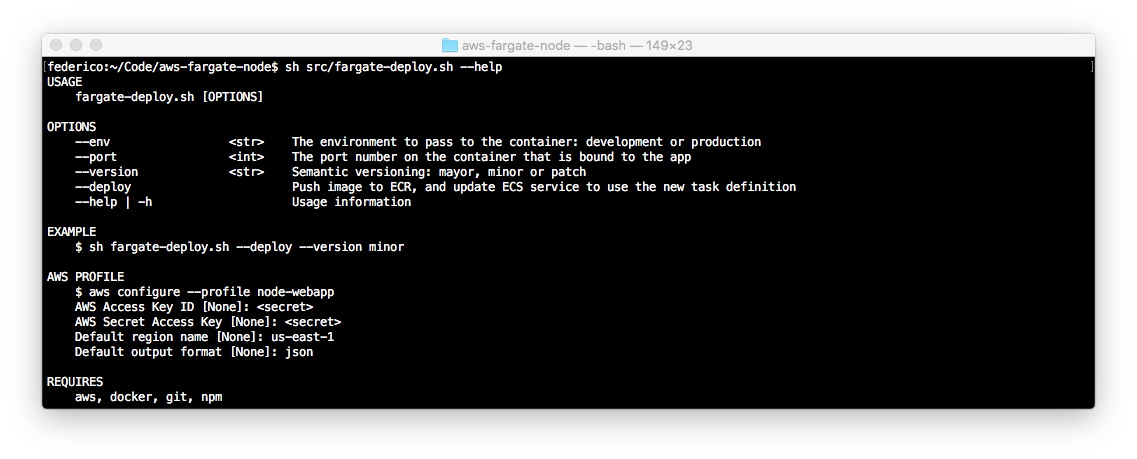
The fargate-deploy.sh bash script allows Node.js developers to deploy high-availability apps to Amazon ECS using Docker, AWS Fargate and the AWS CLI. See PoC: http://fargate.nodejsapp.cloud
There is also another script available, fargate-setup.sh, that may help you automate some common task in ECS using the AWS CLI, for example: set up a cluster, register a task definition and create a service.
Ensure you are using the latest version of the AWS CLI. For more information on how to use AWS Fargate, see What is Amazon Elastic Container Service?
You're going to need:
- Linux or macOS
- AWS CLI, version 1.15.20 or newer
- Docker, latest version
Install the AWS CLI using pip:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -qq -y python-pip libpython-dev
curl -O https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py
sudo python get-pip.py
sudo pip install awscli --upgrade
Install the AWS CLI using brew:
brew install awscli
- Clone (or download) this GitHub repo
- Build your AWS infrastructure using Terraform or CloudFormation
- Provision Docker container
$ src/fargate-deploy.sh --help
Sometimes deployments are problematic due to bad configuration variables that are un-testable before releasing to dev/test/prod. Having the ability to 'dry run' a deployment and see all the information with specific highlighting for variables allows the identification of changes that need to be made before actually deploying to an environment.
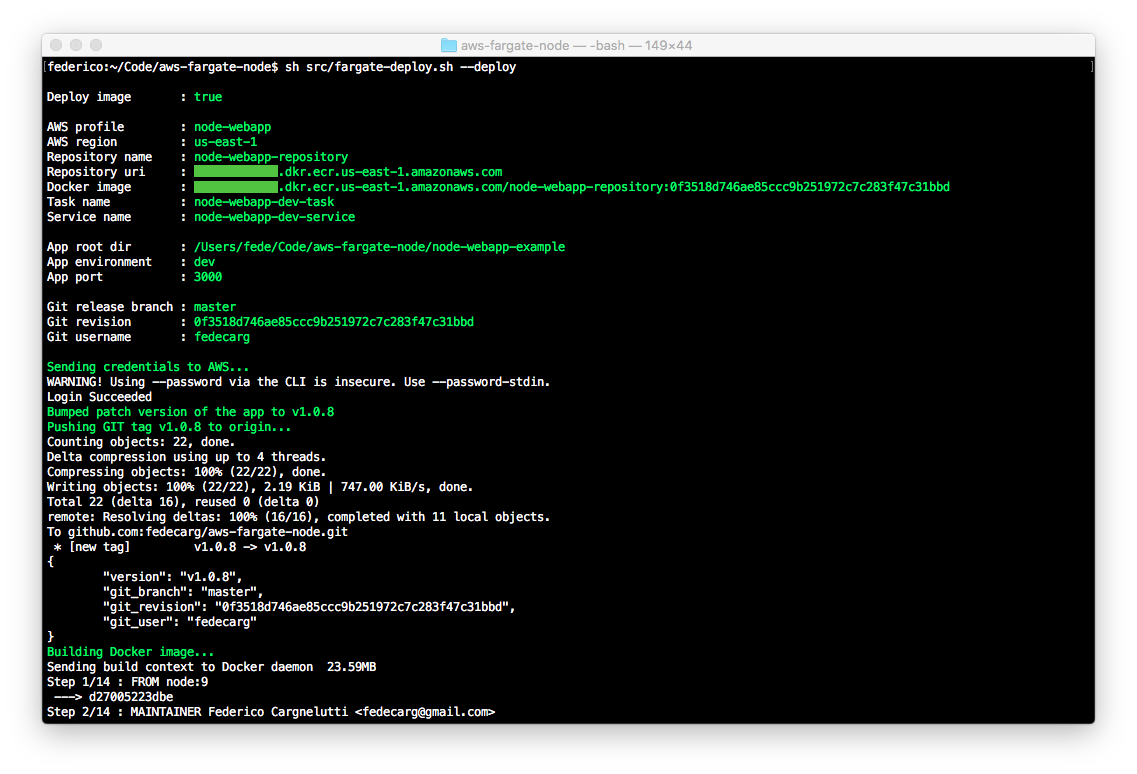
Not passing the --deploy option to src/fargate-deploy.sh causes the script to print config variabes needed to build and deploy a Docker image to an environment:
$ src/fargate-deploy.sh --env dev --port 3000 --version minor
$ src/fargate-deploy.sh --env dev --port 3000 --version minor --deploy